Element and Mineral Characteristics of Tailings in the Porphyry-Type Iron Deposit from Ningwu Basin
-
摘要:
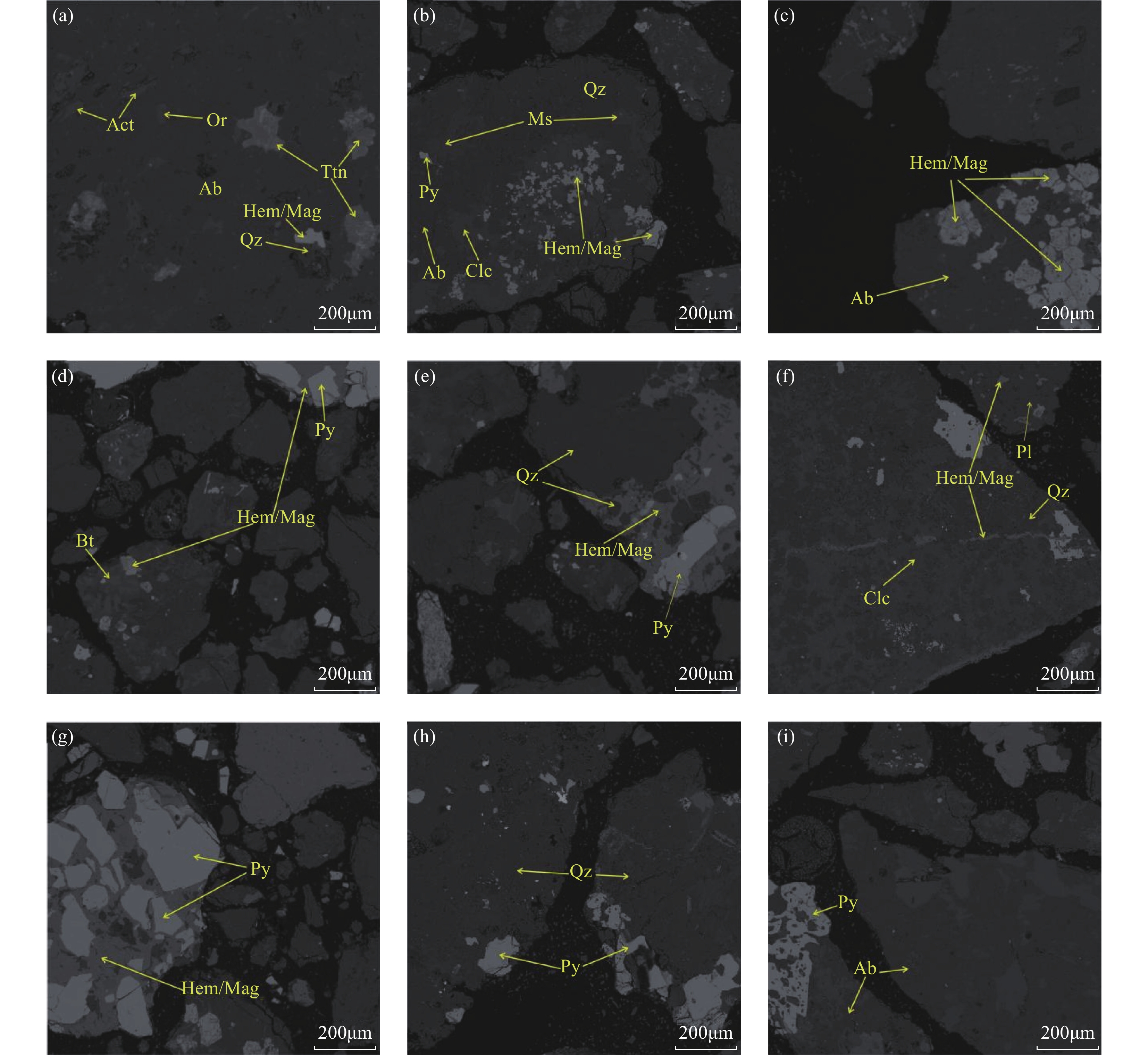
宁芜盆地玢岩型铁矿是中国重要的铁资源来源,其尾矿成分复杂,而对复杂尾矿进行高效综合利用的前提是充分了解其工艺矿物学特征。本文以宁芜盆地和尚桥铁矿床尾矿样品为研究对象,在常规X射线荧光光谱(XRF)、电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)、粉晶X射线衍射(XRD)分析的基础上,借助综合矿物分析仪(TIMA),对尾矿的矿物与化学组成、元素赋存状态、矿物粒度分布、嵌布关系以及解离度和连生关系进行分析。结果表明:尾矿的主量元素为SiO2 (47.18%~50.08%)、Fe2O3 (15.40%~17.91%)和Al2O3 (12.12%~13.34%);微量元素中Cu、Zn、V含量较高,但均未达到其工业品位;矿物组成主要为钠长石(23.26%~24.58%)、赤铁矿和磁铁矿(17.30%~21.99%)以及石英(15.31%~17.08%),总体以脉石矿物为主,金属矿物较少。Si主要赋存于石英(平均值为33.89%)与钠长石(平均值为33.75%)中;Fe主要赋存于赤铁矿和磁铁矿(平均值为73.56%)中;有害元素S主要赋存于黄铁矿中(平均值为96.86%)。尾矿粒度较细,主要分布于50~2000μm;矿物嵌布关系较为复杂且嵌布粒度较细;矿物解离度较低,大部分低于10%,单体颗粒较少,连生关系复杂。宁芜盆地玢岩型铁矿尾矿与中国其他类型铁矿尾矿相比,具有高铝的特征,黄铁矿含量相对较高。
Abstract:The porphyrite-type iron deposit in Ningwu Basin is an important source of iron resources in China, and the premise for the efficient and comprehensive utilization of its complex tailings is a thorough understanding of their mineral processing characteristics. In order to provide a reference for the comprehensive utilization of porphyrite-type iron deposit tailings in Ningwu Basin, the process mineralogy characteristics were explored by using the combined methods of X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), and TESCAN integrated mineral analyzer (TIMA). The results show that the tailings are composed of mainly Si, Fe and Al. The mineral compositions are mainly albite, hematite, magnetite and quartz. Silicon mainly occurs in quartz and albite, whereas Fe mainly occurs in hematite/magnetite. The tailings have a fine particle size and low mineral liberation degree. Compared to other types of iron deposit tailings in China, these tailings are characterized by a high content of Al and a relatively high proportion of pyrite.
-

-
表 1 和尚桥铁矿尾矿主量元素XRF分析结果
Table 1. Analytical results of major elements in tailings of the Heshangqiao Fe deposit determined by XRF
样品编号 主量元素(%) SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 Na2O S MgO CaO K2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO DS-1-A 49.94 15.59 13.25 4.09 3.439 3.06 2.67 0.87 0.599 0.488 0.340 DS-1-B 50.08 15.40 13.34 4.12 3.484 3.05 2.78 0.85 0.614 0.497 0.333 DS-2-A 47.18 17.91 12.23 3.82 3.467 3.23 3.40 0.77 0.621 0.455 0.369 DS-2-B 47.28 17.71 12.12 3.90 3.888 3.23 3.43 0.75 0.666 0.458 0.358 表 2 和尚桥铁矿尾矿微量元素ICP-MS分析结果
Table 2. Analytical results of trace elements in tailings of the Heshangqiao Fe deposit determined by ICP-MS
样品编号 微量元素(μg/g) Li Be Sc V Cr Co Ni Cu Zn Ga As Rb Sr Y Zr Nb DS-1-A 16 1.9 11 89 9.5 72 23 156 143 13 10 38 279 17 84 3.0 DS-1-B 15 1.9 11 90 8.3 78 25 189 143 14 11 36 299 16 87 3.2 DS-2-A 15 2.0 12 119 11 73 25 142 141 14 11 33 269 17 88 3.0 DS-2-B 14 2.1 12 129 11 74 26 137 152 14 13 32 308 19 94 3.1 样品编号 Cs Ba La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu DS-1-A 2.6 340 28 41 5.1 18 3.5 0.77 3.2 0.47 2.5 0.47 1.4 0.22 1.5 0.26 DS-1-B 2.6 302 30 43 5.1 19 3.6 0.82 3.2 0.48 2.6 0.50 1.5 0.22 1.5 0.27 DS-2-A 2.6 322 30 50 5.6 20 4.0 0.87 3.4 0.53 2.9 0.54 1.6 0.24 1.6 0.29 DS-2-B 2.6 317 30 48 6.0 21 4.0 0.85 3.6 0.52 3.0 0.55 1.6 0.27 1.8 0.31 样品编号 Hf Ta Pb Th U Ge Mo Ag Cd In Sn Sb W Tl Bi DS-1-A 2.1 1.1 19 4.7 1.8 5.0 1.4 0.28 0.27 0.15 1.9 1.1 189 0.25 3.5 DS-1-B 2.1 0.78 17 4.7 1.1 5.0 1.2 0.40 0.21 0.16 1.4 1.0 222 0.24 2.9 DS-2-A 2.2 0.62 16 5.0 1.1 5.5 1.2 0.23 0.23 0.19 2.7 1.2 185 0.23 2.3 DS-2-B 2.5 0.54 16 5.3 1.1 6.2 1.1 0.22 0.21 0.20 1.9 1.3 149 0.24 2.5 表 3 和尚桥铁矿尾矿矿物含量TIMA分析结果
Table 3. Mineral content of tailings of the Heshangqiao Fe deposit determined by TIMA.
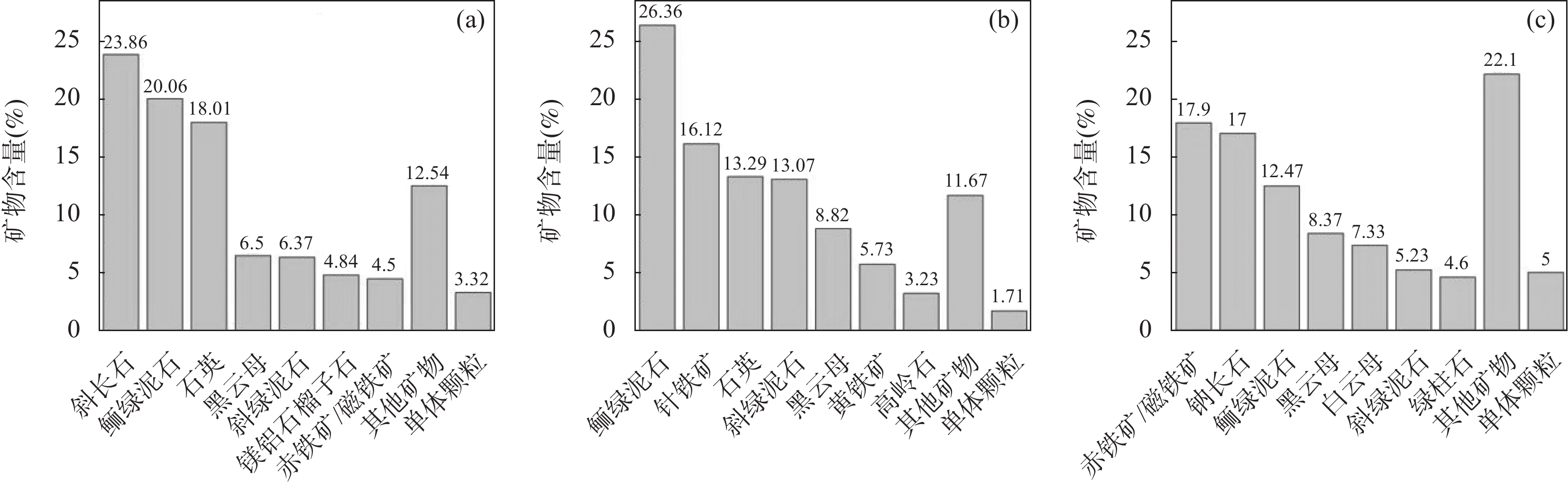
矿物名称 含量(%) 平均含量
(%)矿物名称 含量(%) 平均含量
(%)DS-1 DS-2 DS-1 DS-2 钠长石 23.26 24.58 23.92 磷灰石 0.89 0.90 0.90 赤铁矿/磁铁矿 17.30 21.99 19.65 钛闪石 0.76 0.70 0.73 石英 15.31 17.08 16.19 方解石 0.37 0.71 0.54 斜长石 10.20 8.50 9.35 黝帘石 0.46 0.56 0.51 黄铁矿 8.26 4.37 6.32 黑电气石 0.47 0.48 0.48 黑云母 5.08 3.71 4.39 透辉石 0.24 0.66 0.45 斜绿泥石 4.31 2.80 3.56 针铁矿 0.43 0.34 0.39 阳起石 2.87 3.96 3.42 正长石 0.30 0.36 0.33 鲕绿泥石 3.50 2.45 2.97 磁黄铁矿 0.46 0.13 0.30 白云母 2.07 2.27 2.17 绿柱石 0.20 0.20 0.20 镁铝石榴子石 1.69 0.86 1.41 其他矿物总和 0.77 0.74 0.76 高岭石 0.78 1.62 1.20 表 4 和尚桥铁矿尾矿元素赋存状态TIMA分析结果
Table 4. The occurrence state of elements in tailings of the Heshangqiao Fe deposit determined by TIMA
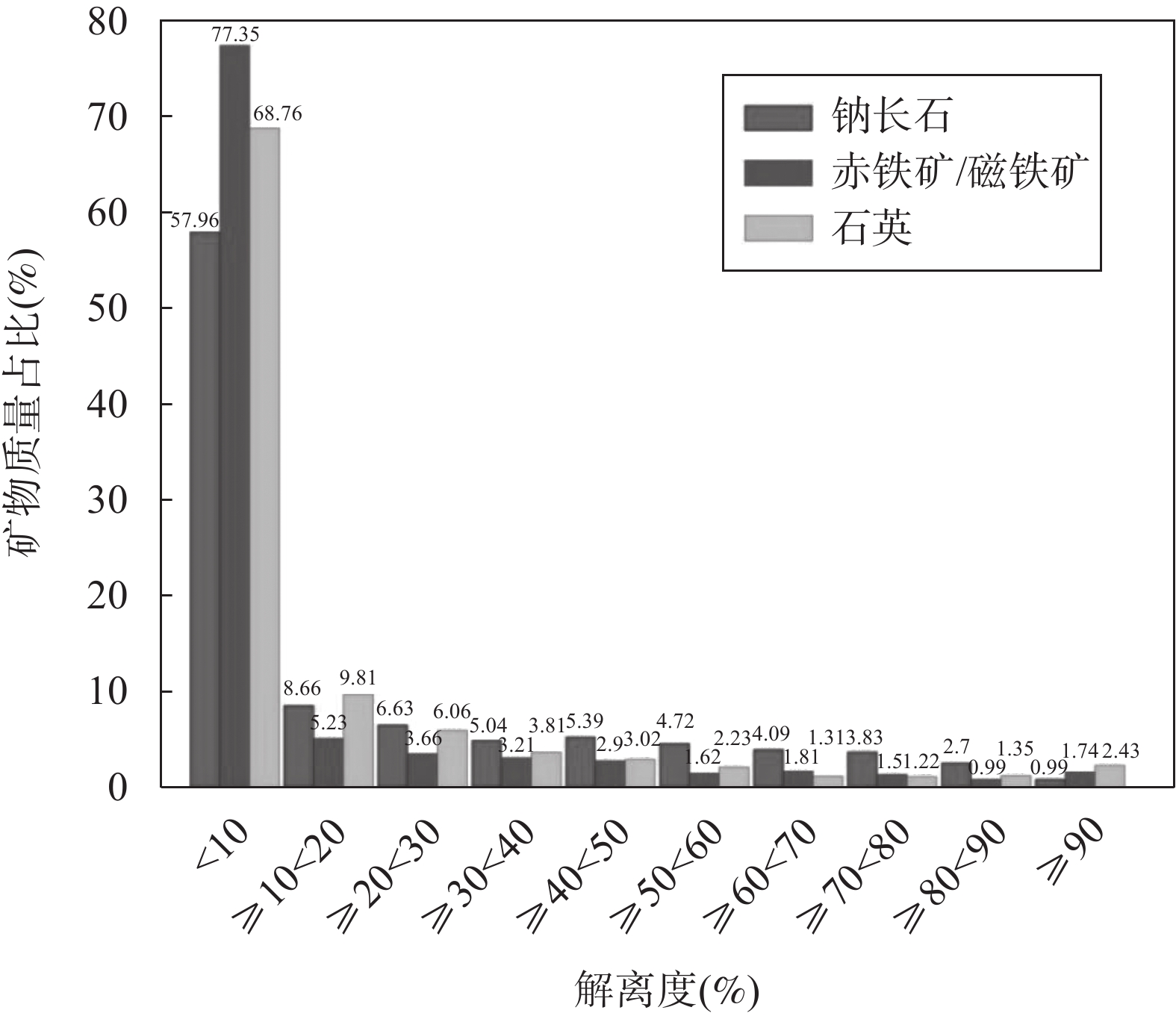
矿物名称 Si含量占比(%) 矿物名称 Fe含量占比(%) DS-1 DS-2 DS-1 DS-2 石英 32.46 35.32 赤铁矿/磁铁矿 66.51 80.60 钠长石 33.24 34.26 黄铁矿 21.13 10.66 斜长石 14.40 11.70 斜绿泥石 2.78 1.72 阳起石 3.34 4.49 鲕绿泥石 2.25 1.50 黑云母 4.48 3.19 阳起石 1.35 1.78 斜绿泥石 2.77 1.76 黑云母 1.80 1.25 白云母 1.98 2.12 针铁矿 1.49 1.13 鲕绿泥石 2.25 1.53 磁黄铁矿 1.59 0.44 镁铝石榴子石 1.60 0.80 黑电气石 0.41 0.40 高岭石 0.77 1.56 钛铁矿 0.24 0.17 钛闪石 0.67 0.60 其他 0.46 0.34 透辉石 0.29 0.76 正长石 0.41 0.48 其他 1.34 1.42 表 5 和尚桥铁矿尾矿及主要矿物钠长石、赤铁矿/磁铁矿、石英的粒度分布TIMA分析结果统计
Table 5. Statistics of particle size distribution of tailings, albite, hematite/magnetite and quartz from the Heshangqiao Fe deposit determined by TIMA
矿物名称 不同粒径矿物在尾矿中的质量占比(%) >2000μm
砾2000~500μm
粗砂500~250μm
中砂250~50μm
细砂50~5μm
粉砂<5μm
泥尾矿 0 40.12 35.07 20.20 4.10 0.51 钠长石 0 34.01 27.31 24.66 13.83 0.19 赤铁矿/磁铁矿 0 25.48 27.41 29.44 17.32 0.35 石英 0 27.99 25.68 29.21 16.90 0.22 表 6 中国不同类型单金属类铁矿尾矿工艺矿物学特性[9,32-35]
Table 6. Process mineralogy characteristics of different types of monometallic iron tailings in China
单金属类铁矿尾矿
类型元素含量特征 主要矿物组成 尾矿粒度主要分布 铁主要赋存矿物 高硅型 Si、Fe含量较高,Al含量较低 石英、阳起石、透辉石、长石 集中在50~350μm 透辉石、赤铁矿 高铝型 Si、Fe和Al含量较高 钠长石、赤铁矿/磁铁矿和石英 集中在50~2000μm 赤铁矿/磁铁矿、黄铁矿 高钙镁型 Si、Ca和Mg含量较高 方解石、钠长石和白云母 集中在3~155μm 赤铁矿 低钙镁铝硅型 Si、Ca、Mg和Al含量都较低 云母、石英、方解石、斜长石、重晶石 集中在75μm以下 赤铁矿、菱铁矿 -
[1] 邓文, 江登榜, 杨波, 等. 我国铁尾矿综合利用现状和存在的问题[J]. 现代矿业, 2012, 27(9): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2012.09.001
Deng W, Jiang D B, Yang B, et al. Current situation and existing problems of comprehensive utilization of iron tailings in China[J]. Modern Mining, 2012, 27(9): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2012.09.001
[2] Wan H, Yi P, Luukkanen S, et al. Recovering iron concentrate from low-grade siderite tailings based on the process mineralogy characteristics[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(6): 676. doi: 10.3390/min12060676
[3] 刘文博, 姚华彦, 王静峰, 等. 铁尾矿资源化综合利用现状[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(S1): 268−270.
Liu W B, Yao H Y, Wang J F, et al. Current status of comprehensive utilization of iron tailings[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(S1): 268−270.
[4] 陈邢, 于峰, 曹越, 等. 铁尾矿粉-脱硫灰胶凝材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42(1): 180−187.
Chen X, Yu F, Cao Y, et al. Preparation and properties of iron tailings powder-desulfurization ash cementitious material[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Silicate Society, 2023, 42(1): 180−187.
[5] Alfonso P, Ruiz M, Zambrana R N, et al. Process mineralogy of the tailings from Llallagua: Towards a sustainable activity[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(2): 214. doi: 10.3390/min12020214
[6] 杨杰, 董静, 宋洲, 等. 鄂西铜铅锌尾矿库周边农田土壤-水稻重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(5): 867−879.
Yang J, Dong J, Song Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and risk assessment of soil and rice in farmland around the copper-lead-zinc tailing, Western Hubei Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(5): 867−879.
[7] 曹惠昌, 郑竞, 高淑玲. 我国铁尾矿综合利用研究进展[J]. 现代矿业, 2011, 27(10): 68−71.
Cao H C, Zheng J, Gao S L. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of iron tailings in China[J]. Modern Mining, 2011, 27(10): 68−71.
[8] 蒋京航, 叶国华, 胡艺博, 等. 铁尾矿再选技术现状及研究进展[J]. 矿冶, 2018, 27(1): 1−4.
Jiang J H, Ye G H, Hu Y B, et al. Present situation and research progress of iron tailings reconcentration technology[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2018, 27(1): 1−4.
[9] 刘鹏, 刘磊, 田馨, 等. 我国铁尾矿工艺矿物学特性及其资源化技术研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2022, 42(3): 169−178.
Liu P, Liu L, Tian X, et al. Reviews of the process mineralogy characteristics and comprehensive utilization technology of iron ore tailings in China[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resource, 2022, 42(3): 169−178.
[10] 任明昊, 谢贤, 李博琦, 等. 铁尾矿综合利用研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2022, 42(3): 155−168.
Ren M H, Xie X, Li B Q, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of iron tailings[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resource, 2022, 42(3): 155−168.
[11] 赵新福, 曾丽平, 廖旺, 等. 长江中下游成矿带玢岩铁矿研究新进展及对矿床成因的启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(2): 197−217.
Zhao X F, Zeng L P, Liao W, et al. An overview of recent advances in porphyrite iron (iron oxide-apatite, IOA) deposits in the middle-lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt and its implication for ore genesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(2): 197−217.
[12] Wanhainen C, Pålsson B I, Martinsson O, et al. Rare earth mineralogy in tailings from Kiirunavaara iron ore, Northern Sweden: Implications for mineral processing[J]. Minerals & Metallurgical Processing, 2017, 34(4): 189−200.
[13] Peelman S, Kooijman D, Sietsma J, et al. Hydrometallurgical recovery of rare earth elements from mine tailings and WEEE[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2018, 4(3): 367−377. doi: 10.1007/s40831-018-0178-0
[14] 梁朝杰. 姑山尾矿磁化焙烧及磁选试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2014, 30(9): 83−84, 87.
Liang C J. Magnetic roasting and magnetic separation test of Gushan tailings[J]. Modern Mining, 2014, 30(9): 83−84, 87.
[15] 李广, 王化军, 孙体昌, 等. 梅山铁矿尾矿浮选铁的试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2015, 34(3): 173−175.
Li G, Wang H J, Sun T C, et al. Flotation of iron minerals from Meishan iron tailings[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2015, 34(3): 173−175.
[16] 丁开振, 王小玉, 胡炳胜, 等. 马钢罗河尾矿强磁-反浮选工艺研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2019, 35(11): 14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.11.005
Ding K Z, Wang X Y, Hu B S, et al. Research on strong magnetic-reverse flotation process of Luohe tailings in Masteel[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(11): 14−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.11.005
[17] 段超, 李延河, 毛景文, 等. 宁芜和尚桥铁氧化物-磷灰石矿床(IOA)成矿过程研究: 来自磁铁矿LA-ICP-MS原位分析的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(11): 3471−3483.
Duan C, Li Y H, Mao J W, et al. Study on the ore-forming process of the Heshangqiao IOA deposit in Ningwu ore district: Insight from magnetite LA-ICP-MS in-situ analysis data[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(11): 3471−3483.
[18] 谢小敏, 李利, 袁秋云, 等. 应用TIMA分析技术研究Alum页岩有机质和黄铁矿粒度分布及沉积环境特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 50−60.
Xie X M, Li L, Yuan Q Y, et al. Grain size distribution of organic matter and pyrite in Alum shale by TIMA and its paleo-environmental significance[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 50−60.
[19] 陈倩, 宋文磊, 杨金昆, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统的基本原理及其在岩矿研究中的应用——以捷克泰思肯公司TIMA为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(2): 345−368.
Chen Q, Song W L, Yang J K, et al. Principle of automated mineral quantitative analysis system and its application in petrology and mineralogy: An example from TESCAN TIMA[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(2): 345−368.
[20] 郑意, 刘文胜, 李杰, 等. 和尚桥铁矿隔离堤边坡治理复垦实践[J]. 现代矿业, 2022, 38(3): 223−225.
Zheng Y, Liu W S, Li J, et al. Practice of reclamation and treatment of isolation dike slope in Heshangqiao iron mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2022, 38(3): 223−225.
[21] 朱末琳, 武飞. 东山铁矿剩余资源开发利用论证[J]. 矿业工程, 2014, 12(6): 1−3.
Zhu M L, Wu F. Demonstration of exploration and utilization of remaining resources of Dongshan iron mine[J]. Mining Engineering, 2014, 12(6): 1−3.
[22] 徐嘉辰, 寿震宇, 曾霄祥, 等. 东山铁矿露天采场改建尾矿库边坡稳定性研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2016(7): 175−178.
Jia C, Shou Z Y, Zeng X X, et al. Study on the slope stability of the tailing pond built at open-pit stope in Dongshan iron mine[J]. Metal Mine, 2016(7): 175−178.
[23] 武飞. 安徽马鞍山东山铁矿Ⅰ区剩余资源开发方案可行性论证[J]. 现代矿业, 2017, 33(11): 79−82.
Wu F. Discussion on the development feasibility of the remaining resources of Ⅰ area in Dongshan iron mine in Ma’anshan City, Anhui Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2017, 33(11): 79−82.
[24] 刘义云. 和尚桥铁矿石选矿试验研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2013, 29(5): 172−173.
Liu Y Y. Experimental study on beneficiation of Heshang-qiao iron ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2013, 29(5): 172−173.
[25] Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2000, 51: 507−513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
[26] 张凤英, 张文捷, 刘春丽. X射线粉晶衍射(XRD)法在粘土矿物岩矿鉴定中的应用[J]. 低碳世界, 2018(9): 279−281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2018.09.174
Zhang F Y, Zhang W J, Liu C L. Application of X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) method in the identification of clay mineral rock[J]. Low Carbon World, 2018(9): 279−281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2018.09.174
[27] 何袖辉, 唐帅帅, 程江, 等. 碳酸钠-氧化锌半熔电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地球化学样品中的碘[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(4): 606−613.
He X H, Tang S S, Cheng J, et al. Determination of iodine in geochemical samples by ICP-MS with sodium carbonate-zinc oxide semi-melting[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(4): 606−613.
[28] 刘金, 王剑, 王桂君, 等. 利用电子探针和X射线衍射研究准噶尔盆地风城组淡钡钛石矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(5): 764−773.
Liu J, Wang J, Wang G J, et al. Analysis of mineralogical characteristics of leucosphenite from the Fengcheng Formation in the Junggar Basin by electron probe microanalyzer and X-ray diffractometer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(5): 764−773.
[29] 杨召群, 揣新, 张宏光, 等. 某铁矿超细碎尾矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2019, 35(10): 135−138.
Yang Z Q, Qi X, Zhang H G, et al. Study on ultrafine tailings process mineralogy in an iron ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(10): 135−138.
[30] 秦玉芳, 李娜, 王其伟, 等. 白云鄂博选铁尾矿稀土的工艺矿物学研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2021, 39(5): 796−804.
Qin Y F, Li N, Wang Q W, et al. Technological mineralogy of rare earth in Bayan Obo iron tailings[J]. Journal of the China Society of Rare Earths, 2021, 39(5): 796−804.
[31] 张燕, 宋志娇, 陈翠华, 等. 重庆城口高燕锰矿床矿物解离度与工艺粒度研究[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(1): 285−286.
Zhang Y, Song Z J, Chen C H, et al. Study on the liberation degree and processing size of mineral in Gaoyan Mn deposit, Chengkou, Chongqing[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(1): 285−286.
[32] 李德先, 王锦, 张长青, 等. 冀东司家营铁矿尾矿特征及综合利用建议[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(4): 1460−1468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.022
Li D X, Wang J, Zhang C Q, et al. Tailings characteristics and comprehensive utilization suggestions of the Sijiaying iron ore deposit in Eastern Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(4): 1460−1468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.022
[33] 韩波, 孙熠, 李月明, 等. 高掺量高钙型铁尾矿建筑瓷砖的制备及性能研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2023, 59(6): 68−73.
Han B, Sun Y, Li Y M, et al. Study on preparation and properties of building tiles with high content and high calcium iron tailings[J]. China Ceramics, 2023, 59(6): 68−73.
[34] 袁晨光, 黄自力, 刘楚玉, 等. 酒钢镜铁矿尾矿中铁矿物再回收试验研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2023, 48(1): 98−105.
Yuan C G, Huang Z L, Liu C Y, et al. Experimental research on recovery of iron minerals from specularite tailings in JISCO[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2023, 48(1): 98−105.
[35] 刘金长, 张双爱. 酒钢尾矿再利用实验室试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2017(12): 185−188.
Liu J C, Zhang S A. Laboratory research on recycling of ore tailing in JISCO[J]. Metal Mine, 2017(12): 185−188.
-



 下载:
下载: