DIAGENESIS OF CORAL REEFS: AN IN-SITU GEOCHEMICAL STUDY OF CORAL REEFS AT THE YONGXING ISLAND, SOUTH CHINA SEA
-
摘要:
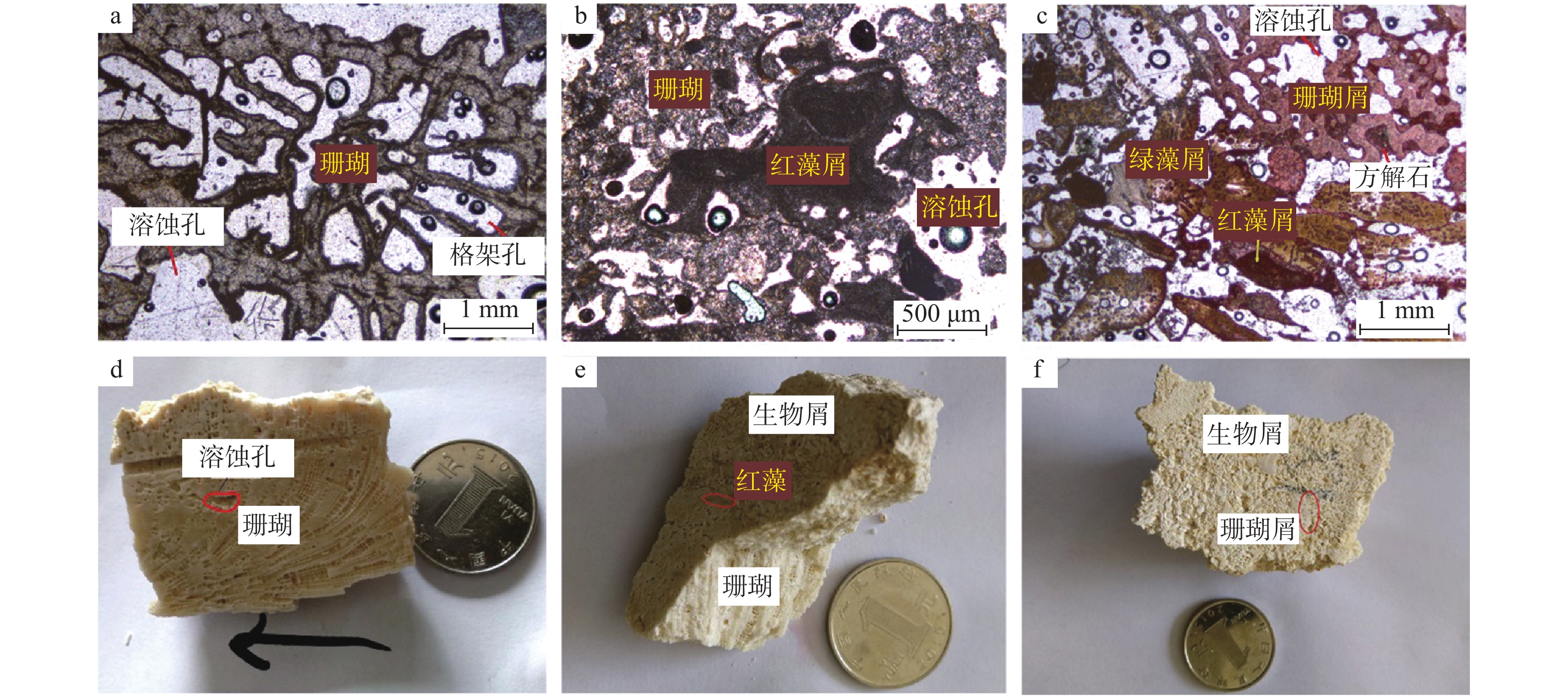
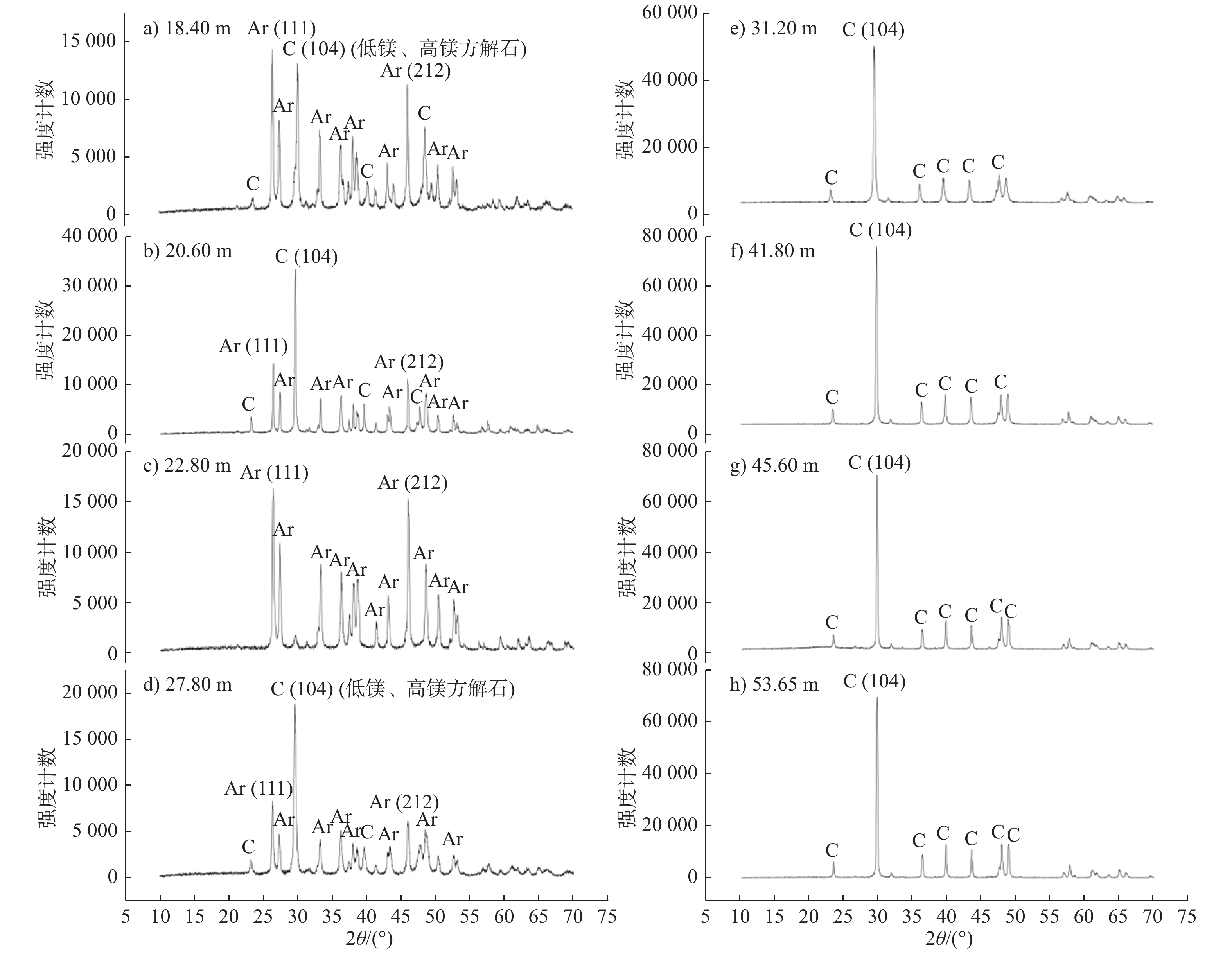
珊瑚礁的地球化学特征记录了其形成时周围海水的状况,能够反映古海洋、古气候和古环境变化;然而珊瑚礁形成过程中及其形成后,容易受到成岩作用的影响,导致其矿物组成和地球化学特征发生变化;因此,在对珊瑚礁的研究中,首先要识别出保存原始沉积特征的组分,并排除后期成岩改造的影响。以西沙群岛永兴岛的SSZK1珊瑚礁钻孔岩心为研究对象,通过矿物学、岩相学和地球化学相结合的研究方法,对不同层位的生物化石、碳酸盐胶结物进行原位地球化学分析,探索成岩作用对不同形成阶段矿物的改造。SSZK1井岩心的岩石类型主要为骨架灰岩和生物碎屑灰岩两大类;岩心礁相碳酸盐岩沉积后主要受控于早期大气成岩作用,成岩层段揭示的主要成岩作用类型有胶结作用、新生变形作用和溶解作用。电子探针和LA-ICP-MS的原位分析结果表明,不同阶段的珊瑚礁碳酸盐岩的矿物成分较为单一,主要是由方解石组成,仅在局部的生物化石中保存了原始形成的文石。后期形成的碳酸盐胶结物(低Sr/Ca、低Sr、高Mg/Ca)和原始的生物化石(高Sr/Ca、高Sr、低Mg/Ca)具有明显不同的地球化学特征,表明不同阶段的碳酸盐矿物受不同来源流体的制约。
Abstract:The geochemistry of coral reefs provides evidence for surrounding seawater conditions and may reflect the paleoceanographic, paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental variations at the time of deposition. However, coral reefs are apt to be altered by diagenesis during and after their formation, which can lead to substantial changes in mineralogy, geochemistry and biological characteristics. In such a circumstance, the geochemistry of coral reefs is not able to reflect the characteristics of the surrounding water. Therefore, the influences of diagenesis must be excluded before the geochemical indicators are applied to coral reef research if the surrounding water conditions are studied. Our study this time focuses on the cores from the well SSZK1 drilled at the Yongxing Island, Xisha Islands. Microfacies with different fossils and carbonate cements are studied in-situ based on mineralogy, petrography and geochemistry of the reef so as to explore the history of diagenesis. Observation of hand specimens and thin sections suggests that, the carbonate rock types from the well SSZK1 core are mainly composed of branching coral skeleton, bioclast and others fossils, such as calcareous algae, gastropod and foraminifera, dominated by aragonite, high-magnesium calcite and low-magnesium calcite. Early atmospheric diagenesis, which includes cementation, neomorphism and dissolution, play critical roles in determination of the composition of reef rocks. The in-situ analysis with electronic probe and LA-ICP-MS suggests that the diagenetic minerals in different diagenetic stages are extensively dominated by low-magnesium calcite. Diagenetic aragonite is only observed in some local fossils. The primary fossils are characterized by high Sr/Ca and Sr, with low Mg/Ca, while the diagenetic cements characterized by low Sr/Ca and Sr, with high Mg/Ca). It indicates that the coral reefs have been reformed by the diagenetic fluids of different origin, which controlled the mineralogy and geochemical characteristics of the coral reef in different stages.
-
Key words:
- Yongxing Island /
- coral reef /
- diagenesis /
- geochemical characteristics
-

-
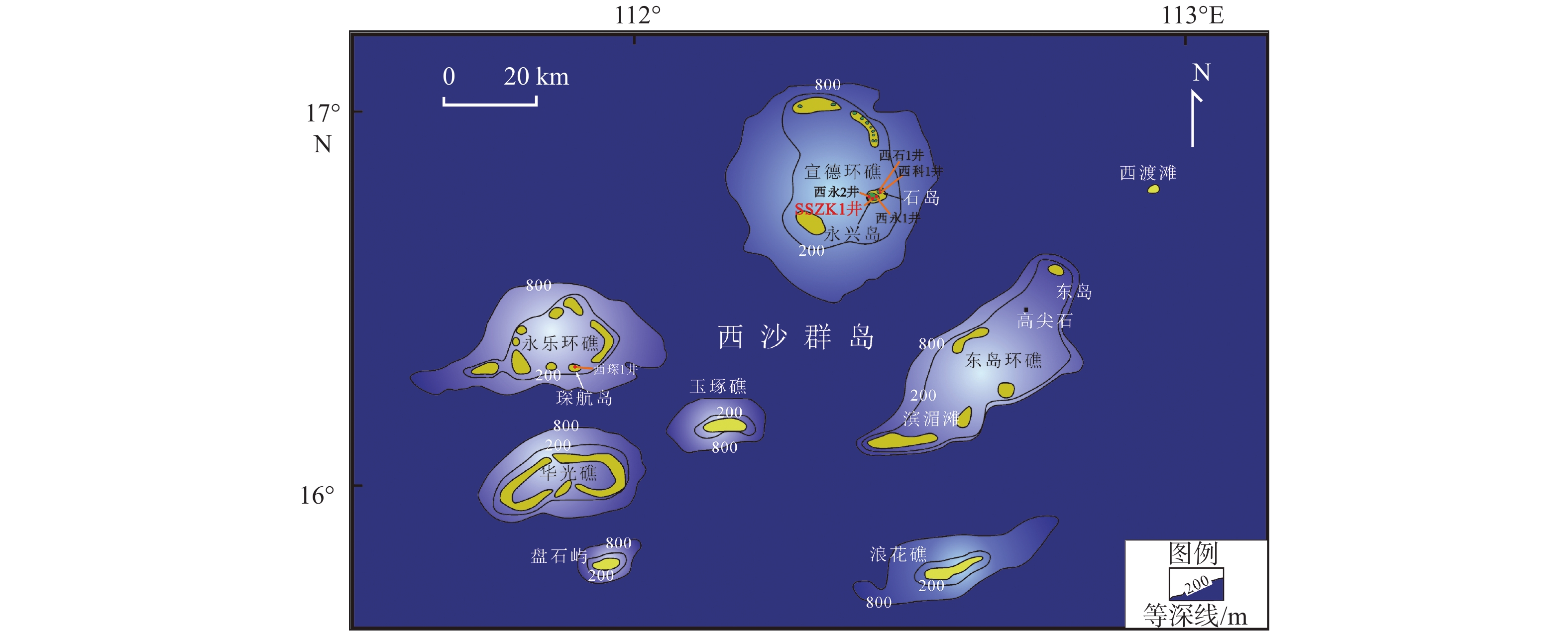
图 1 南海永兴岛和SSZK1井位置图[29]
Figure 1.
表 1 中国南海西沙群岛永兴岛珊瑚礁SSZK1井岩心样品的电子探针分析结果
Table 1. The results of core samples by electron probe analysis for well SSZK1 in the coral reef of Yongxing Island,Xisha Islands,South China Sea
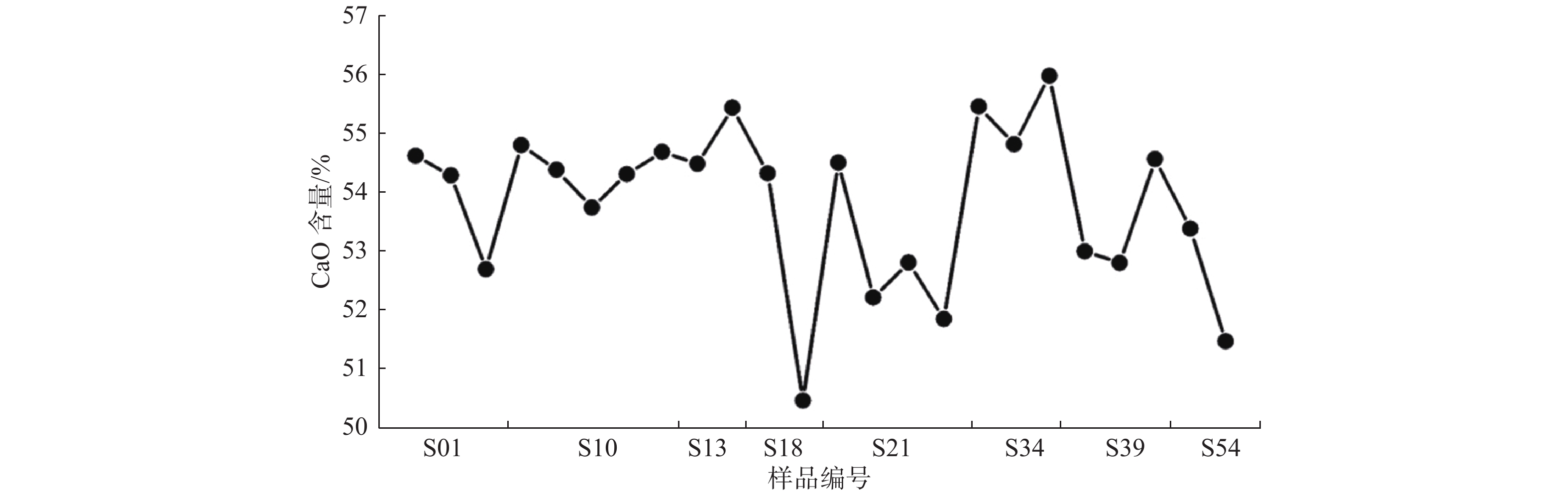
/% 样品编号 MgO K2O FeO Al2O3 CaO MnO SiO2 P2O5 Cr2O3 Na2O TiO2 SrO CO2 Total S01-1 − 0.029 0.016 − 54.666 0.002 − 0.071 0.286 0.18 − 1.082 43.75 100.082 S01-2 0.065 0.051 − − 54.326 − 0.011 0.077 − 0.165 − 1.113 43.868 99.676 S01-3 0.784 0.027 0.032 0.036 52.708 0.042 0.057 0.016 − 0.141 0.027 0.154 44.537 98.561 S10-1 0.054 0.022 − − 54.845 − − 0.038 0.032 0.322 0.024 0.908 43.785 100.03 S10-3 0.148 − − 0.019 54.421 − − 0.005 0.024 0.287 − 0.865 43.907 99.676 S10-4 0.112 0.015 0.002 − 53.774 0.015 − 0.06 − 0.302 − 0.816 44.076 99.172 S10-5 0.026 0.101 − 0.033 54.345 − 0.059 0.054 0.037 0.386 0.006 0.186 44.142 99.375 S10-6 0.019 0.027 − 0.001 54.734 0.006 0.024 0.022 − 0.268 0.023 0.154 44.123 99.401 S13-1 0.024 0.034 0.014 − 54.524 − − 0.005 0.008 0.214 − 1.023 43.84 99.686 S13-2 0.04 0.029 − − 55.491 − 0.006 − 0.011 0.095 − 1.022 43.655 100.349 S18-1 0.354 0.114 − − 54.362 − 0.041 0.011 − 0.266 0.027 0.059 44.182 99.416 S18-2 − 0.078 0.016 0.028 50.447 − 0.050 0.022 0.048 0.228 − 0.839 44.228 96.625 S21-1 0.141 0.036 0.034 − 54.543 − − 0.038 0.019 0.365 − 0.845 43.848 99.869 S21-2 0.15 0.126 0.018 − 52.221 0.004 0.033 − 0.037 0.425 − 0.791 44.362 98.167 S21-3 0.121 0.041 0.004 0.004 52.825 − 0.008 0.016 − 0.383 − 0.798 44.275 98.475 S21-4 0.089 0.038 0.028 0.008 51.855 − − 0.088 0.013 0.281 − 0.773 44.547 97.720 S34-1 0.695 0.043 0.03 0.011 55.51 0.001 0.004 0.109 0.024 0.179 0.016 0.051 43.93 100.603 S34-2 0.686 − 0.028 0.022 54.862 0.001 0.011 − 0.179 0.021 0.023 0.172 44.049 100.054 S34-3 0.685 0.017 0.01 0.017 56.036 − 0.02 − 0.059 0.042 − 0.155 43.807 100.848 S39-1 1.104 0.099 0.042 − 53.02 0.05 0.015 0.022 − 0.095 − 0.219 44.385 99.051 S39-2 1.397 0.112 0.022 0.043 52.821 0.002 0.018 0.066 0.013 0.102 − 0.159 44.44 99.195 S39-3 0.129 0.057 − 0.007 54.605 0.012 − 0.033 − 0.249 − 0.775 43.894 99.761 S54-1 3.027 0.025 0.006 0.006 53.409 − 0.028 0.038 − 0.303 − 0.215 44.102 101.159 S54-2 1.625 0.024 − 0.003 51.468 − 0.011 0.022 − 0.046 − 0.256 44.758 98.213 注:表中编号相应位置具体见图6蓝色标记;−表示未检测出。 表 2 LA-ICP-MS测定SSZK1井岩心样品中不同组分的地球化学组成
Table 2. Geochemical composition of different components by LA-ICP-MS for core samples of well SSZK1
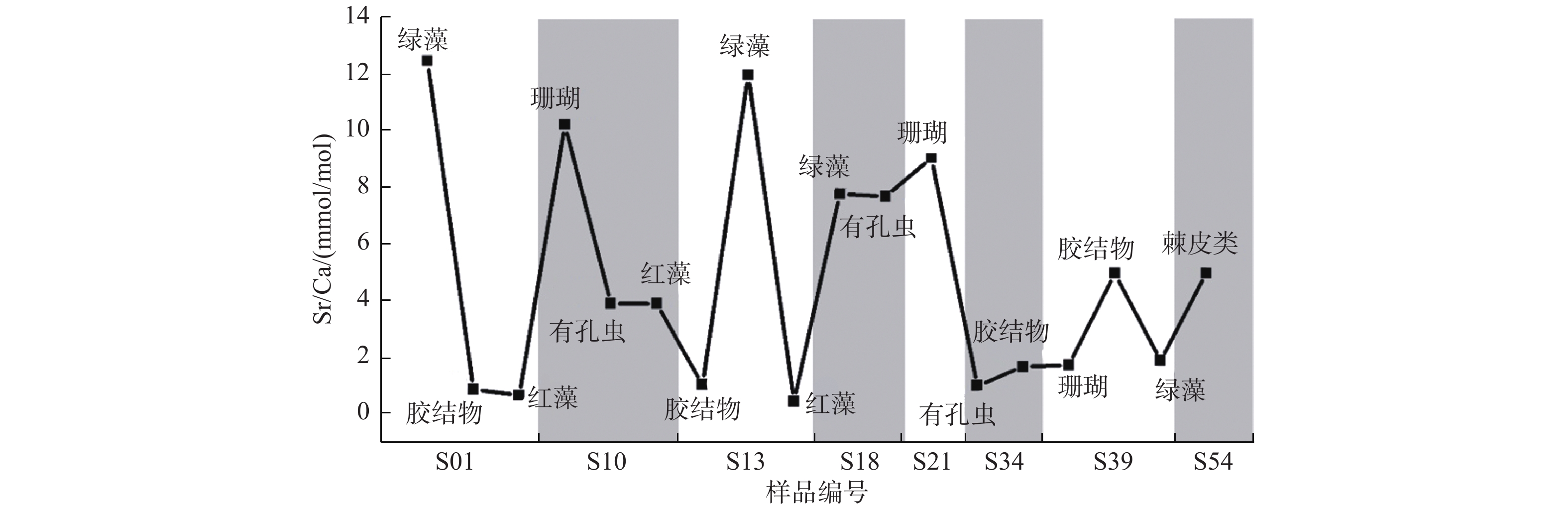
样品 Sr/Ca/
(mmol/mol)Mg/Ca/
(mmol/mol)U/Ca/
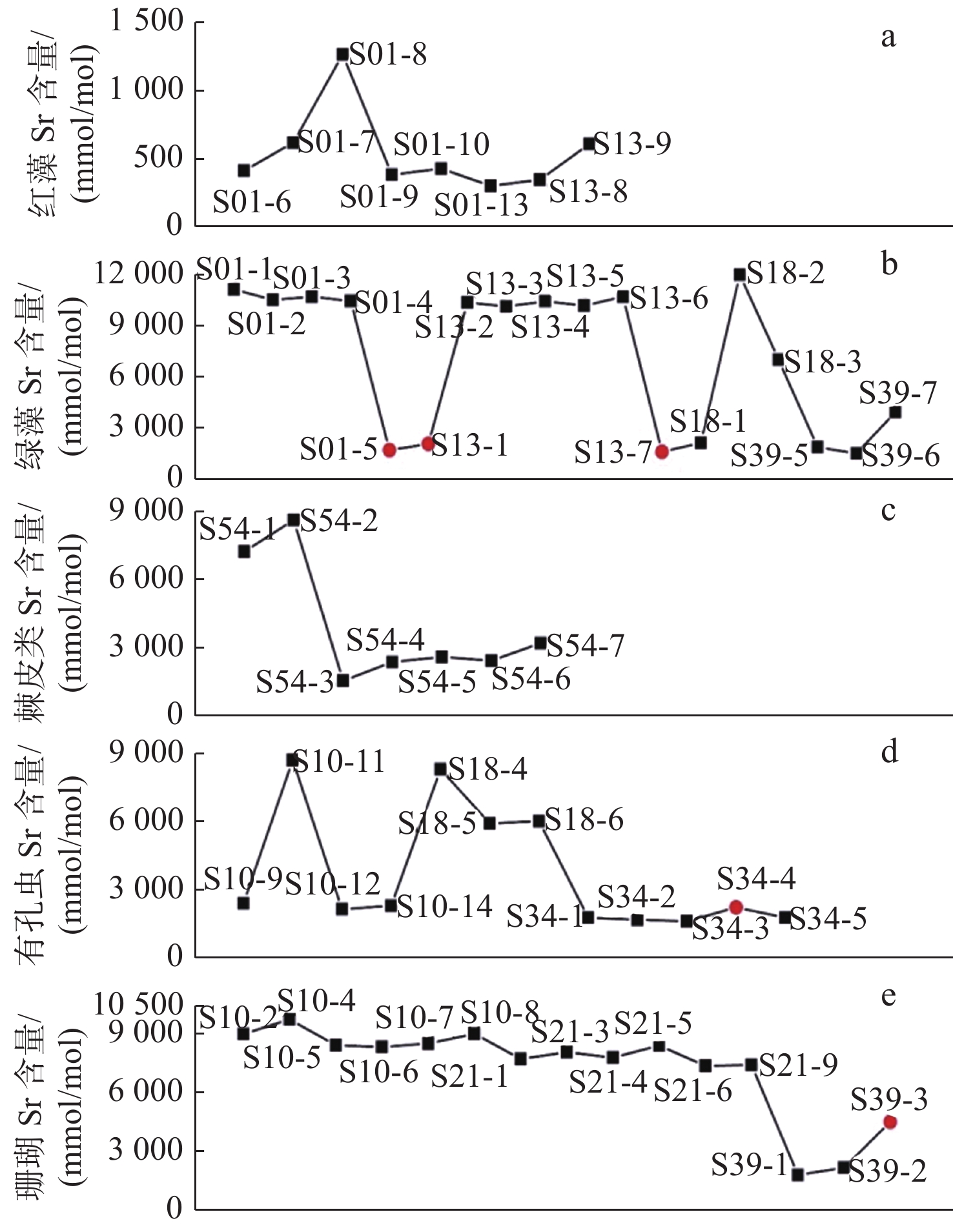
(μmol/mol)珊瑚 S10 10.24 2.82 1.61 S21 9.08 3.20 0.97 S39 1.83 45.91 0.23 绿藻 S01 12.47 0.61 1.04 S13 11.98 0.71 1.07 S18 7.82 5.70 1.06 S39 1.99 27.92 0.37 红藻 S01 0.76 31.88 0.44 S10 0.36 19.52 0.26 S13 0.56 22.80 0.30 有孔虫 S10 3.98 1.62 1.07 S18 7.72 1.83 1.31 S34 1.10 25.07 0.31 棘皮类 S54 5.05 20.04 0.63 方解石胶结物 S01 0.97 65.18 0.45 S13 1.14 24.00 0.59 S34 1.77 30.32 0.29 S39 5.04 35.37 0.38 -
[1] MELTZNER A J,SWITZER A D,HORTON B P,et al. Half-metre sea-level fluctuations on centennial timescales from mid-Holocene corals of Southeast Asia[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8(1):14387. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14387
[2] YAN H,SOON W,WANG Y H. A composite sea surface temperature record of the northern South China Sea for the past 2500 years:a unique look into seasonality and seasonal climate changes during warm and cold periods[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2015,141:122-135. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.12.003
[3] YU K F,ZHAO J X,LIU T S,et al. High-frequency winter cooling and reef coral mortality during the Holocene climatic optimum[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2004,224(1/2):143-155.
[4] 黄德银,施祺,张叶春. 海南岛鹿回头珊瑚礁与全新世高海平面[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2005,25(4):1-7.
[5] 余克服,陈特固,黄鼎成,等. 中国南沙群岛滨珊瑚δ18O的高分辨率气候记录[J]. 科学通报,2001,46(14):1199-1204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.14.015
[6] 余克服,钟晋梁,赵建新,等. 雷州半岛珊瑚礁生物地貌带与全新世多期相对高海平面[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2002,22(2):27-33.
[7] 修淳,罗威,杨红君,等. 西沙石岛西科1井生物礁碳酸盐岩地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):645-652.
[8] JIANG W,YU K F,SONG Y X,et al. Coral trace metal of natural and anthropogenic influences in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,607-608:195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.105
[9] COBB K M,CHARLES C D,CHENG H,et al. El Niño/Southern Oscillation and tropical Pacific climate during the last millennium[J]. Nature,2003,424(6946):271-276. doi: 10.1038/nature01779
[10] HENDY E J,GAGAN M K,ALIBERT C A,et al. Abrupt decrease in Tropical Pacific Sea surface salinity at end of little ice age[J]. Science,2002,295(5559):1511-1514. doi: 10.1126/science.1067693
[11] El-SOROGY A S,NOUR H,ESSA E,et al. Quaternary coral reefs of the Red Sea coast,Egypt:diagenetic sequence,isotopes and trace metals contamination[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2013,6(12):4981-4991. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0806-0
[12] El-SOROGY A S,ALMADANI S A,AL-DABBAGH M E. Microfacies and diagenesis of the reefal limestone,Callovian Tuwaiq Mountain Limestone Formation,central Saudi Arabia[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,2016,115:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.12.013
[13] El-YAMANI M S,Al-RAMADAN K,MUNNECKE A,et al. Microfacies,depositional environments and meter-scale cycles of the middle Jurassic Tuwaiq Mountain formation,central Saudi Arabia[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,2018,145:80-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.04.002
[14] 赵爽,张道军,刘立,等. 南海西沙海域西科1井第四系生物礁:碳酸盐岩成岩作用特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):711-717.
[15] WEBB G E,NOTHDURFT L D,KAMBER B S,et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of scleractinian coral skeleton during meteoric diagenesis:a sequence through neomorphism of aragonite to calcite[J]. Sedimentology,2009,56(5):1433-1463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2008.01041.x
[16] MCGREGOR H V,GAGAN M K. Diagenesis and geochemistry of porites corals from Papua New Guinea:implications for paleoclimate reconstruction[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2003,67(12):2147-2156. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01050-5
[17] ALLISON N,FINCH A A,WEBSTER J M,et al. Palaeoenvironmental records from fossil corals:the effects of submarine diagenesis on temperature and climate estimates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2007,71(19):4693-4703. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.026
[18] BRAITHWAITE C J R,CAMOIN G F. Diagenesis and sea-level change:lessons from Moruroa,French Polynesia[J]. Sedimentology,2011,58(1):259-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2010.01182.x
[19] SAYANI H R,COBB K M,COHEN A L,et al. Effects of diagenesis on paleoclimate reconstructions from modern and young fossil corals[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2011,75(21):6361-6373. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.08.026
[20] RIBAUD-LAURENTI A,HAMELIN B,MONTAGGIONI L,et al. Diagenesis and its impact on Sr/Ca ratio in Holocene Acropora corals[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2001,90(2):438-451. doi: 10.1007/s005310000168
[21] 王国忠,吕炳全,全松青. 永兴岛珊瑚礁的沉积环境和沉积特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1986,17(1):36-44.
[22] 冯杨伟,张功成,屈红军. 南海新生代生物礁发育规律与油气勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(6):18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.06.003
[23] MA Y B,WU S G,LV F L,et al. Seismic characteristics and development of the Xisha carbonate platforms,northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2011,40(3):770-783. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.003
[24] 许红,蔡峰,王玉净,等. 西沙中新世生物礁演化与藻类的造礁作用[J]. 科学通报,1999,44(13):1435-1439. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.13.017
[25] TIAN J,WU S G,LV F L,et al. Middle Miocene mound-shaped sediment packages on the slope of the Xisha carbonate platforms,South China Sea:Combined result of gravity flow and bottom current[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2015,122:172-184. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.06.016
[26] 张海洋,许红,赵新伟,等. 西永2井中新世白云岩储层特征及成岩作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(3):41-47.
[27] 翟世奎,米立军,沈星,等. 西沙石岛生物礁的矿物组成及其环境指示意义[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):597-605.
[28] 蔡峰,许红,郝先锋,等. 西沙—南海北部晚第三纪生物礁的比较沉积学研究[J]. 沉积学报,1996,14(4):62-70.
[29] 朱伟林,王振峰,米立军,等. 南海西沙西科1井层序地层格架与礁生长单元特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):677-687.
[30] 张明书, 何起祥, 业治铮, 等. 西沙生物礁碳酸盐沉积地质学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1-128.
[31] 赵焕庭,王丽荣,宋朝景. 南海诸岛灰沙岛淡水透镜体研究述评[J]. 海洋通报,2014,33(6):601-610. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.06.001
[32] ZHANG R X,YANG S Y. A mathematical model for determining carbon coating thickness and its application in electron probe microanalysis[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis,2016,22(6):1374-1380. doi: 10.1017/S143192761601182X
[33] ZHANG X,YANG S Y,ZHAO H,et al. Effect of beam current and diameter on electron probe microanalysis of carbonate minerals[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2019,30(4):834-842. doi: 10.1007/s12583-017-0939-x
[34] 李晓,刘娜,吴仕玖,等. 南海西沙群岛西科1井上新统-全新统碳酸盐岩微相分析[J]. 科技导报,2016,34(7):103-110. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2016.07.009
[35] 孙志鹏,尤丽,李晓,等. 西沙西科1井第四系生物礁-碳酸盐岩的岩石学特征[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2015,40(4):653-659.
[36] FLÜGEL E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks, Analysis, Interpretation and Application[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2010: 1-488.
[37] 解习农, 谢玉洪, 李绪深, 等. 南海西科1井碳酸盐岩生物礁储层沉积学: 层序地层与沉积演化[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2016: 1-135.
[38] 刘健,韩春瑞,吴建政,等. 西沙更新世礁灰岩大气淡水成岩的地球化学证据[J]. 沉积学报,1998,16(4):71-77.
[39] VEIZER J. Trace elements and isotopes in sedimentary carbonates[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,1983,11(1):265-299.
[40] GRIFFITHS N,MÜLLER W,JOHNSON K G,et al. Evaluation of the effect of diagenetic cements on element/Ca ratios in aragonitic Early Miocene (~16 Ma) Caribbean corals:implications for ‘deep-time’ palaeo-environmental reconstructions[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2013,369:185-200.
[41] NOTHDURFT L D,WEBB G E,BOSTROM T,et al. Calcite-filled borings in the most recently deposited skeleton in live-collected Porites (Scleractinia):implications for trace element archives[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2007,71(22):5423-5438. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.09.025
[42] HENDY E J,GAGAN M K,LOUGH J M,et al. Impact of skeletal dissolution and secondary aragonite on trace element and isotopic climate proxies in Porites corals[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology,2007,22(4):PA4101.
[43] STANLEY S M,HARDIE L A. Secular oscillations in the carbonate mineralogy of reef-building and sediment-producing organisms driven by tectonically forced shifts in seawater chemistry[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,1998,144(1/2):3-19.
[44] MONTAGGIONI L F,BRAITHWAITE C J R. Chapter eight reef diagenesis[J]. Developments in Marine Geology,2009,5:323-372. doi: 10.1016/S1572-5480(09)05008-8
[45] GREEGOR R B,PINGITORE JR N E,LYTLE F W. Strontianite in coral skeletal aragonite[J]. Science,1997,275(5305):1452-1454. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5305.1452
[46] HOUCK J E,BUDDEMEIER R W,CHAVE K E. Skeletal low-magnesium calcite in living scleractinian corals[J]. Science,1975,189(4207):997-999. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4207.997
[47] 王瑞,余克服,王英辉,等. 珊瑚礁的成岩作用[J]. 地球科学进展,2017,32(3):221-233. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.03.0221
[48] 赵强,许红,吴时国,等. 西沙石岛风成碳酸盐沉积的早期成岩作用[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(2):220-236.
[49] 孙启良,马玉波,赵强,等. 南海北部生物礁碳酸盐岩成岩作用差异及其影响因素研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2008,19(5):665-672. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.05.665
[50] 赵强. 西沙群岛海域生物礁碳酸盐岩沉积学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2010: 1-170.
[51] 张明书,刘健,李绍全,等. 西沙群岛西琛一井礁序列成岩作用研究[J]. 地质学报,1997,71(3):236-244.
[52] PERRY C T,HEPBURN L J. Syn-depositional alteration of coral reef framework through bioerosion,encrustation and cementation:taphonomic signatures of reef accretion and reef depositional events[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2008,86(1/4):106-144.
[53] 赵新伟,许红. 中新世礁相碳酸盐岩沉积构成及成礁模式:以西沙海域为例[J]. 科技导报,2016,34(18):194-202.
[54] 王崇友,何希贤,裘松余. 西沙群岛西永一井碳酸盐岩地层与微体古生物的初步研究[J]. 石油实验地质,1979,1:23-38. doi: 10.11781/sysydz197900023
[55] 余克服. 珊瑚礁科学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1-399.
[56] SCHROEDER J H. Fabrics and sequences of submarine carbonate cements in Holocene Bermuda cup reefs[J]. Geologische Rundschau,1972,61(2):708-730. doi: 10.1007/BF01896342
[57] PIERSON B, SHINN E. Cement distribution and carbonate mineral stabilization in Pleistocene limestones of Hogsty Reef, Bahamas[M]//SCHNEIDERMANN N, HARRIS P M. Carbonate Cements. Tulsa: The Society1985: 153-168.
[58] BOGGS S. Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy: International Edition[M]. 5th ed. Boston: Pearson, 2012: 1-600.
[59] FOLK R L. Some aspects of recrystallization in ancient limestones[M]//PRAY LC, MURRAY R C. Dolomitization and Limestone Diagenesis. Tulsa: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, 1965: 14-48.
[60] FOLK R L,ASSERETO R. Comparative fabrics of length-slow and length-fast calcite and calcitized aragonite in a Holocene Speleothem,Carlsbad Caverns,New Mexico[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1976,46(3):486-496.
[61] SANDBERG P A,SCHNEIDERMANN N,WUNDER S J. Aragonitic ultrastructural relics in calcite-replaced Pleistocene skeletons[J]. Nature Physical Science,1973,245(148):133-134. doi: 10.1038/physci245133a0
[62] SANDBERG P A,HUDSON J D. Aragonite relic preservation in Jurassic calcite-replaced bivalves[J]. Sedimentology,1983,30(6):879-892. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1983.tb00716.x
[63] MALIVA R G,MISSIMER T M,DICKSON J A D. Skeletal aragonite neomorphism in Plio-Pleistocene sandy limestones and sandstones,Hollywood,Florida,USA[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2000,136(1/2):147-154.
[64] 赵新伟,许红,孙志鹏. 西沙海域新生代生物礁序列的沉积构成:以西科1井为例[J]. 现代地质,2016,30(4):852-862. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.04.014
[65] JAMES N P. Diagenesis of scleractinian corals in the subaerial vadose environment[J]. Journal of Paleontology,1974,48(4):785-799.
[66] 魏喜,贾承造,孟卫工,等. 南海西沙海域西琛1井生物礁的性质及岩石学特征[J]. 地质通报,2008,27(11):1933-1938. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.11.024
[67] TUCKER M E, WRIGHT V P. Carbonate Sedimentology[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Company, 1990: 314-364.
[68] 何起祥,张明书. 西沙群岛新第三纪白云岩的成因与意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1990,10(2):45-55.
-



 下载:
下载: