A SUBMARINE IMAGING AND LASER PROFILING SYSTEM AND ITS APPLICATION TO COLD SEEP SITE INVESTIGATION OFF SOUTHWESTERN TAIWAN
-
摘要:
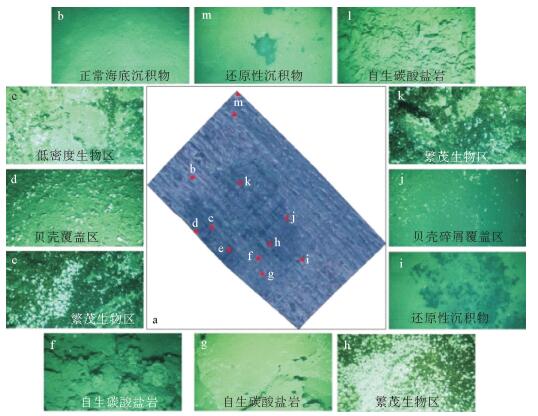
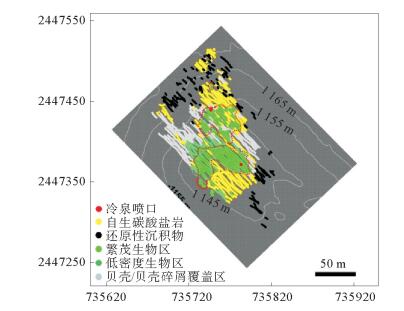
利用深潜器及其搭载光学设备获得重点调查区的高分辨率影像资料是深远海调查的重要内容,对于研究冷泉、热液等特殊海底环境及其生态系统的组成、空间规模、分布特征以及演化规律具有重要意义。主要介绍了搭载于“发现”ROV的4 500 m级L1000型图像和激光扫描系统及其应用实例。利用该系统拍摄并带有位置信息的海底高清照片,首次获得了台西南冷泉区的高清全幅海底拼接图像,并根据该拼接图像对台西南冷泉区的海底特征、空间分布规律和规模进行了直观分析和量化研究,有效地提高了我国深远海近海底测绘的能力。
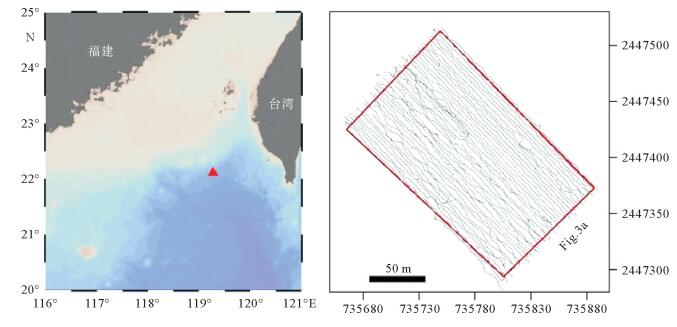
Abstract:Submarine vehicles (SVs) have been widely used in marine investigations that have greatly enhanced the human ability to explore the deep ocean. High quality videos and photos obtained with cameras mounted on SVs are essential data of submarine investigations for the time being since they may provide indispensable information for the study of hydrothermal and cold seep systems. In this paper, a Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) "Faxian", equipped with a 4500-m-rated L1000 Imaging and Laser Profiling system designed and supplied by Cathx Ocean Ltd was introduced and applied at the Taiwan Ridge for cold seep site investigation, The imaging and profiling system includes a M12 L1000 Dual Mode Laser Profiler Camera and an Aphos 16(S16) 110VAC LED light and a DGL300 Green Line Laser. This system was fastened to the bottom of "Faxian" and was pointed downward at the seafloor. In 2016, more than 300 thousand seafloor images of the cold seep site with coordinate information were collected covering an area of around 20 000 m2 in about 30 hours with a imaging frequency of 3 images per second. A high-definition panoramic image covering the most part of the cold seep site was finally achieved by merging all the georeferenced photos. Based on this panoramic image, seabed features and the scales and distribution patterns of these features were analyzed. The installation and successful application of the imaging and laser profiling system will significantly enhance our ability to explore the deep oceans.
-
Key words:
- panoramic image /
- laser profiling system /
- cold seep /
- ROV
-

-
[1] Corliss J B, Dymond J, Gordon L I, et al. Submarine thermal springs on the Galapagos Rift[J]. Science, 1979, 203(4385): 1073-1083. doi: 10.1126/science.203.4385.1073
[2] Fisher C, Roberts H, Cordes E, et al. Cold seeps and associated communities of the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Oceanography, 2007, 20(4): 118-129. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2007.12
[3] Wynn R B, Huvenne V A I, Le Bas T P, et al. Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): Their past, present and future contributions to the advancement of marine geoscience[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 451-468. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.012
[4] Wynn R B, Huvenne V A I, Le Bas T P, et al. Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): Their past, present and future contributions to the advancement of marine geoscience[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 451-468. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.012
[5] Yoerger D R, Bradley A M, Jakuba M, et al. Autonomous and remotely operated vehicle technology for hydrothermal vent discovery, exploration, and sampling[J]. Oceanography, 2007, 20(1): 152-161. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2007.89
[6] Huvenne V A I, Robert K, Marsh L, et al. Rovs and auvs[M]. Submarine Geomorphology. Springer, Cham, 2018: 93-108.
[7] 马小川, 栾振东, 张 鑫,等. 基于ROV的近海底地形测量及其在马努斯盆地热液区的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3):76-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.03.007
[8] 盛 堰, 谭 鹰, 陈宗恒, 等. ROV在我国海洋区域地质调查中的应用[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(11):67-71. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98440A/201311/48065131.html
[9] 张同伟, 唐嘉陵, 李正光, 等. 蛟龙号载人潜水器在深海精细地形地貌探测中的应用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018(7):947-955. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98491A/20187/675747776.html
[10] Boetius A, Wenzhfer F. Seafloor oxygen consumption fuelled by methane from cold seeps[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(9): 725-734. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1926
[11] Bayon G, Dupré S, Ponzevera E, et al. Formation of carbonate chimneys in the Mediterranean Sea linked to deep-water oxygen depletion[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(9): 755-760. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1888
[12] Roalkvam I, Jrgensen S L, Chen Y, et al. New insight into stratification of anaerobic methanotrophs in cold seep sediments[J]. FEMS microbiology ecology, 2011, 78(2): 233-243. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01153.x
[13] Baco A R, Rowden A A, Levin L A, et al. Initial characterization of cold seep faunal communities on the New Zealand Hikurangi margin[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 272(1-4): 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.06.015
[14] Lessard-Pilon S, Porter M D, Cordes E E, et al. Community composition and temporal change at deep Gulf of Mexico cold seeps[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(21/23): 1891-1903. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=33caa6cebee8e1c33e3f35f668ac4c53
-



 下载:
下载: