SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATION OF SUSPENDED SEDIMENT IN THE AREA SURROUNDING MIAODAO ISLANDS AND ITS RESPONSE TO SUMME TIDE
-
摘要:
根据庙岛海峡附近海域6个站位的大潮和小潮期海流资料和悬浮泥沙浓度等实测资料,分析了庙岛海峡附近海域悬浮泥沙时空分布及变化规律,并初步探讨了潮流对悬浮泥沙浓度的影响。结果表明,在水平方向上,庙岛海峡处悬浮泥沙浓度较大,周边深水区浓度较小;在垂向上,悬浮泥沙浓度呈现从表层至底层逐渐增加的规律。在时间序列上,研究区悬浮泥沙浓度大潮期较大,小潮期较小;悬浮泥沙浓度随时间呈现明显的周期性变化,大潮期悬浮泥沙浓度变化周期主要集中在6~8 h,小潮期各站均存在4~6 h和6~8 h两类尺度变化周期。悬浮泥沙浓度随着潮流流速的增大而增加,但是悬浮泥沙浓度的最大值较流速峰值存在1~2 h的滞后;由于再悬浮作用、水体层化和表中层落淤的原因,悬浮泥沙浓度对流速的响应表现为底层对高流速的响应比较明显,表层对低流速的响应比较明显。
Abstract:Data of suspended sediment concentration and spring and neap tidal fluctuation are collected at 6 stations in the vicinity of the Miaodao Strait. Temporal and spatial distribution and variation in suspended sediment are studied. Upon the basis, we discussed the influence of tidal current onto the concentration of suspended matter. The results show that the concentration of suspended sediment is quite high in the Strait, but lower in the deepwater area surrounding the strait in horizontal direction. The suspended concentration gradually increases from the surface to the bottom and decreases from spring to neap tide. The variation of the concentration of suspended sediment has an obvious periodic pattern with time. In spring tide, the change mainly happened on 6-8 h, while in neap tide there are two kinds of cycle happened at 4-6 h and 6-8 h respectively. The concentration of suspended matter increases with increasing flow velocity. However, the maximum concentration of suspended sediment is 1-2 hours behind the peak value of current. Owing to the resuspension, water stratification and deposition in surface layer, the response of suspended sediment concentration to the flow velocity is in a specific manner. It is obviously responding to high flow velocity in the bottom layer, but to low velocity in the surface layer.
-

-
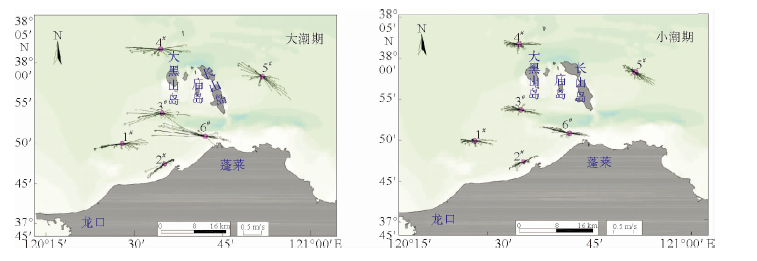
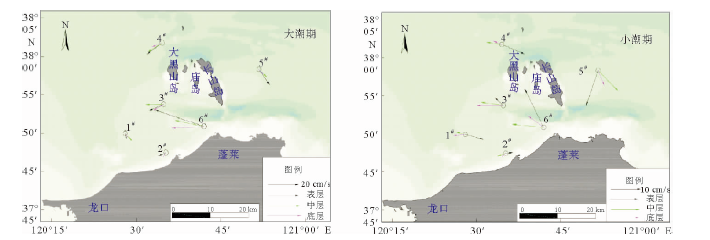
表 1 大潮期各站涨、落潮段平均流速垂向分布
Table 1. Vertical distribution of average velocity for flood and ebb tide in a spring tide
站位 涨潮流速/(cm/s) 落潮流速/(cm/s) 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 1# 43.7 43.9 29.7 21.5 16.9 13.6 28.5 23.4 18.9 17.3 14.6 11.7 2# 32.9 25.8 21.9 22.6 19.1 14.3 20.6 17.3 33.5 15.9 13.6 9.9 3# 66.1 67.1 57.1 52.3 43.8 33.6 84.3 78.8 72.6 60.8 54.5 43.6 4# 28.9 26.3 25.6 23.4 18 13.2 60.3 60.8 58.5 53 45.3 29.2 5# 36.6 46.5 51.3 58.2 56.2 37.3 19.3 22 35.3 36 5 11.7 6# 82.3 92.3 91.3 82.3 71 54 106 89.3 80.3 61.3 67 46.7 表 2 小潮各站涨、落潮段平均流速垂向分布
Table 2. Vertical distribution of average velocity for flood and ebb tide in a neap tide
站位 涨潮流速/(cm/s) 落潮流速/(cm/s) 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 1# 21.9 29.2 30.1 28.8 23.2 16.8 52.4 55.3 52.7 42.1 33.7 25.6 2# 5.3 7.4 6.5 6.5 9.5 8.1 23.4 20.6 16.5 16.6 14.1 13 3# 46.9 46.9 40.1 31.1 23.4 18.8 31.8 30.8 32.2 34.7 28.7 25.1 4# 31.4 24.6 17.7 31.6 27.1 18.2 47 38 35.3 31.1 26.7 19.8 5# 59.4 57.3 56.6 50.9 45.6 35.8 28.5 21.5 13.3 12.3 10.7 12.2 6# 68.1 61.7 37.9 26.6 25 19.9 28.3 17.3 29.3 28.7 27.3 20.7 表 3 各站大朝和小潮垂向平均悬浮泥沙浓度统计表
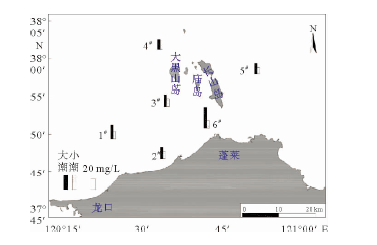
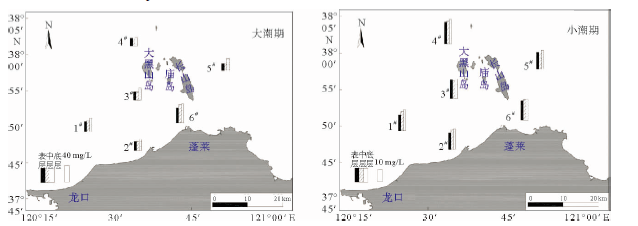
Table 3. The vertical average maximum sediment concentration in spring/neap tide
站位 涨潮/(mg/L) 落潮/(mg/L) 大潮 小潮 大潮 小潮 1# 29.2 16.6 30.3 14.2 2# 23.6 18.4 23.7 14.5 3# 25.6 15.5 20.5 16.2 4# 19.5 16 23.3 20.8 5# 20.6 14.1 19.8 13.1 6# 43.9 16.9 38.1 14.6 -
[1] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 赵松龄, 等.渤海地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985:1-232.
[2] 乔璐璐.冬季大风事件下渤黄海环流及泥沙输运过程研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
[3] 秦蕴珊, 李凡.渤海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1982, 4(2):191-200.
[4] Wang H, Wang A, Bi N, et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended sediment in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 17-32. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.006
[5] Bi N, Yang Z, Wang H, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239-247. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5cdca6a3f99d9ed54be98fa1aea31bc5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] 魏泽勋, 李春雁, 方国洪, 等.渤海夏季环流和渤海海峡水体输运的数值诊断研究[J].海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(4):454-464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.04.013
[7] 赵保仁, 方国洪, 曹德明.渤海、黄海和东海的潮余流特征及其与近岸环流输送的关系[J].海洋科学集刊, 1995(00):4-14.
[8] 万修全, 鲍献文, 吴德星, 等.渤海夏季潮致-风生-热盐环流的数值诊断计算[J].海洋与湖沼, 2004, 35(1):41-47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2004.01.007
[9] 林霄沛, 吴德星, 鲍献文, 等.渤海海峡断面温度结构及流量的季节变化[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 32(3):355-360. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200203003
[10] 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 等.渤海的环流, 潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J].海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(5):466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
[11] 王勇智, 乔璐璐, 杨作升, 等.夏、冬季山东半岛东北部沿岸悬浮物输送机制的初步研究[J].泥沙研究, 2012(5):49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.05.008
[12] 鲍献文, 苏洁, 郭心顺, 等.黄、渤海热结构及环流季节变化的数值模拟[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 34(4):513-522. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200404001
[13] Martin J M, Zhang J, Shi M C, et al. Actual flux of the Huanghe (yellow river) sediment to the Western Pacific ocean[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1993, 31(3):243-254. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(93)90025-N
[14] 陈沈良.崎岖列岛海区的水文泥沙及其峡道效应[J].海洋学报, 2000, 22(3):123-131. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2000.03.017
[15] Farge M. Wavelet transforms and their applications to turbulence[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 24:395-457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.24.010192.002143
[16] Lafrenière M, Sharp M. Wavelet analysis of inter-annual variability in the runoff regimes of glacial and nival stream catchments, Bow Lake, Alberta[J]. Hydrological Process, 2003, 17(6):1093-1118. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1187 https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1187
[17] 林纪江, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等.潮流作用下蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙的时空分布及变化特征[J].海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(12):13-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201712003
[18] 尹东晓, 吴建政, 胡日军, 等.登州浅滩近期演变及沉积物输运趋势[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(8):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201308004
-




 下载:
下载: