A NEWLY DISCOVERED SOURCE ROCK IN THE MID-LOWER ORDOVICIAN IN LOWER YANGTZE AREA
-
摘要:
中下奥陶统通常主要作为储层看待,然而皖南地区的下奥陶统宁国组主要为一套富含笔石的灰黑色—黑色薄层硅质、碳质泥岩,属广海陆棚相至深海盆地相沉积;而中奥陶统胡乐组主要为一套同样富含笔石的深灰色薄层粉砂质泥岩和中厚层硅质泥岩,属深海陆棚相至盆地相沉积。二者分布范围相当,但宁国组厚度明显大于胡乐组。下奥陶统宁国组6个样品的岩石热解数据显示,恢复后的TOC均值为1.24%。根据上升流的识别标准,宁国组和胡乐组的岩性和岩相特征以及宁国组地球化学测试结果,推测皖南地区中下奥陶统可能是一套受上升流影响的中—好烃源岩。鉴于南黄海是下扬子的主体,建议加强南黄海中下奥陶统烃源岩的研究。
Abstract:The Mid-lower Ordovician usually acts as reservoir for oil and gas accumulation in the Yangtze area, However, in the southern Anhui Province, there occurs a sequence of gray black to black siliceous mudstone and carbonaceous mudstone in the Ningguo Formation of Lower Ordovician. It consists of rich graptolite and is inferred as an open sea shelf or deep sea facies. The Hule Formation of Middle Ordovician which consists of thin-layered dark grey silty mudstone and thick-layered siliceous mudstone with rich graptolite, is also deposited in a shelf to deep basin environment. The two Formations are similar in depositional features and distribution patterns with rich graptolite fossil, but the Ningguo Formation is obviously thicker than the Hule Formation. Organic geochemistry of Ningguo Formation source rocks show that the average TOC is 1.24%. According to the upwelling features, and studies on lithology, lithofacies and organic geochemistry, it is concluded that the Middle-Lower Ordovician is likely to be a medium-good source rocks deposited by upwelling flow in the southern Anhui region. Since the South Yellow Sea Basin is the major part of the Lower Yangtze, it is suggested that the research of the Middle-Lower Ordovician source rocks be strengthened in the South Yellow Sea Basin.
-
Key words:
- Lower Yangtze /
- Mid-Lower Ordovician /
- Ningguo Formation /
- Hule Formation /
- source rocks
-

-
表 1 上下扬子早中奥陶世地层对比简表(据[7]修改)
Table 1. Early and medium Ordovician stratigraphic correlation between Upper and Lower Yangtze area (from reference [7])
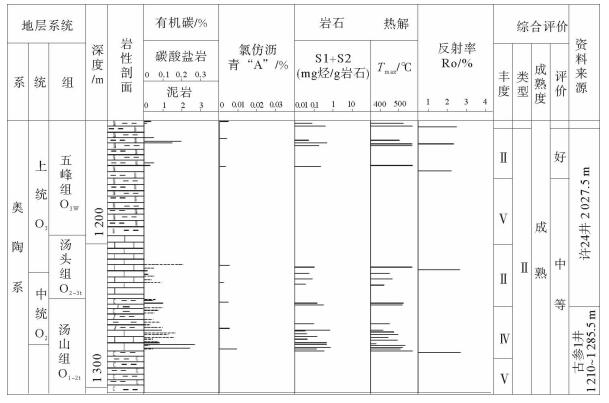
地区 四川秀山大田坝 江苏南京地区 安徽和县狮碾潘 安徽宿松地区 皖南地区 浙西北 浙西 江西武宁 江西崇义 湖南桃江-安华地区 粤北-粤中 胡乐阶 大田坝组 灰岩与泥质条带灰岩互层6 m 大田坝组 微晶生物碎屑灰岩2.2 m 庙坡组 上部泥质灰岩下部页岩4.5 m 庙坡组 黄灰色页岩1.4 m 胡乐组 硅质页岩、硅质岩、砂质页岩25 m 胡乐组 硅质泥岩夹硅质页岩63 m 胡乐组 黑色燧石层夹炭质页岩360 m 胡乐组 硅质泥岩顶部钙质泥岩10 m 胡乐组 硅质、炭质板岩互层81 m 胡乐组 硅质页岩夹炭质页岩28 m 长坑水组 硅质页岩夹砂岩68 m 宁国阶 牯牛潭组 灰岩与泥质瘤状灰岩31 m 牯牛潭组 微晶生物碎屑灰岩13 m 牯牛潭组 灰色中厚层灰岩7.1 m 油榨岭组 黄绿色瘤状泥灰岩9 m 宁国组 上段硅质页岩下段页岩、粉砂质页岩200 m 宁国组 灰黑色硅质泥页岩234 m 宁国组 黑色页岩含黄铁矿结核50 m 宁国组 砂质泥岩及硅质泥岩139 m 宁国组 黑色炭质硅质板岩670 m 烟溪组 硅质页岩夹炭质页岩208 m 下黄坑组 炭质泥质硅质页岩 大湾组 上部粗晶灰岩下部页岩20.2 m 蒋家围组 黄绿色页岩夹灰岩43 m 大湾组 页岩、瘤状灰岩、灰岩互层204 m 大湾组 上部页岩下部生物碎屑灰岩15 m 红花园组 含燧石结核灰岩56 m 红花园组 微晶及生物碎屑灰岩150 m 红花园组 厚层灰岩24.2 m 红花园组 灰色厚层白云岩 > 36 m 表 2 宁国组岩石热解数据
Table 2. Organic geochemistry of Ningguo Formation source rocks from Hule
原始编号 原始TOC/% 总烃 饱芳比 氯仿沥青“A”/(mg/g) PIR Ro/% 恢复后TOC/% HL-O1-2n-1 0.16 3.53 3.9 0.002 51 0.889 2.1 0.507 HL-O1-2n-3 0.08 - - - - - 0.257 HL-O1-2n-5 0.48 2.04 14.25 0.003 44 0.802 1.48 1.417 HL-O1-2n-7 0.21 - - - - - 0.634 HL-O1-2n-9 0.2 2.16 15.75 0.003 77 0.838 1.74 0.595 HL-O1-2n-11 1.01 5.74 2.567 0.004 72 0.846 1.79 3.038 -
[1] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 陈建平, 等.中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(一)南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的分布[J].海相油气地质, 2008, 13(2):1-16.
[2] 杨方之, 闫吉柱, 苏树桉, 等.下扬子地区海相盆地演化及油气勘探选区评价[J].江苏地质, 2001, 25(3):134-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsdz200103002
[3] 郭念发, 尤效忠, 刘德法.下扬子区古生界油气地质条件及勘探选区[J].石油勘探与开发-地质勘探, 1998, 25(1):4-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800908461
[4] 龚建明, 陈建文, 孙晶, 等.下扬子高家边组烃源岩展布及其对南黄海的启示[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1):54-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201601007
[5] 林小云, 刘建, 陈志良, 等.中下扬子区海相烃源岩分布与生烃潜力评价[J].石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(3):15-19.
[6] 安徽省地矿局区域地质调查大队.安徽地层志(奥陶系分册)[M].合肥:安徽科学技术出版社, 1989:1-164.
[7] 黄志诚, 朱嗣昭.安徽奥陶系石灰岩中含铁非骨架核形石的成因及其聚铁作用[J].沉积学报, 1987, 5(2):29-38, 148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CJXB198702003.htm
[8] 庞雄奇, 方祖康, 陈章明.地史过程中的岩石有机质含量变化及其计算[J].石油学报, 1988, 9(1):17-24 doi: 10.7623/syxb198801003
[9] 金强.生油岩原始有机碳恢复方法的探讨[J].石油大学学报:自然科学版, 1989, 13(5):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYDX198905002.htm
[10] 吴应琴, 王永莉, 雷天柱, 等.下古生界高过成熟烃源岩成熟度指标-姥鲛烷异构化指数研究[J].质谱学报, 2014, 35(4):317-323. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HYC201507200000004940
[11] 李天义, 何生, 杨智.海相优质烃源岩形成环境及其控制因素分析[J].地质科技情报, 2008, 27(6):63-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2008.06.012
[12] 胡望水, 吕炳全, 王红罡, 等.扬子地块东南陆缘寒武系上升流沉积特征[J].江汉石油学院学报, 2004, 26(4):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2004.04.003
[13] 吕炳全, 王红罡, 胡望水, 等.扬子地块东南古生代上升流沉积相及其与烃源岩的关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4):29-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200404005
[14] 李双建, 肖开华, 沃玉进, 等.南方海相上奥陶统-下志留统优质烃源岩发育的控制因素[J].沉积学报, 2008, 26(5):872-880.
-




 下载:
下载: