CHARACTERISTICS OF N-ALKANES IN THE SURFACE SEDIMENTS OF THE EAST CHINA SEA AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR THE DISTRIBUTION OF TERRIGENOUS ORGANIC MATTER
-
摘要:
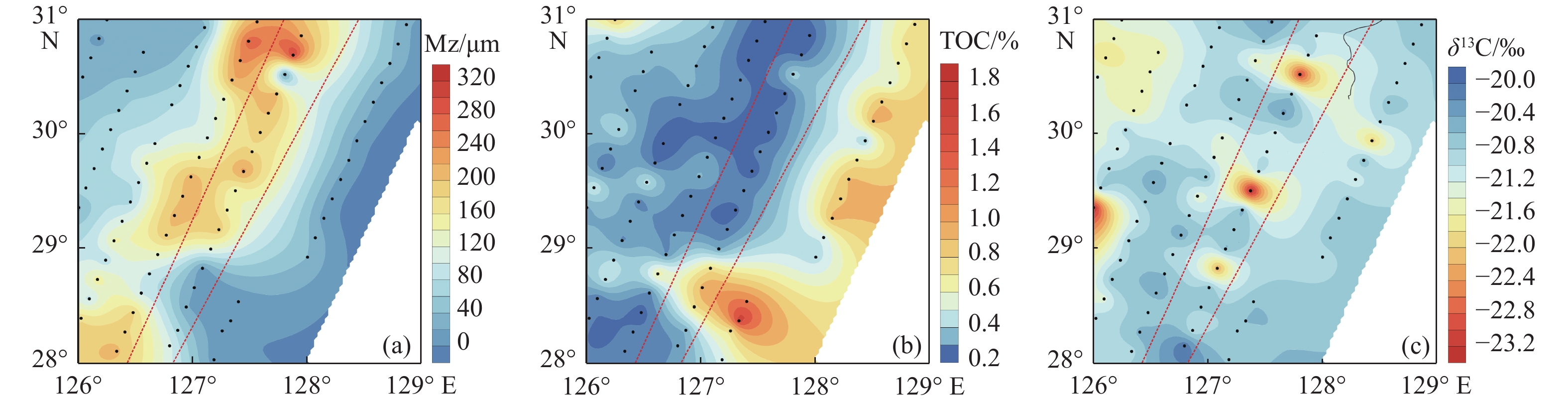
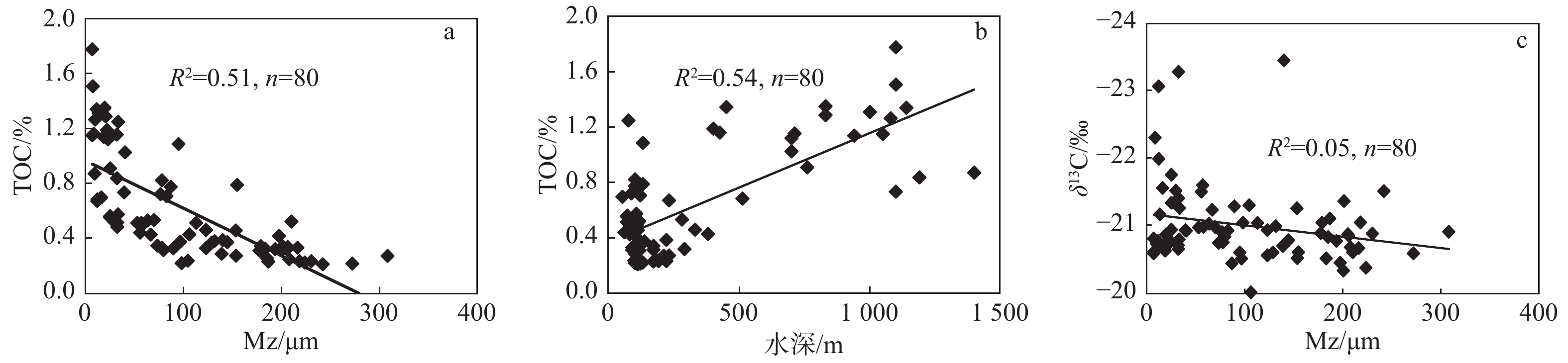
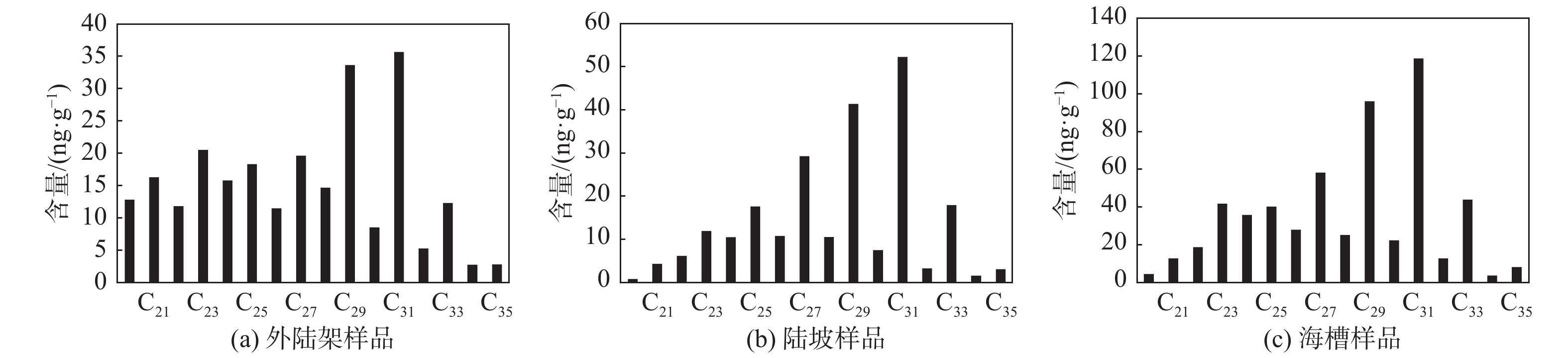
东海埋藏了通过长江、黄河以及台湾河流进入的巨量陆源有机碳,是重要的有机碳碳“汇”。识别东海沉积物中陆源有机碳的分布特征和搬运过程,是东海碳通量研究不可或缺的内容。目前关于陆源有机碳在东海沉积物中分布的研究区域主要集中在河口、内陆架以及水深<120 m的中、外陆架地区;针对东海外陆架和冲绳海槽陆坡的研究较少,仅少量研究对东海陆架与冲绳海槽南部沉积物的陆源有机碳特征进行了对比分析,对陆源有机碳的“源-汇”过程、分布特征、沉积动力机制等诸多问题尚缺乏系统性的认识。通过对东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽80个表层沉积物的长链正构烷烃含量及组成特征进行分析,并结合粒度、总有机碳(TOC)及稳定碳同位素(δ13C)指标,讨论了研究区沉积物中陆源有机碳的含量及运移分布。结果显示,δ13C和(ΣC27+C29+C31 n-alkane)/TOC指示的陆源有机碳相对含量在研究区变化范围很大,从外陆架到海槽,有先降低后增高的变化趋势,陆源有机碳在陆坡以及海槽的一些特定区域选择性的大量沉积。东海内陆架的陆源有机碳在横穿东海陆架后,可以在陆坡处通过搬运-沉积-再悬浮-再搬运的方式运移至冲绳海槽沉积。长链正构烷碳优势指数(CPI)的结果表明,来自东海内陆架的陆源有机碳主要在冲绳海槽28.5°—30°N范围内沉积,28.5°N以南的陆源有机质主要受到台湾物质的影响,而30°N以北沉积物中的陆源有机质主要是来源于黄河和日本岛。
Abstract:The East China Sea (ECS) is an important sink of organic carbon with complicated and diverse sources, in which there is a huge amount of terrigenous organic carbon coming from the Yangtze River, the Yellow River and the rivers from Taiwan. Therefore, it is indispensable to identify the composition of terrigenous sedimentary organic carbon and trace its fluvial source for carbon flux research. Up to date, the study on the distribution of terrigenous organic carbon in sediments of the ECS is mainly concentrated in some areas such as the estuary areas and the middle and outer shelf regions in a water depth < 120 m, but rare is devoted to the slope of Okinawa Trough (OT) and the outer shelf of the ESC. Little is known about the source-sink process, distribution patterns, sedimentary dynamic mechanisms, and other problems concerning the origin of terrigenous organic carbon. In this paper, we discussed the distribution and transportation of terrigenous organic carbon in the sediment, through the distribution and composition of n-alkanes for 80 surface sediment samples from the ECS outer shelf, slop and trough, together with other indexes such as grain-size, total organic carbon (TOC) and stable carbon isotope δ13C. The results show that the terrigenous organic carbon content indicated by δ13C and(ΣC27+C29+C31,n-alkane)/TOC vary in a large range in the study area, and from the outer shelf to the trough, they decrease first and increase later. There is a great amount of terrigenous organic carbon deposited on slope and in some special areas of the OT. Dominated by the process of “transportation-deposition-resuspension-transportation” in the slope area, the terrigenous organic matter (TOM) is continuously transported from the interior shelf of ECS to the OT across the outer shelf. The results of CPI suggest that the TOM from ECS inner shelf was mainly sourced from the area of 28.5°—30°N in the Okinawa Trough. To the south of 28.5°N, the TOM in sediments was mainly affected by the materials from Taiwan, while to the north of 30°N, the TOM was mainly derived from the Yellow River and Japan Islands.
-
Key words:
- terrigenous organic carbon /
- n-alkanes /
- δ13Corg /
- Okinawa Trough /
- East China Sea
-

-
[1] Hedges J I,Keil R G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation:an assessment and speculative synthesis[J]. Marine Chemistry,1995,49(2/3):81-115.
[2] Schlesinger W H,Melack J M. Transport of organic carbon in the world's rivers[J]. Tellus,1981,33(2):172-187. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v33i2.10706
[3] Milliman J D,Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology,1983,91(1):1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[4] 段晓勇,印 萍,刘 金,等. 中国东部近海现代沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(2):14-20.
[5] Milliman J D,Shen H T,Yang Z S,et al. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research,1985,4(1/2):37-45.
[6] Kao S J,Liu K K. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope systematics in a human-disturbed watershed (Lanyang-Hsi) in Taiwan and the estimation of biogenic particulate organic carbon and nitrogen fluxes[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles,2000,14(1):189-198. doi: 10.1029/1999GB900079
[7] Chen C T A,Kandasamy S,Chang Y P,et al. Geochemical evidence of the indirect pathway of terrestrial particulate material transport to the Okinawa Trough[J]. Quaternary International,2017,441:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.08.006
[8] Hu L M,Shi X F,Lin T,et al. Perylene in surface sediments from the estuarine-inner shelf of the East China Sea:a potential indicator to assess the sediment footprint of large river influence[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,90:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.04.014
[9] Hu L M,Shi X F,Yu Z G,et al. Distribution of sedimentary organic matter in estuarine–inner shelf regions of the East China Sea:implications for hydrodynamic forces and anthropogenic impact[J]. Marine Chemistry,2012,142/144:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2012.08.004
[10] Wu Y,Zhang J,Liu S M,et al. Sources and distribution of carbon within the Yangtze River system[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2007,71(1/2):13-25.
[11] Xing L,Zhang H L,Yuan Z N,et al. Terrestrial and marine biomarker estimates of organic matter sources and distributions in surface sediments from the East China Sea shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2011,31(10):1106-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.04.003
[12] Zhang H L,Xing L,Zhao M X. Origins of terrestrial organic matter in surface sediments of the East China Sea Shelf[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2017,16(5):793-802. doi: 10.1007/s11802-017-3216-9
[13] Zhu C,Xue B,Pan J M,et al. The dispersal of sedimentary terrestrial organic matter in the East China Sea (ECS) as revealed by biomarkers and hydro-chemical characteristics[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2008,39(8):952-957. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.04.024
[14] Oguri K,Matsumoto E,Yamada M,et al. Sediment accumulation rates and budgets of depositing particles of the East China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(2):513-528. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00465-4
[15] Li Y H. Material Exchange between the East China Sea and the Kuroshio Current[J]. Terrestrial,Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences,1994,5(4):625-631. doi: 10.3319/TAO.1994.5.4.625(O)
[16] Peng T H,Hung J J,Wanninkhof R,et al. Carbon budget in the East China Sea in spring[J]. Tellus B:Chemical and Physical Meteorology,1999,51(2):531-540. doi: 10.3402/tellusb.v51i2.16337
[17] Tsunogai S,Watanabe S,Sato T. Is there a "continental shelf pump" for the absorption of atmospheric CO2?[J]. Tellus B:Chemical and Physical Meteorology,1999,51(3):701-712. doi: 10.3402/tellusb.v51i3.16468
[18] Wang S L,Chen C T A,Hong G H,et al. Carbon dioxide and related parameters in the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2000,20(4/5):525-544.
[19] Chen C T A,Wang S L. Carbon dioxide and related parameters in the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1999,104(20):675-686.
[20] Kao S J,Lin F J,Liu K K. Organic carbon and nitrogen contents and their isotopic compositions in surficial sediments from the East China Sea shelf and the southern Okinawa Trough[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(6/7):1203-1217.
[21] Katayama H,Watanabe Y. The Huanghe and Changjiang contribution to seasonal variability in terrigenous particulate load to the Okinawa Trough[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(2):475-485. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00469-1
[22] Bian C W,Jiang W S,Song D H. Terrigenous transportation to the Okinawa Trough and the influence of typhoons on suspended sediment concentration[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2010,30(10/11):1189-1199.
[23] Wang J Z,Li A C,Xu K H,et al. Clay mineral and grain size studies of sediment provenances and paleoenvironment evolution in the middle Okinawa Trough since 17 ka[J]. Marine Geology,2015,366:49-61. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.04.007
[24] Dou Y G,Yang S Y,Liu Z X,et al. Provenance discrimination of siliciclastic sediments in the middle Okinawa Trough since 30 ka:constraints from rare earth element compositions[J]. Marine Geology,2010,275(1/4):212-220.
[25] Dou Y G,Yang S Y,Liu Z X,et al. Sr–Nd isotopic constraints on terrigenous sediment provenances and Kuroshio Current variability in the Okinawa Trough during the late Quaternary[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,365/366:38-47.
[26] Zheng X F,Li A C,Kao S,et al. Synchronicity of Kuroshio Current and climate system variability since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2016,452:247-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.07.028
[27] Zhao D B,Wan S M,Toucanne S,et al. Distinct control mechanism of fine‐grained sediments from Yellow River and Kyushu supply in the northern Okinawa Trough since the last glacial[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2017,18(8):2949-2969.
[28] Iseki K,Okamura K,Kiyomoto Y. Seasonality and composition of downward particulate fluxes at the continental shelf and Okinawa Trough in the East China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(2):457-473. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00468-X
[29] Lin S,Hsieh I J,Huang K M,et al. Influence of the Yangtze River and grain size on the spatial variations of heavy metals and organic carbon in the East China Sea continental shelf sediments[J]. Chemical Geology,2002,182(2/4):377-394.
[30] Yuan D L,Zhu J R,Li C Y,et al. Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2008,70(1/2):134-149.
[31] Chung Y C,Hung G W. Particulate fluxes and transports on the slope between the southern East China Sea and the South Okinawa Trough[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2000,20(4/5):571-597.
[32] He X Q,Bai Y,Chen C T A,et al. Satellite views of the episodic terrestrial material transport to the southern Okinawa Trough driven by typhoon[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2014,119(7):4490-4504.
[33] Li Y H,Wang A J,Qiao L,et al. The impact of typhoon Morakot on the modern sedimentary environment of the mud deposition center off the Zhejiang–Fujian coast,China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2012,37:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.02.020
[34] Zhu C,Wagner T,Talbot H M,et al. Mechanistic controls on diverse fates of terrestrial organic components in the East China Sea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2013,117:129-143. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.04.015
[35] 冯 利,冯秀丽,宋 湦,等. 莱州湾表层沉积物粒度和黏土矿物分布特征与运移趋势分析[J]. 海洋科学,2018,42(2):1-9.
[36] 沈昆明,蒋玉波,李安龙,等. 舟山群岛表层沉积物粒度和黏土矿物分布特征与物源指示[J]. 海岸工程,2020,39(1):24-33.
[37] Mei X,Li X X,Wang Z B,et al. Cross shelf transport of terrigenous organic matter in surface sediments from outer shelf to Okinawa Trough in East China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2019,199:103224. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2019.103224
[38] Mei X,Li R H,Zhang X H,et al. Reconstruction of phytoplankton productivity and community structure in the South Yellow Sea[J]. China Geology,2019,2(3):315-324.
[39] 梅 西, 李学杰, 密蓓蓓, 等. 中国海域表层沉积物分布规律及沉积分异模式[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5): 1447-1462.
[40] 王骏博. 溶解有机碳同位素测定方法研究及其在九龙江的应用[D]. 厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所, 2015.
[41] Eglinton G,Hamilton R J. Leaf epicuticular waxes[J]. Science,1967,156(3780):1322-1335. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3780.1322
[42] Meyers P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic,paleolimnologic,and paleoclimatic processes[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1997,27(5/6):213-250.
[43] Hedges J I,Oades J M. Comparative organic geochemistries of soils and marine sediments[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1997,27(7/8):319-361.
[44] Weijers J W H,Schouten S,Schefuß E,et al. Disentangling marine,soil and plant organic carbon contributions to continental margin sediments:a multi-proxy approach in a 20,000 year sediment record from the Congo deep-sea fan[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2009,73(1):119-132. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.10.016
[45] Fry B, Sherr E B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems[M]//Rundel P W, Ehleringer J R, Nagy K A. Stable Isotopes in Ecological Research. New York: Springer, 1989.
[46] Wu W C,Zhao L,Pei Y D,et al. Variability of tetraether lipids in Yellow River-dominated continental margin during the past eight decades:implications for organic matter sources and river channel shifts[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2013,60:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.04.014
[47] Xing L,Zhao M X,Gao W X,et al. Multiple proxy estimates of source and spatial variation in organic matter in surface sediments from the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2014,76:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.07.005
[48] Guo Z G,Li J Y,Feng J L,et al. Compound-specific carbon isotope compositions of individual long-chain n-alkanes in severe Asian dust episodes in the North China coast in 2002[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2006,51(17):2133-2140. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2071-7
[49] 杨 莹,田 军,黄恩清. 末次盛冰期巽他大陆北部草本植被扩张[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(1):85-93.
[50] Xing L,Zhang R P,Liu Y G,et al. Biomarker records of phytoplankton productivity and community structure changes in the Japan Sea over the last 166 kyr[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2011,30(19/20):2666-2675.
[51] Ternois Y,Kawamura K,Keigwin L,et al. A biomarker approach for assessing marine and terrigenous inputs to the sediments of Sea of Okhotsk for the last 27,000 years[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2001,65(5):791-802. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00598-6
[52] 丁喜桂,王吉松,赵广明,等. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地演化过程中的碳埋藏效率及其控制因素[J]. 中国地质,2016,43(1):319-328.
[53] Rieley G,Collier R J,Jones D M,et al. Sources of sedimentary lipids deduced from stable carbon-isotope analyses of individual compounds[J]. Nature,1991,352(6334):425-427. doi: 10.1038/352425a0
[54] Jeng W L,Huh C A. Lipids in suspended matter and sediments from the East China Sea Shelf[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2004,35(5):647-660. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.12.002
[55] Jeng W L,Lin S,Kao S J. Distribution of terrigenous lipids in marine sediments off northeastern Taiwan[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2003,50(6/7):1179-1201.
[56] Jeng W L,Huh C A. A comparison of sedimentary aliphatic hydrocarbon distribution between East China Sea and southern Okinawa Trough[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2008,28(4/5):582-592.
[57] Saito Y,Katayama H,Ikehara K,et al. Transgressive and highstand systems tracts and post-glacial transgression,the East China Sea[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1998,122(1/4):217-232.
[58] 陈珊珊,王中波,陆 凯,等. 东海北部外陆架MIS 6以来的沉积地层格架及古环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(6):124-137.
[59] Chung Y,Chang W C. Pb-210 fluxes and sedimentation rates on the lower continental slope between Taiwan and the South Okinawa Trough[J]. Continental Shelf Research,1995,15(2/3):149-164.
[60] Ikehara K,Satoh M,Yamamoto H. Sedimentation in the Oki Trough,southern Japan Sea,as revealed by high resolution seismic records (3.5 kHz echograms)[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan,1990,96(1):37-49. doi: 10.5575/geosoc.96.37
[61] 王越奇,宋金明,袁华茂,等. 台湾东黑潮主流区近千年来沉积物稀土元素的变化特征与来源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(2):104-113.
[62] Honda M C,Imai K,Nojiri Y,et al. The biological pump in the northwestern North Pacific based on fluxes and major components of particulate matter obtained by sediment-trap experiments (1997-2000)[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2002,49(24/25):5595-5625.
[63] 杨作升,郭志刚,王兆祥,等. 黄、东海水体中的有机包膜及其沉积作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1992(02):222-226,228.
[64] 郭志刚,杨作升,张东奇,等. 冬、夏季东海北部悬浮体分布及海流对悬浮体输运的阻隔作用[J]. 海洋学报,2002,24(5):71-80.
[65] Zhu C,Pan J M,Lu B,et al. Compositional feature of n-alkanes in modern sediment from the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent area and its implication to transport and distribution of organic carbon[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2005,27(4):59-67.
[66] Jiang F Q,Li A C,Li T G. Sediment pathway of the East China Sea inferred from an R-mode factor analysis of surface sediments in the Okinawa Trough[J]. Quaternary International,2011,230(1/2):13-20.
[67] 鲁晓红,陈颖军,黄国培,等. 黄渤海表层沉积物中正构烷烃和甾醇的分布及来源研究[J]. 生态环境学报,2011,20(6):1117-1122.
-




 下载:
下载: