SPATIO-TEMPORAL DISTRIBUTION AND VARIATION OF SUSPENDED SEDIMENT BY THE ACTION OF TIDE IN PENGLAI COASTAL AREA
-
摘要:
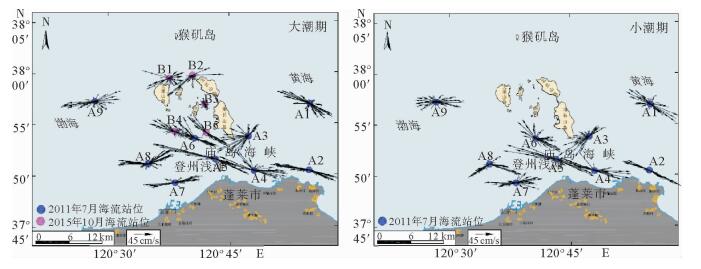
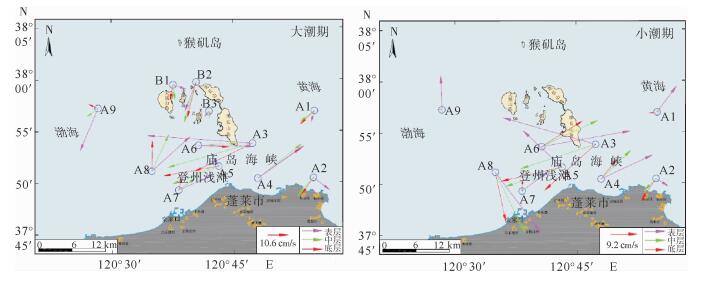
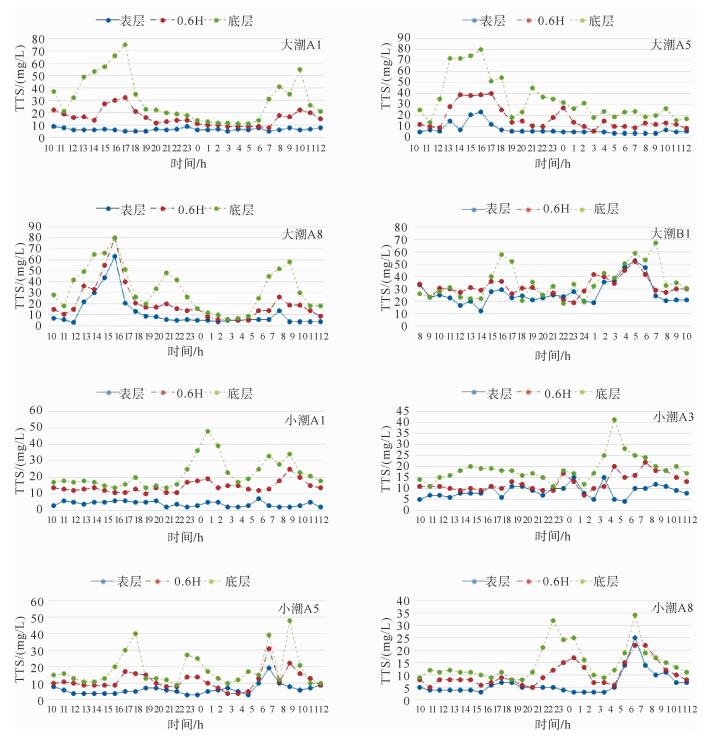
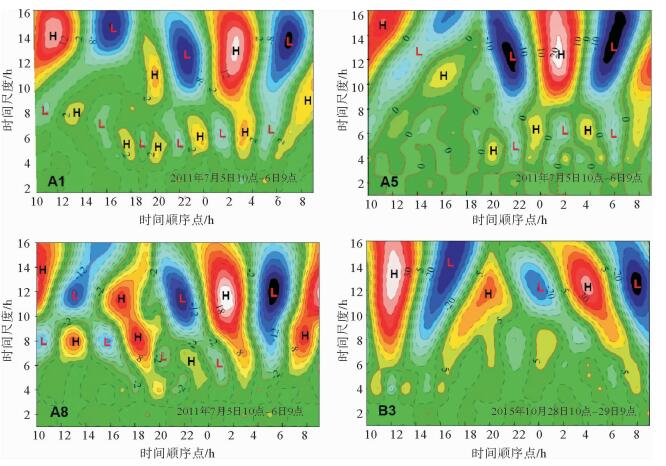
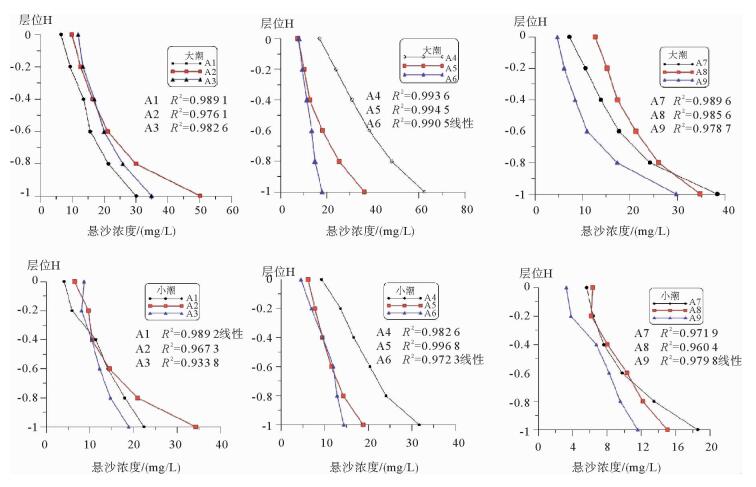
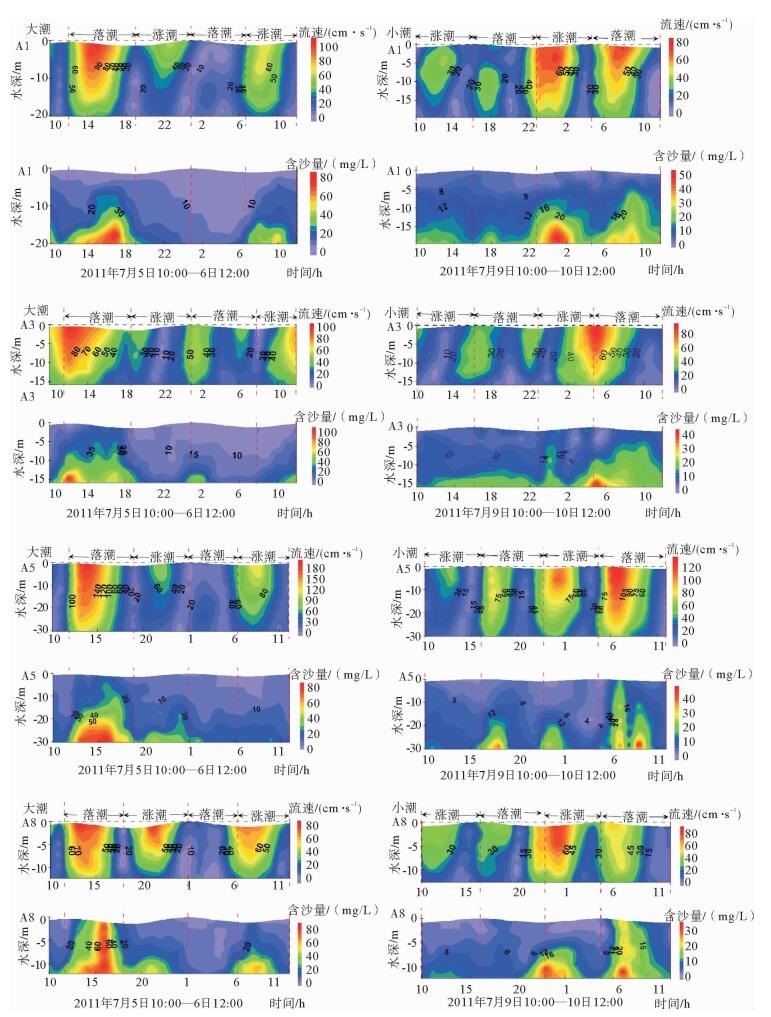
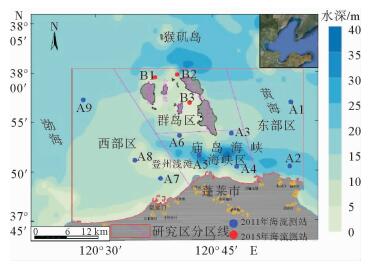
水体中悬浮泥沙浓度的变化过程是泥沙运动的重要表现形式,客观反映了不同的水动力环境。根据蓬莱近岸海流、悬浮泥沙等实测资料,分析了研究区悬浮泥沙浓度时空分布特征和变化规律,并初步探讨了悬浮泥沙浓度变化对潮流的响应。研究结果表明,时间上,研究区平均含沙量落潮段大于涨潮段,大潮期大于小潮期;不同层位悬浮泥沙浓度随时间的周期性波动大潮期强于小潮期,悬浮泥沙浓度时间周期变化的9~16 h尺度在研究区具有全域性。空间上,研究区各层平均悬浮泥沙浓度由表层至底层递增,悬浮泥沙浓度垂向梯度变化大潮期群岛区最小,海峡区最大,小潮期西部区最小,东部区最大,悬浮泥沙浓度的垂向分布类型以指数型、斜线型为主;潮周期平均悬浮泥沙浓度群岛区最大,海峡区次之,西部区最小;悬浮泥沙浓度潮周期变化与该海域潮流流速周期变化具有较好的相关性,潮流流速超过40 cm/s时,发生明显的再悬浮现象。
Abstract:The change in suspended sediment concentration of a water body is an important manifestation of sediment movement, which may objectively reflect the difference in hydrodynamic environment. Using the measured data of nearshore current as well as the suspended sediment from the Penglai area, this paper concentrates itself into the temporal and spatial distribution patterns and variations in suspended sediment concentrations in the area, and their response to tidal current. Results show that the average sediment concentration in the ebb tide period is usually larger than that in the high tide period, and that in the spring tide is larger than that in the neap tide. The cyclical fluctuation of the suspended sediment concentration in different layers is stronger in the spring tide rather than in the neap tide. The periodic change in the suspended sediment concentration on a scale of 9 ~ 16 h in the study area is same as the global. With regard to the spatial distribution, the average suspended sediment concentration increases from the surface to the bottom. During the spring tide, the vertical gradient of the suspended sediment concentration is the smallest in the Island area, but the largest in the Strait area. However, suspended sediment concentration in a neap tide is the smallest in the west but the largest in the east area. And the vertical distribution of suspended sediment concentration is in an exponential and linear relationship with depth. In a tidal cycle, the largest average suspended sediment concentration is at the Island area, followed by the Strait area, with the western region as the smallest. There is a good correlation between the suspended sediment concentration and the tidal current velocity. When the current velocity exceeds 40 cm/s, significant resuspension will occur.
-
Key words:
- Penglai coast /
- suspended sediment /
- temporal and spatial distribution /
- tide
-

-
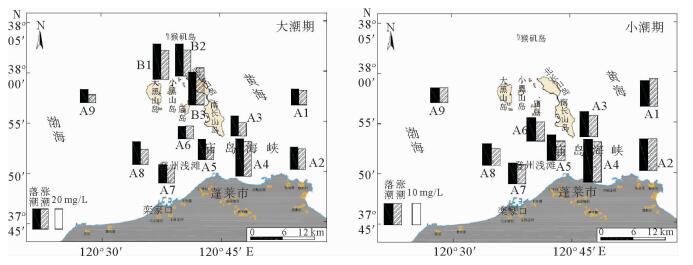
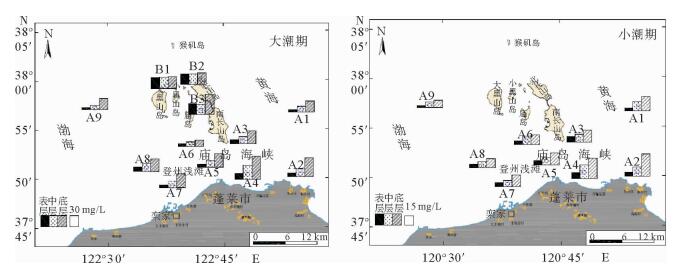
表 1a B1-B3各站最大含沙量
Table 1a. Maximum sediment concentration at stations B1-B3
/(mg/L) 站名 落潮 涨潮 含沙量 层位 含沙量 层位 B1 58.8 底层 66.8 底层 B2 68.8 底层 51.6 底层 B3 130.2 底层 166.4 底层 表 1b A1-A9各站最大含沙量
Table 1b. Maximum sediment concentration at stations A1-A9
/(mg/L) 站名 落潮 涨潮 大潮 小潮 大潮 小潮 A1 75 34 55 48 A2 116 73 111 66 A3 103 41 46 17 A4 155 81 97 44 A5 80 48 45 27 A6 63 39 33 22 A7 102 53 81 37 A8 80 34 58 32 A9 104 18 32 19 表 2a A1-A9各站垂线平均最大含沙量
Table 2a. Average vertical maximum sediment concentration at stations A1-A9
/(mg/L) 站名 落潮 涨潮 大潮 小潮 最大值 大潮 小潮 最大值 A1 33 22 33 23 20 23 A2 57 27 57 43 30 43 A3 41 18 41 24 11 24 A4 113 32 113 56 33 56 A5 41 29 41 19 13 19 A6 41 27 41 18 14 18 A7 49 18 49 27 16 27 A8 75 24 75 28 13 28 A9 34 10 34 14 11 14 表 2b B1-B3各站垂线平均最大含沙量
Table 2b. Average vertical maximum sediment concentration at stations B1-B3
/(mg/L) 站名 落潮 涨潮 B1 54.5 40.1 B2 47.9 33.9 B3 55.5 116.2 -
[1] 秦蕴珊, 李凡.渤海海水中悬浮体的研究[J].海洋学报, 1982, 4(2):191-200. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19820207
[2] 江文胜, 苏健, 杨华, 等.渤海悬浮物浓度分布和水动力特征的关系[J].海洋学报, 2002, 24(S1):213-218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC2002S1021.htm
[3] 江文胜, 王厚杰.莱州湾悬浮泥沙分布形态及其与底质分布的关系[J].海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(2):97-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.02.001
[4] 于炜.渤海表层悬浮物分布变异规律的研究[D].北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011.
[5] Yang Z, Ji Y, Bi N, et al.Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J].Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3):173-181. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272771410002143
[6] 庞重光, 于炜.渤海表层悬浮泥沙的空间模态及其时间变化[J].水科学进展, 2013, 24(5):722-727. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=skxjz201305015
[7] 李福林, 夏东兴, 王文海, 等.登州浅滩的形成、动态演化及其可恢复性研究[J].海洋学报, 2004, 26(6):65-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.06.008
[8] 王庆, 仲少云, 刘建华, 等.山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200602003
[9] 陈雪英, 胡泽建.山东蓬莱西庄附近海域波浪与海岸侵蚀[J].海洋科学进展, 1992, 10(2):18-26. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/91338X/199202/790814.html
[10] 董超.登州浅滩表层沉积物输运特征的研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.
[11] Farge M.Wavelet transforms and their applications to turbulence[J].Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 24:395-457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.24.010192.002143
[12] Lafrenière M, Sharp M.Wavelet analysis of inter-annual variability in the runoff regimes of glacial and nival stream catchments, Bow Lake, Alberta[J].Hydrological Process, 2003, 17: 1093-1118. doi: 10.1002/hyp.1187
[13] 王文圣.水文小波分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2005.
[14] 贺松林, 孙介民.长江河口最大浑浊带的悬沙输移特征[J].海洋与湖沼, 1996, 27(1):60-66. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1996.01.011
[15] 刘潇, 冯秀丽, 刘杰, 等.山东半岛靖海湾及其附近海域悬浮泥沙分布与变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):9-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206002
[16] Clarke S, Elliott A J.Modelling suspended sediment concentrations in the Firth of Forth[J].Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 1998, 47(3):235-250. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=54e01f79a1507e1bbcf6470ef32fa1d8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] Chen S.Seasonal, neap-spring variation of sediment concentration in the joint area between Yangtze Estuary and Hangzhou Bay[J].Science China Chemistry, 2001, 44(1):57-62. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=eff3bf8f35b781d3c923c3f6849ec5a3
[18] 谷国传.长江口外水域悬沙分布特征[J].海洋学研究, 1986, 4(1):16-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DHHY198601003.htm
-



 下载:
下载: