Longkou Bay undertheInfluence of Summer Tidal Current
-
摘要:
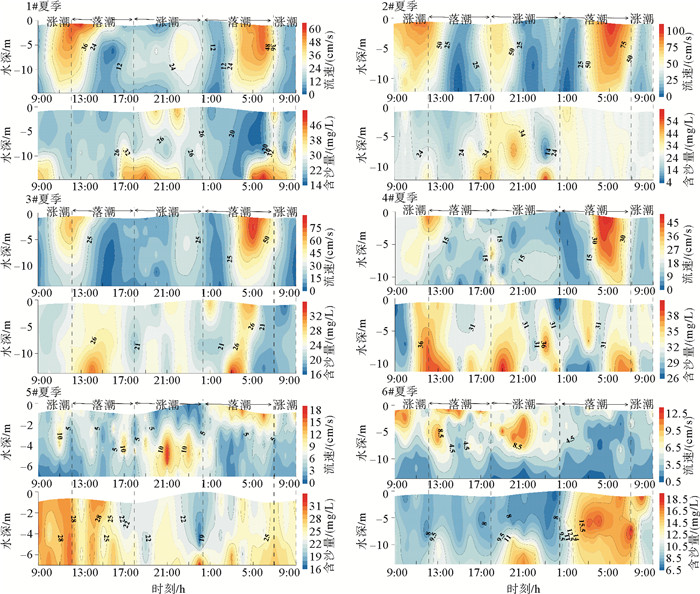
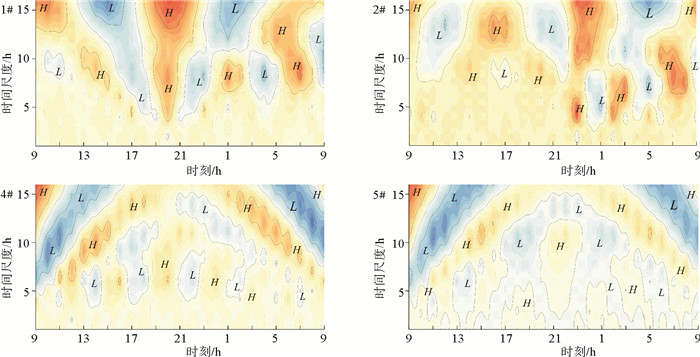
根据龙口湾海域海流、悬浮泥沙等实测资料,利用Morlet小波分析与单宽悬沙通量机制分解法,分析了研究区悬浮泥沙浓度时空分布特征和变化规律,并探讨了悬浮泥沙的输运机制。研究结果表明,平面分布上,研究区的悬浮泥沙分布呈现人工岛外悬沙浓度大于岛内水道海域的分布特征;垂向上,各站位平均含沙量由底层向表层逐层递减,特征明显。悬浮泥沙浓度在潮周期的变化较为复杂,各站位悬浮泥沙浓度在单日内一般出现2~4次峰值;悬浮泥沙浓度峰值往往滞后于流速峰值0.5~2 h;悬浮泥沙浓度在时间上的变化以12~16 h尺度为主要周期。研究区单宽输沙通量主要介于2.64~24.68 gs-1m-1;整体上呈现人工岛外海域悬沙通量高于人工岛内的平面分布格局。悬浮泥沙输运方向与潮致余流方向基本一致;受余流、地形、悬沙浓度等影响,各个输沙分项对输沙率的贡献相差较大,平流输运在悬沙输移中占绝对优势,其次为垂向净环流输沙。
Abstract:According to the measured data of sea current and suspended sediment in Longkou Bay, the temporal and spatial distribution patterns and the variation of suspended sediment concentration in the study area were discussed in order to explore the transport mechanism of suspended matter with Morlet wavelet analysis and decomposition method of unit-width suspended sand flux. The results show that, horizontally, the concentration of suspended sediment outside the artificial island is larger than that within the island. Vertically, the average sediment concentration of each station decreases obviously from the bottom to the surface layers. The variation of suspended sediment concentration in the tidal cycle is complicated. The concentration of suspended sediment in each station generally shows 2~4 peaks in a single day; the peak concentration of suspended sediment tends to lag behind the peak value of flow rate for half an hour to two hours; and the change cycle of suspended sediment concentration is basically 12~16 h. The unit-width sediment transport flux in the study area mainly ranges from 2.64 to 24.68 gs-1m-1. The overall distribution of suspended sand flux outside the artificial island is higher than that within the artificial island. The direction of suspended sediment transport is basically consistent with the direction of the tidal residual current. Due to the influence of residual current, topography and suspended sediment concentration, the contribution of each sediment transport to the sediment transport rate is quite different, and the advection transport has an absolute advantage in suspended sediment transport, followed by vertical net circulation sediment transport.
-

-
表 1 1#~6#站位涨、落潮段平均流速垂向分布
Table 1. The average vertical velocity at 1#~6# stations at flood and ebb tide
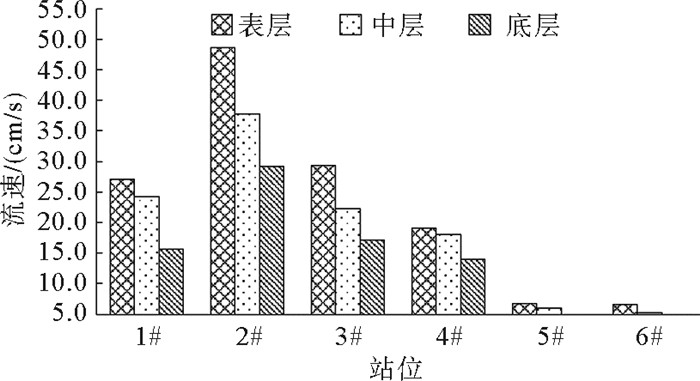
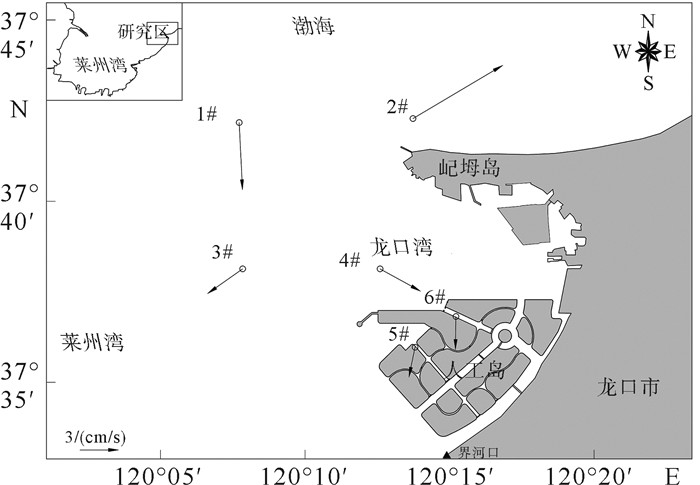
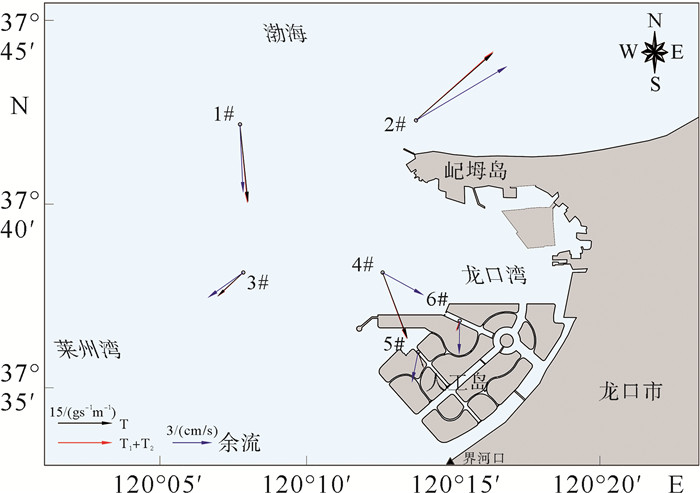
站位 层位 涨潮 落潮 最大 平均 最大 平均 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 1# 表层 55.3 240.3 20.5 184.5 61.0 243.0 33.1 175.3 0.6H 42.3 233.7 24.0 176.0 44.7 48.0 24.5 107.5 底层 29.0 231.7 15.5 185.9 30.3 44.3 15.8 98.2 2# 表层 89.0 255.3 46.6 245.9 101.2 81.0 50.4 162.0 0.6H 67.7 256.3 35.6 211.9 80.0 83.0 39.7 140.5 底层 58.7 248.7 28.9 188.9 65.0 86.0 29.5 126.0 3# 表层 59.3 225.0 23.1 203.0 78.0 47.3 35.1 169.5 0.6H 39.3 252.3 21.2 182.3 49.7 43.3 23.2 134.7 底层 30.3 254.0 16.2 233.5 37.3 47.0 18.0 135.0 4# 表层 42.3 190.3 16.3 240.9 49.7 68.0 21.6 153.2 0.6H 26.7 239.7 17.4 209.5 44.7 68.0 18.5 81.9 底层 22.0 154.0 13.8 215.8 32.7 70.3 14.3 122.9 5# 表层 12.0 327.3 4.9 256.5 15.3 310.3 8.6 238.7 0.6H 17.0 125.7 8.0 140.6 11.7 136.7 4.2 217.1 底层 10.0 135.7 5.0 176.7 6.0 326.7 4.1 215.0 6# 表层 10.3 243.0 6.2 209.5 13.0 301.3 7.0 276.2 0.6H 12.3 121.7 6.3 182.6 10.7 159.7 4.2 220.4 底层 5.7 125.3 3.0 160.2 7.0 10.0 3.5 162.0 表 2 各站位垂向平均余流
Table 2. Vertical average residual current of stations
站位 余流/(cm/s) 方向/(°) 1# 5.3 177.2 2# 8.2 59.3 3# 3.3 239.0 4# 3.6 118.8 5# 2.4 191.7 6# 2.6 180.8 表 3 各站位平均悬沙浓度
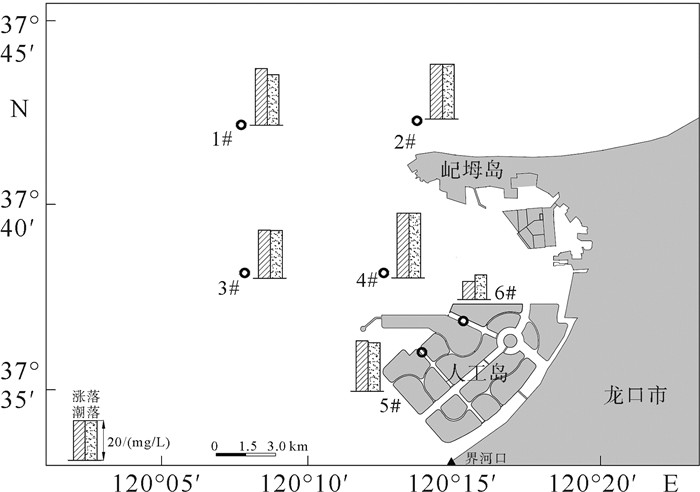
Table 3. The average suspended sediment concentration of each station
/(mg/L) 站位 涨潮 落潮 1# 28.4 25.3 2# 27.6 27.6 3# 22.7 24.1 4# 32.6 32.5 5# 25.0 24.7 6# 9.6 11.8 表 4 各站位悬浮泥沙垂向变化分布统计表
Table 4. Vertical variation of suspended sediment at each station
/(mg/L) 站位 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 6# 表层 24.3 25.6 21.0 29.0 22.0 10.6 中层 24.4 27.0 22.9 31.0 24.2 10.6 底层 31.7 32.1 26.1 33.4 26.9 12.1 表 5 各站位最大含沙量出现的层位与阶段
Table 5. he horizons and stages of maximum sediment concentration
站位 含沙量/(mg/L) 层位 阶段 1# 50.0 底层 落潮 2# 61.8 底层 涨潮 3# 34.4 底层 落潮 4# 54.6 表层 落潮 5# 32.8 底层 落潮 6# 25.0 底层 落潮 表 6 各站位悬浮泥沙输运项及单宽净输沙率
Table 6. Flux decomposition and sediment net transport rate of each station
输沙率/(gs-1m-1), 方向/(°) 站位 项目 T1 T2 T1+T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T总 1# 输沙率 22.31 0.48 22.03 0.31 0.70 0.07 21.74 方向 173. 5 299.5 174.5 198.6 17.9 165.7 174.0 2# 输沙率 25.55 0.63 24.92 0.16 0.53 0.03 24.68 方向 38.7 224.0 38.6 290.5 154.1 33.0 39.3 3# 输沙率 9.55 0.38 9.64 0.12 0.03 0.01 9.68 方向 228.3 227.5 316.2 27.2 232.3 229.2 230.1 4# 输沙率 18.93 1.42 19.64 0.02 4.51 0.05 19.63 方向 156.2 217.9 159.9 320.3 86.5 350.1 159.3 5# 输沙率 4.20 0.42 4.61 0.03 0.01 0.01 4.56 方向 162.4 146.7 161.0 345.0 314.9 348.3 161.1 6# 输沙率 2.60 0.50 2.96 0.02 0.41 0.07 2.64 方向 206.0 157.5 198.7 116.1 343.2 343.2 192.6 -
[1] 陈勇, 韩震, 杨丽君, 等.长江口水体表层悬浮泥沙时空分布对环境演变的响应[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2012, 34(1):145-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201201018
[2] 乔璐璐.冬季大风事件下渤黄海环流及泥沙输运过程研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-2008175673.htm [3] 李九发.长江河口南汇潮滩泥沙输移规律探讨[J].海洋学报(中文版), 1990(1):75-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC199001008.htm
[4] Xie D F, Gao S, WANG Z B, et al. Numerical modeling of tidal currents, sediment transport and morphological evolution in Hangzhou Bay, China [J].International Journal of Sediment Research, 2013, 28(3):316-328. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(13)60042-6
[5] Yang Y P, Zhang M J, Li Y T, et al. The variations of suspended sediment concentration in Yangtze River Estuary[J].Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2015, 27(6):845-856. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(15)60547-9
[6] Liu J H, Yang S L, Zhu Q, et al. Controls on suspended sediment concentration profiles in the shallow and turbid Yangtze Estuary[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90:96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.021
[7] Stephens J D, Allison M A, Di D R, et al. Sand dynamic in the Mekong River channel and export to the coastal ocean[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 147:38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.08.004
[8] 刘潇, 冯秀丽, 刘杰, 等.山东半岛靖海湾及其附近海域悬浮泥沙分布与变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):9-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201206002
[9] Yang Z, Ji Y, Bi N, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3):173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005
[10] 秦蕴珊, 李凡.渤海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1982, 4(2):191-200. http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19820207
[11] 江文胜, 苏健, 杨华, 等.渤海悬浮物浓度分布和水动力特征的关系[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2002(S1):212-217. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1000451372
[12] Liu J H, Yang S L, Zhu Q, et al. Controls on suspended sediment concentration profiles in the shallow and turbid Yangtze Estuary[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90:96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.021
[13] 杜家笔, 裴艳东, 高建华, 等.弱动力浅海中的悬沙输运机制:以天津港附近海域为例[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2012, 34(1):136-144.
[14] Jingbang M, Xingquan L. A numerical study of the wintertime circulation in the Northern Huanghai Sea and the Bohai Sea part I: Basic characteristics of the circulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 1988, 6(3):216-226. doi: 10.1007/BF02846499
[15] 蓝先洪, 密蓓蓓, 李日辉, 等.渤海东部和黄海北部沉积物中重金属分布特征[J].中国环境科学, 2014, 34(10):2660-2668. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zghjkx201410031
[16] 赵保仁, 方国洪, 曹德明.渤海、黄海和东海的潮余流特征及其与近岸环流输送的关系[J].海洋科学集刊, 1995, 36:1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKJK199500000.htm
[17] 方国洪, 杨景飞.渤海潮运动的一个二维数值模型[J].海洋与湖沼, 1985(5):337-346. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1985-HYFZ198505000.htm
[18] Yang S Y, Jung H S, Lim D I, et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2003, 63(1):93-120. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0012825203000333
[19] Guan B. Patterns and structures of the currents in Bohai, Huanghai and East China Seas[J]. Oceanology of China Seas, 1994, 1:17-26. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313742312_Patterns_and_structures_of_the_currents_in_Bohai_Huanghai_and_East_China_Seas
[20] 韦钦胜, 于志刚, 冉祥滨, 等.黄海西部沿岸流系特征分析及其对物质输运的影响[J].地球科学进展, 2011, 26(2):145-156. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201102002
[21] 冯兴如, 杨德周, 尹宝树. FVCOM在龙口海域潮汐潮流模拟中的应用研究[J].海洋科学, 2010, 34(6):94-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx201006018
[22] 王从敏, 彭马川, 张启龙.龙口湾潮流场的数值模拟[J].海岸工程, 1996, 15(4):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HAGC199604000.htm
[23] 安永宁, 吴建政, 朱龙海, 等.龙口湾冲淤特性对人工岛群建设的响应[J].海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(10):24-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDT201010005.htm
[24] 吕双燕, 金秉福, 贺世杰, 等.莱州湾-龙口湾表层沉积物有机质特征及来源分析[J].环境化学, 2017, 36(3):650-658. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hjhx201703024
[25] 任鹏, 孙志高, 王传远, 等.人工岛建设对龙口湾表层沉积物粒度及黏土矿物组成特征的影响[J].海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(4):578-587. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.04.014
[26] 中国海湾志编纂委员会.中国海湾志(第三分册)[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1998.
[27] 杨晓东.乐清湾悬沙输移特性研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 2010.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1713279 [28] 吴德安.江苏辐射沙洲水道潮流及悬沙动力研究[D].南京: 南京师范大学, 2004.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y642374 [29] Venugopal V, Foufoula-Georgiou E. Energy decomposition of rainfall in the time-frequency-scale domain using wavelet packets [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1996, 187(1/2):3-27. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169496030843
[30] Kumar P, Foufoula-Georgiou E. A multicomponent decomposition of spatial rainfall fields: 2. Self-similarity in fluctuations[J]. Water Resources Research, 1993, 29(8):2533-2544. doi: 10.1029/93WR00549
[31] 胡日军, 吴建政, 朱龙海, 等.东海舟山群岛海域表层沉积物运移特性[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3):495-500, 442. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200903027
[32] 陈斌, 刘健, 高飞.莱州湾悬沙输运机制研究[J].水科学进展, 2015, 26(6):857-866. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=skxjz201506012
[33] Ingram R. G. Characteristics of the Great Whale River Plume [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C3): 2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[34] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary [J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 1985, 8(3):256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[35] 范恩梅, 陈沈良, 张国安.连云港海域水文泥沙运动特征[J].世界科技研究与发展, 2009, 31(4):703-707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2009.04.040
[36] Dyer K R. Coastal and estuarine sediment dynamics[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1988, 12(1):106. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjnsyj-e201402009
[37] 李远.近期长江口北槽水沙特性及悬沙浓度垂向分布规律[D].上海: 华东师范大学, 2018.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10269-1018177337.htm [38] 杨晓东, 姚炎明, 蒋国俊, 等.乐清湾悬沙输移机制分析[J].海洋通报, 2011, 30(1):53-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.01.009
-



 下载:
下载: