CHARACTERISTICS AND TRANSPORTATION OF SURFACE SEDIMENTS IN HONGTANG BAY OF SANYA, HAINAN ISLAND
-
摘要:
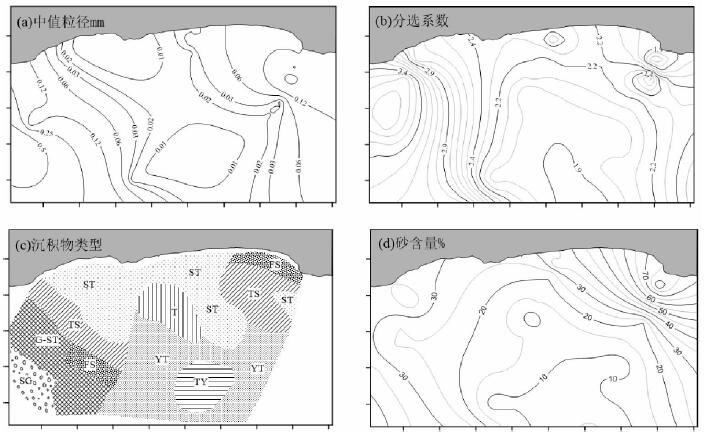
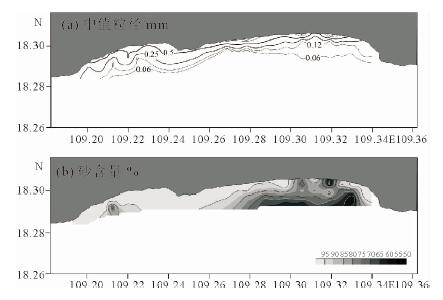
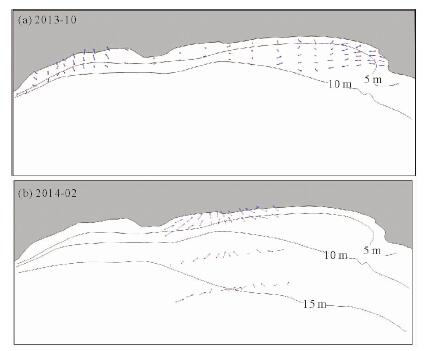
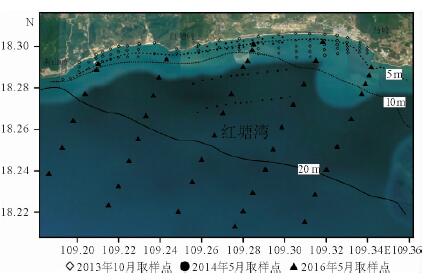
根据红塘湾海域不同时期海床表层沉积物资料,分析研究该海域表层沉积物分布与泥沙运动特征。结果显示:该海域近岸海床表层泥沙颗粒较粗,主要以中粗砂和粗中砂为主;5~10 m等深线之间,底质以中砂和中细砂为主;10~12 m等深线附近以细砂为主,12 m等深线以外底质主要为粉砂和黏土类;底质泥沙颗粒从岸向海逐渐变细。在波流共同作用下,当地泥沙较易起动,波浪对泥沙运动起到关键性作用;该岸段沿岸输沙量级不大,而且保持相对稳定状态,其输沙性质与弧形海岸的动力环境和地形特征相一致。目前各段海岸泥沙运动近似于动态平衡,没有大规模的冲刷和堆积现象。
Abstract:Distribution and transportation of surface sediments are analyzed in this paper based on grain size data. Results show that: (1) bottom sediment particle is generally getting finer from land to sea. Within the water depth of 5 m, coarse sand and coarse-medium sand dominate; (2) the sediment is mainly medium sand and fine sand in the area between 5 - 10 m in water depth; (3) fine sand dominates the area of 10 ~ 12 m in depth, while in the area deeper than 12m, silt and clay dominate. Waves play a key role in initiation of sediment moving. Under the action of wave flow, sediments are easy to start moving. Longshore sediment transportation is limited, but remains in a relatively stable status. The sediment transport is consistent with the hydrodynamic and topographic features. At present, the sediment is under a status of dynamic balance and no large-scale erosion and/or deposition is expectable.
-

-
表 1 近岸水流作用下泥沙起动流速计算结果
Table 1. Critical starting velocity under the action of the current
水深/m 中值粒径/ mm 实验起动流速/(m/s) 计算起动流速/(m/s) 实测大潮最大流速/(m/s) 窦国仁公式 张瑞瑾公式 5 0.60 0.42~0.50 0.43 0.48 0.37~0.44 表 2 不同波况作用下不同粒径泥沙的临界起动水深
Table 2. The critical water depth of sediment under different wave function
/m /m 特征波况 起动状态 0.125 mm 0.25 mm 0.5 mm 1.0 mm 2.0 mm H=0.9 m 表层起动 3.0 2.3 1.7 1.1 0.8 T=4.6 s 完全起动 1.5 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 H=2.8 m 表层起动 10.7 9 7.4 5.8 4.4 T=6.4 s 完全起动 5.7 4.4 3.3 2.4 1.6 H=5.2 m 表层起动 21.6 18.7 15.8 13.0 10.3 T=8.4 s 完全起动 12.4 10.0 7.8 5.9 4.2 -
[1] 左书华, 韩志远, 赵洪波, 等.九龙江—厦门湾表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其动力响应[J].水利水运工程学报, 2011(4):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2011.04.012
[2] 左书华, 韩志远, 许婷.烟台套子湾海域表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其动力响应[J].泥沙研究, 2013 (5): 41-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nsyj201305007
[3] 张伯虎, 陈沈良, 刘焱雄, 等.广西钦州湾海域表层沉积物分异特征与规律[J].热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(4): 66-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.04.010
[4] 中国海湾志编纂委员会.中国海湾志(第十一分册:海南省海湾)[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1992.
[5] 赵永印, 吕彪.三亚红塘湾海域岸线及海床冲淤演变分析[J].中国水运, 2017, 17(4):269-371. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsy-xby201704102
[6] 王艳红.三亚新机场人工岛对红塘湾岸滩的影响研究[C]//第十八届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集.舟山: 2017.09.
[7] GB/T13909-1992.海洋调查规范——海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 1992.
[8] Gao S, Collins M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain size trends, based upon definition of "transport vectors" [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1992, 81(1/2): 47-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0037-0738(92)90055-v
[9] 窦国仁.论泥沙起动流速[J].水利学报, 1960 (4):44-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SLXB196004003.htm
[10] 张瑞瑾, 谢鉴衡, 王明甫, 等.河流泥沙动力学[M].北京:水利电力出版社, 1989.
[11] 王宝灿, 陈沈良, 龚文平, 等.海南岛港湾海岸的形成与演变[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2006.
[12] JTS145—2015.港口与航道水文规范[S]. 2015.
-



 下载:
下载: