DYNAMIC ENVIRONMENT DIVISION AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT TREND IN THE AREA OFF MIAODAO ISLANDS
-
摘要:
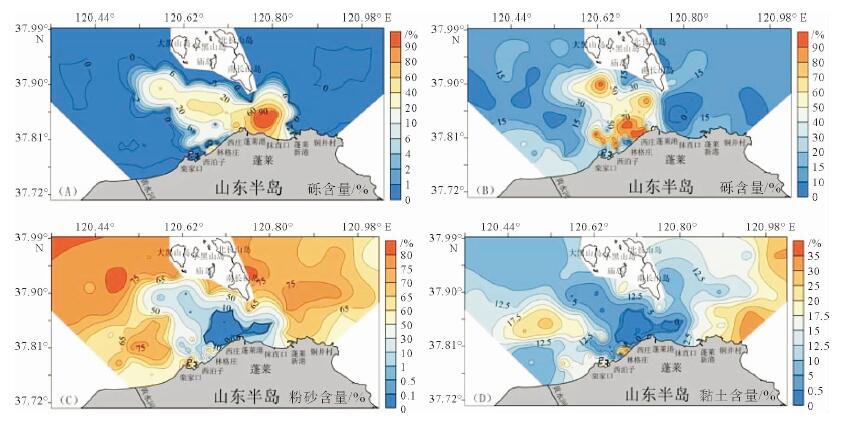
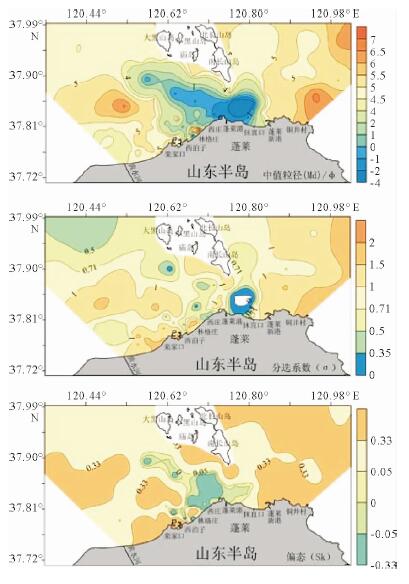
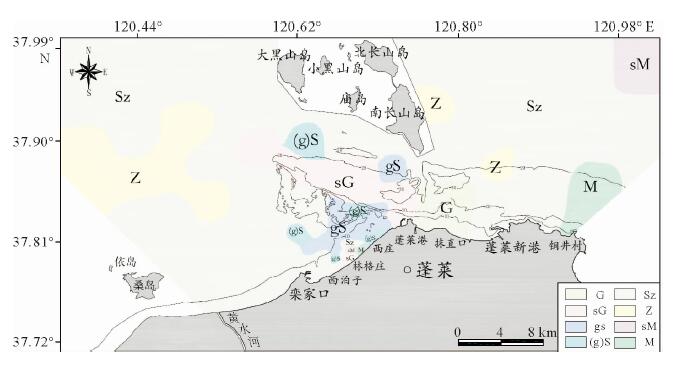
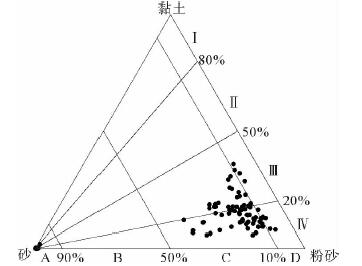
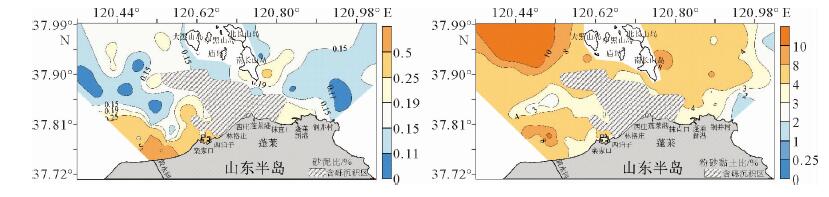
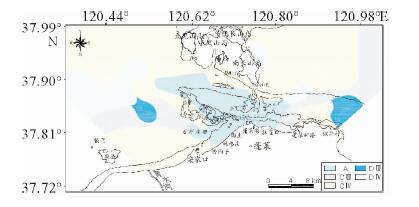
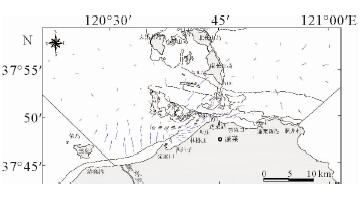
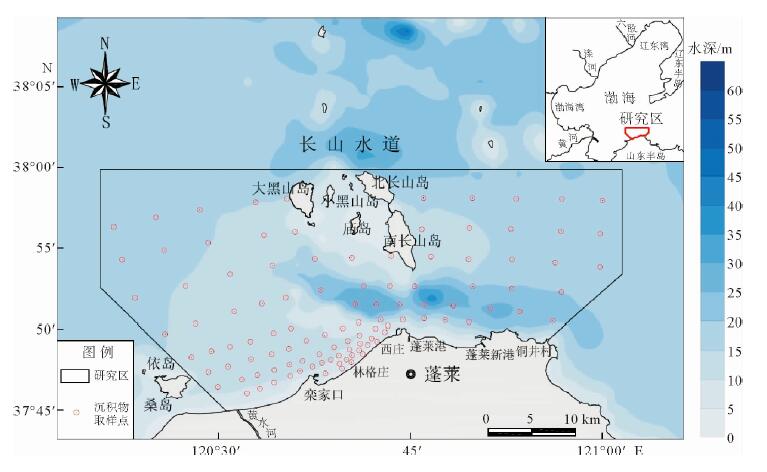
基于庙岛群岛海域的107个表层沉积物样品粒度分析结果,利用Pejrup三角图、Gao-Collins粒径趋势分析等方法,对庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境进行分区,并探讨了沉积物的输运趋势。结果表明,研究区沉积动力环境可划分为5个分区(A、CⅢ、CⅣ、DⅢ、DⅣ),以庙岛海峡为中心,各分区基本呈左右对称分布,与潮流流速中部辐聚、两侧辐散的分布特征相对应,研究区沉积物分布及沉积动力格局主要受潮流控制。研究区内存在两个沉积物输运趋势的汇聚中心,沉积物的长期输运趋势在海峡区主要受控于往复潮流,波流共同作用在外海区影响较为显著,使其具有与海峡区截然不同的特点。
Abstract:Based on the grain size data of 107 surface sediment samples, Pejrup triangular graph and Gao-Collins grain size trend analysis are used to divide sedimentary dynamic environment and to reveal the sediments transport trend in the area off the Miaodao islands. Results show that the study area can be divided into 5 subregions (A, CIII, CIV, DIII and DIV) around the Miaodao Strait, and for each subarea, the distribution of sediemnts is basically symmetrical. There are two converging centers of sediment in the study area, the Dengzhou shoal and the central part of the Miaodao Strait. They are particularly affected by westward ebb current which leads the sediments transporting towards the Dengzhou shoal.The long-term transport trend of sediments is more pronounced by the combined action of wave and current, making it different from the strait area.
-

-
表 1 庙岛群岛海域表层沉积物类型及粒度参数
Table 1. Statistics of the surface sediment type and grain size parameters
沉积物类型 样品数 取值 砾/% 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% D50/mm σ Sk 砾(G) 4 最大值 100.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 - - - 最小值 100.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 - - - 平均值 100.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 - - - 砂质砾(sG) 9 最大值 75.0 63.1 0.5 0.0 4.60 1.14 -0.03 最小值 36.3 25.0 0.0 0.0 1.33 0.35 -0.32 平均值 50.7 49.0 0.2 0.0 2.26 0.84 -0.10 砾质砂(gS) 12 最大值 25.0 93.9 0.8 0.4 1.09 0.75 -0.01 最小值 5.2 74.9 0.0 0.0 0.39 0.43 -0.24 平均值 14.7 85.0 0.2 0.1 0.64 0.59 -0.08 含砾砂((g)S) 6 最大值 5.0 98.7 0.8 1.7 0.49 0.58 0.02 最小值 1.0 94.9 0.0 0.0 0.31 0.26 -0.16 平均值 2.5 96.9 0.2 0.3 0.42 0.38 -0.05 砂质粉砂(sZ) 64 最大值 0.0 39.1 79.8 25.7 0.05 1.73 0.81 最小值 0.0 10.1 49.0 5.6 0.02 0.46 0.04 平均值 0.0 18.9 66.8 14.4 0.03 1.08 0.40 粉砂(Z) 7 最大值 0.0 9.4 85.1 28.6 0.04 1.49 0.62 最小值 0.0 7.0 63.3 7.9 0.01 0.55 0.09 平均值 0.0 8.5 77.2 14.2 0.03 0.95 0.31 砂质泥(sM) 2 最大值 0.0 13.9 57.1 30.6 0.02 1.81 0.69 最小值 0.0 12.3 56.9 29.2 0.01 1.68 0.27 平均值 0.0 13.1 57.0 29.9 0.02 1.75 0.48 泥(M) 3 最大值 0.0 9.5 59.8 35.9 0.01 1.78 0.58 最小值 0.0 8.3 55.5 31.9 0.01 1.13 0.16 平均值 0.0 8.8 57.5 33.7 0.01 1.48 0.31 -
[1] 袁 萍. 渤海表层沉积物的空间分布及其与物源和沉积动力环境的关系[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2015.
[2] 张 伟, 周连成, 吴建政, 等. 渤海海峡南部海域表层沉积物分布特征及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(5):19-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505004
[3] 夏东兴, 伯 尼. 渤海东部更新世末期以来的沉积环境[J]. 海洋学报, 1995, 17(2):86-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1995.02.016
[4] 刘振夏. 渤海东部潮流动力地貌特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 1996,14(1):7-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH601.001.htm
[5] 曹家欣. 山东庙岛列岛与蓬莱沿岸地貌[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11(5):602-610.
[6] 李培英. 庙岛群岛的晚新生界与环境变迁[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1987,7(4):113-124.
[7] 尹延鸿, 周青伟. 渤海东部地区沉积物类型特征及其分布规律[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1994,14(2):47-54.
[8] 程 鹏, 高 抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度特征和净输运趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2000,31(6):604-615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.004
[9] 尹文昱, 张永宁. 渤海海峡风浪特征统计分析[J]. 大连海事大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 32(4):84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7736.2006.04.022
[10] 朱玉荣. 潮流场对渤、黄、东海陆架底质分布的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2001,21(2):7-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200102002
[11] 李福林, 夏东兴, 王文海, 等. 登州浅滩的形成、动态演化及其可恢复性研究[J]. 海洋学报,2004,26(6):65-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.06.008
[12] 赵迎春. 蓬莱新港潮汐,波浪及海流特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1992,11(2):85-88.
[13] Wentworth C K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments[J]. Journal Geology, 1922, 30(5):377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=877b4246a8af14c4c92d73a2ba55f4e4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] Mcmanus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[J]. Techniques in Sedimentology, 1988:63-85. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4ee38a0151a315269f30b7493db23d88&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[16] Gao S, Collins M. Net Sediment Transport Patterns Inferred from Grain-Size Trends, Based upon Definition of “Transport Vectors”[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1992, 81(1/2): 47-60.
[17] 王 伟. 北黄海表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其对沉积环境的指示[D]. 青岛:中国科学院海洋研究所, 2008.
[18] 李广雪, 杨子赓, 刘 勇. 中国东部海域海底沉积环境成因研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 33-44.
[19] 尹东晓, 吴建政, 胡日军,等. 登州浅滩近期演变及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(8):25-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201308004
[20] 王 庆, 仲少云, 刘建华,等. 山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200602003
[21] 赵奎寰. 登州浅滩物质来源及运移趋势[J]. 海岸工程,1992,11(1):32-40. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95947X/199201/769034.html
[22] 陈雪英, 胡泽建. 山东蓬莱西庄附近海域波浪与海岸侵蚀[J]. 海洋科学进展, 1992,10(2):18-26. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/91338X/199202/790814.html
[23] 王桂芝, 高 抒. 黄渤海水体交换、悬沙特征及其对渤海海峡沉积的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 2002, 21(1):43-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.01.007
[24] 肖合辉. 渤黄海海域悬浮体分布:季节性变化及扩散通量[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2014.
[25] 高瑞华, 王式功, 张孝峰,等. 渤海海峡大风的气候特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2008, 25(3):7-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2008.03.002
-



 下载:
下载: