Assessment of Selenium Bioavailability in Natural Selenium-rich Soil Based on Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films
-
摘要:
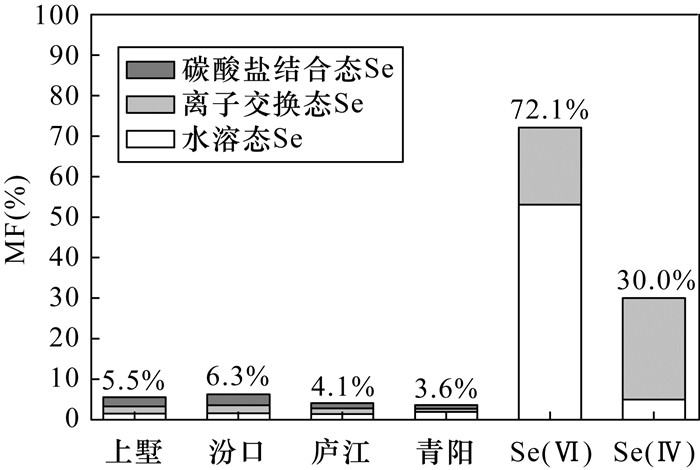
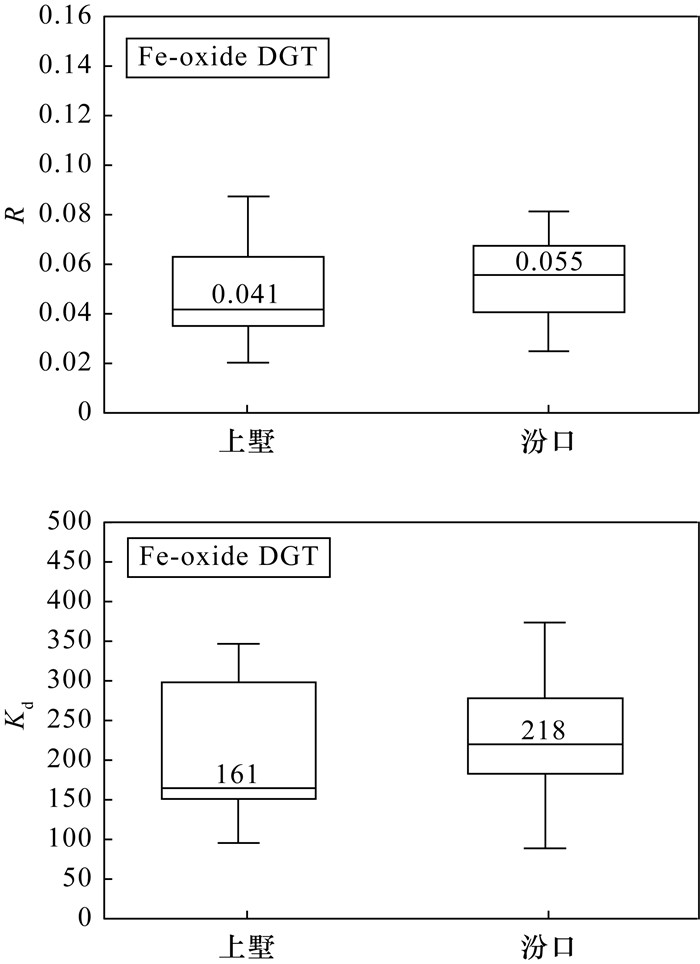
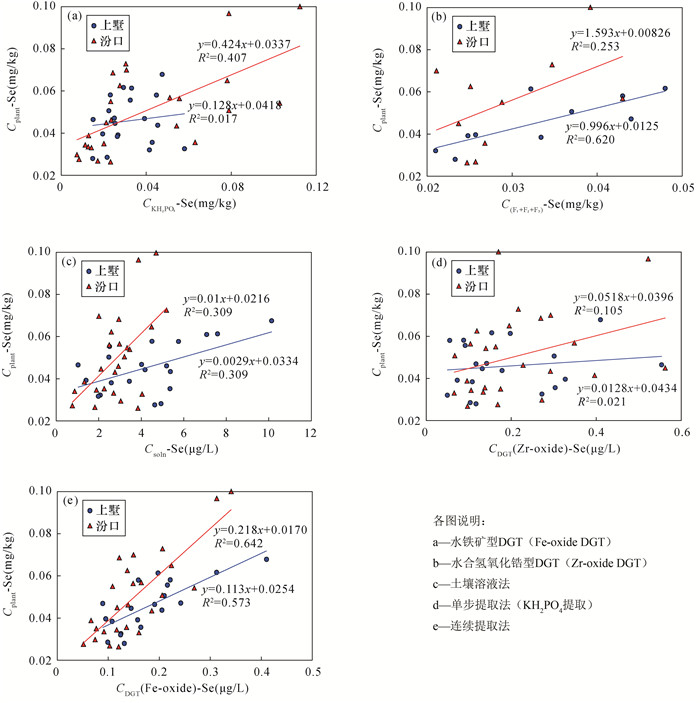
有效硒是评价土壤中硒对植物供给能力的重要指标,中国目前尚无测定土壤有效硒的统一方法。化学提取法、土壤溶液法常用于测定土壤有效硒含量,但存在缺乏普遍适用提取剂类型、目标态提取不完全和对非目标态溶解等问题。梯度扩散薄膜(DGT)技术是一种基于解离、扩散动力学的有效态测定方法,已有学者将其应用于土壤有效硒的测定并取得良好效果,但是否适用于天然富硒土壤中硒生物有效性评价尚不明确。为探明梯度扩散薄膜技术评价天然富硒土壤中硒生物有效性的可行性,本文以浙江省上墅乡和汾口镇分布的天然富硒土壤为研究对象,实验应用化学提取法、土壤溶液法和DGT技术[包括Fe-oxide(水铁矿型)DGT、Zr-oxide(水合氢氧化锆型)DGT]评价土壤中硒的生物有效性。结果表明:①Fe-oxide DGT测得的有效硒平均含量为0.17±0.076μg/L,Zr-oxide DGT测得的有效硒平均含量为0.20±0.13μg/L。两种类型DGT测得有效硒含量差异不大,但由于Zr-oxide DGT对Se4+具有专性吸附特征,导致Zr-oxide DGT无法有效反映植物体内硒含量水平。对于检测土壤硒生物有效量,Fe-oxide DGT要优于Zr-oxide DGT;②植物体内硒含量Cplant-Se与三种方法测定的有效硒含量均呈显著正相关,但Cplant-Se与Fe-oxide DGT测定的有效硒含量相关系数(r=0.705)大于其他两种方法;③基于DGT技术计算得出的R值(土壤颗粒向土壤溶液补充硒的能力)和Kd值(土壤固相与液相之间的分配系数)表明上墅研究区相较于汾口研究区土壤中硒具有更强的迁移性,但其土壤固相向土壤溶液补充硒离子的速率小于汾口研究区。综上认为,对于评价天然富硒土壤中硒生物有效性而言,DGT方法优于化学提取法和土壤溶液法,在测试性能和反映土壤动力学过程信息方面更具优势。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Available selenium is an important index to evaluate the supply capacity of selenium from the soil to plants. Unfortunately, there is no general method for the determination of available selenium in soil in China. Chemical extraction and soil solution methods are commonly used to evaluate bioavailability of selenium. Furthermore, there are problems such as the lack of universally applicable extractant types, incomplete extraction of target states, and dissolution of non-target states. The diffusive gradient in thin-films (DGT) technique is a method based on dissociation and diffusion kinetics which has been successfully used to assess the bioavailability of selenium. However, it is not clear whether the DGT technique can be used in natural selenium-rich soil.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the feasibility of the DGT technique to evaluate the bioavailability of selenium in natural selenium-rich soil.
METHODS Natural selenium-rich soils from Shangshu and Fenkou in Zhejiang Province were chosen as the research objects. Fe-oxide DGT, Zr-oxide DGT, chemical extraction, and soil solution methods were used to evaluate selenium bioavailability.
RESULTS (1) The average of available selenium measured by Fe-oxide DGT was 0.17±0.076μg/L, whereas the average of available selenium measured by Zr-oxide DGT was 0.20±0.13μg/L. Zr-oxide DGT cannot be used effectively to reflect the content of selenium in plants due to the specific adsorption characteristics to Se4+. Fe-oxide DGT was suitable for the bioavailability evaluation of selenium in soil rather than Zr-oxide DGT. (2) There was a significant positive correlation between the selenium content in plants (Cplant-Se) and the available selenium content determined by the three methods. The correlation between available Se by Fe-oxide DGT and Se concentration in plants (r=0.705) was greater than the chemical extraction method and soil solution method. (3) The Kd value and R value calculated from DGT and soil solution methods indicated that the soil of the Shangshu area had stronger selenium mobility than the Fenkou area, but the rate of Se supply from the soil solid phase to the soil solution was less than the Fenkou area.
CONCLUSIONS DGT is more suitable for evaluating selenium bioavailability compared with chemical extraction and soil solution methods because it has more advantages in testing performance and reflecting the information of soil dynamics process.
-

-
表 1 DGT装置规格参数
Table 1. Specifications of DGT equipment
DGT参数 Fe-oxide DGT Zr-oxide DGT 吸附膜 厚度0.6mm 厚度0.4mm 应用条件 pH:3.0~7.0 pH:3~10;离子强度:
10-5~0.75mol/L
硝酸钠溶液扩散膜 聚丙烯酰胺:
厚度0.8mm聚丙烯酰胺:
厚度0.8mm滤膜 PES(聚醚砜):
厚度0.14mm,
孔径0.45μmPES(聚醚砜):
厚度0.14mm,
孔径0.45μm采样面积 3.14cm2 2.54cm2 D0(扩散系数) 7.44(E-6cm2/s) 7.44(E-6cm2/s) 表 2 不同方法测得土壤有效Se与作物Se含量相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficent between available Se in soil by different methods and Se concentration in plants
参数 上墅 汾口 全部 CDGT(Fe-oxide)-Se 0.757** 0.790** 0.705** CDGT(Zr-oxide)-Se 0.144 0.324 0.263 Csoln-Se 0.556* 0.556** 0.369* CKH2PO4-Se 0.130 0.638** 0.565** C(F1+F2+F3)-Se 0.787** 0.503 0.465* 注:“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;“**”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 3 DGT测定土壤有效Se含量结果
Table 3. Analytical results of available Se in soil with DGT measurement method
DGT类型 研究区 CDGT(μg/L) R(CDGT/Csoln) 最小值 最大值 平均值 中位数 最小值 最大值 平均值 中位数 Fe-oxide
DGT上墅 0.089 0.41 0.18 0.16 0.020 0.087 0.049 0.041 汾口 0.051 0.34 0.15 0.14 0.024 0.13 0.056 0.055 全部 0.051 0.41 0.17 0.15 0.020 0.13 0.053 0.050 Zr-oxide
DGT上墅 0.050 0.55 0.19 0.14 0.0096 0.23 0.058 0.034 汾口 0.066 0.56 0.21 0.17 0.016 0.27 0.085 0.073 全部 0.050 0.56 0.20 0.16 0.0096 0.27 0.072 0.049 -
[1] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 31(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
[2] 成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906026.htm
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recom-mendations selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201906026.htm
[3] Dinh Q T, Cui Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112: 294-309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
[4] 周国华. 土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6): 1097-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201406001.htm
Zhou G H. Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6): 1097-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201406001.htm
[5] 梁东丽, 彭琴, 崔泽玮, 等. 土壤硒的形态转化及其对有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705010.htm
Liang D L, Peng Q, Cui Z W, et al. Progress on selenium bioavailibility and influential factors in soil[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705010.htm
[6] Menzies N W, Donn M J, Kopittke P M. Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phyto available trace metals in soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 145(1): 121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.03.021
[7] Tian Y, Wang X, Luo J, et al. Evaluation of holistic approaches to predicting the concentrations of metals in field-cultivated rice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(20): 7649-7654. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18983088/
[8] Luo J, Zhang H, Zhao F J, et al. Distinguishing diffusional and plant control of Cd and Ni uptake by hyperaccumulator and nonhyperaccumulator plants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 4(4): 6636-6641.
[9] Luo J, Zhang H, Santner J, et al. Performance characteristics of diffusive gradients in thin films equipped with a binding gel layer containing precipitated ferrihydrite for measuring arsenic(Ⅴ), Selenium(Ⅵ), vanadium(Ⅴ), and antimony(Ⅴ)[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(21): 8903-8909. doi: 10.1021/ac101676w
[10] Davison W, Zhang H. Progress in understanding the use of diffusive gradients in thin films(DGT)-back to basics[J]. Environment Chemistry, 2012, 9(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1071/EN11084
[11] Zhang H, Davison W. Use of diffusive gradients in thin-films for studies of chemical speciation and bioavailability[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 12(2): 85-101. doi: 10.1071/EN14105
[12] Wang M K, Cui Z W, Xue M Y, et al. Assessing the uptake of selenium from naturally enriched soils by maize (Zea mays L. ) using diffusive gradients in thin-films technique (DGT) and traditional extractions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689: 1-9.
[13] Peng Q, Wang M K, Cui Z W, et al. Assessment of bio-availability of selenium in different plant-soil systems by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT)[J]. Environment Pollution, 2017, 225: 637-643. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.036
[14] Peng Q, Li J, Wang D, et al. Effects of ageing on bio-availability of selenium in soils assessed by diffusive gradients in thin-films and sequential extraction[J]. Plant Soil, 2019, 436: 159-171. doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-03920-y
[15] 赵万伏, 宋垠先, 管冬兴, 等. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1332-1341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHBH201807005.htm
Zhao W F, Song Y X, Guan D X, et al. Pollution status and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of a typical black shale area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1332-1341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NHBH201807005.htm
[16] 宋明义. 浙西地区下寒武统黑色岩系中硒与重金属的表生地球化学及环境效应[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2009: 14-15.
Song M Y. Supergenic geochemistry and environmental effects of selenium and heavy metals in the lower Cambrian black series of western Zhejiang Province, China[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2009: 14-15.
[17] Ding S, Xu D, Wang Y, et al. Simultaneous measurements of eight oxyanions using high-capacity diffusive gradients in thin films (Zr-oxide DGT) with a high-efficiency elution procedure[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7572-7580. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016EnST...50.7572D/abstract
[18] 陈海杰, 马娜, 陈卫明, 等. 抑制植物样品消解过程中硒挥发的方法[J]. 分析化学报告, 2020, 48(9): 1268-1272. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX202009021.htm
Chen H J, Ma N, Chen W M, et al. A method for suppressing volatile loss of selenium in digestion of plant samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 48(9): 1268-1272. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX202009021.htm
[19] 罗军, 王晓蓉, 张昊, 等. 梯度扩散薄膜技术(DGT)的理论及其在环境中的应用Ⅰ: 工作原理、特性与在土壤中的应用[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(2): 205-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201102003.htm
Luo J, Wang X R, Zhang H, et al. Theory and application of diffusive gradients in thin films in soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(2): 205-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201102003.htm
[20] 戴高乐, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 洞庭湖平原土壤铅活动性影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 783-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201904011.htm
Dai G L, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Factors affecting mobility of lead in the soils of the Dongting Lake Plain, China[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(4): 783-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201904011.htm
[21] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤-作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 449-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202001054.htm
Ma H H, Peng M, Liu F, et al. Bioavailability, translocation, and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 449-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202001054.htm
[22] 陈静, 孙琴, 姚羽, 等. DGT和传统化学方法比较研究复合污染土壤中Cd的生物有效性[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(10): 1172-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201410014.htm
Chen J, Sun Q, Yao Y, et al. Comparison of DGT technique with traditional method for evaluating cadmium bioavailability in soils with combined pollution[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(10): 1172-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201410014.htm
[23] 吴雄平, 鲍俊丹, 伊田, 等. 石灰性土壤有效硒浸提剂和浸提条件研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(5): 931-936. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.05.012
Wu X P, Bao J D, Yi T, et al. Extractants and optimum extracting conditions of soil available selenium in calcareous soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(5): 931-936. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.05.012
[24] 耿建梅, 王文斌, 罗丹, 等. 不同浸提剂对海南稻田土壤有效硒浸提效果对比[J]. 土壤, 2010, 42(4): 624-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201004022.htm
Geng J M, Wang W B, Luo D, et al. Comparative studies on effects of several extractants on available selenium of paddy soils in Hainan[J]. Soils, 2010, 42(4): 624-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201004022.htm
[25] 谢薇, 杨耀栋, 管桂芹, 等. 四种浸提剂对果园与菜地土壤有效硒浸提效果的对比研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 434-441. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905150063
Xie W, Yang Y D, Jian G Q, et al. A comparative study of four extractants on the extraction of available selenium in vegetable and orchard soils[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 434-441. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905150063
[26] 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 胡秋辉, 等. 江苏省几种低硒土壤中硒的形态分布及生物有效性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, 8(3): 355-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2002.03.018
Zhang Y L, Pan G X, Hu Q H, et al. Selenium fractionation and bio-availabiliyt in some low-Se soils of central Jiangsu Province[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2002, 8(3): 355-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2002.03.018
[27] Dillon K S, Rani N, Dillon S K. Evaluation of different extractants for the estimation of bioavailable selenium in seleniferous soils of northwest India[J]. Soil Research, 2005, 43(5): 639-645. doi: 10.1071/SR04166
[28] Wang J, Bai L, Zeng X, et al. Assessment of arsenic availability in soils using the diffusive gradients in thin films(DGT) technique-A comparison study of DGT and classic extraction methods[J]. Environmental Science-Processess & Impacts, 2014, 16(10): 2355-2361. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2014/em/c4em00215f
[29] Bade R, Oh S, Shin W S. Diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) for the prediction of bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soils to earthworm (Eisenia foetida) and oral bioavailable concentrations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 416(2): 127-136.
[30] 彭琴. 基于梯度扩散薄膜技术评价土壤硒的生物有效性[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017: 19-21.
Peng Q. Assessment of selenium bioavailability in soils based on diffusion gradients in thin films technique[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2017: 19-21.
[31] 伊芹, 程皝, 尚文郁. 土壤硒的存在特征及分析测试技术研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 461-475. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006230095
Yi Q, Cheng H, Shang W Y. Review on characteristics of selenium in soil and related analytical techniques[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 461-475. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006230095
[32] Cartes P, Gianfreda L, Mora M L. Uptake of selenium and its antioxidant activity in ryegrass when applied as selenate and selenite forms[J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 276(1-2): 359-367. doi: 10.1007/s11104-005-5691-9
[33] Zhao C, Ren J, Xue C. Study on the relationship between soil selenium and plant selenium uptake[J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 277(1-2): 197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11104-005-7011-9
[34] Pezzarossa B, Petruzzelli G, Petacco F, et al. Absorption of selenium by Lactuca sativa as affected by carboxymethylcellulose[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67: 322-329. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.073
[35] Mason S, Mcneill A, Mclaughlin M J, et al. Prediction of wheat response to an application of phosphorus under field conditions using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) and extraction methods[J]. Plant Soil, 2010, 337(1-2): 243-258. doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0521-0
[36] Nolan A L, Zhang H, Mclaughlin M J. Prediction of zinc, cadmium, lead, and copper availability to wheat in contaminated soils using chemical speciation, diffusive gradients in thin films, extraction, and isotopic dilution techniques[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2005, 34(14): 496-507. https://acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2134/jeq2005.0496
[37] 宋宁宁, 王芳丽, 沈跃, 等. 梯度薄膜扩散技术(DGT)与传统化学方法评估黑麦草吸收Cd的对比[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(12): 1960-1967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201212021.htm
Song N N, Wang F L, Shen Y, et al. Comparison of the method of diffusive gradients in thin films with traditional chemical extraction techniques for evaluating cadmium bioavailability in ryegrass[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(12): 1960-1967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201212021.htm
[38] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020: 2621.
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Geochmical parameters of soils in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 2621.
[39] 柳云龙, 章立佳, 韩晓非, 等. 上海城市样带土壤重金属空间变异特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 599-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201202045.htm
Liu Y L, Zhang L J, Han X F, et al. Spatial variability and evaluation of soil heavy metal contamination in the urban-transect of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 599-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201202045.htm
[40] 杨奎, 李湘凌, 张敬雅, 等. 安徽庐江潜在富硒土壤硒生物有效性及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(4): 715-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201804015.htm
Yang K, Li X L, Zhang J Y, et al. Selenium bioavailability and influential factors in potentially selenium enriched soils in Lujiang County, Anhui Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(4): 715-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201804015.htm
[41] 王潇, 张震, 朱江, 等. 青阳县富硒土壤中硒的形态与水稻富硒的相关性研究[J]. 地球科学与环境, 2019, 47(3): 336-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201903013.htm
Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhu J, et al. Study of correlation between rice selenium and status of selenium in selenium-rich soil in Qingyang County[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(3): 336-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201903013.htm
[42] 樊俊, 王瑞, 胡红青, 等. 不同价态外源硒对土壤硒形态及酶活性、微生物数量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201505025.htm
Fan J, Wang R, Hu H Q, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium with different valences on Se forms, enzyme activities and microbial quantity of soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(5): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201505025.htm
[43] Shaheen S M, Kwon E E, Biswas J K, et al. Arsenic, chromium, molybdenum, and selenium: Geochemical fractions and potential mobilization in riverine soil profiles orginating from Germang and Egypt[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 180: 553-563. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.054
[44] Li J, Peng Q, Liang D L, et al. Effects of aging on the fraction distribution and bioavailability of selenium in three different soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 2351-2359. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.011
[45] 况琴, 吴山, 黄庭, 等. 生物炭质和钢渣对江西丰城典型富硒区土壤硒有效性的调控效果与机理研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 705-714. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901190014
Kuang Q, Wu S, Huang T, et al. Effect and mechanism of biomass carbon and steel slag as ameliorants on soil selenium availability in typical Se-rich are of Fengcheng City, Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 705-714. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901190014
[46] Peng Q, Guo L, Ali F, et al. Influence of Pak choi plant cultivation on Se distribution, speciation and bioavailability in soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 403: 331-342. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-2810-8
[47] Luo J, Cheng H, Ren J, et al. Mechanistic insights from DGT and soil solution measurements on the uptake of Ni and Cd by radish[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(13): 7305-7313. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24853263/
[48] Zhang H, Davison W, Knight B, et al. In situ measurements of solution concentrations and fluxes of trace metals in soils using DGT[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1998, 32(5): 704-710. http://lib3.dss.go.th/fulltext/Journal/Environ%20Sci.%20Technology1998-2001/1998/no.5/5,1998%20vol.32no.5,p704-710.pdf
[49] Guan D X, Zheng J L, Luo J, et al. A diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for the assessment of bisphenols desorption from soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 331: 321-328. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.02.053
[50] 魏天娇, 管冬兴, 方文, 等. 梯度扩散薄膜技术(DGT)的理论及其在环境中的应用Ⅲ: 植物有效性评价的理论基础与应用潜力[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 841-849. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201805001.htm
Wei T J, Guan D X, Fang W, et al. Theory and application of diffusive gradients in thin-films(DGT)in the environment Ⅲ: Theoretical basis and application potential in phytoavailability assessment[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 841-849. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201805001.htm
-



 下载:
下载: