Effect of Fluorine on Human Health in High-fluorine Areas in Yuanzhou District, Guyuan City, Ningxia Autonomous Region
-
摘要:
近年来随着人们生活质量的提升,对健康的关注度也不断提高,氟中毒性地方病越来越受到人们的重视。在关注氟污染源分析及暴露途径研究的同时,开展氟暴露途径评价健康风险研究也十分必要。据调查,固原市原州区彭堡镇地区表层土壤氟含量高于当地区域背景值,本文针对当地存在氟超标导致地方病的实际情况,重点采集了固原市原州区彭堡镇地区表层土壤、地层岩石、农作物、地下水等样品,主要采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)、原子荧光光谱法(AFS)等分析方法对相关元素进行分析测试,研究固原市原州区彭堡镇高氟区氟超标对人体健康的影响,并运用健康风险评价模型对人体健康风险进行评价。评价结果表明:谷物和蔬菜氟暴露途径健康风险指数HQ < 1,没有非致癌风险。当地人体氟暴露风险主要途径为饮用地下水摄入,相关的健康风险指数HQ>1,这表明通过饮用氟超标的地下水,可能具有潜在的非致癌风险。年度总健康风险为1.69×10-8,低于国际辐射防护委员会(ICRP)建议的最大可接受年健康风险水平5.0×10-5,属于人类可接受的风险水平。根据氟健康风险评价结果,本文提出该地区饮用水安全性方面还需多给予关注。
Abstract:BACKGROUND In recent years, with the improvement of people's quality of life, people pay more and more attention to health, and thus endemic fluorosis attracts more and more attention. While paying attention to the analysis of the fluorine pollution source and research on exposure pathways, it is also necessary to carry out health risk evaluations of fluorine exposure pathways. According to the survey, the fluorine content in the surface soil of Pengbao Town, Yuanzhou District, and Guyuan City is higher than the local background value.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the effect of fluorine on human health.
METHODS The health risk assessment model recommended by the US Environmental Protection Agency was used to assess the human health risk. According to the actual situation of endemic diseases caused by excessive fluorine, the samples of surface soil, stratum rocks, crops and groundwater in Pengbao Town, Yuanzhou District, and Guyuan City were collected. The related elements were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry, atomic fluorescence spectrometry and other analytical methods to study the influence of excessive fluorine on human health in Pengbao Town of Yuanzhou District, and Guyuan City.
RESULTS The evaluation results showed that the health risk index (HQ) of fluorine exposure pathways in cereals and vegetables was less than 1, and there was no non-carcinogenic risk. The main way of exposure risk of local fluorine was drinking groundwater, and the related health risk index (HQ) was more than 1, which indicated that drinking groundwater with excessive fluorine may have potential non-carcinogenic risk. The annual total health risk was 1.69×10-8, which was lower than the maximum acceptable annual health risk level of 5.0×10-5 recommended by the International Commission for Radiological Protection (ICRP).
CONCLUSIONS Based on the results of the fluorine health risk assessment, it is proposed that the safety of drinking water in this area needs more attention.
-

-
表 1 样品指标分析质量参数
Table 1. Quality parameters of index analysis for the samples
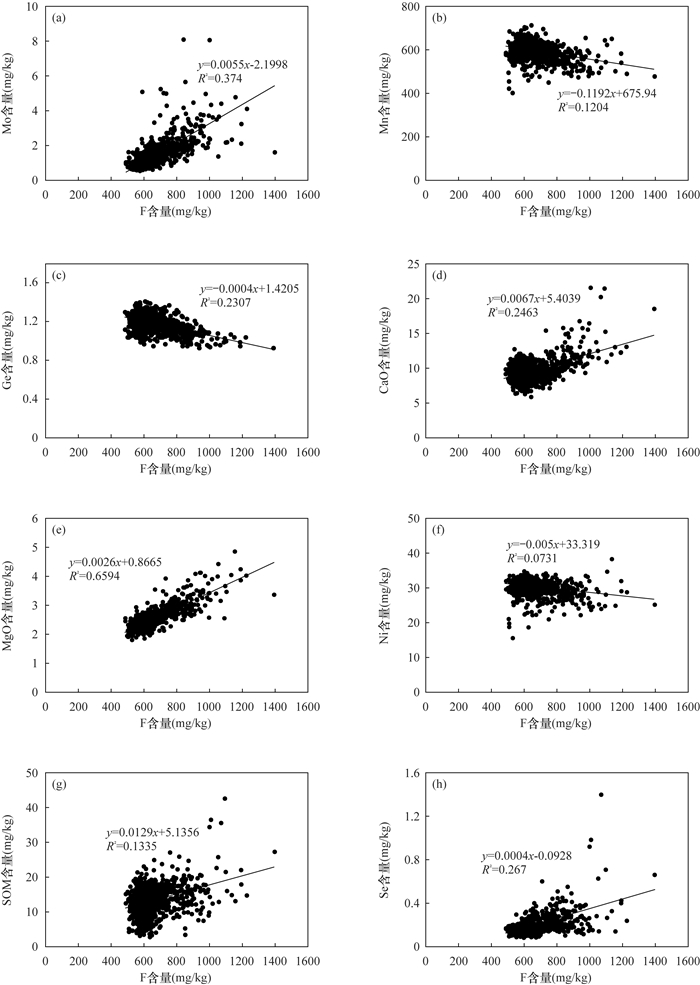
指标 分析方法 检出限 报出率(%) 准确度合格率(%) 精密度合格率(%) 重复检验合格率(%) F 离子选择电极法(ISE) 50.0×10-6 100 100 100 100 Mo 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 0.1×10-6 100 100 100 100 Mn 粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 10.0×10-6 100 100 100 100 Ge 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) 0.01×10-6 100 100 100 100 SOM 重铬酸钾容量法(VOL) 0.01×10-6 100 100 100 100 CaO 粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 0.03×10-2 100 100 100 100 MgO 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) 0.02×10-2 100 100 100 100 Ni 粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) 2.0×10-6 100 100 100 100 Se 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) 0.01×10-6 100 100 100 100 表 2 氟元素与其他元素的相关性
Table 2. Correlationship of fluorine and other elements
元素 F 元素 F Mo 0.612** CaO 0.496** Mn -0.347** MgO 0.812** Ge -0.480** Ni -0.270** SOM 0.365** Se 0.517** 注:样品数1100,“**”表示0.01水平(双侧)显著相关;“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)显著相关。 表 3 不同介质中氟元素含量
Table 3. Fluorine contents in different media
介质类别 样品数 氟含量最小值(mg/kg) 氟含量最大值(mg/kg) 氟含量平均值(mg/kg) 国家标准限量(mg/kg) 小麦 39 0.12 1.21 0.37 1 玉米 41 0.14 1.08 0.52 1 辣椒 10 0.43 0.99 0.70 1 饮用水 7 0.96 1.24 1.07 1 注:饮用水中氟含量的单位为mg/L。 表 4 氟元素对人体健康暴露风险
Table 4. Exposure risk of fluorine to human health
介质类型 日消费量(kg/d)& (L/d) 氟平均含量(mg/kg)& (mg/L) 日暴露剂量 健康风险指数 年健康风险 谷物 0.609 0.61 5.31×10-3 0.089 1.26×10-9 蔬菜 0.426 0.70 4.26×10-3 0.071 1.02×10-9 饮用水 2 1.07 3.06×10-2 1.023 1.46×10-8 总风险(年) 1.69×10-8 -
[1] 桂建业, 韩占涛, 张向阳, 等. 土壤中氟的形态分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2008, 27(4): 284-286 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.04.010 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080495
Gui J Y, Han Z T, Zhang X Y, et al. Speciation analysis of fluorine in soil samples[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(4): 284-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.04.010 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080495
[2] 涂成龙, 何令令, 崔丽峰, 等. 氟的环境地球化学行为及其对生态环境的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 39(1): 21-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201901004.htm
Tu C L, He L L, Cui L F, et al. Environmental and geochemical behaviors of fluorine and its impacts on ecological environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 30(1): 21-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201901004.htm
[3] 何令令. 不同地质背景区氟的分布特征与人体氟暴露水平研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020.
https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/D02025764 He L L. Study on the distribution characteristics of fluorine in different geological background areas and the levels of human fluoride exposure[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020.
[4] 何锦, 张福存, 韩双宝, 等. 中国北方高氟地下水分布特征和成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.012
He J, Zhang F C, Han S B, et al. The distribution and genetic types of high-fluoride groundwater in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.012
[5] 莫春雷, 宁立波, 卢天梅. 土壤中氟的垂向分布特征及其与岩性的关系[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(10): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201310009.htm
Mo C L, Ning L B, Lu T M. Vertical distribution characteristics of fluorine in the soil and its relationship with lithology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 36(10): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201310009.htm
[6] 何令令, 何守阳, 陈琢玉, 等. 环境中氟污染与人体氟效应[J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(1): 87-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202001011.htm
He L L, He S J, Chen J Y, et al. Fluorine pollution in the environment and human fluoride effect[J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(1): 87-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202001011.htm
[7] 吴功建, 李家熙, 硒氟的地球化学特征与人体健康[J]. 岩矿测试, 1996, 15(4): 241-250. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19960481
Wu G J, Li J X. Geochemical characters of selenium, fluorine and human health[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1996, 15(4): 241-250. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19960481
[8] 李静. 重金属和氟的土壤环境质量评价及健康基准的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10335-2006085253.htm Li J. Study on evaluation and health guideline for heavy metals and fluorine of soil environmental quality[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006.
[9] 张树海, 魏固宁. 宁夏固原市原州区耕地地力评价与测土配方施肥[M]. 银川: 阳光出版社, 2011: 3.
Zhang S H, Wei G N. Evaluation of cultivated land fertility and soil testing and fertilization in Yuanzhou District, Guyuan City, Ningxia[M]. Yinchuan: Sunshine Publishing, 2011: 3.
[10] 李静, 谢正苗, 徐建明. 我国氟的土壤环境质量指标与人体健康关系的研究概况[J]. 土壤通报, 2006, 37(1): 194-199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.01.042
Li J, Xie Z M, Xu J M. Research progress in the relationship between soil environmental quality index of fluorine and human health in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 37(1): 194-199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.01.042
[11] 杨忠芳, 汤奇峰, 成杭新, 等. 爱恨交织的化学元素[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2019: 37.
Yang Z F, Tang Q F, Cheng H X, et al. The chemical elements of love and hate[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2019: 37.
[12] 雷德林, 付学功, 耿红凤, 等. 沧州市高氟水分布规律及环境影响分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2007, 23(2): 43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2007.02.011
Lei D L, Fu X G, Geng H F, et al. Distribution rules of high fluoride water and its environmental impacts in Cangzhou City[J]. Water Resources Protetion, 2007, 23(2): 43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2007.02.011
[13] 杨海君, 张海涛, 许云海, 等. 长株潭地区集中式饮用水水源地周边土壤环境质量监测与评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(3): 150-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201803025.htm
Yang H J, Zhang H T, Xu Y H, et al. Monitoring and evaluation of soil environmental quality around the concentrated drinking water source in Changsha Zhuzhou-Xiangtan area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(3): 150-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201803025.htm
[14] 陈少贤. 饮水型氟病区改水后儿童健康风险度评价[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90023-1014101096.htm Chen S X. Children's health risk assessment in the drinking water type endemic fluorosis areas after supplying low fluoride public water[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2013.
[15] 张晓平. 西藏土壤中氟的含量及其分布[J]. 环境科学, 1998(1): 66-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1998.01.017
Zhang X P. Contents of fluorine in soil and their distribution in Xizang[J]. Environmental Science, 1998(1): 66-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1998.01.017
[16] 吴淑岱. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Wu S D. Chinese soil element background value[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 1990.
[17] US EPA. Available information on assessment exposure from pesticides in food[R]. US Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pesticide Programs, 2000.
[18] 黄磊, 李鹏程, 刘白薇. 长江三角洲地区地下水污染健康风险评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2008, 15(2): 26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2008.02.007
Huang L, Li P C, Liu B W. Health risk assessment of pollution in groundwater-A case study in Changjiang Delta[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2008, 15(2): 26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2008.02.007
[19] 向全永. 环境中氟对居民健康影响的危险评价[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2004.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10246-2004135028.htm Xiang Q Y. Fluoride health risk assessment in environment[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2004.
[20] 黄珊. 重金属污染土壤风险评价及化学淋洗研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-1013044169.htm Huang S. Research of heavy metals pollution soil risk evaluation and chemical leaching[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2013.
[21] 沈丽峰, 王文义. 临汾市尧都区氟离子分布状况及形成原因[J]. 水资源保护, 2005, 21(5): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200505019.htm
Shen L F, Wang W Y. Distribution of fluorin ion in Yaodu District of Linfen City and causes of formation[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2005, 21(5): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200505019.htm
[22] 焦有, 宝德俊, 尹川芬. 氟的土壤地球化学[J]. 土壤通报, 2000, 31(6): 251-254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2000.06.013
Jiao Y, Bao D J, Yin C F. Geochemistry of fluorine[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2000, 31(6): 251-254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2000.06.013
[23] 刘征原, 郝瑞彬. 氟的环境地球化学特征及生物效应[J]. 唐山师范学院学报, 2007, 29(2): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9115.2007.02.013
Liu Z Y, Hao R B. Environmental geochemistry characteristics of fluorine and its biological effects[J]. Journal of Tangshan Teachers College, 2007, 29(2): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9115.2007.02.013
[24] 杨金燕, 苟敏. 中国土壤氟污染研究现状[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(3): 506-513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201703021.htm
Yang J Y, Gou M. The research status of fluorine contamination in soils of China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(3): 506-513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201703021.htm
[25] 杨忠芳, 成杭新, 奚小环, 等. 区域生态地球化学评价思路及建议[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(8): 687-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200508002.htm
Yang Z F, Cheng H X, Xi X H, et al. Regional ecolopical geochemical assessment: Ideas and praspects[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(8): 687-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200508002.htm
[26] 邵宗臣, 陈家坊. 土壤和氧化铁对氟化物的吸附和解吸[J]. 地质学报, 1986, 23(3): 236-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198603005.htm
Shao Z C, Chen J F. Adsorption and desorption of fluoride by some soils and iron oxides[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1986, 23(3): 236-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198603005.htm
[27] 万红友, 黎成厚, 师会勤, 等. 几种土壤的氟吸附特性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2003, 22(3): 329-332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200303020.htm
Wan H Y, Li C H, Shi H Q, et al. Study on adsorption characters of fluorine in several soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2003, 22(3): 329-332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200303020.htm
[28] 何志润. 宁夏清水河流域氟化物(F-)的分布特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2020.
He Z R. Study on the distribution characteristics and influencing factors of fluoride (F-) in Oingshui River Basin of Ningxia[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2020.
[29] Mondal D, Gupta S. Fluoride hydrogeochemistry in alluvia-laquifer: An implication to chemical weathering and ion-exchange phenomena[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(7): 3537-3554. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037620626710_791e.html
[30] 张惠英, 宋琦如, 赵海萍, 等. 宁夏农村居民膳食结构及营养状况调查分析[J]. 宁夏医学院学报, 2005, 27(2): 104-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNXY200502006.htm
Zhang H Y, Song Q R, Zhao H P, et al. Analysis of dietary structure and nutrition state in rural area of Ningxia[J]. Joural of Ningxia Medical College, 2005, 27(2): 104-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNXY200502006.htm
[31] 郭晋燕. 吉兰泰沙漠盆地地下水环境特征及高氟区饮用水安全风险控制[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1014070029.htm Guo J Y. Groundwater environmental evolution in Jilantai Desert Basin and safety risk control of drinking water in high fluoride area[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2014.
[32] 赵庆令, 李清彩, 谢江坤, 等. 鲁中南地区双村岩溶水系统地下水中化学致癌物和非致癌物的健康风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1): 90-97. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.015
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Xie J K, et al. Health risk assessment of carcinogenic and non-carcingenic substances in underground water from the Shuangcun karst system of central-southern Shandong Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1): 90-97. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.015
-



 下载:
下载: