WEATHERING CHARACTERISTICS AND PROVENANCE OF THE SURFACE SEDIMENTS IN THE OFFSHORE OF NORTHERN FUJIAN
-
摘要:
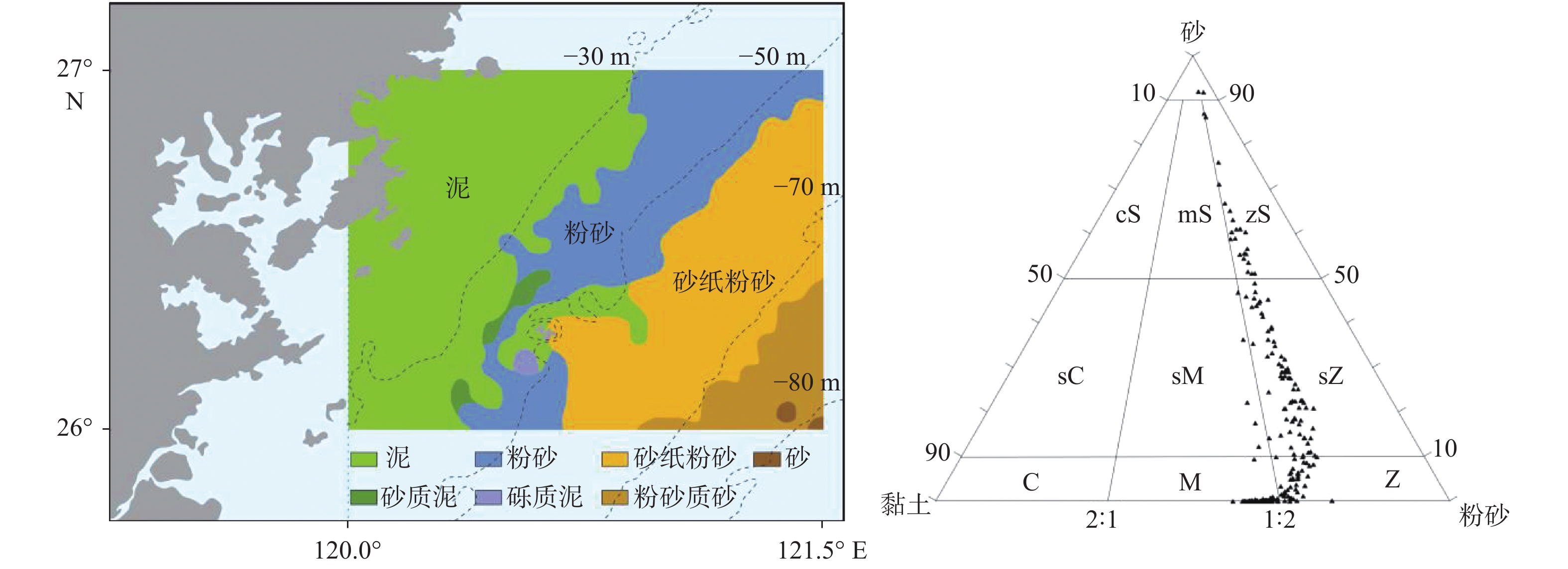
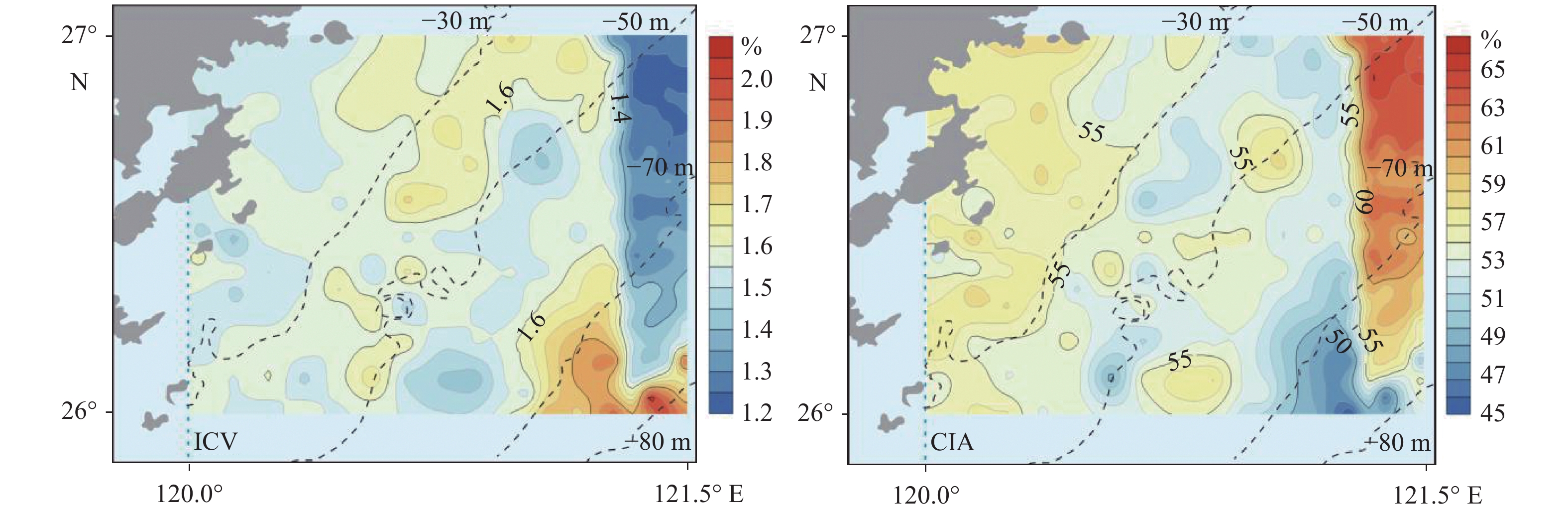
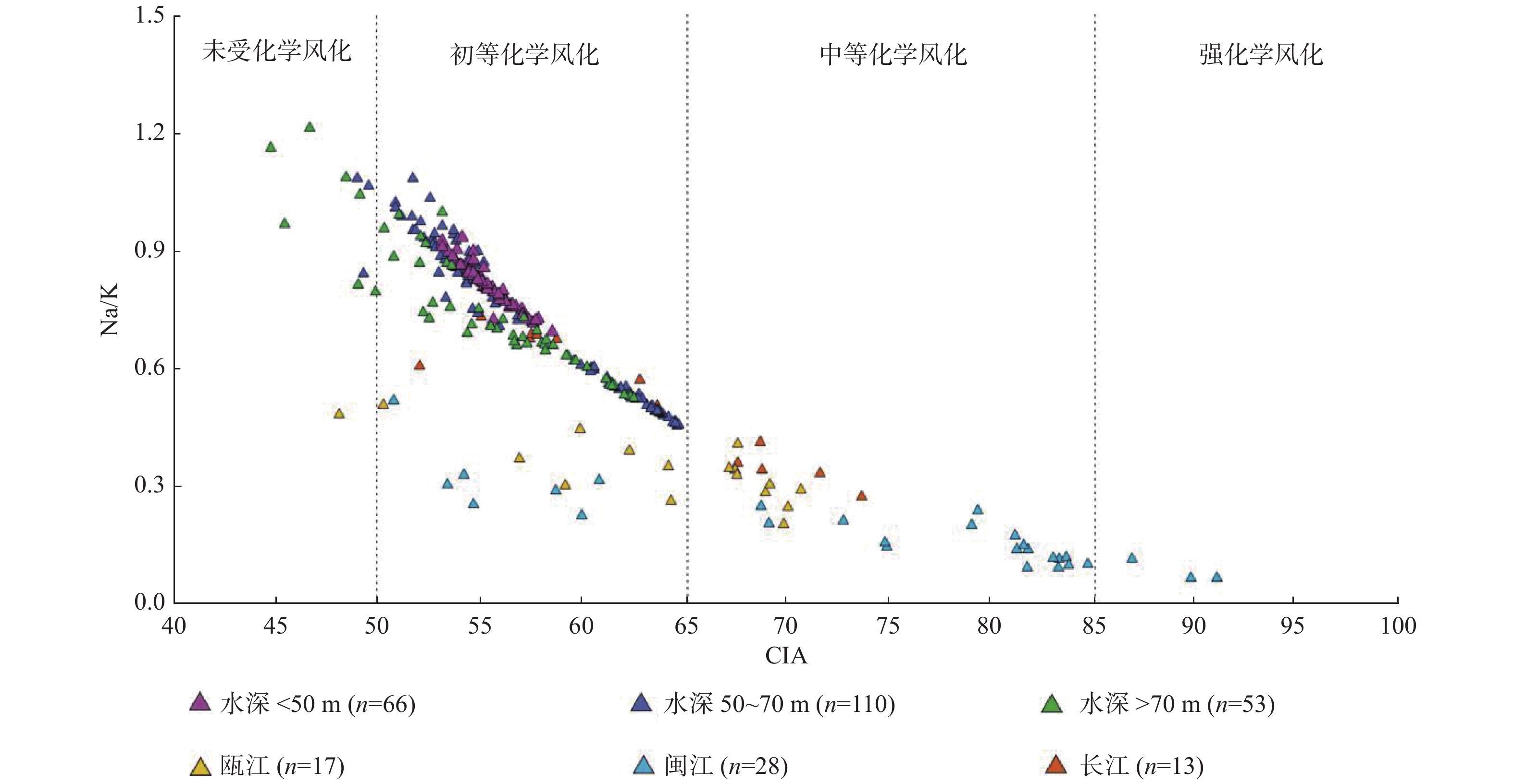
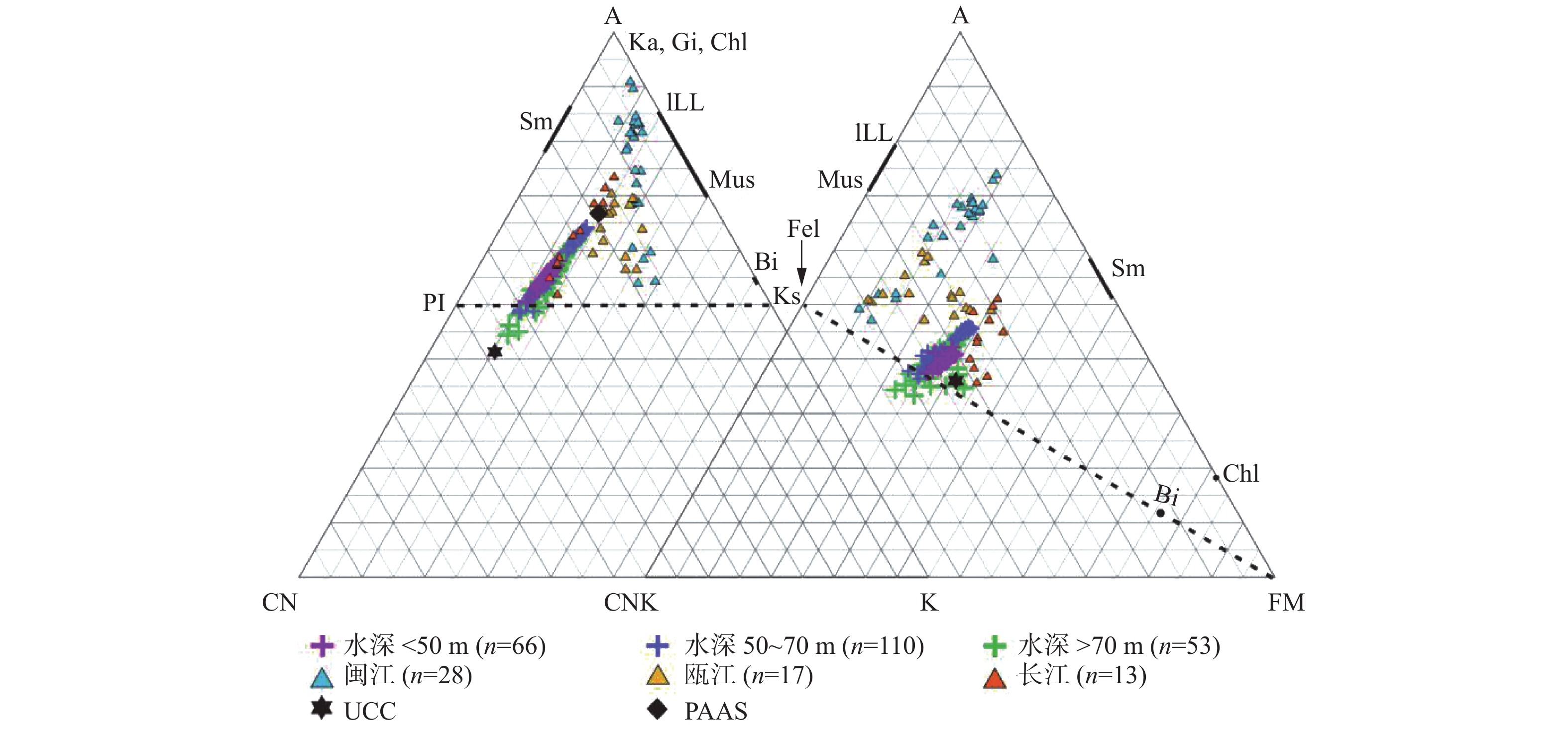
通过对闽北近岸海域的229个表层沉积物样品和周边河流的54个表层沉积物样品进行粒度和常量元素测试,分析了研究区常量元素分布及粒度控制效应,并运用成分变异指数(ICV)和化学蚀变指数(CIA) 2种风化指标,结合(A-CN-K)-(A-CNK-FM)三角图,探讨了其风化特征及物源指示。研究表明,闽北近岸海域从岸向海表层沉积物粒径变粗,底质类型表现为明显的条带状,依次为泥-粉砂-砂质粉砂-砂。分析认为,形成这种条带状的主要原因是其物源及动力机制的不同,近岸主要为长江及周边河流物质输送,分布在50 m水深以浅,而在70 m以深的粗砂主要为残留沉积,50~70 m表现为过渡类型。风化程度研究表明,在空间分布上,从岸向海化学风化程度逐渐增强,70 m以深的异常区是以石英为主的残留沉积,抗风化能力强,黏土矿物含量低,表现为弱化学风化程度。长江、瓯江、闽江沉积物的风化程度表现为随着地理纬度的降低而增强,气候效应明显,研究区与长江沉积物风化趋势更为接近,所经历的形成环境最为相似,受物源效应影响。
Abstract:The analysis of grain size and major elements was carried out for 229 surface sediment samples collected from the coastal area of northern Fujian and 54 surface samples from the surrounding rivers. The factors controlling the distribution patterns of the major elements and grain size are studied. Two weathering indicators, the component variation index (ICV) and the chemical alteration index (CIA), are used together with the (A-CN-K)-(A-CNK-FM) triangle chart to reveal the weathering characteristics and provenance indicators. Results show that the surface sediments along the coast are distributed in a quite regular pattern. From the coast to the sea, the deposits are getting thicker, and spatially in a banded manner. Sands occur near the land followed by mud-silt-sand silt-sand towards the sea. It is believed that the banded distribution pattern depends on sediment source and water dynamics. The near shore sediments are mainly coming from the Yangtze River and surrounding rivers, and deposited in the area less than 50 m in water depth. The coarse sands found in the area under 70 m of water depth are mainly residual sediments. In the area between 50~70 m in water depth, there occur the mixed sediments of the above two. Research of weathering degree suggests that chemical weathering becomes stronger off shore. The sediments below 70 m are mainly the residual sands dominated by high quartz and low clay mineral content, indicating a weak chemical weathering. The weathering degree of fluvial sediments in the Yangtze River, Oujiang River and Minjiang River shows an increase trend with the decrease in geographical latitude, and the effect of climate is obvious. The weathering status of the study area is rather similar to the Yangtze River sediments, and thus the environments are also similar and both affected by sediment sources.
-

-
表 1 表层沉积物常量元素含量统计
Table 1. Contents of major elements in surface sediments
元素含量/% 区域 参数指标 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO CaO Na2O K2O CIA 平均粒径(Mz) 研究区(n=229) 最大值 66.04 18.96 14.58 4.21 19.21 3.91 3.56 64.74 7.83Φ 最小值 29.73 6.85 4.36 1.81 2.82 1.36 1.21 44.80 1.26Φ 平均值 55.62 15.99 6.19 2.59 4.19 2.68 3.09 56.14 6.42Φ 标准偏差 4.23 1.86 1.05 0.35 1.61 0.61 0.30 3.40 1.19 变异系数 0.07 0.12 0.17 0.13 0.39 0.23 0.10 0.07 0.19 上陆壳 平均值 66.00 15.20 5.00 2.20 4.20 3.90 3.40 47.92 \ 长江(n=13) 最大值 72.42 16.10 6.62 2.83 8.84 1.79 2.89 73.76 \ 最小值 49.16 8.36 3.38 1.81 3.62 0.82 2.08 52.09 平均值 61.28 12.68 5.27 2.32 5.66 1.38 2.39 62.78 瓯江(n=17) 最大值 77.08 17.13 6.84 2.41 1.44 2.85 5.01 70.79 \ 最小值 58.79 11.45 2.02 0.28 0.33 0.82 3.15 48.15 平均值 69.14 14.27 3.88 1.03 0.83 1.58 3.91 63.43 闽江(n=28) 最大值 87.78 24.06 7.69 1.00 1.09 1.19 4.24 91.15 \ 最小值 51.49 6.12 1.29 0.16 0.15 0.13 1.72 50.83 平均值 68.67 16.58 4.21 0.58 0.49 0.64 3.01 74.68 注:上陆壳数据引自文献[22]。 表 2 主要常量元素与平均粒径的相关性
Table 2. Correlation coefficients of grain size and main elements
X Y 方程 R2 Mz SiO2 y = −2.985 2x + 74.945 0.771 8 Mz Al2O3 y = 1.472 8x + 6.609 8 0.921 8 Mz CaO y = −0.740 8x + 8.786 5 0.647 5 Mz MgO y = 0.247 6x + 1.003 6 0.752 7 Mz K2O y = 0.221 7x + 1.677 3 0.822 4 Mz Na2O y = 0.293 1x + 0.799 0 0.299 5 Mz Fe2O3 y = 0.748 0x + 1.321 4 0.871 4 -
[1] Kump L R,Brantley S L,Arthur M A. Chemical weathering,atmospheric CO2,and climate[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2000,28(1):611-667. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.611
[2] 解晨骥,高全洲,陶 贞. 流域化学风化与河流水化学研究综述与展望[J]. 热带地理,2012,32(4):331-337,356.
[3] 严桃桃,吴 轩,权养科,等. 从岩石到土壤再到水系沉积物:风化过程的岩性地球化学基因[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):453-467.
[4] 付 玲,关 平,赵为永,等. 柴达木盆地古近系路乐河组重矿物特征与物源分析[J]. 岩石学报,2013,29(8):2867-2875.
[5] 杨守业,印 萍. 自然环境变化与人类活动影响下的中小河流沉积物源汇过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(1):1-10.
[6] 林 刚,陈琳莹,罗 敏,等. 西太平洋新不列颠海沟表层沉积物的地球化学特征及其物源指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(3):12-27.
[7] Rowland R A. Handbook of geochemistry:K. H. Wedepohl (Executive editor),1969. Springer,Berlin. Vol. I:442 pp.,60 fig.,Vol. II; Loose-leaf,DM 224.00(both volumes)[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,1970,6(1):A24-A25. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(70)90013-9
[8] Nesbitt H W,Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature,1982,299(5885):715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[9] 徐小涛,邵龙义. 利用泥质岩化学蚀变指数分析物源区风化程度时的限制因素[J]. 古地理学报,2018,20(3):515-522.
[10] Gallet S,Jahn B M,Torii M. Geochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence,China,and paleoclimatic implications[J]. Chemical Geology,1996,133(1/4):67-88.
[11] 陈 骏,安芷生,刘连文,等. 最近2.5 Ma以来黄土高原风尘化学组成的变化与亚洲内陆的化学风化[J]. 中国科学(D辑),2001,31(2):136-145.
[12] 张西营,马海州,谭红兵. 青藏高原东北部黄土沉积化学风化程度及古环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004,24(2):43-47.
[13] 李冠华,夏敦胜,柳加波,等. 新疆塔城黄土沉积常量地球化学元素特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):183-191.
[14] Wentworth C K. A scale of grade and class terms for Clastic sediments[J]. The Journal of Geology,1922,30(5):377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[15] Folk R L,Ward W C. Brazos river bar:a study in the signification of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1957,27(1):3-27. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[16] Cox R,Lowe D R,Cullers R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1995,59(14):2919-2940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
[17] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology,1993,101(2):295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[18] Nesbitt H W,Young G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1984,48(7):1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
[19] Nesbitt H W,Young G M,McLennan S M,et al. Effects of chemical weathering and sorting on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments,with implications for provenance studies[J]. The Journal of Geology,1996,104(5):525-542. doi: 10.1086/629850
[20] 田姗姗,张富元,阎丽妮,等. 东海西南陆架表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(5):13-20.
[21] 刘剑刚,张 华,朱夏夏,等. 辽东山地冰缘地貌上覆土壤粒度及元素地球化学[J]. 水土保持研究,2015,22(5):331-335,341.
[22] Gibbs A K. The continental crust:its composition and evolution. Stuart Ross Taylor,Scott M. McLennan[J]. The Journal of Geology,1985,94(4):632-633.
[23] 邵菁清,杨守业. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)反映长江流域的硅酸盐岩化学风化与季风气候?[J]. 科学通报,2012,57(11):933-942.
[24] 张 威,董应巍,于 洋,等. 辽南黄土化学风化特点及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(5):163-171.
[25] 张晓东,翟世奎,许淑梅. 长江口外近海表层沉积物粒度的级配特性及其意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报,2007,37(2):328-334.
[26] 刘升发,刘焱光,朱爱美,等. 东海内陆架表层沉积物粒度及其净输运模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(1):1-6.
[27] 黄 龙,张志珣,耿 威,等. 闽浙沿岸东部海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014,34(6):161-169.
[28] 曾定勇,倪晓波,黄大吉. 冬季浙闽沿岸流与台湾暖流在浙南海域的时空变化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2012,42(7):1123-1134.
[29] 秦蕴珊. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.
[30] 肖尚斌,李安春,蒋富清,等. 近2 ka闽浙沿岸泥质沉积物物源分析[J]. 沉积学报,2005,23(2):268-274.
[31] 周晓静. 东海陆架细颗粒沉积物组成分布特征及其物源指示[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2009.
[32] 杨旭辉,冯秀丽,褚忠信,等. 中国东部陆架表层沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境浅析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报,2012,42(7/8):126-134.
[33] Yang S Y,Wang Z B,Dou Y G,et al. A review of sedimentation since the last glacial maximum on the continental shelf of eastern China[J]. Geological Society,London,Memoirs,2014,41(1):293-303.
[34] 张晓娟. 东海内陆架南部表层沉积特征及物源分析[D]. 宜昌: 三峡大学, 2015.
[35] 杨光复, 董太禄, 徐善民, 等. 东海大陆架南部更新世末期以来的沉积特征[M]//中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 黄东海地质. 北京: 科学出版社, 1982: 67-81.
[36] 杨作升. 黄河、长江、珠江沉积物中粘土的矿物组合、化学特征及其与物源区气候环境的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1988,19(4):336-346.
[37] Rudnick R,Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry,2014,4:1-51.
[38] 郭玉龙,杨守业,苏 妮,等. 中国东南入海河流沉积物的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(1):139-149.
[39] 沙旭光,刘 健,程新民,等. 强制海退沉积作用及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质动态,2006,22(11):13-17.
[40] 杨守业,李从先. 长江与黄河现代表层沉积物元素组成及其示踪作用[J]. 自然科学进展,1999,9(10):930-937.
[41] 范德江,杨作升,毛 登,等. 长江与黄河沉积物中粘土矿物及地化成分的组成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2001,21(4):7-12.
[42] 刘升发,石学法,刘焱光,等. 东海内陆架泥质区表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 海洋科学进展,2010,28(1):80-86.
[43] 马晓红,韩宗珠,毕世普,等. 闽江河口表层沉积物重矿物特征与物源示踪[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(1):87-95.
[44] 李国刚,胡邦琦,李 军,等. 山东半岛沿岸海域表层沉积物的常量元素及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(3):45-54.
[45] 凌超豪,龙 进,贾玉连,等. 赣北鄱阳湖地区土塘剖面第四纪红土地球化学特征及古气候意义[J]. 古地理学报,2015,17(5):699-708.
-




 下载:
下载: