DIFFERENTIATED GAS DISTRIBUTION, MIGRATION AND ACCUMULATION IN THE CENTRAL DIAPIR BELT OF THE YINGGEHAI BASIN
-
摘要:
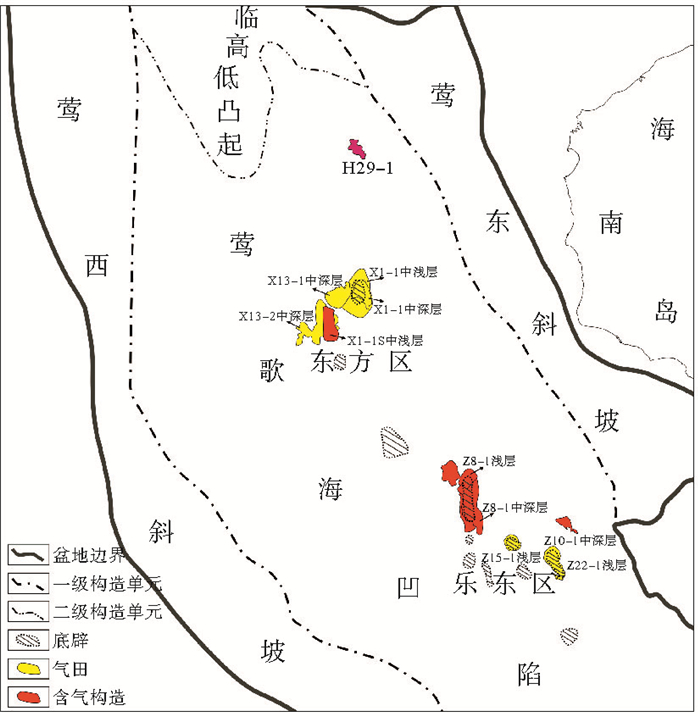
在地质地球化学综合分析研究的基础上,重点对莺歌海盆地东方区与乐东区天然气成因类型进行了系统分析总结,并结合区域构造演化、烃源岩展布特点与底辟上侵活动之成因联系等分析研究成果,深入剖析了东方区与乐东区天然气成藏特征及其控制因素。在此基础上,将研究区煤型天然气成因类型进一步细分为梅山型和三亚型2类,其分别来自中中新统梅山组和下中新统三亚组海相陆源烃源岩,且两者在东方区与乐东区分布差异明显。梅山组烃源岩厚度、生烃过程及输导体系等因素是导致两区天然气成藏过程及分布特征差异较大的主要原因,具体表现为乐东区梅山组和三亚组烃源岩生成天然气均可运移至浅层和中深层成藏;在东方区则仅梅山组烃源岩生成天然气可在浅层和中深层成藏,而三亚组烃源岩生成天然气多局限在底辟核部或构造脊周缘成藏,故导致了东方区与乐东区天然气分布之差异。两区天然气成藏均受控于底辟活动,且两区成藏特征也具有一定相似性和差异,因此,东方区与乐东区天然气成藏的相似性和差异决定了两区应采取针对性的勘探策略。
Abstract:The gas found in the Yinggehai Basin is a kind of coal-type gas from Miocene source rocks. However, the gas accumulation models based on it is hard to explain the differentiation of gas geochemistry in the Dongfang and Ledong areas. Based on the comprehensive study of gas geochemistry, source rock, tectonic evolution and diapir activity, it is concluded that the coal-type gas can be further subdivided into the Meishan type and the Shanya type. The two groups of gas distributed in the Dongfang area and the Ledong area, are respectively from Meishan source rock and Shanya source rock. The differentiation of distribution depends upon three factors, say: the thickness of Meishan formation, the generation process and the migration system. In the Ledong area, both the gas from Meishan and Shaya Formations can migrate into the shallow and middle-deep reservoirs. Same process might happen for the gas from Meishan Formation in the Dongfang area. However, the gas from the Shaya Formation is only accumulated in the cores of diapirs as well as the traps closed to the structural ridge in the Dongfang area. Therefore, the difference in gas accumulation in the Dongfang and Ledong areas are result from the different distribution of gas groups. As both of them are controlled by the diapir activity, the gas accumulations in the Dongfang area and the Ledong area are certainly similar. The similarity and difference should be careful considered in the selection of exploration targets.
-
Key words:
- natural gas /
- type classification /
- differentiated distribution /
- accumulation /
- Yinggehai Basin
-

-
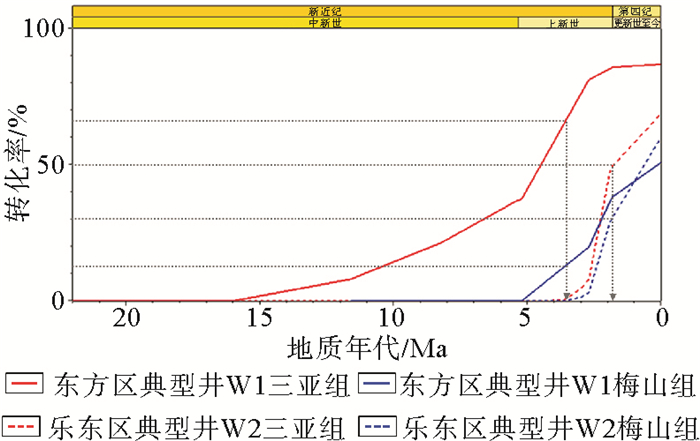
图 7 莺歌海盆地东方区与乐东区中新统烃源岩转化率(据文献[21]修改)
Figure 7.
-
[1] 刘铁树, 王俊兰.莺歌海盆地演化及天然气分布[J].中国海上油气(地质), 1994, 8(6):394-400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHSD199406004.htm
[2] 王善书, 胡仲琴.中国近海超压含气盆地的地质特点及勘探工作建议[J].中国海上油气(地质), 1998, 12(2):73-81. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800756369
[3] 谢玉洪, 李绪深, 童传新, 等.莺歌海盆地中央底辟带高温高压天然气富集条件、分布规律和成藏模式[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4):1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201504001
[4] 谢玉洪, 张迎朝, 徐新德, 等.莺歌海盆地高温超压大型优质气田天然气成因与成藏模式——以东方13-2优质整装大气田为例[J].中国海上油气, 2014, 26(2): 1-5, +34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHSD201402001.htm
[5] 童传新, 谢玉洪, 黄志龙, 等.莺歌海盆地高温高压天然气地球化学特征及底辟翼部高效成藏模式[J].天然气工业, 2015, 35(2):1-11. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.02.001
[6] 徐新德, 张迎朝, 裴健翔, 等.莺歌海盆地东方区天然气成藏模式及优质天然气勘探策略[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(5):956-965. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201405012
[7] 谢玉洪, 黄保家.南海莺歌海盆地东方13-1高温高压气田特征与成藏机理[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(8):1731-1739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201408012
[8] 何家雄, 陈伟煌, 李明兴.莺-琼盆地天然气成因类型及气源剖析[J].中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(6):398-405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2000.06.005
[9] 董伟良, 黄保家.南海莺-琼盆地煤型气的鉴别标志及气源判识[J].天然气工业, 2000, 20(1):23-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2000.01.006
[10] 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良.莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生烃演化模式[J].天然气工业, 2002, 22(1):26-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007
[11] 谢玉洪, 张迎朝, 李绪深, 等.莺歌海盆地高温超压气藏控藏要素与成藏模式[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(4):601-609. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201204009
[12] 何家雄, 杨计海, 陈志宏, 等.莺歌海盆地中深层天然气成藏特征[J].天然气工业, 2003, 23(3):15-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.03.005
[13] 张敏强.莺歌海盆地底辟构造带天然气运聚特征[J].石油大学学报, 2000, 24(4):39-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200004010
[14] 何家雄, 李明兴, 陈伟煌.莺歌海盆地热流体上侵活动与天然气运聚富集关系探讨[J].天然气地球科学, 2000, 11(6):29-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDKX200006005.htm
[15] 王振峰, 何家雄, 解习农.莺歌海盆地泥-流体底辟热流体活动对天然气运聚成藏的控制作用[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(3):203-210. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200402013
[16] 张士亚, 郜建军, 蒋泰然.利用甲、乙烷碳同位素判识天然气类型的一种新方法[C]//中国煤成气研究.北京:地质出版社, 1988.
[17] 戴金星, 邹才能, 张水昌, 等.无机成因和有机成因烷烃气的鉴别[J].中国科学(D辑), 2008, 38(11):1329-1341. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2008.11.001
[18] 戴金星.天然气中烷烃气碳同位素研究的意义[J].天然气工业, 2011, 31(12):1-6. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.001
[19] 刘文汇, 陈孟晋, 关平, 等.天然气成烃、成藏三元地球化学示踪体系及实践[M].兰州:甘肃科学技术出版社, 2009.
[20] 任建业, 曾佐勋, 雷超, 等.莺琼盆地构造演化及其成盆动力学机制分析[R].武汉:中国地质大学, 2009:98-118. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/93453x/201124/40536451.html
[21] 熊小峰, 徐新德, 郭潇潇, 等.沉积过程对莺歌海盆地烃源岩生气的控制作用[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(2):2169-2175. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201612008
[22] 徐新德, 张迎朝, 裴健翔, 等.构造演化对莺歌海盆地天然气成藏差异性的控制作用[J].天然气工业, 2015, 35(2):12-20. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.02.002
[23] 袁玉松, 范明, 刘伟新, 等.盖层封闭性研究中的几个问题[J].石油实验地质, 2011, 33(4):336-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.04.003
[24] 吕延防, 张绍臣, 王亚明.盖层封闭能力与盖层厚度的定量关系[J].石油学报, 2000, 21(2):27-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.02.005
[25] 付广, 许凤鸣.盖层厚度对封闭能力控制作用分析[J].天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(3):186-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.03.006
-



 下载:
下载: