SEABED SEDIMENT CLASSIFICATION BASED ON MULTIBEAM BACKSCATTER DATA
-
摘要:
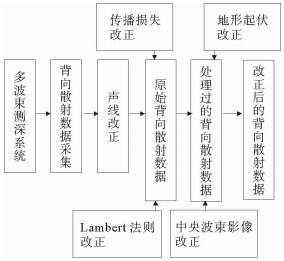
基于精细处理后的多波束数据生成背向散射影像图,利用灰度纹理共生阵提取影像纹理特征参数,采用支持向量机的神经网络(SVM)对背向散射影像进行底质分类研究。通过实测大面积、海量数据对该方法进行评价和验证,结果表明,该方法可获得比传统分类方法更高的分类精度,这种面状的分类弥补了传统点状分类的缺陷,使得大规模、大范围、高效快速的海底底质分类成为可能,为海洋地质调查、海洋工程建设、海底矿产资源开发等提供一种新型的科学的技术方法和可靠的地质基础资料。
Abstract:This paper introduces a method for seabed sediment classification.At first, texture features are extracted by gray level co-occurrence matrix based on backscatter image of multibeam data, then seabed sediment classification is carried out with supporting vector machine(SVM) using the backscatter combined with backscatter image.The result of classification by this method is better than the traditional method based on point data according to our practice.It will certainly make the regional marine geological survey more efficient and reliable.
-
Key words:
- backscatter /
- seabed classification /
- SVM /
- GLCM /
- texture features
-

-
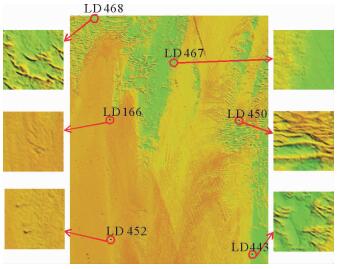
表 1 取样站位信息明细
Table 1. The list of the Geological sampling station
编号 水深/m 粒级含量/% 底质类型 LD466 40 0.00 15.56 63.74 20.7 黏土质砂 LD467 43 42.4 25.92 23.67 8.01 砂质砾石 LD468 35 10.64 20.01 52.10 17.25 砂质粉砂 LD443 41 0.00 38.43 47.54 14.12 砂质粉砂 LD450 31 0.17 99.83 0.00 0.00 砂 LD452 36 0.00 47.06 41.89 11.05 粉砂质砂 表 2 三种分类方法分类精度对比
Table 2. Accuracy comparison of three classification methods
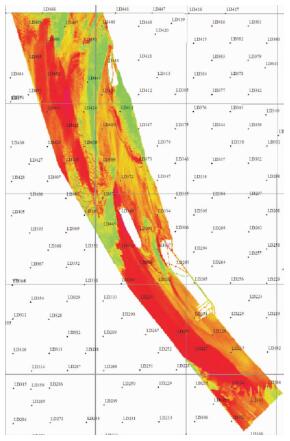
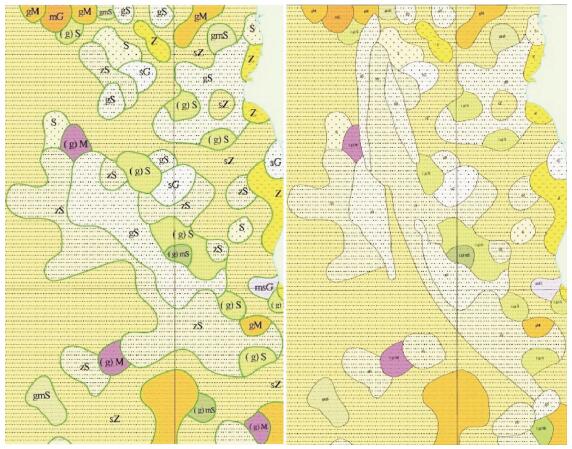
分类方法 精度 Kappa系数 背向散射强度 73.22% 0.613 0 纹理信息 90.36% 0.812 8 纹理结合背向散射强度 96.65% 0.885 7 表 3 背向散射强度与站位底质类型对应关系
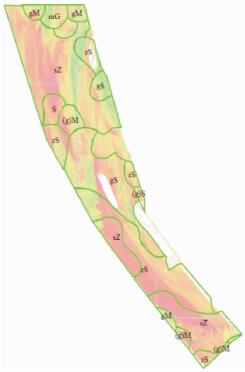
Table 3. Relational form of backscatter intensity and seabed types of the station
区域颜色 落在该区域的站位编号 底质类型 推算的区域底质类型 红色 LD227、LD253、LD291、LD308、LD332、LD452、LD466 砂质粉砂(sZ) 砂质粉砂(sZ) LD253、LD332 粉砂质砂(zS) 橙色 LD217、LD226、LD254、LD292、LD334、LD372、LD444 粉砂质砂(zS) 粉砂质砂(zS) LD183和LD410 砂质粉砂(sZ) 绿色 LD307、LD371、LD411、LD450 砾质砂(gS) 砾质砂(gS) -
[1] 陶春辉, 金翔龙, 许枫, 等.海底声学底质分类技术的研究现状与前景[J].东海海洋, 2004, 22(3):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2004.03.004
[2] Anderson J T, Van Holliday D, Kloser R, et al.Acoustic seabed classification of marine physical and biological landscapes[R].ICES Cooperative Research Report No.286.Copenhagen V, Denmark: International Council for the exploration of the Sea, 2007: 1-7.
[3] Anderson J T, Van Holliday D, Kloser R, et al.Acoustic seabed classification:current practice and future directions [J].ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2008, 65(6):1004-1011. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsn061
[4] Preston J M, Christney A C, Bloomer S F, et al.Seabed classification of multibeam sonar image [J].Oceans, 2001(4):2616-623. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/968411
[5] Michalopoulou Z H, de Moustierc A D.Application of neural and statistical classifiers to the problem of seafloor characterization [J].IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1995, 20(3):190-197. doi: 10.1109/48.393074
[6] 郭军, 马金凤.基于粒子群优化算法的SVM神经网络在海底底质分类中的应用[J].测绘与空间地理信息, 2012, 35(12):66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2012.12.021
[7] 张国堙, 陶春辉, 李怀明, 等.多波束声参数在海底热液区底质分类中的应用[J].海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(7):59-65. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201207009
[8] 金绍华, 翟金生, 刘雁春, 等.Simrad EM多波束反向散射强度数据精细处理研究[J].测绘科学, 2010, 35(2):106-108. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/chkx201002035
-



 下载:
下载: