GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SURFACE SEDIMENS IN BOHAI STRAIT AND CONTROLLING FACTORS
-
摘要:
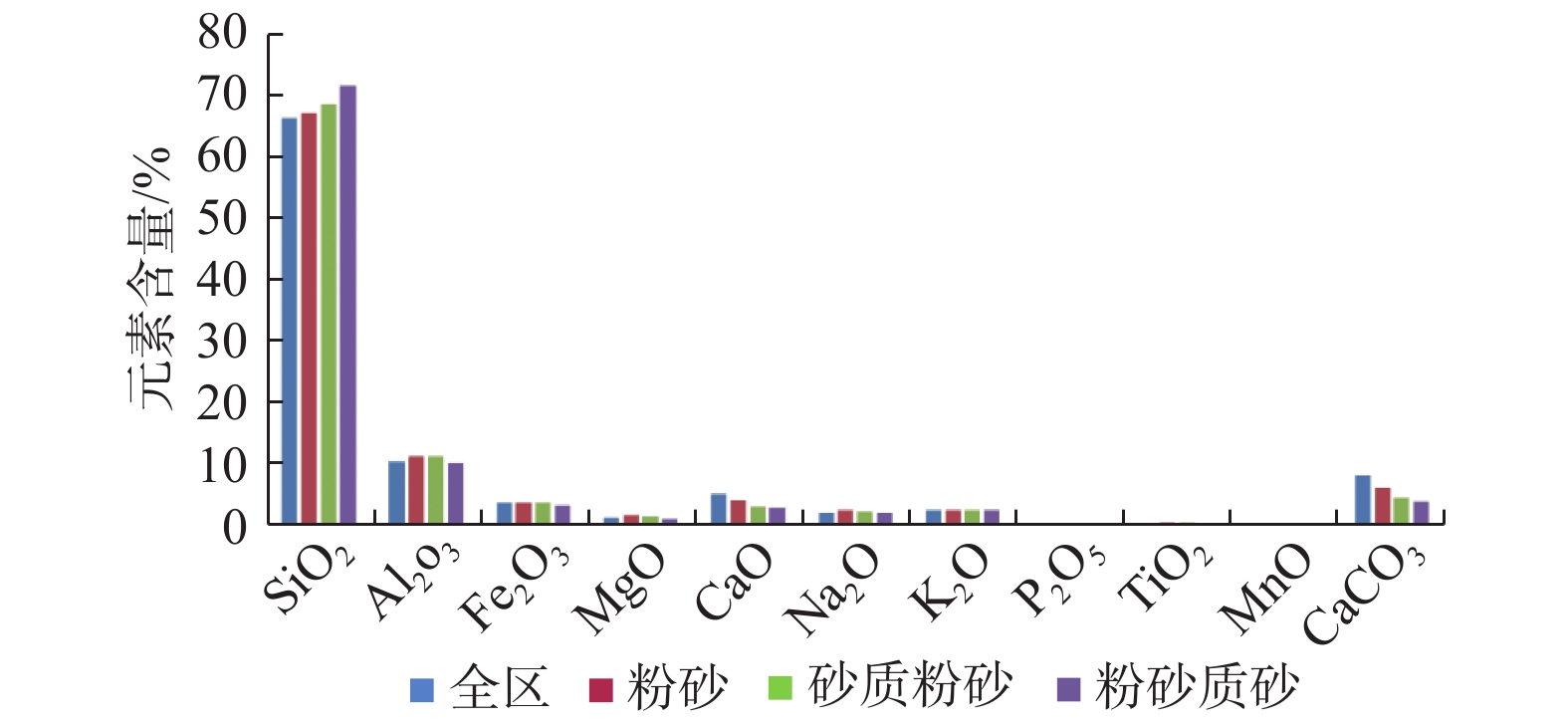
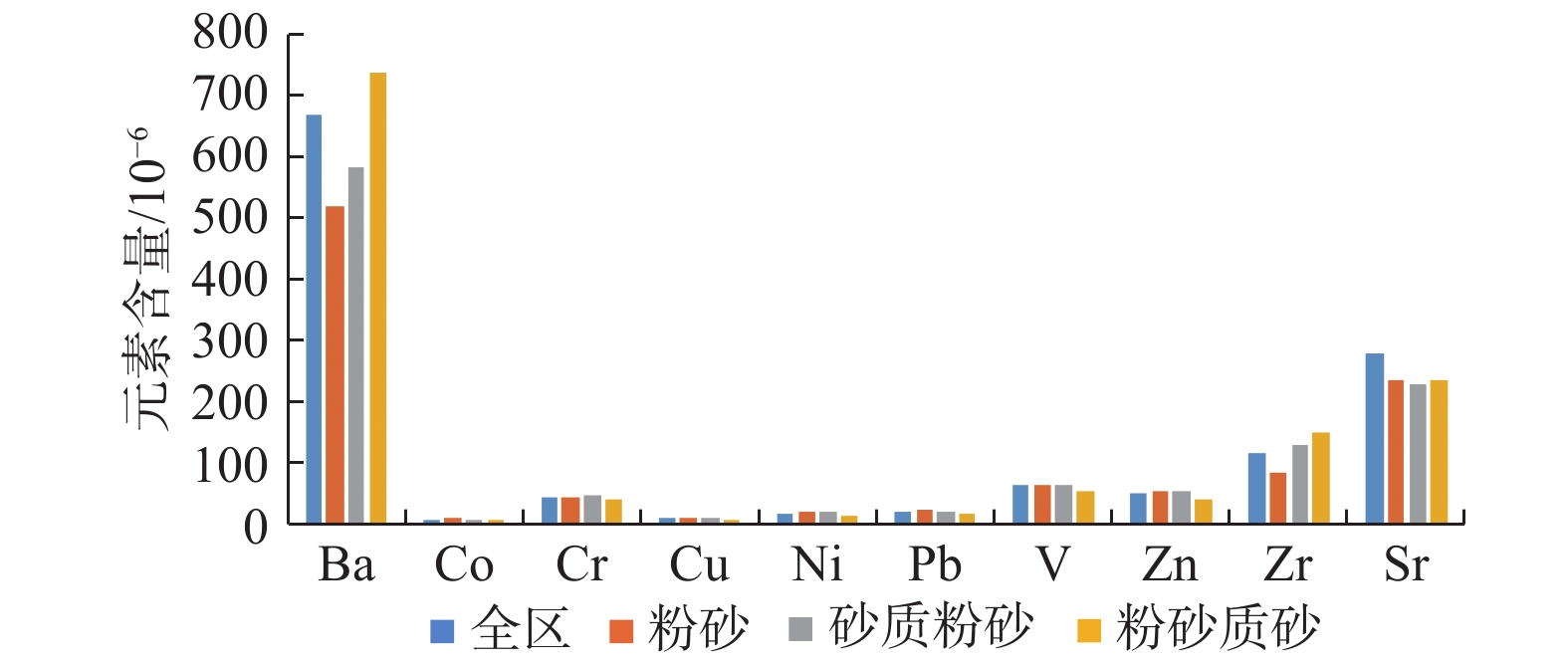
通过对渤海海峡412个站位的表层沉积物粒度及123个站位的表层沉积物地球化学特征分析,探讨了其空间分布特征、元素相关性、元素组合特征、表层沉积物沉积动力环境及沉积物输运方式,揭示了沉积物地球化学特征的环境意义。结果表明:研究区表层沉积物常量元素以SiO2和Al2O3为主,随着沉积物粒径变粗SiO2含量逐渐增加,Al2O3含量逐渐减小。全区表层沉积物微量元素含量最高为Ba。各类型沉积物中元素的富集因子表明元素含量的变化服从粒度控制规律。采用聚类分析方法,将元素分布划分为5个分区:残留沉积区、老铁山水道区、水道东西两侧区、海峡中部区和海峡南部区。
Abstract:Based on the grain size data of surface sediments collected at 412 stations and the geochemical data from 123 stations in the Bohai Strait, we discussed in this paper the spatial distribution pattern of elements, elements correlation, element assemblages, sedimentary dynamic environment and sediment transportation mechanism of the surface sediments, aiming at revealing the environmental significance of sediment geochemistry. The results indicate that the major elements of the surface sediments in the study area are predominated by SiO2 and Al2O3. The content of SiO2 increase and Al2O3 decrease gradually with the increase in grain size of sediments. The highest trace element in the surface sediments is Ba. The element enrichment factors of the sediments from the study area also indicate that the distribution of element content is controlled by the grain size of sediments. The results of cluster analysis further suggest that the spatial distribution of elements in the study area could be subdivided into 5 areass, namely, the relict deposits area, the Laotieshan area, the east and west sides of the watercourse, the central area of the Straits and the southern part of the Straits.
-
Key words:
- surface sediments /
- grain size /
- geochemistry /
- trace elements /
- major elements /
- Bohai Strait
-

-
表 1 研究区表层沉积物元素相关系数表(n=247)
Table 1. Correlation coefficient of elements in surface sediments of the study area(n=247)
Mz SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 TiO2 MnO CaCO3 Ba Co Cr Cu Ni Pb V Zn Zr Sr Mz 1.00 SiO2 −0.86 1.00 Al2O3 0.90 −0.73 1.00 Fe2O3 0.83 −0.76 0.89 1.00 MgO 0.68 −0.78 0.82 0.77 1.00 CaO 0.65 −0.86 −0.48 0.10 −0.04 1.00 Na2O −0.72 0.75 0.54 −0.02 0.34 −0.88 1.00 K2O −0.09 0.28 0.74 0.49 0.56 −0.78 0.65 1.00 P2O5 0.74 −0.68 0.05 0.87 0.39 0.30 −0.16 0.11 1.00 TiO2 −0.43 −0.25 0.91 0.51 0.87 −0.46 0.69 0.53 0.07 1.00 MnO 0.59 −0.43 −0.09 0.35 0.06 0.29 −0.36 −0.05 0.57 −0.11 1.00 CaCO3 0.68 −0.75 −0.49 0.08 −0.07 1.20 −0.89 −0.66 0.24 −0.48 0.28 1.00 Ba 0.59 −0.04 −0.29 0.30 −0.26 0.10 −0.22 0.12 0.48 −0.41 0.19 0.11 1.00 Co 0.81 −0.59 0.69 0.75 0.82 −0.10 0.37 0.49 0.56 0.70 0.21 −0.12 −0.02 1.00 Cr 0.86 −0.71 0.76 0.57 0.77 −0.08 0.07 0.42 0.17 0.71 0.05 −0.09 −0.22 0.59 1.00 Cu −0.26 −0.90 0.65 0.60 0.69 0.11 −0.16 0.33 0.23 0.58 0.20 0.10 −0.13 0.56 0.90 1.00 Ni 0.84 −0.67 0.83 0.66 0.91 −0.12 0.28 0.51 0.32 0.80 0.13 −0.14 −0.24 0.87 0.85 0.81 1.00 Pb 0.58 −0.24 0.53 0.66 0.53 −0.24 0.37 0.50 0.51 0.50 0.28 −0.25 0.11 0.80 0.36 0.39 0.64 1.00 V 0.60 −0.81 0.63 0.86 0.74 0.01 0.04 0.44 0.61 0.59 0.29 0.00 0.14 0.80 0.80 0.80 0.85 0.64 1.00 Zn 0.08 −0.62 0.81 0.67 0.83 −0.15 0.31 0.54 0.30 0.77 0.05 −0.17 −0.16 0.83 0.78 0.76 0.90 0.70 0.76 1.00 Zr −0.87 −0.03 0.13 0.02 −0.06 −0.11 −0.19 0.10 −0.15 0.12 0.06 −0.11 0.05 −0.27 0.41 0.40 0.03 −0.24 0.19 −0.01 1.00 Sr 0.79 −0.82 −0.67 −0.04 −0.31 0.88 −0.66 −0.59 0.26 −0.61 0.23 0.89 0.34 −0.25 −0.33 −0.14 −0.35 −0.26 −0.15 −0.33 −0.16 1.00 表 2 研究区元素富集因子
Table 2. Element enrichment factors in the study area
Ba Co Cr Cu Ni Pb V Zn Zr Sr 全区 1.48 1.32 1.44 1.02 1.37 1.83 1.27 1.10 0.98 1.38 粉砂 1.01 1.38 1.36 0.91 1.41 1.81 1.19 1.14 0.63 1.00 砂质粉砂 1.18 1.26 1.40 1.04 1.37 1.73 1.21 1.10 0.96 0.99 粉砂质砂 1.61 1.09 1.37 0.89 1.17 1.61 1.14 0.97 1.21 1.10 表 3 研究区元素因子载荷矩阵(经过方差极大旋转)
Table 3. Element factor loading matrix in the study area(rotated by variance maxima)
元素 F1 F2 F3 F4 Ni 0.97 0.10 0.06 −0.03 MgO 0.94 0.02 −0.02 −0.13 Zn 0.92 0.14 0.09 −0.08 Cr 0.88 0.02 −0.03 0.39 Cu 0.84 −0.16 0.08 0.42 Al2O3 0.84 0.46 −0.11 0.06 V 0.84 −0.01 0.45 0.14 Co 0.84 0.13 0.31 −0.37 TiO2 0.84 0.37 −0.21 −0.04 Fe2O3 0.69 −0.06 0.61 −0.03 Pb 0.60 0.28 0.46 −0.37 CaO −0.02 −0.99 0.08 −0.06 CaCO3 −0.04 −0.98 0.08 −0.05 Sr −0.30 −0.85 0.25 −0.10 SiO2 −0.56 0.78 −0.17 −0.03 Na2O 0.22 0.77 −0.19 −0.38 K2O 0.46 0.69 0.23 0.07 P2O5 0.31 −0.20 0.82 −0.21 Ba −0.28 0.00 0.81 0.10 MnO 0.09 −0.23 0.59 0.05 Zr 0.07 0.08 0.00 0.94 表 4 研究区地球化学分区常量元素含量特征统计
Table 4. Content of major elements in each geochemical areas of the study area
/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 TiO2 MnO CaCO3 残留沉积区 最大值 70.02 11.96 10.12 2.22 9.15 2.35 3.13 0.32 0.51 0.32 16.39 最小值 54.02 8.07 3.62 1.04 3.40 1.69 2.42 0.13 0.31 0.05 5.07 均值 62.61 9.61 5.58 1.46 7.01 2.11 2.71 0.18 0.39 0.17 11.73 变异系数 8.27 11.72 30.53 24.58 26.21 10.39 8.67 29.06 15.62 53.60 29.68 老铁山水道区 最大值 65.80 9.82 3.97 2.13 21.87 2.00 2.47 0.16 0.39 0.20 40.33 最小值 43.91 4.69 2.30 0.67 7.60 1.13 1.28 0.07 0.23 0.06 12.77 均值 58.32 7.65 2.97 1.21 12.49 1.45 2.10 0.11 0.34 0.09 22.26 变异系数 14.39 20.93 18.14 35.51 41.32 19.91 17.98 24.70 17.63 49.63 44.08 水道东西两侧区 最大值 76.98 11.56 3.86 1.53 4.79 2.86 2.75 0.14 0.52 0.09 7.27 最小值 67.75 9.26 2.26 0.82 1.90 1.88 2.47 0.07 0.33 0.04 2.13 均值 71.57 10.32 3.14 1.15 2.97 2.22 2.60 0.10 0.43 0.06 4.03 变异系数 3.74 7.38 13.60 17.82 36.61 12.26 3.44 19.15 13.08 25.03 49.13 海峡中部区 最大值 76.98 10.83 3.31 1.42 4.03 2.74 2.84 0.12 0.51 0.07 5.55 最小值 71.66 9.26 2.51 0.86 1.95 2.42 2.52 0.09 0.37 0.05 2.25 均值 73.96 10.11 2.92 1.17 2.62 2.55 2.64 0.10 0.44 0.06 3.43 变异系数 1.72 3.45 7.06 10.92 22.11 3.14 2.97 8.86 8.68 10.01 28.59 海峡南部区 最大值 70.62 13.82 5.28 2.49 6.83 2.89 2.90 0.16 0.69 0.17 11.07 最小值 59.63 10.30 3.39 1.54 2.98 2.31 2.44 0.12 0.52 0.06 2.95 均值 65.58 11.99 4.15 1.96 4.21 2.64 2.63 0.13 0.60 0.09 6.23 变异系数 5.32 7.49 13.37 14.04 22.46 5.12 4.61 7.70 6.22 29.92 29.23 表 5 研究区地球化学分区微量元素含量特征统计
Table 5. Statistics of trace element contents in geochemical areass of the study area
/10−6 Ba Co Cr Cu Ni Pb V Zn Zr Sr 残留沉积区 最大值 2217.00 17.27 57.30 21.82 29.46 36.20 140.70 72.72 167.10 488.00 最小值 738.00 10.76 28.54 5.97 16.45 21.64 52.52 41.32 46.20 263.00 均值 1410.33 13.99 42.67 12.00 21.14 27.43 76.97 56.50 88.20 373.98 变异系数 34.73 14.82 23.06 44.22 21.69 14.31 30.10 19.70 50.86 17.76 老铁山水道区 最大值 638.20 11.20 55.10 15.70 24.70 20.80 71.30 53.10 189.40 693.20 最小值 235.20 4.60 29.50 9.00 9.50 13.00 38.00 21.60 87.30 304.20 均值 477.29 7.88 40.96 12.89 16.25 18.25 54.68 35.90 137.58 472.96 变异系数 24.95 25.96 19.99 16.25 26.60 13.25 18.27 26.81 26.61 30.81 水道东西两侧区 最大值 1359.40 11.50 61.30 20.40 23.60 25.40 69.50 57.80 395.40 289.70 最小值 529.40 3.90 37.10 9.60 12.70 15.00 42.60 30.90 146.40 192.10 均值 735.06 7.84 49.20 13.27 17.22 19.85 60.20 42.22 240.45 226.34 变异系数 36.73 23.89 14.50 22.56 18.87 13.86 12.22 20.31 30.53 14.26 海峡中部区 最大值 598.00 11.82 50.06 9.04 21.84 25.47 57.53 51.10 85.29 274.00 最小值 467.00 8.62 31.19 5.09 14.61 21.04 41.20 37.12 61.32 220.00 均值 531.74 10.29 37.55 7.03 17.84 23.25 49.76 42.08 74.09 232.74 变异系数 7.85 7.42 10.52 15.39 8.64 6.64 7.26 9.32 9.34 5.62 海峡南部区 最大值 543.00 17.78 65.14 23.53 37.06 32.96 92.82 92.38 105.19 280.00 最小值 402.00 12.33 41.21 8.88 21.95 23.45 62.14 47.65 79.75 199.00 均值 447.69 14.68 52.06 14.27 26.80 26.19 73.64 63.02 94.79 225.12 变异系数 5.72 10.71 10.43 26.54 14.18 7.85 11.57 16.33 6.91 8.38 -
[1] 徐东浩,李 军,赵京涛,等. 辽东湾表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(5):35-42.
[2] 袁 萍. 渤海表层沉积物的空间分布及其物源和沉积动力环境的关系 [D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.
[3] 王 伟,李安春,徐方建,等. 北黄海表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其沉积环境分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2009,40(5):525-531. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.05.001
[4] 赵 利,彭学超,钟和贤,等. 南海北部陆架区表层沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(6):111-122.
[5] 肖 晓,石要红,冯秀丽,等. 北部湾表层沉积物粒度分布规律及沉积动力分区[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2016,46(5):83-89.
[6] 赵广明,叶 青,薛春汀,等. 现代黄河三角洲陆上表层沉积物类型与沉积环境分区及岸线演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(5):47-52.
[7] 张 盼,吴建政,胡日军,等. 莱州湾西南部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其现代沉积环境分区[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(9):11-17.
[8] 廖永杰. 渤海中南部沉积地球化学特征和黄河改道事件[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[9] 李淑媛,苗丰民,赵全民,等. 辽东半岛西南及渤海中部海域表层沉积物的地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(4):123-130.
[10] 蓝先洪,顾兆峰,密蓓蓓,等. 渤海西部表层沉积物中重金属的环境地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(2):367-373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.02.015
[11] 蓝先洪,李日辉,张志珣,等. 渤海东部与黄海北部表层沉积物的元素地球化学记录[J]. 地球学报,2015,36(6):718-728. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.06.04
[12] 塔金璐. 渤黄海黏土粒级沉积物地球化学记录对物源和沉积环境的释读 [D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[13] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[C]//Tucker M ed. Techniques in Sedimentology, Backwell, Oxford 1988: 63 - 85.
[14] 林炳煌,雷怀彦,官宝聪,等. 九龙江河口表层沉积物元素特征及地球化学意义[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2009,48(3):450-455.
[15] 王蒙光. 九龙江河口湾沉积物粒度和元素地球化学特征对沉积动力环境的指示[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2008.
[16] Han D L. Geochemistry of core E in the Laizhou Bay since late stage of Middle Pleistocene[J]. 海洋学报,2001,23(1):79-85.
[17] 窦衍光,李 军,杨守业. 山东半岛东部海域表层沉积物元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2012,34(1):109-119.
[18] 郭 飞,高茂生,侯国华,等. 莱州湾07钻孔沉积物晚更新世以来的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2016,38(3):145-155.
[19] 陈 弘,刘 坚,王宏斌. 琼东南海域表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(6):39-45.
[20] Nesbitt H W,Young G M,Mclennan S M et.al. Effects of Chemical Weathering and Sorting On the Petrogenesis of Siliciclastic Sediments,with Implications for Provenance Studies[J]. The Journal of Geology,1996,104(5):525-542. doi: 10.1086/629850
-




 下载:
下载: