SUBMARINE TOPOGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTARY CHARACTERISTICS OF OFFSHORE WIND FARM IN HEISHAN ISLAND OF SHANDONG
-
摘要:
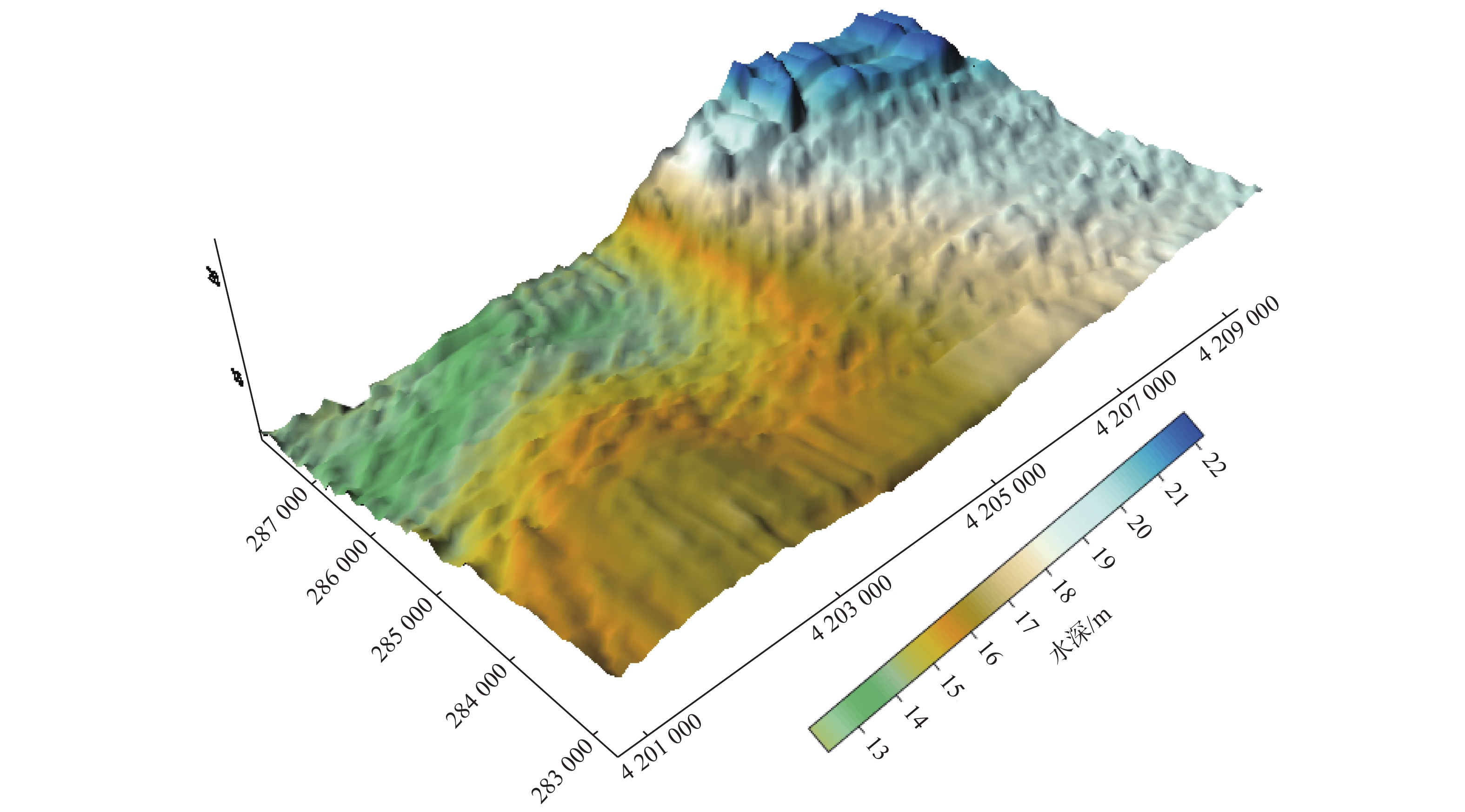
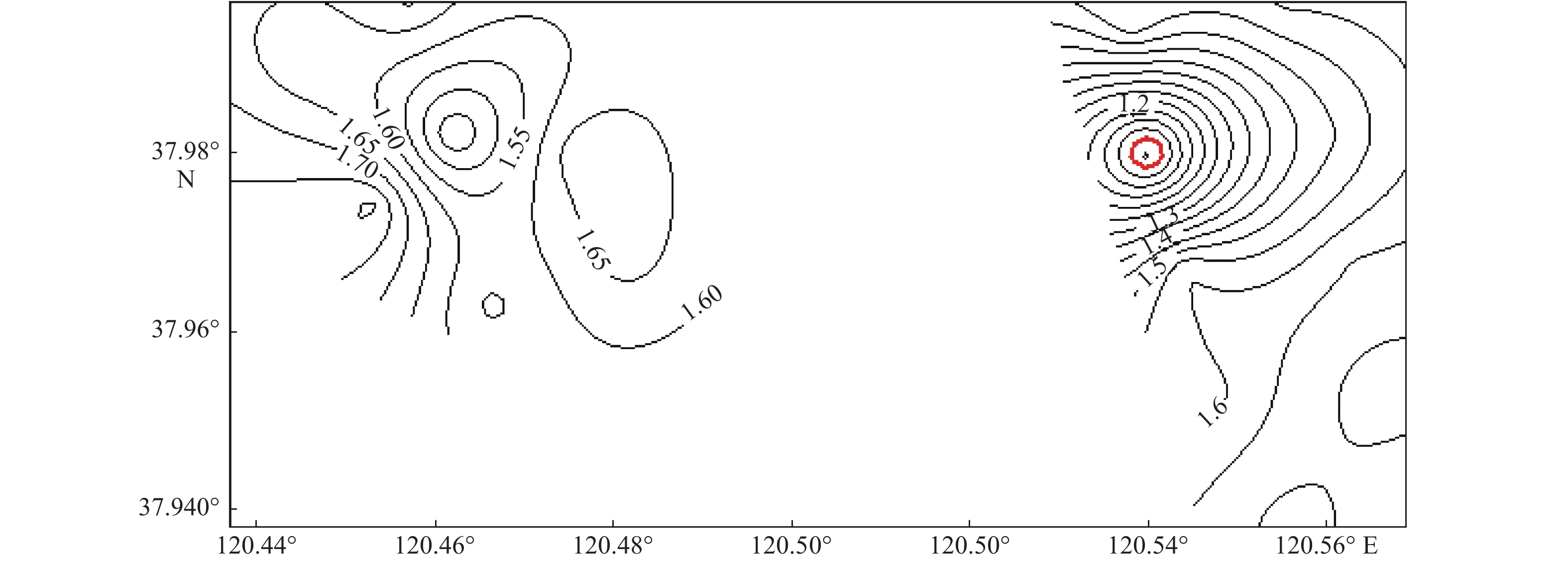
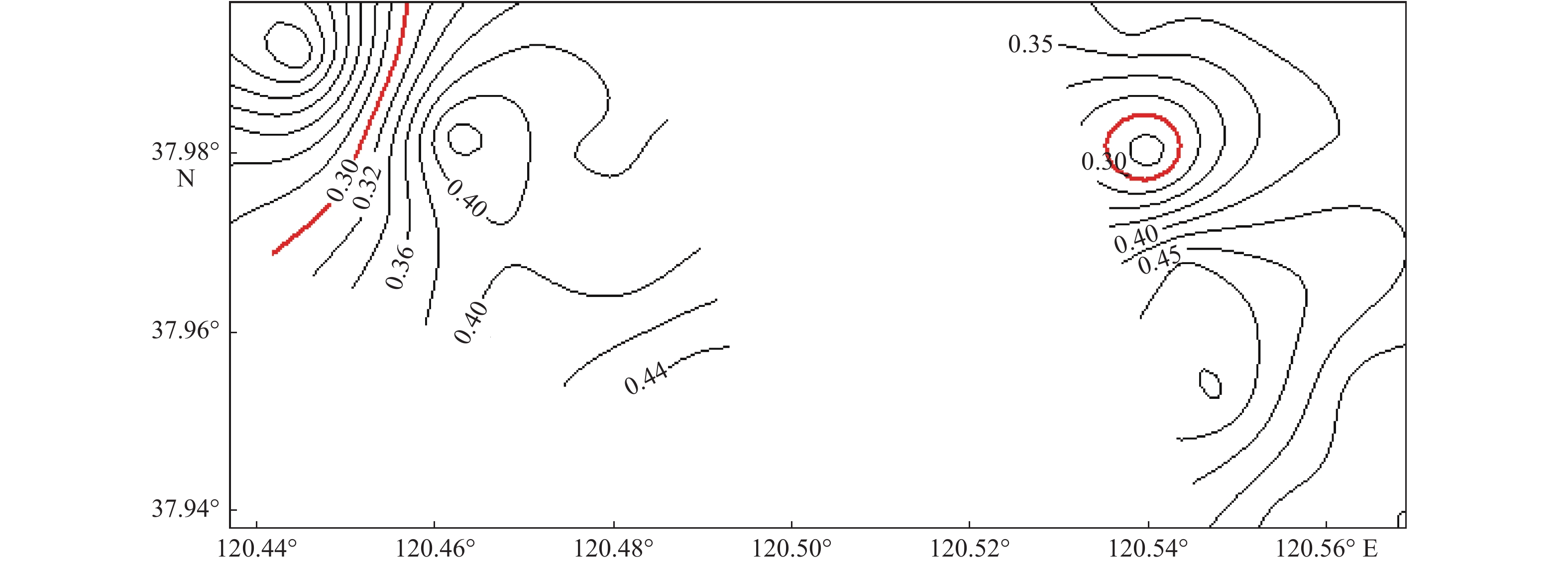
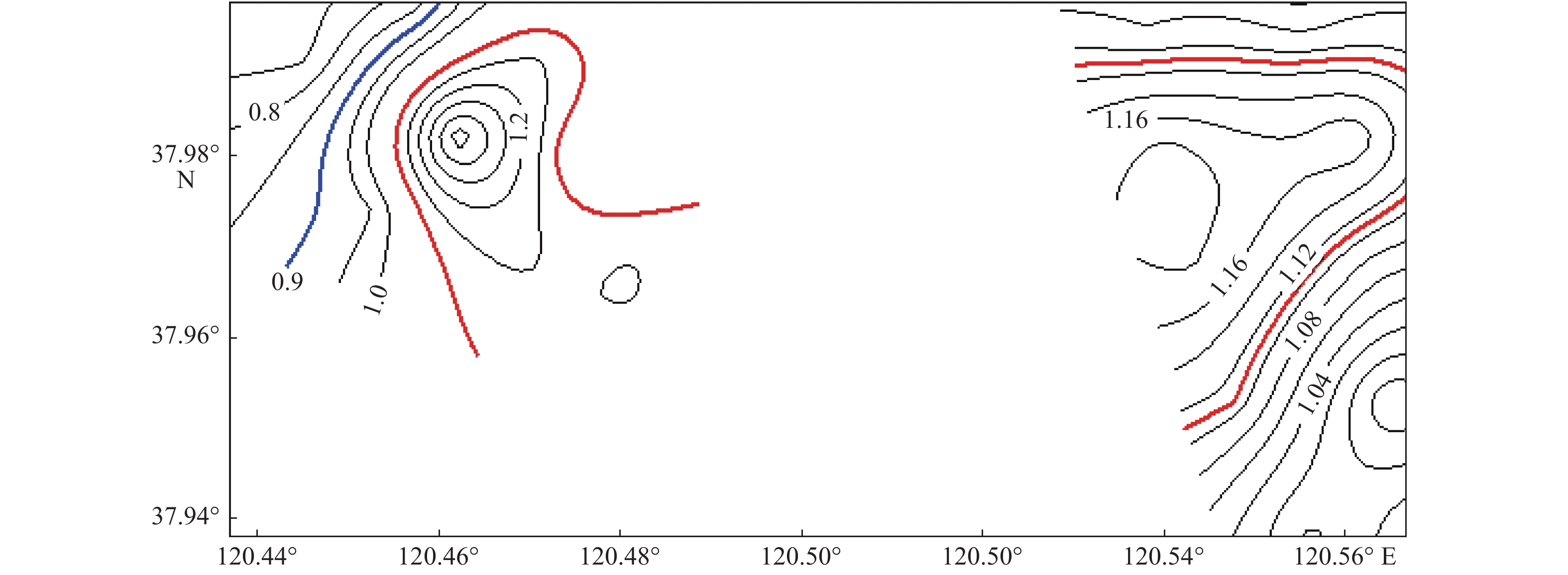
山东海域海上风资源丰富,风电规模化开发条件好。为了解海底地形地貌及沉积物分布特征,以顺利推进近海风电场的开发,选取黑山岛附近海域作为研究对象,在研究海域进行了综合地质地球物理调查。对调查数据的分析表明,研究区域海底地形平缓,整体水体较浅,最浅10 m,最深25 m,平均17.5 m。研究区内沉积物主要呈青灰色、灰色、浅褐色。沉积物类型主要粉砂,粉砂含量均在75%以上,全区分布。沉积物峰态主要表现为平坦、中等、尖锐3种。研究区西区海底表层沉积物分选系数为1.35~1.8,东区海底表层沉积物分选系数为0.9~1.75。整个研究区海域表层沉积物平均粒径在4.3Φ~5.9Φ之间变化,沉积物颗粒较细,以粉砂为主。分析表明,这种地形地貌及沉积物特点反映出研究海域属于离岸海域,水动力作用较弱,适于进行海上风电开发等工程建设。
Abstract:The sea area off the Shandong Peninsula is rich in wind resources and there are excellent conditions for large-scale development of wind energy. In order to understand the topography and sediment distribution patterns of the seabed, so as to promote the development of offshore wind farms smoothly, the sea area near the Heishan island was selected as a case for geological study. An integrated geological and geophysical survey was then undertaking in the selected area. The survey data suggests that the seafloor topography of the study area is rather gentle and the water depth changes from 10 m to 25 m, 17.5 m on average. The sediment in the study area is cyan gray, gray and light brown in color and dominated by silty sand which covers over 75% of the whole area. The kurtosis of the sediment varies from flat to medium to sharp. In the west part of the study area, the sorting of the seafloor sediment changes from 1.35 up to 1.80. while in the east part the sorting of the sea bottom sediment varies from 0.90 to 1.75. The mean grain size of bottom sediments of the whole study area ranges from 4.3Φ to 5.9 Φ and is silt dominated. The topography and sediment characteristics reflect that the study area is an area with weak hydrodynamic effect and therefore suitable for offshore wind power development and other kinds of sub-bottom constructions.
-

-
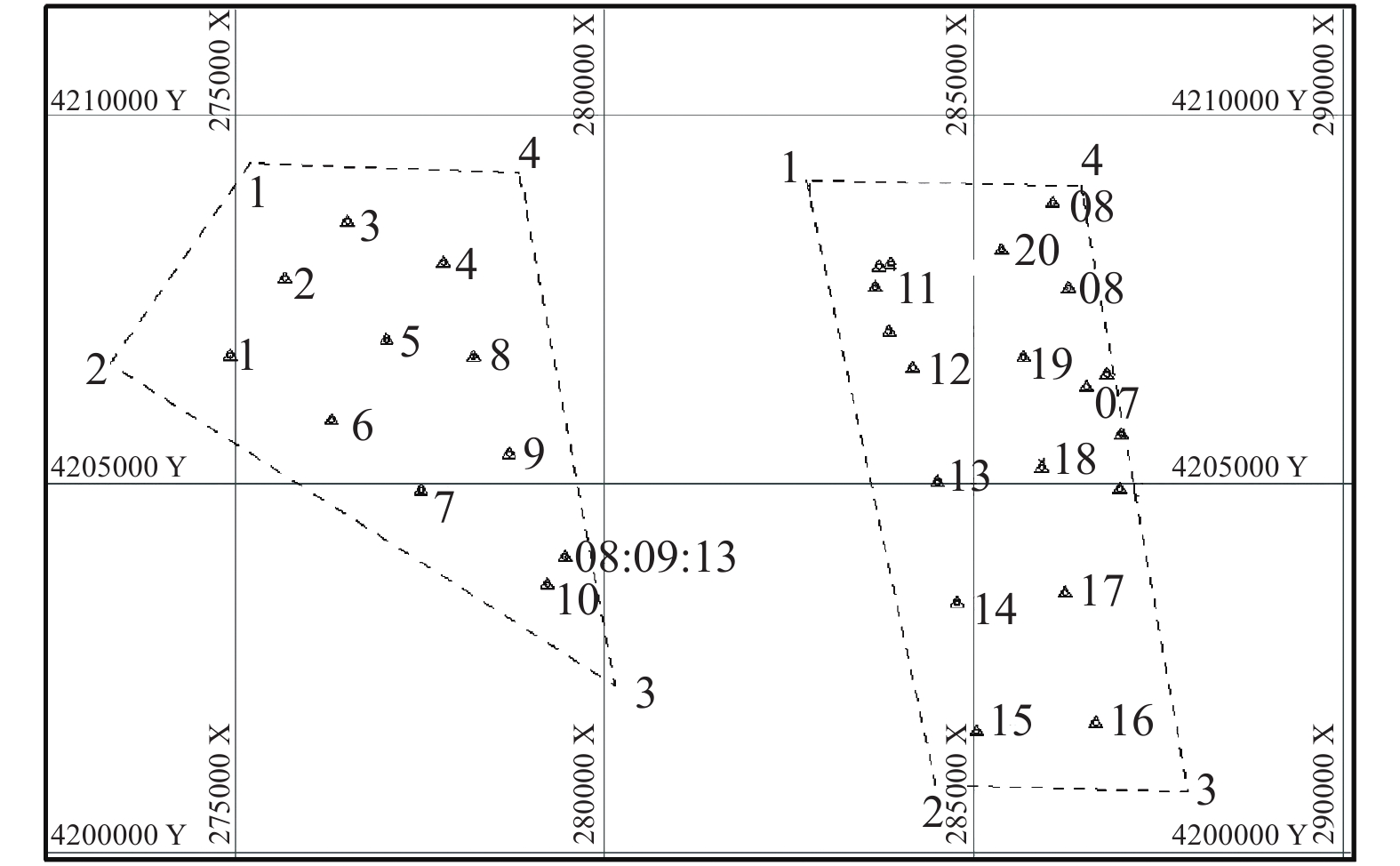
表 1 表层沉积物站位数据表
Table 1. Grain-size analysis data of surface sediment
样品号 位置 水深/m 现场样品简单描述 E-18 120°33.7821′,37°58.1076′ 16.9 青灰色泥 E-19 120°33.6307′,37°58.9138′ 19.2 青灰色泥 E-20 120°33.3053′,37°59.7163′ 20.3 青灰色泥 E-11 120°32.2771′,37°56.6427′ 19.3 青灰色泥 E-12 120°32.4200′,37°58.8020′ 18.3 青灰色泥 E-13 120°32.6652′,37°58.0220′ 16.8 青灰色泥 E-14 120°32.9010′,37°57.2039′ 16.0 青灰色泥 E-17 120°33.8759′,37°57.1794′ 15.3 青灰色泥 E-16 120°34.1631′,37°56.3191′ 14.5 灰色淤泥 E-15 120°33.3567′,37°56.2673′ 15.8 灰色淤泥 W-10 120°29.3701′,37°57.1553′ 17.5 灰色淤泥 W-9 120°28.8818′,37°58.0796′ 17.5 灰色淤泥 W-8 120°28.5575′,37°58.8159′ 17.8 浅褐色泥 W-4 120°28.2711′,37°59.4851′ 18.0 浅褐色泥 W-3 120°27.4069′,37°59.8412′ 18.2 浅褐色泥 W-2 120°26.7031′,37°59.4582′ 18.1 浅褐色泥 W-1 120°26.2132′,37°58.9088′ 17.8 浅褐色泥 W-5 120°27.7114′,37°58.9444′ 17.9 浅褐色泥 W-6 120°27.1874′,37°58.4267′ 17.6 浅褐+深灰色泥 W-7 120°27.9331′,37°57.8077′ 17.3 浅褐色泥 表 2 表层沉积物粒度参数及沉积物类型
Table 2. Grain size parameters and types of surface sediments
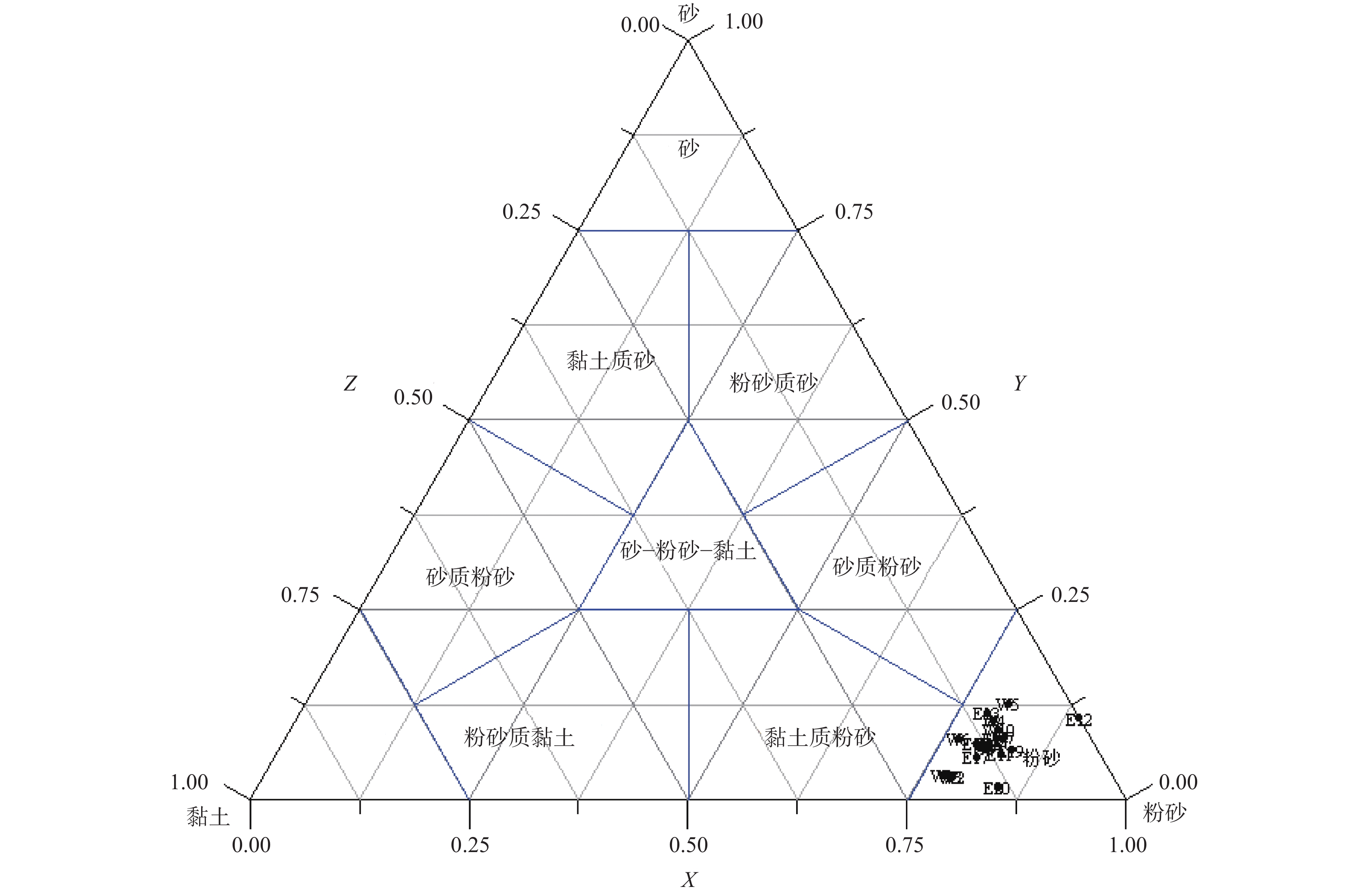
样品号 分选系数(So) 偏态(SKl) 峰态(Kg) 平均粒径/Φ 中值粒径/Φ 命名 W10 1.563 0.460 1.125 4.934 4.482 粉砂 E20 1.600 0.420 1.060 5.479 5.065 粉砂 E19 1.499 0.399 1.174 5.007 4.681 粉砂 E18 1.652 0.445 1.072 5.116 4.656 粉砂 E17 1.721 0.375 0.961 5.374 4.990 粉砂 E16 1.652 0.403 1.047 5.156 4.745 粉砂 E15 1.724 0.379 0.996 5.275 4.863 粉砂 E14 1.590 0.503 1.110 4.974 4.456 粉砂 E13 1.598 0.488 1.178 4.878 4.372 粉砂 E12 0.918 0.249 1.191 4.361 4.218 粉砂 E11 1.581 0.410 1.081 5.138 4.764 粉砂 W1 1.729 0.250 0.808 5.864 5.700 粉砂 W2 1.601 0.141 0.738 5.896 5.875 粉砂 W3 1.711 0.302 0.817 5.801 5.583 粉砂 W4 1.567 0.384 1.151 4.955 4.597 粉砂 W5 1.398 0.431 1.387 4.641 4.304 粉砂 W6 1.812 0.322 0.952 5.411 5.048 粉砂 W7 1.538 0.403 1.132 4.980 4.618 粉砂 W8 1.689 0.378 1.015 5.256 4.866 粉砂 W9 1.673 0.383 1.153 5.213 4.826 粉砂 表 3 表层沉积物各粒级百分含量
Table 3. Percentage contents of the surface sediments
/% 样品号 粗砂 中砂 细砂 粗粉砂 细粉砂 粗黏土 细黏土 W10 0.00 0.00 9.14 61.78 19.07 8.46 1.56 E20 0.00 0.00 1.53 56.31 28.20 11.54 2.42 E19 0.00 0.00 6.51 65.06 18.52 8.25 1.67 E18 0.00 0.00 7.40 60.68 20.01 9.72 2.20 E17 0.00 0.00 5.63 55.30 24.79 11.56 2.72 E16 0.00 0.00 7.48 59.02 21.60 9.73 2.18 E15 0.00 0.00 7.37 55.90 23.34 11.06 2.33 E14 0.00 0.00 8.01 62.92 18.25 9.17 1.66 E13 0.00 0.00 11.42 61.31 17.09 8.55 1.63 E12 0.00 0.00 10.72 78.85 10.42 0.00 0.00 E11 0.00 0.00 5.95 62.48 20.24 9.36 1.97 W1 0.00 0.00 3.24 42.61 34.78 15.63 3.74 W2 0.00 0.00 2.99 38.67 40.05 16.75 1.54 W3 0.00 0.00 3.10 45.26 33.02 14.81 3.82 W4 0.00 0.00 10.35 60.58 19.15 8.31 1.61 W5 0.00 0.00 12.57 66.68 13.63 6.25 0.88 W6 0.00 0.00 7.98 50.80 25.96 12.33 2.92 W7 0.00 0.00 8.21 62.26 19.62 8.23 1.68 W8 0.00 0.00 6.87 57.26 23.07 10.39 2.41 W9 0.00 0.00 7.16 58.46 22.03 10.02 2.33 -
[1] 孙 雷,汪 锋,张 雯,等. 海上风电运维:从近海走向深远海域[J]. 太阳能,2018(6):6-10.
[2] 杨红生,茹小尚,张立斌,等. 海洋牧场与海上风电融合发展:理念与展望[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2019,34(6):700-707.
[3] 曾 亮,储韬玉,王占华,等. 海上风电勘测中的物探技术[J]. 工程勘察,2019,47(7):66-72.
[4] 高 抒,Collins M. 沉积物粒径趋势与海洋沉积动力学[J]. 中国科学基金,1998,12(4):241-246.
[5] Ashley G M. Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms:a new look at an old problem[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1990,60(1):160-172. doi: 10.2110/jsr.60.160
[6] 林纪江,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 潮流作用下蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙的时空分布及变化特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2017,33(12):13-23.
[7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.
[8] McLaren P. An interpretation of trends in grain size measurements[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1981,51:611-624.
[9] Livingstone I,Wiggs G F S,Weaver C M. Geomorphology of desert sand dunes:a review of recent progress[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2007,80(3/4):239-257.
[10] 左书华,韩志远,许 婷. 烟台套子湾海域表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其动力响应[J]. 泥沙研究,2013(5):41-46.
[11] 陈燕萍,李 琰. 舟山DZ-1钻孔沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境辨别[J]. 海洋学研究,2018,36(4):53-59.
[12] 刘春秀. 烟台近海海底表层沉积物粒度分布特征[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2010.
[13] Doeglas D J. Loess deposits of Mississippi. Krinitzsky E L,Turnbull W J.1967. Geological Society of America,Boulder,Colo. (Special Paper 94),64 pp.,U.S. $3.50[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,1968,4:71.
[14] 汤世凯,于剑峰,李金鹏,等. 烟台芝罘湾底质沉积物粒度特征和沉积动力环境研究[J]. 山东国土资源,2020,36(1):22-28.
[15] 贾海林,刘苍字,杨 欧. 长江口北支沉积动力环境分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版),2001,1(1):90-96.
[16] 韦钦胜,于志刚,冉祥滨,等. 黄海西部沿岸流系特征分析及其对物质输运的影响[J]. 地球科学进展,2011,26(2):145-156.
[17] 张秀芝, 朱 蓉. 中国近海风电场开发指南[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2010: 60-61.
[18] 张 伟. 渤海海峡南部海域地貌特征及控制因素研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[19] Pejrup M. The triangular diagram used for classification of estuarine sediments: a new approach[M]//de Boer P L, van Gelder A, Nio S D. Tide-Influenced Sedimentary Environments and Facies. Netherlands: D. Reidel Publishing, 1988: 289-300.
-



 下载:
下载: