Seasonal variation of radionuclides in surface sediments off the east coast of Shandong Peninsula and its environmental implications
-
摘要:
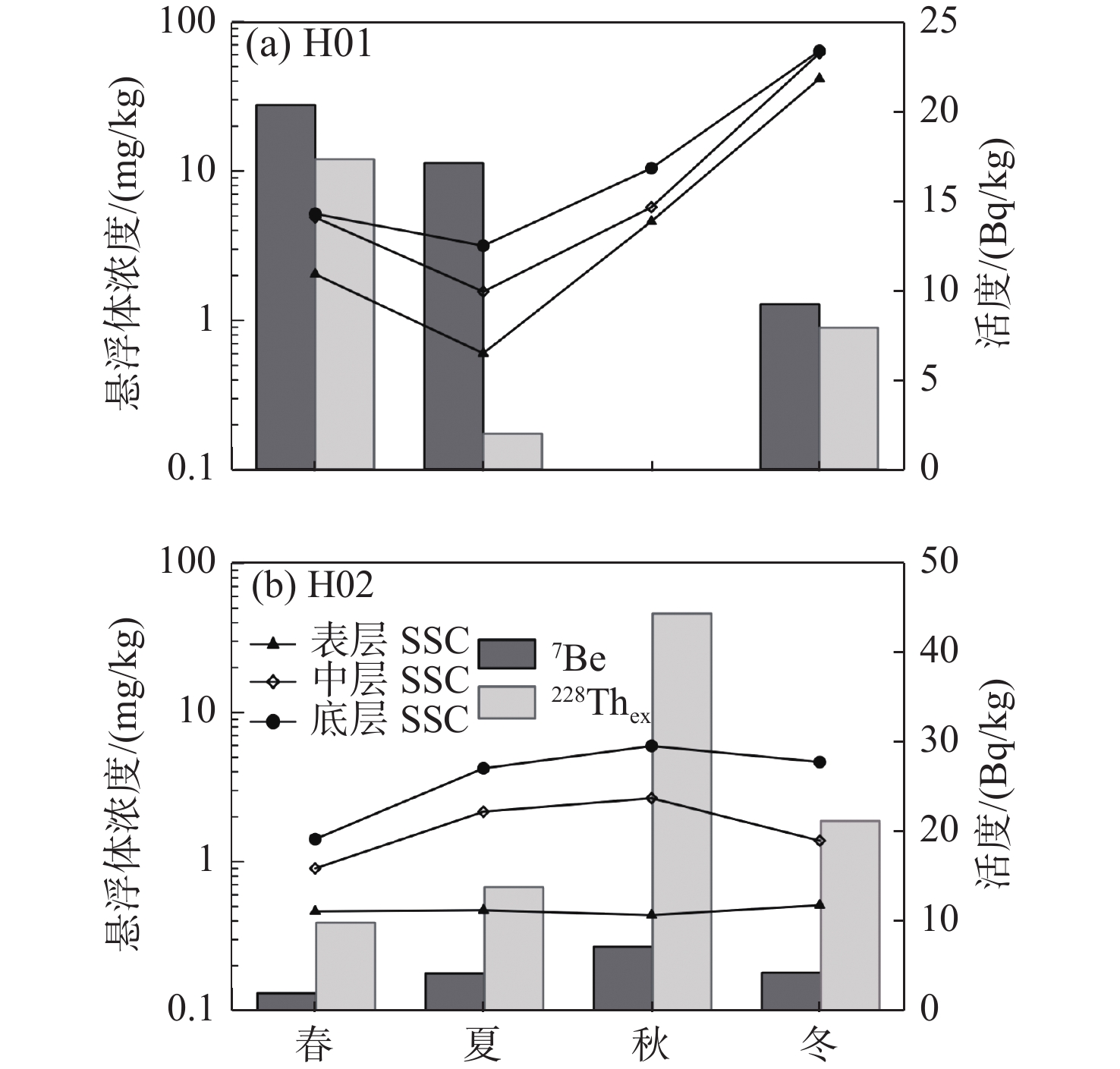
基于2019年4月、7月、10月、12月渤黄海共享航次取得山东半岛东部近岸H01和H02站位多个季节沉积物样品,通过低本底γ能谱仪分析得到其表层沉积物放射性核素7Be、210Pbex、228Thex和 137Cs活度数据。结果表明,短半衰期核素7Be、228Thex与长半衰期核素210Pbex、137Cs在同一站位的季节分布存在差异,同一核素在H01和H02站位的季节分布也存在差异;H01站位的7Be和228Thex,H02站位的210Pbex和137Cs,受表层沉积物粒度影响较不明显,7Be和228Thex的季节变化受悬浮物质的输运和沉降的影响显著,而210Pbex和137Cs更多指示的是环流作用下的沉积物再分配;与H02相比,H01站位表层沉积物核素变化受大气沉降影响较低。H01和H02站位分别位于“Ω”形泥质体顶部和东部边缘,其物源和沉积动力环境存在差异,放射性核素7Be、210Pbex、228Thex和137Cs在示踪物质输运和沉降过程中具有重要意义。
Abstract:Surface sediment samples were collected off the east coast of Shandong Peninsula in April, July, October and December of 2019 respectively. Radionuclides 7Be, 210Pbex, 228Thex and 137Cs of the surface sediments are analysed and discussed for different seasons. The results suggest that the seasonal distributions of 7Be and 228Thex are different from 210Pbex and 137Cs at same station, and the seasonal distribution of the same radionuclide vary from station to station. The variations of radionuclides seem to have nothing to do with the grain size of surface sediments. The seasonal variations of 7Be and 228Thex are significantly affected by the transport and settlement of suspended matter, while 210Pbex and 137Cs are more closely related to sediment redistribution. Comparing to the station H02, the changes of radionuclides in surface sediments at the station H01 are less affected by atmospheric sedimentation. H01 and H02 are located in different parts of the omega-shaped (Ω) mud deposits, owing to different sediment sources and dynamic environments. The study results further confirm that 7Be、210Pbex、228Thex and 137Cs are good tracers for illustrating sediment transport and deposition.
-

-
图 6 青岛地区7Be日均大气沉降通量和月降雨量[46]
Figure 6.
图 9 中国东部陆架海冬季与夏季环流示意图[30]
Figure 9.
图 10 表层沉积物7Be/210Pbex活度比值季节变化和上海、厦门和青岛大气沉降7Be/210Pbex活度比值变化[44]
Figure 10.
表 1 表层沉积物采样站位
Table 1. Location of surface sediment sampling stations
季节 站位 采样日期 E/(°) N/(°) 水深/m 春 H01 2019-04-29 123.01 37.00 29.4 春 H02 2019-04-29 123.50 37.02 72.9 夏 H01 2019-07-27 123.00 37.00 28.0 夏 H02 2019-07-27 123.50 37.00 73.0 秋 H02 2019-10-12 123.51 37.00 73.0 冬 H01 2019-12-18 123.01 37.00 30.4 冬 H02 2019-12-18 123.50 37.00 72.7 -
[1] SYVITSKI J P M,SAITO Y. Morphodynamics of deltas under the influence of humans[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2007,57(3/4):261-282.
[2] LIU J P,LI A C,XU K H,et al. Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2006,26(17-18):2141-2156. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013
[3] KUEHL S A,DEMASTER D J,NITTROUER C A. Nature of sediment accumulation on the Amazon continental shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research,1986,a,6(1/2):209-225.
[4] KUEHL S A,NITTROUER C A,DEMASTER D J. Distribution of sedimentary structures in the Amazon subaqueous delta[J]. Continental Shelf Research,1986,b,6(1/2):311-336.
[5] NITTROUER C A,KUEHL S A,DEMASTER D J,et al. The deltaic nature of Amazon shelf sedimentation[J]. GSA Bulletin,1986,97(4):444-458. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1986)97<444:TDNOAS>2.0.CO;2
[6] CATTANEO A,CORREGGIARI A,LANGONE L,et al. The late-Holocene Gargano subaqueous delta,Adriatic shelf:sediment pathways and supply fluctuations[J]. Marine Geology,2003,193(1):61-91.
[7] CATTANEO A,TRINCARDI F,LANGONE L,et al. Clinoform Generation on Mediterranean Margins[J]. Oceanography,2004,17(4):104-117. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2004.08
[8] NIEDORODA A W,REED C W,DAS H,et al. Analyses of a large-scale depositional clinoformal wedge along the Italian Adriatic coast[J]. Marine Geology,2005:179-192.
[9] LIU J P,XUE Z,ROSS K,et al. Fate of sediments delivered to the sea by Asian large rivers:long-distance transport and formation of remote alongshore clinothems[J]. The Sedimentary Record,2009,7(4):4-9. doi: 10.2110/sedred.2009.4.4
[10] 藏政晨. 黄海水体温盐结构的季节性变化对悬浮体分布的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.
[11] YANG Z S,LIU J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,240(1/4):169-176.
[12] 吴梅桂. 多核素在长江口崇明东滩表层沉积物的分布及其环境指示意义[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2011.
[13] 吴梅桂,杜金洲,张敬,等. 210Pb、228Th、7Be和137Cs在崇明东滩表层沉积物的季节性特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 海洋环境科学,2011,30(6):792-797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2011.06.008
[14] 姜亦飞. 多核素示踪近代环境演变在河口沉积物中的记录[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012.
[15] 姜亦飞,杜金洲,张敬,等. 长江口崇明东滩不同植被带沉积速率研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2012,34(2):114-121.
[16] WOODRUFF J D,GEYER W R,SOMMERFIELD C K,et al. Seasonal variation of sediment deposition in the Hudson River estuary[J]. Marine Geology,2001,179(1/2):105-119.
[17] DONG L X,GUAN W B,CHEN Q,et al. Sediment transport in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2011,93(3):248-258. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.04.003
[18] 王安国,张训华,李广雪,等. 山东半岛近岸海区全新世泥质沉积体研究现状[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(10):52-58.
[19] 程鹏,高抒,刘敬圃,等. 北黄海西部全新统分布的初步认识[J]. 第四纪研究,2001,21(4):379-379. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.04.013
[20] 刘欣,高抒. 北黄海西部晚第四纪浅层地震剖面层序分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2005,25(3):61-68.
[21] LIU J,SAITO Y,WANG H,et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Penisula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,236(3/4):165-187.
[22] 刘健,王红,李绍全,等. 南黄海北部泥质沉积区冰后期海侵沉积记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004,24(3):1-10.
[23] 刘健,朱日祥,李绍全,等. 南黄海东南部冰后期泥质沉积物中磁性矿物的成岩变化及其对环境变化的响应[J]. 中国科学(D辑): 地球科学,2003,33(6):583-592.
[24] ALEXANDER C R,DEMASTER D J,NITTROUER C A. Sediment accumulation in a modern epicontinental-shelf setting:the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1991,98(1):51-72. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90035-3
[25] 李凤业,高抒,贾建军,等. 黄、渤海泥质沉积区现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2002,33(4):364-369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004
[26] 李军,胡邦琦,李国刚,等. 山东半岛近海不同粉砂粒级含量分布的空间差异性及其沉积学意义[J]. 海洋学报,2017,39(1):64-75.
[27] 边昌伟. 中国近岸泥沙在渤海、黄海和东海的输运[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
[28] BIAN C W,JIANG W S,RICHARD J,et al. The suspended sediment concentration distribution in the Bohai Sea,Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2013,12(3):345-354. doi: 10.1007/s11802-013-1916-3
[29] ZENG X M,HE R Y,XUE Z,et al. River-derived sediment suspension and transport in the Bohai,Yellow,and East China Seas:a preliminary modeling study[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2015,111:112-125. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.08.015
[30] 苏纪兰. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005.
[31] 肖合辉. 渤黄海海域悬浮体分布: 季节性变化及扩散通量[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[32] 余佳. 黄海悬浮体分布及季节性变化[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
[33] 杨作升,高文兵. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报,1992,14(2):81-90.
[34] 王勇智,乔璐璐,杨作升,等. 夏、冬季山东半岛东北部沿岸悬浮物输送机制的初步研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2012(5):49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.05.008
[35] 王勇智,乔璐璐,杨作升,等. 近岸强海流切变锋作用下悬浮沉积物的输送和沉积:以山东半岛东端外海为例[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(3):486-496.
[36] 王爱美. 黄海中部泥质沉积区温度锋面及层化的时空变化及其沉积效应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2019.
[37] WANG A,RALSTON D K,BI N,et al. Seasonal variation in sediment transport and deposition on a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2019:37-51.
[38] 范德江,杨作升,郭志刚. 中国陆架210Pb测年应用现状与思考[J]. 地球科学进展,2000,15(3):297-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011
[39] SAGAR P, GOEL P S. Cosmogenic and bomb-produced 7Be in stratospheric air[C]// Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1980, 89(2): 133-136.
[40] SILKER W B. Beryllium-7 and fission products in the Geosecs II water column and applications of their oceanic distributions[J]. Earth & Planetary ence Letters,1972,16(1):131-137.
[41] YOUNG J A,SILKER W B. Aerosol deposition velocities on the Pacific and Atlantic oceans calculated from 7Be measurements[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters,1980,50(1):92-104.
[42] 朱厚玲,汤洁,郑向东. 天然放射性核素铍-7和铅-210在大气示踪研究中的应用[J]. 气象科技,2003(3):131-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2003.03.001
[43] 贾成霞,刘广山,杨伟锋,等. 厦门地区7Be和210Pb的大气沉降通量[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2003, 42(3):352-357.
[44] DU J Z,ZHANG J,WU Y F. Deposition patterns of atmospheric 7Be and 210Pb in coast of East China Sea,Shanghai,China[J]. Atmospheric Environment,2008,42(20):5101-5109. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.02.007
[45] 宋为娟,孔然,周立旻,等. 上海市大气降水中^(210)Pb、~7Be的变化特征[J]. 城市环境与城市生态,2014,27(2):1-4.
[46] 易勇. 胶州湾沉积物放射性核素和矿物地球化学[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2006.
[47] 门武,刘广山,陈志刚,等. 镭同位素在海洋学研究中的应用及进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2010,25(1):33-42.
[48] COCHRAN J K. The oceanic chemistry of the U- and Th-series nuclides in the oceans[M]//IVANOVICH M, HARMON R S, eds. Uranium series disequilibrium: applications to environmental problems. Oxford Clarendon Press, 1982: 384-430.
[49] 黄德坤. 基于核素示踪的长江口、东海和海南东部近海泥沙的沉降过程[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012.
[50] 齐君,李凤业,宋金明. 黄海和渤海沉积物210Pb活度的分布特征[J]. 地球化学,2005,34(4):351-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.04.005
[51] ZHANG F L,WANG J L,LIU D T,et al. Distribution of 137Cs in the Bohai Sea,Yellow Sea and East China Sea:sources,budgets and environmental implications[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,672:1004-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.001
[52] JOSEPH M S,DEMASTER D J,STEVEN A K,et al. The behavior of particle-reactive tracers in a high turbidity environment:234Th and 210Pb on the Amazon continental shelf[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1996,60(12):2123-2137. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00092-0
[53] FENG H,COCHRAN J K,HIRSCHBERG D J. 234Th and 7Be as tracers for the transport and dynamics of suspended particles in a partially mixed estuary[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1999,63(17):2487-2505. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00060-5
[54] WILSON C G,MATISOFF G,WHITING P J. The use of 7Be and 210Pbxs to differentiate fine suspended sediment sources in South Slough,Oregon[J]. Estuaries and Coasts,2007,30(2):348-358. doi: 10.1007/BF02700177
[55] DU J,DU J Z,HUANG D K,et al. Seasonal distribution patterns of 7Be and 210Pb in surface sediments in the Changjiang Estuary,China and their implication[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2016(154):41-49.
[56] 赵胜,于非,刁新源,等. 黄海暖流的路径及机制研究[J]. 海洋科学,2011,35(11):73-80.
[57] 臧家业,汤毓祥,邹娥梅,等. 黄海环流的分析[J]. 科学通报,2001,46(S1):7.
[58] 王辉武,于非,吕连港,等. 冬季黄海暖流区的空间变化和年际变化特征[J]. 海洋科学进展,2009,27(2):140-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.003
[59] 宋新,林霄沛,王悦. 冬季黄海暖流变化及其原因浅析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2009(S1):259-266.
-




 下载:
下载: