DETAILED ASSESSMENT OF MESO-PALEOZOIC HYDROCARBON SOURCE ROCKS: IMPLICATIONS FROM WELL CSDP-2 ON THE CENTRAL UPLIFT OF THE SOUTH YELLOW SEA BASIN
-
摘要:
CSDP-2井是在南黄海中部隆起上首钻的全取心深钻,在新近系之下钻遇下三叠统青龙组—上奥陶统多套碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩地层。钻井揭示的烃源岩有机质丰度、类型、热演化程度、可溶有机物分析及生烃强度计算证实,中部隆起发育倾油型的青龙组上段灰岩、上奥陶统—下志留统上部泥岩、油气型的石炭系中—上部灰岩3套有效烃源岩;生气为主的有效烃源岩主要为大隆组—龙潭组泥岩和炭质泥岩、栖霞组上部富含炭质的臭灰岩、石炭系中—下部灰岩和底部炭质泥岩。目前钻井揭示的中—古生界总生烃强度是(20.761 9~31.283 9)×108 m3气当量/km2,与国内外大中型气田分布区域的生气强度相当。其中,油源岩的总生油强度为(43.076~55.30)×104 t/km2,气源岩的总生气强度为(16.454 3~25.753 9)×108 m3/km2;同时,烃源岩的总生气强度是生油强度的4~5倍,碎屑岩的生烃强度是灰岩的2倍以上。巨大的生烃强度和多源层供烃为形成大—中型的油气聚集和成藏提供了充分的物质基础,显示了南黄海中部隆起中—古生界良好的油气勘探前景。
Abstract:The well CSDP-2 is the first whole coring deep hole ever drilled on the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin. It penetrated many sets of clastic and carbonate rocks from the Late Ordovician Formation up to the Early Triassic Qinglong Formation unconformably under the Neogene. The data of organic abundance, organic types, thermal evolution history, soluble organic matter and hydrocarbon-generating intensity of the sequence confirms that on the Central Uplift there occurs three sets of effective hydrocarbon source rocks: the lipophilic limestone of the Upper Member of the Qinglong Formation, the mudstone of the Upper Ordovician up to the upper member of the Lower Silurian and the oil-gas type limestone of the Middle and Upper Members of the Carboniferous. The effective hydrocarbon source rocks that generated gas are mainly the mudstone and carbonaceous mudstone of the Dalong Formation-Longtan Formation, the stink limestone of Upper Qixia Formation which is rich in organic, limestone of middle-lower Carboniferous and the carbonaceous mudstone in the bottom of Carboniferous. The Mesozoic and Paleozoic total hydrocarbon-generating intensity revealed by the drilling is (20.7619-31.2839)×108m3gas equivalent/km2 and its gas-generating intensity is roughly comparable to large and medium-sized gas fields of the world. According to our calculation, the total oil-generating intensity of the oil source rock is (43.076-55.30)×104t/km2, and the total gas-generating intensity of gas source rock is (16.4543-25.7539)×108m3/km2. The total gas-generating intensity of source rocks is 4-5 times higher than the oil-generating intensity, and the hydrocarbon-generating intensity of clastic rocks is twice higher than that of limestone. High hydrocarbon-generating intensity and abundance of hydrocarbon source layers have provide sufficient materials for a medium-large oil and gas accumulation, showing a good oil and gas exploration prospect of the Mesozoic-Paleozoic in the region of the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea Basin.
-

-
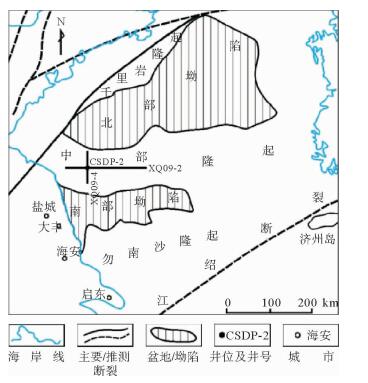
图 1 南黄海盆地构造单元划分及CSDP-2井位置(据文献[2])
Figure 1.
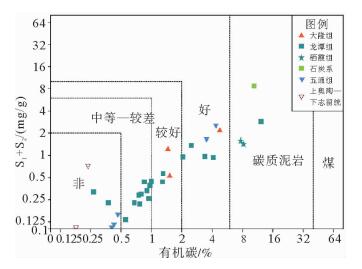
表 1 海相泥质烃源岩分类评价标准(据文献[3])
Table 1. Classification and evaluation standard of marine hydrocarbon source rocks (from reference [3])
岩性 评价级别 最好 好 中等 差 非烃源岩 泥岩 有机碳/% >2.0 1.0~2.0 0.6~1.0 0.4~0.6 <0.4 氯仿沥青"A"/% >0.2 0.1~0.2 0.05~0.1 0.015~0.05 <0.015 总烃/10-6 >1 000.0 500.0~1 000.0 200.0~500.0 100.0~200.0 <100.0 生烃潜量S1+S2/(mg/g) >20.0 6.0~20.0 2.0~6.0 1.0~2.0 <1.0 炭质泥岩 有机碳/% >10.0 4.0~10.0 2.0~4.0 0.7~2.0 <0.7 氯仿沥青"A"/% >0.15 0.065~0.15 0.035~0.065 0.015~0.035 <0.015 总烃/10-6 >350.0 200.0~350.0 150.0~200.0 70.0~150.0 <70.0 生烃潜量S1+S2/(mg/g) >20.0 6.0~20.0 2.0~6.0 0.5~2.0 <0.5 表 2 CSDP-2井烃源岩有机质丰度及有效性评价简表
Table 2. Organic matter abundance and effectiveness evaluation of hydrocarbon source rocks of well CSDP-2

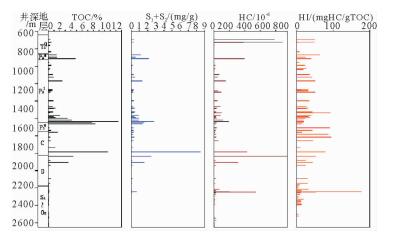
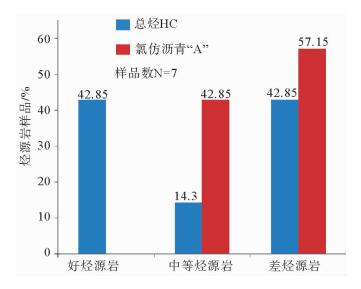
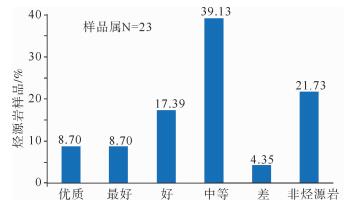
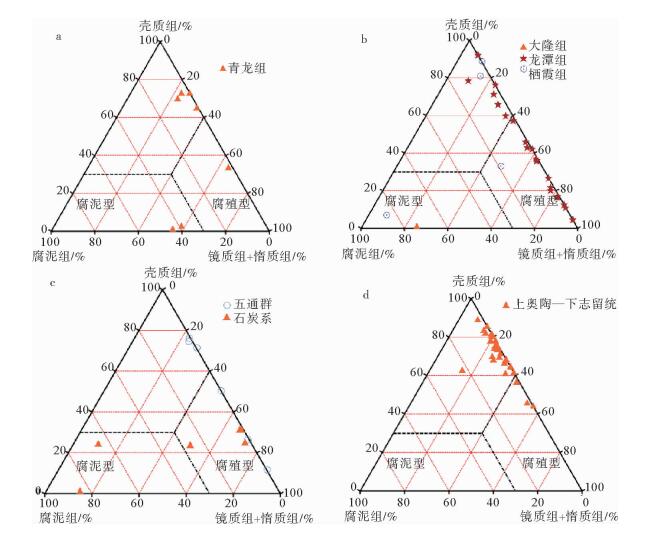
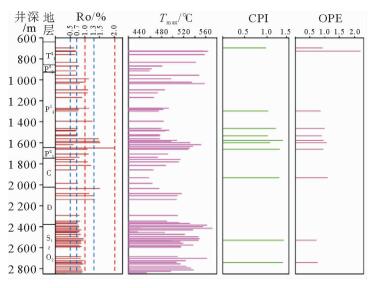
有机质类型 TOC含量/% 氯仿沥青“A”含量/% 产油潜量(S1+S2)/(mg/g) 总烃/10-6 镜质体反射率Ro/% 烃源岩有效性评价 碳酸盐岩 青龙组泥质灰岩 Ⅱ2为主,部分Ⅲ $ \frac{{0.25 \sim 0.65}}{{0.40\left( 7 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.009 \sim 0.1164}}{{0.04631\left( 7 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.001 \sim 0.310}}{{0.1261\left( 7 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{2.81 \sim 887.12}}{{370.13\left( 7 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.64 \sim 0.75}}{{0.683\left( 7 \right)}} $ 低成熟—成熟,近60%为中等—好、其余为差—非烃源岩 栖霞组灰岩 Ⅱ2及Ⅰ $ \frac{{0.22 \sim 0.49}}{{0.355\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0004 \sim 0.0086}}{{0.0056\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.25 \sim 0.28}}{{0.262\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{22.47 \sim 34.70}}{{28.585\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.82 \sim 1.13}}{{0.975\left( 2 \right)}} $ 成熟,中等—差,部分为非烃源岩 石炭系 1 757.5 m、1 857.78 m灰岩 Ⅰ $ \frac{{0.43 \sim 1.64}}{{1.035\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0033 \sim 0.0079}}{{0.0056\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.25 \sim 0.29}}{{0.27\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{13.55 \sim 55.73}}{{34.64\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0.65 \sim 0.70}}{{0.675\left( 2 \right)}} $ 低成熟,中等和最好烃源岩 石炭系泥质灰岩 Ⅲ $ \frac{{0.16 \sim 1.20}}{{0.567\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0015 \sim 0.0103}}{{0.0059\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.16 \sim 0.37}}{{0.237\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{2.776 \sim 29.66}}{{18.58\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{1.10 \sim 1.21}}{{1.115\left( 3 \right)}} $ 成熟,非均质性强,部分中等、部分差—非烃源岩 泥盆系底部灰色灰岩 Ⅱ2 0.28(1) 0.003 4(1) 0.08(1) 16.24(1) 0.84(1) 非烃源岩 碎屑岩 石炭系底部炭质泥岩 Ⅲ 10.59(1) 0.114 6(1) 8.49(1) 427.92(1) 0.77(1) 低熟,好—最好烃源岩 大隆组泥岩 Ⅱ1 $ \frac{{1.48 \sim 4.85}}{{2.62\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0434 \sim 0.0877}}{{0.06217\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.52 \sim 2.14}}{{1.283\left( 3 \right)}} $ 395.28(1) $ \frac{{0.71 \sim 0.807}}{{0.7585\left( 3 \right)}} $ 成熟,总体为好烃源岩,下部优于中上部 龙潭组泥岩 Ⅲ为主,部分Ⅱ2 $ \frac{{0.18 \sim 4.18}}{{1.145\left( 22 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0015 \sim 0.0489}}{{0.01245\left( 20 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.01 \sim 1.32}}{{0.3977\left( 22 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{4.62 \sim 154.18}}{{54.29\left( 20 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.62 \sim 1.52}}{{0.975\left( 20 \right)}} $ 总体成熟,上部120 m差—非烃源岩,中部近500 m地层烃源岩以中等为主,夹80余米好—最好烃源层,下部发育32 m优质烃源岩 龙潭组—孤峰组炭质泥岩 Ⅱ1 12.41(1) 0.025 5(1) 2.79(1) 190.48(1) / 成熟,好烃源岩 栖霞组顶部富含炭质臭灰岩 Ⅱ2 $ \frac{{7.77 \sim 8.36}}{{8.065\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0059 \sim 0.0067}}{{0.0063\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{1.39 \sim 1.56}}{{1.475\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{25.48 \sim 35.87}}{{30.675\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{1.09 \sim 2.02}}{{1.555\left( 2 \right)}} $ 成熟—过成熟,好烃源岩 泥盆系五通群 上部2 034.80 m和2 104.65 m处灰黑色泥岩 Ⅲ $ \frac{{3.56 \sim 4.43}}{{3.995\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0749 \sim 0.2794}}{{0.1772\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{1.58 \sim 2.45}}{{2.015\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{312.86 \sim 1317.93}}{{815.40\left( 2 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{1.32 \sim 1.51}}{{1.415\left( 2 \right)}} $ 成熟—高成熟,好—最好,部分优质烃源岩 中—下部深灰色泥岩 Ⅱ2及Ⅲ $ \frac{{0.41 \sim 0.47}}{{0.437\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0038 \sim 0.0048}}{{0.00423\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.10 \sim 0.15}}{{0.12\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{19.25 \sim 24.71}}{{21.66\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.82 \sim 1.34}}{{1.103\left( 3 \right)}} $ 成熟,差—非烃源岩 上奥陶统|下志留统 2 414.6~ 2 446.6 m井段3个泥岩样品 Ⅲ $ \frac{{0.16 \sim 0.24}}{{0.193\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.01 \sim 0.073}}{{0.0364\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.06 \sim 0.69}}{{0.85\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{69.35 \sim 543.85}}{{277.32\left( 3 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.75 \sim 0.82}}{{0.796\left( 3 \right)}} $ 成熟,中等—好烃源岩,局部为差—非烃源岩 2 455.4~ 2 839.6井段28个深灰色—灰黑色泥岩样品 Ⅱ2为主,少数Ⅲ,极少Ⅱ1 $ \frac{{0.08 \sim 0.17}}{{0.138\left( 28 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.0004 \sim 0.0034}}{{0.0018\left( 28 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0 \sim 0.03}}{{0.089\left( 28 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{2.0 \sim 23.18}}{{9.88\left( 28 \right)}} $ $ \frac{{0.71 \sim 0.96}}{{0.864\left( 28 \right)}} $ 低成熟—成熟,非烃源岩 注: $ \frac{{最小值 - 最大值}}{{平均值\left( 样品数 \right)}}$ 表 3 CSDP-2井烃源岩饱和烃气相色谱分析数据简表
Table 3. Chromatogram of saturated gas phase group of hydrocarbon source rocks of well CSDP-2
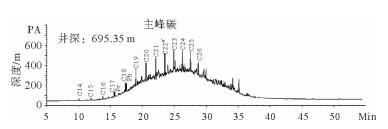
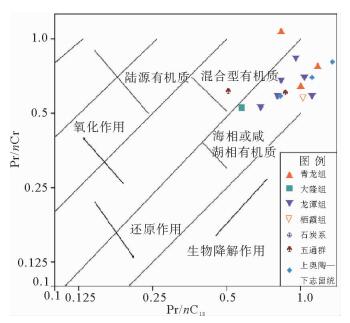
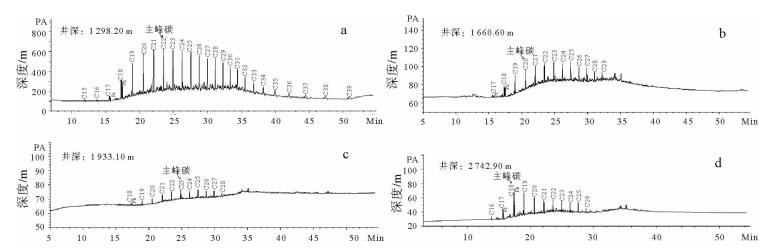
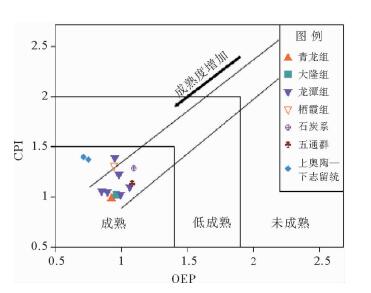
井深/m 碳数分布 主峰碳 Pr Ph Pr/Ph C(21+22)/ C(28+29) ∑nC21-/ ∑nC22+ ∑nC22-/ ∑nC23+ Pr/ nC17 Ph/ nC18 Pr+Ph/ nC17+nC18 CPI OEP 695.35 C14—C26 C22 2.87 4.14 0.69 / 0.83 1.37 1.06 0.84 0.92 0.98 0.93 726.20 C14—C21 C21 6.56 13.98 0.47 / / / 0.77 1.18 1.01 / 2.21 1 298.2 C15—C39 C22 0.27 1.91 0.14 18 0.27 0.42 0.58 0.81 0.77 1.03 0.86 1 464.6 C16—C29 C21 0.65 3.31 0.20 7.73 0.75 1.33 0.52 0.69 0.65 1.20 0.99 1 535.1 C15—C38 C20 1.63 5.10 0.32 2.27 0.52 0.74 0.82 0.96 0.92 1.02 0.90 1 578.3 C17—C29 C22 0.51 3.54 0.14 2.46 0.47 0.77 0.69 1.04 0.97 1.36 0.96 1 599.2 C17—C28 C19 1.09 9.06 0.12 4.79 0.92 1.34 0.58 1.12 1.02 1.07 1.07 1 660.6 C17—C29 C20 0.54 4.28 0.13 1.77 0.51 0.76 0.57 1.03 0.95 1.29 0.95 1 933.1 C18—C28 C23 / 1.34 / 4.57 0.32 0.56 / 0.67 0.67 1.28 1.10 2 414.6 C16—C23 C18 5.34 14.48 0.37 / 5.27 13.79 0.58 0.83 0.74 / 0.83 2 446.6 C14—C20 C18 9.50 14.18 0.67 / / / 0.60 0.87 0.74 / 0.93 2 530.3 C16—C26 C18 3.47 14.29 0.24 / 1.40 2.04 0.69 1.12 1.00 1.38 0.72 2 742.9 C16—C26 C18 4.57 18.28 0.25 / 1.81 2.84 0.80 1.36 1.19 1.36 0.76 -
[1] 郭兴伟, 朱晓青, 宋世杰.大陆架科钻CSDP-2井在南黄海海相地层中首次钻遇油气显示[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):124. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505017
[2] 郭兴伟, 朱晓青,牟林, 等.南黄海中部隆起二叠纪-三叠纪菊石的发现及其意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):21-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201703012
[3] 王东良, 李欣, 李书琴, 等.未成熟—低成熟煤系烃源岩生烃潜力的评价——以塔东北地区为例[J].中国矿业大学学报:自然科学版, 2001, 30(3):317-322. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkydxxb200103025
[4] 郝石生, 高岗, 王飞宇, 等.高过成熟海相烃源岩[M].北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996.
[5] 钟宁宁, 秦勇.碳酸盐岩有机岩石学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1995.
[6] 程克明, 王兆云, 钟宁宁, 等.碳酸盐岩油气生成理论与实践[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1996.
[7] 钟宁宁, 张枝焕.石油地球化学进展[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1998.
[8] 夏新宇.碳酸盐岩生烃与长庆气田气源[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2000.
[9] 梁狄刚, 张水昌, 张宝民, 等.从塔里木盆地看中国海相生油问题[J].地学前缘, 2000, 7(4):543-547. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200004023
[10] 薛海涛, 卢双舫, 钟宁宁.碳酸盐岩气源岩有机质丰度下限研究[J].中国科学(D辑), 2004, 34(A01):127-133.
[11] 陈建平, 梁狄刚, 张水昌, 等.中国古生界海相烃源岩生烃潜力评价标准与方法[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(7):1132-1142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.07.009
[12] 秦建中, 刘宝泉, 国建英, 等.关于碳酸盐烃源岩的评价标准[J].石油实验地质, 2004, 26(3):281-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.03.012
[13] 薛海涛.碳酸盐岩烃源岩有机质丰度评价标准[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2010.
[14] 张善文, 隋风贵, 林会喜, 等.渤海湾盆地前古近系油气地质与远景评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.
[15] 侯读杰, 冯子辉.油气地球化学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2011.
[16] 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良.莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生成演化模式[J].天然气工业, 2002, 22(1):26-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007
[17] 黄保家.莺-琼盆地天然气的成因特征及烃源岩生气潜力[C]//21世纪中国油气勘探国际研讨会论文集, 2002: 400-409.
-



 下载:
下载: