APPLICATION PROSPECT OF CPT IN GAS HYDRATE EXPLORATION
-
摘要:
水合物的勘探方法主要有地球物理方法、地球化学方法、微生物方法和地质学方法等,三维地震为主要而且也是最重要的手段。含有游离天然气和天然气水合物的海底沉积物在物理性质上存在明显差异,三维地震利用这些差异性可以确定天然气水合物的分布,但有些沉积物如碳酸盐岩也可以表现出类似的异常。对于精确确定海底沉积物物性及沉积物类型,静力触探具有非常突出的优势。静力触探可以开展土力学测试、土体摄像、定点地质取样、波速测试、热力学测试、磁力观测、电导率测试、放射性同位素测试和化学分析测试等,调查范围非常广泛。用CPT配合其他方法来联合勘探水合物是精确计算水合物分布及储量的非常有前景的方法。
Abstract:Geophysical, geochemical, microbial and geological methods are widely used in gas hydrate exploration and 3D seismic method is doubtlessly the main and most important one. There are obvious differences in physical properties of sediments containing free natural gas and gas hydrates. The distribution of gas hydrates can be recognized by using these differences with 3D seismic data. However, some sediments, such as carbonate rocks may produce similar anomalies. CPT has prominent advantages in accurately determining the physical properties and types of sediments. It has the capability to carry out tasks such as soil mechanics testing, soil photography taking, geological sampling, P-S logging, thermodynamic testing, magnetic observation, conductivity testing, radioisotope testing and chemical analysis testing, etc. Combined with other methods, CPT is believed a very promising method for accurately determinating hydrate distribution and calculating gas reserves in gas hydrate exploration.
-
Key words:
- gas hydrates /
- CPT /
- in-situ test /
- marine sediments
-

-
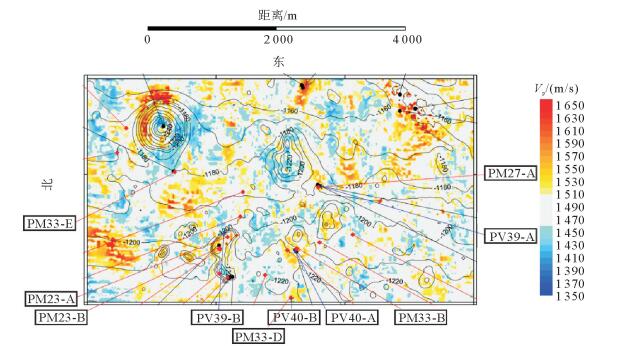
图 2 海底地形图显示的有:波速异常分布图、声速CPT测站(PV39-A、PV39-B、PV40-A、PV40-B)和经典静力触探站位(PM23-A、PM23-B、PM33-B、PM33-E、PM33-D、PM27-A)(据文献[32]修改)
Figure 2.
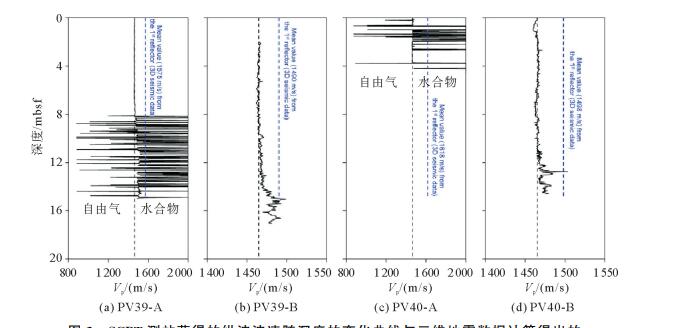
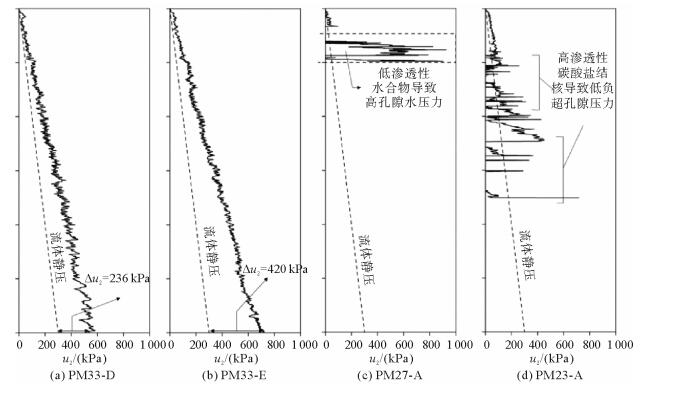
图 4 发现水合物的站位的孔隙水压力随深度变化曲线(修改自文献[32])
Figure 4.
-
[1] 王淑云,鲁晓兵.水合物沉积物力学性质的研究现状[J].力学进展,2009,39(2):176-188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2009.02.004
[2] 张永勤.国外天然气水合物勘探现状及我国水合物勘探进展[J].探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程),2010,37(10):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7428.2010.10.001
[3] Chapman R, Pohlman J, Coffin R, et al. Thermogenic gas hydrates in the Northern Cascadia Margin[J].EOS, 2004,85(38):361-365. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2004EO380001
[4] 梁海峰.多孔介质中甲烷水合物降压分解实验与数值模拟[D].大连:大连理工大学,2009:3-9.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10141-2010111458.htm [5] Collett T S. Natural gas hydrates of the Prudhoe Bay and Kupruk River area, North Slope, Alask[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993,77(5):793-812.
[6] 刘昌岭,陈 敏,业渝光.海洋天然气水合物元素地球化学异常的实验研究[J].现代地质,2005,19(1):96-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.014
[7] 卢振权,吴必豪.海底水合物地球化学探测方法的试验研究[J].现代地质,2002, 16(2):299-304. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz200203014
[8] 杨 涛,蒋少涌,杨竞红.孔隙水中NH+4和HPO2-4浓度异常:一种潜在的天然气水合物地球化学勘查新指标[J].现代地质,2005,19(1):56-60.
[9] 蒋少涌,杨 涛,薛紫晨,等.南海北部海区海底沉积物中孔隙水的Cl-和SO2-4浓度异常特征及其对天然气水合物的指示意义[J].现代地质,2005,19(1):45-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.007
[10] 祝有海,饶 竹,刘 坚,等.南海西沙海槽S14站位的地球化学异常特征及意义[J].现代地质,2005,19(1):39-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.006
[11] 蒋少涌,凌洪飞,杨竞红,等. 海洋浅表层沉积物和孔隙水的天然气水合物地球化学异常识别标志[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2003,23(1):87-94. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200301014
[12] 凌洪飞,蒋少涌,倪 培,等.沉积物孔隙水地球化学异常:天然气水合物存在的指标[J].海洋地质动态,2001,17(7):34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2001.07.008
[13] 许东禹,吴必豪,陈邦彦.海底天然气水合物的识别标志和探测技术[J].海洋石油,2000, 20(4):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000739118
[14] 苏 新,陈 芳,张 勇,等.海洋天然气水合物勘查和识别新技术:地质微生物技术[J].现代地质,2010,24(3):409-423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.001
[15] Kvenvolden K A, Kastner M. Gas hydrate of the Peruvian outer continental margin[C]//Suess E,von Huene R,ed. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1990,112:517-526.
[16] Kvenvolden K A, McDonald T J. Gas hydrates of the Middle America Trench-Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg85, Initial Reports of the DSDP[R].1985,84:667-682.
[17] 龚建明,陈建文,杨金玉,等.国外天然气水合物研究现状及发展趋势[J].海洋地质动态, 2003,19(10):24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.10.009
[18] 苏 新.国外海洋气水合物研究的一些新进展[J].地学前缘,2000,7(3):257-265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.03.024
[19] 苏 新.海洋天然气水合物分布与“气-水-沉积物”动态体系:大洋钻探204航次调查初步结果的启示[J].中国科学:D辑,2004,34(12):1091-1099. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK200412000.htm
[20] 吴能友,苏 新,宋海斌,等.南海北部陆坡天然气水合物成藏机理研究:意义、现状与问题[J].海洋地质,2007,3:1-11. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=25416652
[21] Lunne T, Robertson P K, Powell J J M. Cone Penetration Testing in Geotechnical Practice[J].Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 2009, 6(46),237-237. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11204-010-9072-x
[22] 陈 奇.海底静力触探若干关键技术研究[D].武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2008:1-133.
[23] Liyanapathirana D S. Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian based finite element analysis of cone penetration in soft clay[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36:851-860. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.01.006
[24] 苏 新,宋成兵,方念乔.太平洋水合物海岭BSR以上沉积物粒度变化与气体水合物分布[J].地学前缘,2005,12(1):234-242. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.01.032
[25] 赵丽娜,陈建文,龚建明,等.沉积物粒度与天然气水合物的依存关系[J].海洋地质动态,2006,22(12):28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.12.008
[26] 陈 敏,业渝光,吕万军,等.甲烷水合物在人工毛细管沉积物柱中的形成和分解[J].现代地质,2010,24(3):632-637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.031
[27] Bower P G.Deep ocean field tests of methane hydrate formation from a remotely operated vehicle[J].Geology,1997,25:407-410. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0407:DOFTOM>2.3.CO;2
[28] 梁 劲,王明君,王宏斌,等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物声波测井速度与饱和度关系分析[J].现代地质,2009,23(2):217-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.02.004
[29] Tréhu A M, Bohrmann G, Torres M E, et al. data report: Grain-size and bulk and clay mineralogy of sediments from the summit and flanks of southern hydrate ridge, sites 1244-1250, ODP Leg 204[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2005,204:1-19.
[30] Tillmann A, Englert A, Nyari Z, et al. Characterization of subsoil heterogeneity, estimation of grain size distribution and hydraulic conductivity at the Krauthausen test site using Cone Penetration Test[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2008,95:57-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.07.013
[31] 宋海斌,松林修,吴能友,等.海洋天然气水合物的地球物理研究(I):岩石物性[J].地球物理学进展,2001,16(2): 118-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2001.02.015
[32] Sultan N, Voisset M, Marsset T.Detection of free gas and gas hydrate based on 3D seismic data and cone penetration testing: An example from the Nigerian Continental Slope[J].Marine Geology, 2007,240:235-255. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.02.012
[33] 张 剑,业渝光,刁少波,等.超声探测技术在天然气水合物模拟实验中的应用[J].现代地质,2005,l9(1): 113-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.017
[34] 胡高伟,业渝光,张 剑,等.松散沉积物中天然气水合物生成、分解过程与声学特性的实验研究[J].现代地质,2008,22(3): 465-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.018
[35] 胡高伟,张 剑,业渝光,等.天然气水合物的声学探测模拟实验[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(1):135-141. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200801019
[36] Winters W J,Waite W F,Mason D H,et al.Methane gas hydrate efect of sediment acoustic and strength properties[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2007,56:127-l35. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2006.02.003
[37] Priest J,Best A,Clayton C,et al.Seismic properties of methane gas hydrate—bearing sand[M]//The Proceedings of the 5 Intenational Conference on Gas Hydrate.Trondheim: [s.n.],2005:440-447.-->
[38] Winters W J, Waite W F, Mason D H, et al. Sediment properties associated with gas hydratc formation[C]//4th International Conference on Gas Hydrate,2002:722-727.
[39] Winters W J, Waite W F, Pecher I A, et al. Comparison of methane gas hydrate formation on physical properties of fine and corse-grained sediments[C]//AAPG Hedberg Conference”Gas hydate: Energy Resource Potential and Associated Geologic Hazards”, September 12-16,2004,Vancouver, BC, Canada.
[40] Winters W J, Waite W F, Mason D H, et al. Effect of grain size and pore pressure on acoustic and strength behavior of sediments containing methane gas hydrate[C]//5th International Conference on Gas Hydrate,2005:507-516.
[41] Winters W J, Waite W F, Mason D H, et al. Methane gas hydrate dffect on sediment acoustic and strength properties[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007,56:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2006.02.003
[42] Winters W J, Waite W F, Mason D H, et al. Physical properties of repressurized sediment from hydrate ridge[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Driling Program, Scientific Results Volume 204,2006,Available online at. www.odp.tamu.edu
[43] Katzman R, Holbrook W S, Paul C K.Combined vertical-incidence and wide-angle seismic study of a gas hydrate zone. Blake Ridge[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1994,99:17975-17995. doi: 10.1029/94JB00662
[44] Matsumoto R, Paull C, Wallace P. The Leg 164 scientific party. Gas hydrate sampling on the Blake Ridge and Carolina Rise[R].ODP Leg 164 Preliminary Report,1996.
[45] Gregory A R. Fluid saturation effects on dynamic elastic properties of sedimentary rocks [J]. Geophysics, 1976, 41: 895-921. doi: 10.1190/1.1440671
[46] Domenico S N. Effect of brine-gas mixture on velocity in an unconsolidated sand reservoir[J]. Geophysics,1976,41:882-894. doi: 10.1190/1.1440670
[47] 王宏斌,梁 劲,龚跃华,等. 基于天然气水合物地震数据计算南海北部陆坡海底热流[J].现代地质,2005,19(1):68-73. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz200501010
[48] Whalley E. Speed of longitudinal sound in Clathrate hydrates [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1980, 85: 2539-2542. doi: 10.1029/JB085iB05p02539
[49] 冯 东,陈多福,苏 正,等. 海底天然气渗漏系统微生物作用及冷泉碳酸盐岩的特征[J].现代地质,2005,l9(1):26-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.004
[50] 王宏斌,黄永样,梁 劲,等. 南海北部陆坡坳隆断裂带中水合物赋存的温压场环境[J].现代地质,2006,20(1):103-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2006.01.012
[51] Dickens, Gerald R. Quinby-Hunt, Mary S.Quinby-hunt, Methane hydrate stability in pore water: A simple theoretical approach for geophysical applications, Journal of Geophysical research, 1997, 102(B1):773-783.
[52] Kvenvolden K A, Kastner M. Gas hydrate of the Peruvian outer continental margin [C]//Proceedings ODP Scientific Results, 1990, 112:517-526.
-



 下载:
下载: