GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND DISTRIBUTION PATTERN OF PETROLEUM IN WEST NATUNA BASIN, INDONESIA
-
摘要:
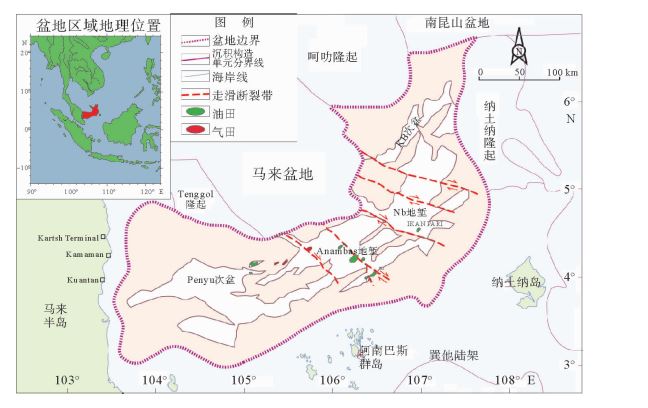
西纳土纳盆地是发育在东南亚巽他克拉通内的裂谷盆地,也是印度尼西亚重要的含油气盆地。运用盆地分析及石油地质学的理论与方法,对盆地构造—沉积演化及主力烃源岩、储集层及盖层等成藏要素进行综合研究,系统总结油气成藏特征及分布规律,并通过对比分析指出构造演化与沉积充填差异是造成盆地内烃源岩演化、储集层发育、油气成藏特征差异的主控因素。研究表明,油气可采储量区域上集中在Anambas地堑和Penyu次盆东北部,主要油气田(藏)类型包括挤压背斜、披覆构造和地层—构造型;层系上,油气主要储集于上渐新统和下中新统。盆地内远景地层圈闭以上始新统—下渐新统Belut组冲积扇相砂砾岩和上渐新统—下中新统Gabus—下Arang组河流下切谷砂岩为有利储层,勘探程度低,资源潜力较大。
Abstract:The West Natuna Basin, an intracratonic rifted basin on the northern Sunda Shelf, is an important petroliferous basin in Indonesia. Following the principles of basin analysis and petroleum geology, taking the tectonic evolution and sedimentary filling history of the whole basin as the major theme, we studied in this paper the forming mechanism of petroleum accumulation, such as source rocks, reservoirs and seals, in the basin. The hydrocarbon distribution and accumulation patterns were systematically summarized. Through comparison, it is concluded that the difference of tectonic evolution and sedimentary filling is the controlling factor over the difference in source maturity, reservoirs and hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics in the basin. Regionally, the discovered oil and gas reserves are largely confined to the Anambas Graben and the Northeastern Penyu Sub-basin and trapped in compressional anticlines, draping structures and structure-stratigraphic traps. Stratigraphically, the oil and gas are mostly reserved in the Upper Oligocene and Lower Miocene. Future exploration potential may exist in the under explored stratigraphic traps in the coarse grained alluvial fan deposits of the Belut Formation and incised valley fills of the Gabus Formation and Lower Arang Formation.
-
Key words:
- Indonesia /
- West Natuna Basin /
- petroleum geology /
- hydrocarbon distribution /
- exploration potential
-

-
图 4 西纳土纳盆地油气成藏模式(据文献[20]修改)
Figure 4.
表 1 西纳土纳盆地构造单元间油气成藏特征
Table 1. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of different tectonic units in the West Natuna Basin
油气聚集带 构造运动强度 圈闭类型 圈闭规模 运移距离 运移通道 Anambas地堑北部和东北部 受中新世反转运动影响强烈,常发育正反转断层,断距大 构造型:挤压背斜、断背斜圈闭类型单一,数量少,规模小 圈闭类型单一,数量少,规模小 本地生烃,运移距离短 边界断层,输导层 AAnambas地堑中部和南部 受中新世反转运动影响,断层部分反转,断距较小,走滑断层活动明显 构造型:挤压背斜、断背斜、断层/断块;地层—构造型 圈闭类型多样,数量多,规模较大 本地生烃,运移距离较长 边界断层,输导层,走滑断层 Penyu次盆东北部 受中新世反转运动影响较弱,断层部分反转或不反转,断距小 构造型:披覆背斜、挤压背斜、断背斜;地层—构造型 圈闭类型多样,数量较多,规模大 异地生烃,运移距离长 输导层 -
[1] IHS Energy Group. Basin Monitor, West Natuna Basin, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam[DB/OL]. [2016-3-11].http://www.ihs.com/.
[2] 朱伟林, 胡平, 江文荣, 等.南亚—东南亚含油气盆地[M].北京:科学出版社, 2012: 9-89.
[3] 金庆焕.南海地质与油气资源[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989: 377-381.
[4] 杨福忠, 薛良清.南亚太地区盆地类型及油气分布特征[J].中国石油勘探, 2006, 65(5): 65-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt200605013
[5] 姚永坚, 吕彩丽, 康永尚, 等.东南亚地区烃源岩特征与主控因素[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(2): 367-378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201302015
[6] Nawawi A, Anwar S, Heriyanto N, et al. West Natuna Basin, Petroleum Geology of Indonesian Basins-Principles, Methods, and Application[M]. Jakarta: Pertamina BPPKA, 1996: 86-88.
[7] Hakin M R, Naiola M Y Y, Simangunsong Y R A, et al. Hydrocarbon play of West Natuna Basin and challenge for new exploration related to structural setting and stratigraphic succession[C]//Indonesian Petroleum Association. 32nd Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 2008, IPA08-SG-039.
[8] Du Bois E P. Review of principal hydrocarbon-bearing basins of the South China Sea area[J]. Energy, 1981, 6(11): 1113-1140. doi: 10.1016/0360-5442(81)90029-3
[9] Madon M B H, Anuar A, Wong R. Structural evolution, maturation history, and hydrocarbon potential of the Penyu Basin, offshore peninsular malaysia[C]// Howes J V C, Noble R A. Proceedings of the Conference on Petroleum Systems of SE Asia and Australasia. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1997: 403-424.
[10] Ginger D C, Ardjakusumah W O, Hedley R J, et al. Inversion history of the West Natuna Basin: Examples from the Cumi-Cumi PSC[C]// Indonesian Petroleum Association. 22nd Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1993: 635-658.
[11] Tjia H D, Liew K K.Changes in tectonic stress field in northern Sunda Shelf basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 1996, 106(1): 291-306. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.106.01.19
[12] Doust H, Noble R A. Petroleum systems of Indonesia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(2): 103-129. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.05.007
[13] Shoup R C, Morley R J, Swiecicki T, et al. Tectono-stratigraphic framework and tertiary paleogeography of Southeast Asia; Gulf of Thailand to South Vietnam Shelf[J]. Houston Geological Society Bulletin, 2013, 55(6): 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39. http://www.searchanddiscovery.com/documents/2012/30246shoup/ndx_shoup.pdf
[14] Burton D, Wood L J, Burton D. Seismic geomorphology and tectonostratigraphic fill of half grabens, West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(11): 1695-1712. doi: 10.1306/06301010003
[15] Michael E, Adrian H. The petroleum systems of west Block B PSC, South Natuna Sea, Indonesia[C]//Indonesian Petroleum Association. 25th Silver Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1996: 465-679.
[16] Phillips S, Little L, Michael E, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of tertiary petroleum systems in the West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[C]// Howes J V C, Noble R A. Proceedings of the Conference on Petroleum Systems of SE Asia and Australasia. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1997: 381-390
http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10009896926 [17] IHS Energy Group. Basin Monitor, Malay Basin, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam[DB/OL]. [2016-3-11].http://www.ihs.com/.
[18] C and C Reservoirs. Belida Field West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[R/OL]. Houston: C and C Reservoirs. [2016-6-15]. http://www.ccreservoirs.com/.
[19] Sutoto A. Reservoir geology of the Belida field South Natuna Sea, Block B[C]//Indonesian Petroleum Association. 20th Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta : Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1991: 453-478.
[20] Wirojudo G K, Wongsosantiko A. Tertiary tectonic evolution and related hydrocarbon potential in the Natuna area[J]. Energy, 1985, 10(3-4): 433-455. doi: 10.1016/0360-5442(85)90059-3
[21] Nagura H, Honda H, Katori S. Tertiary inversion tectonics and petroleum systems in West Natuna Sea Basins, Indonesia[J]. Journal of the Japanese Asssociation for Petroleum Technology, 2000, 65(1): 91-102. doi: 10.3720/japt.65.91
-



 下载:
下载: