Distribution pattern and influence factors of benthic foraminifera in the surface sediments of northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
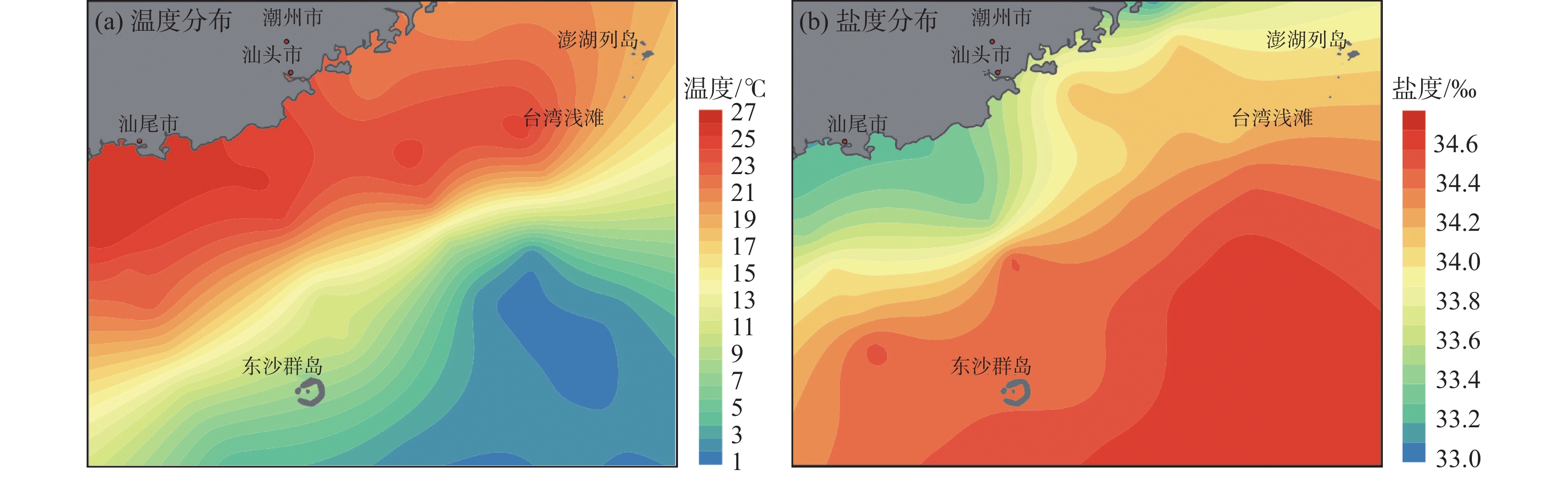
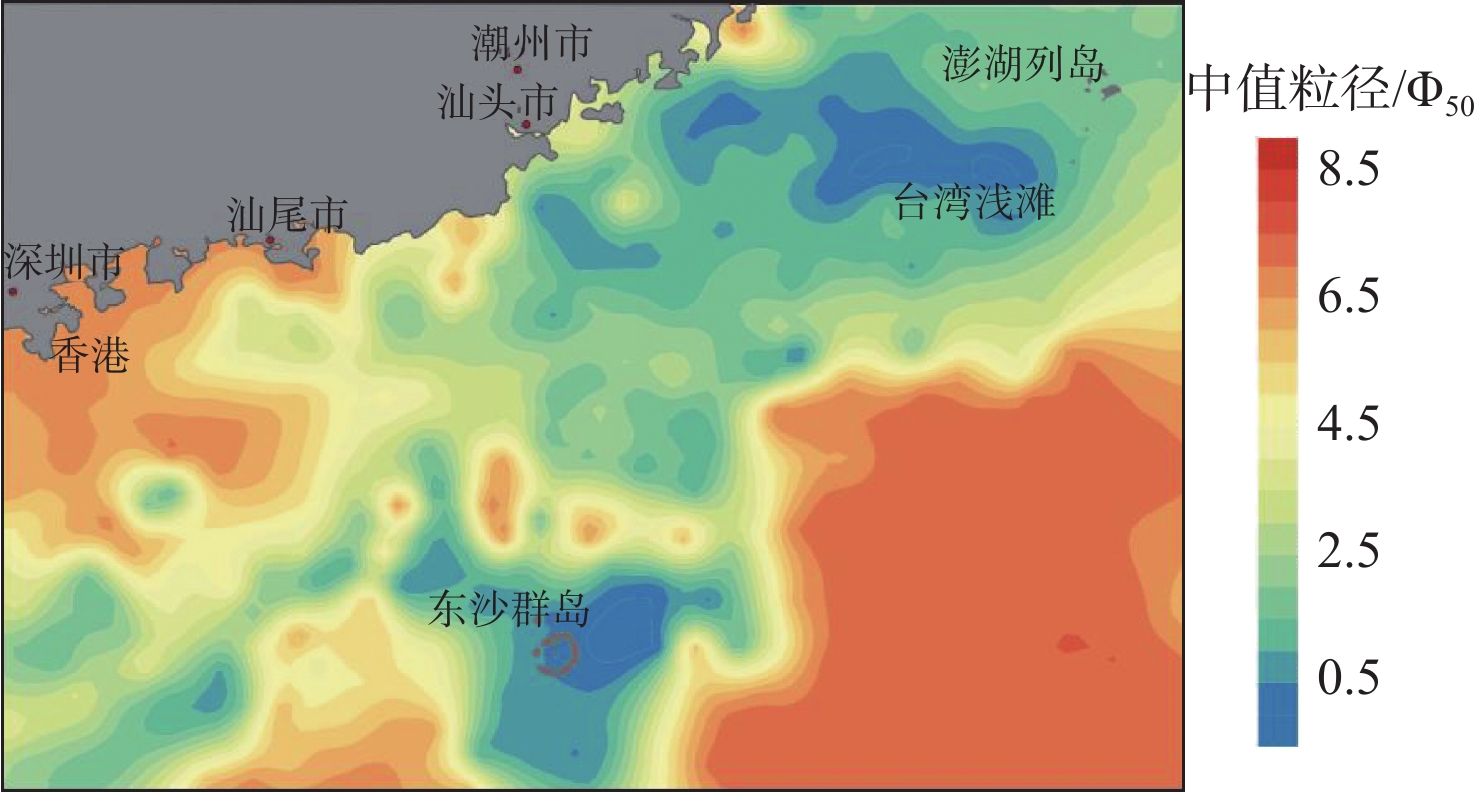
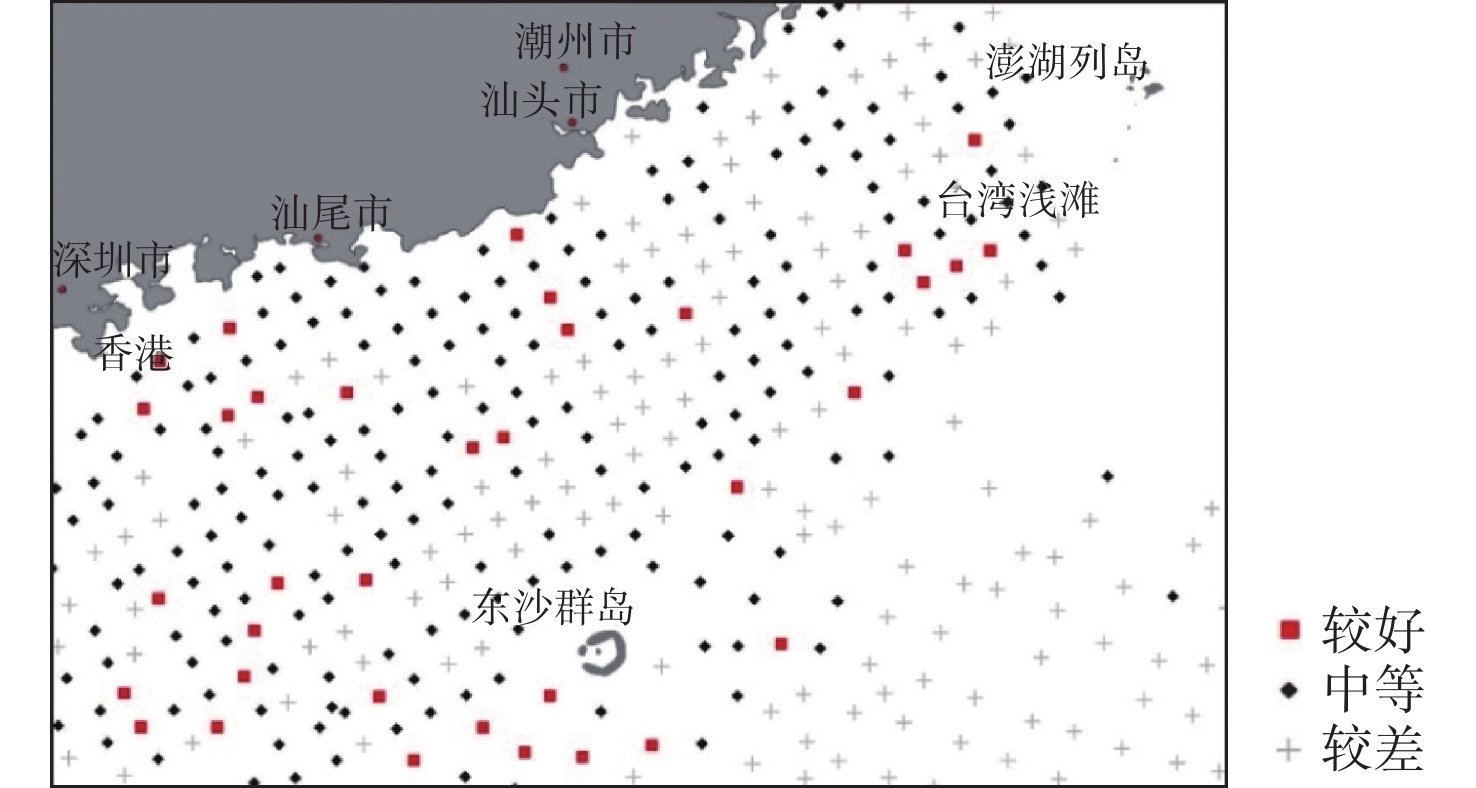
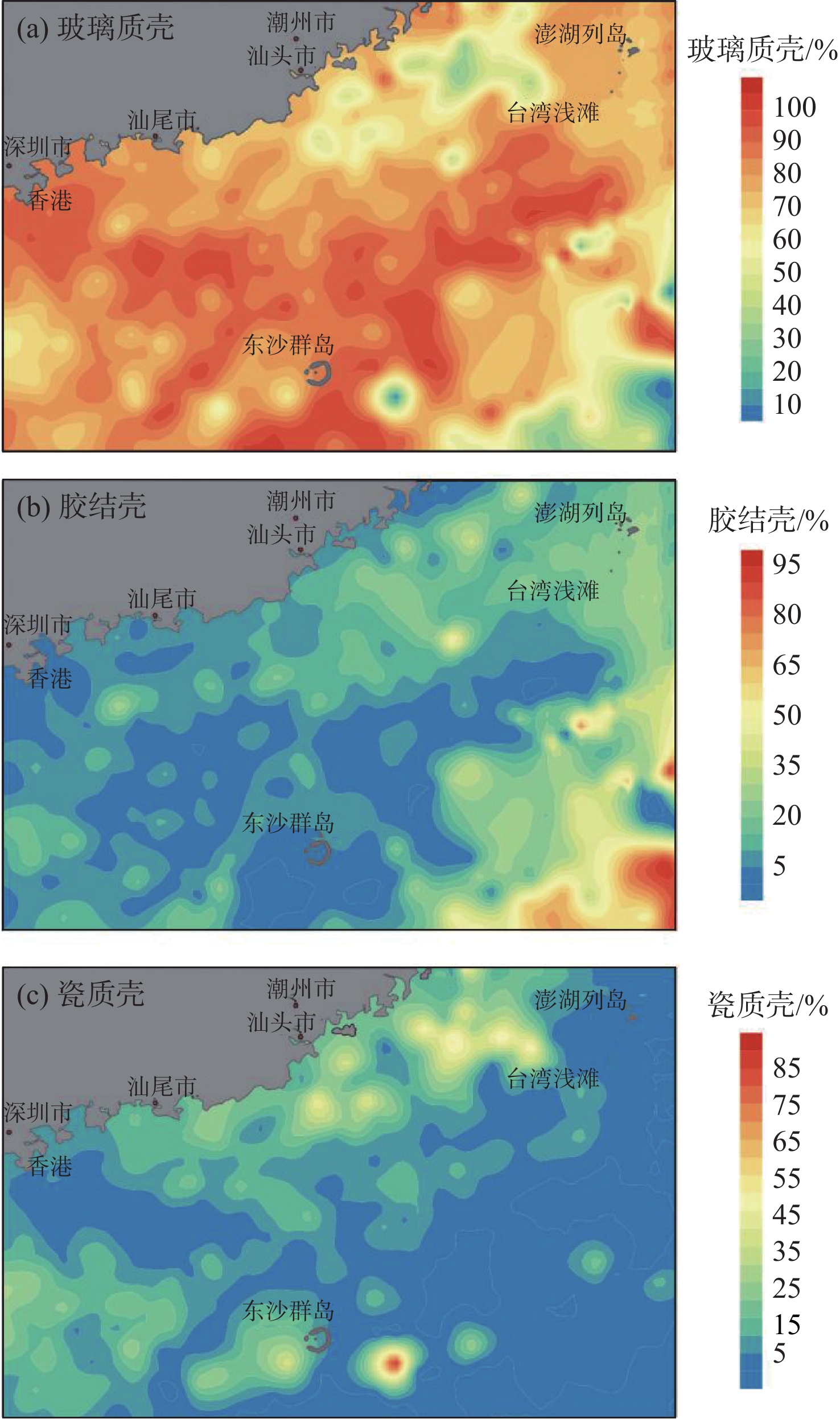
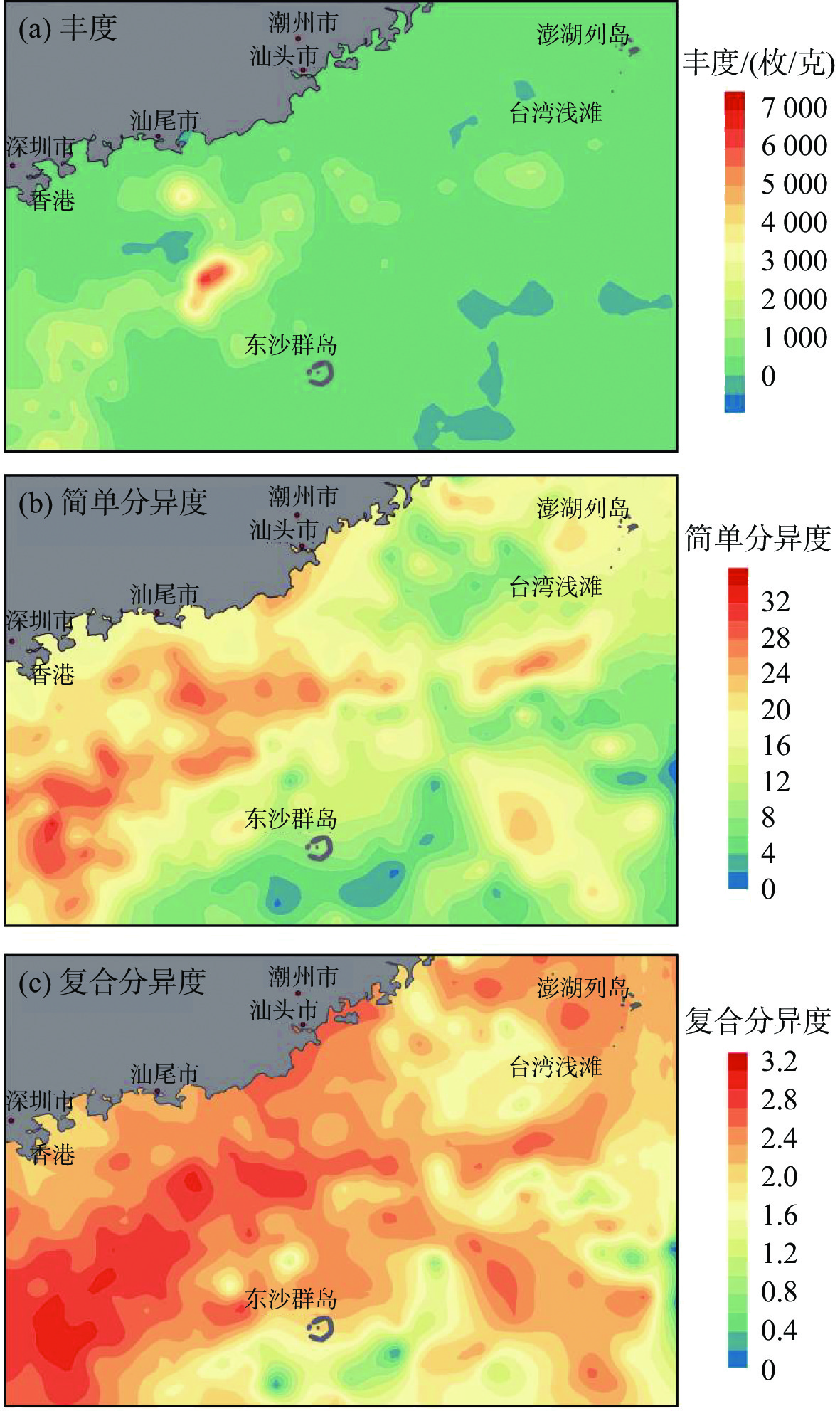
有孔虫在海洋环境指示方面具有重要意义,对现代环境中有孔虫的分布及影响因素进行研究有助于利用有孔虫对地质历史时期的沉积环境进行还原。我国南海海域辽阔,南海有孔虫的相关研究很早便有报道。对我国南海北部海域表层沉积物中的底栖有孔虫分布特征进行了描述,研究区以玻璃质壳底栖有孔虫占主导,胶结壳其次,瓷质壳最少。根据底栖有孔虫的分布特征划分了4个底栖有孔虫组合,组合1为Heterolepa subpraecincta - Hanzawaia mantaensis - Rotalinoides gaimardii;组合2为Bulimina marginate - Lagena substriata;组合3为Elphidium advenum - Pararotalia nipponica;组合4 为Recurvoides contortus - Ammodisus cretaceous - Bulimina aculeata。对影响该区域底栖有孔虫分布的环境因素进行了探究,结果表明,温度、盐度、底质类型等对底栖有孔虫的分布均存在一定程度的影响,海流对研究区底栖有孔虫时空分布的影响值得进一步探究。
Abstract:Foraminifera is an important and sensitive environment indicator. To study the distribution pattern and influencing factors of the foraminifera in the modern environment is the key to the reconstruction of sedimentary environment in the past. South China Sea covers a vast area, researches on the modern foraminifera in that part of the South China Sea have been reported since a long time. Recently, more and more researches have been devoted to the change of foraminifera and its relation to the methane leakage in the South China Sea. However, few studies have been donated to the distribution of foraminifera in the modern environment of northern South China Sea. In this study, we carefully described the distribution pattern of benthic foraminifera in the northern part of the South China Sea and discussed the factors affecting their distribution pattern. In the study area, the calcareous hyaline benthic foraminifera dominate, followed by the agglutinated benthic foraminifera and the calcareous porcelaneous benthic foraminifera. Four benthic foraminifera assemblages are recognized according to their distribution patterns, namely the assemblage 1: Heterolepa subpraecincta-Hanzawaia mantaensis- Rotalinoides gaimardii; the assemblage 2: Bulimina marginata-Lagena substriata; the assemblage 3: Elphidium advenum-Pararotalia nipponica; and the assemblage 4: Recurvoides contortus-Ammodisus cretaceous-Bulimina aculeata. Environmental factors, such as temperature, salinity, and substrate type in the northern part of the South China Sea all have influences on the distribution of benthic foraminifera to certain extent, and the influence of oceanic currents on the spatial and temporal distribution of benthic foraminifera deserves further investigation.
-
Key words:
- northern South China Sea /
- surface sediment /
- benthic foraminifera /
- marine environment
-

-
图 1 南海北部海域采样站位图 [27]
Figure 1.
-
[1] 汪品先, 章纪军, 赵泉鸿, 等. 东海底质中的有孔虫和介形虫[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988: 1-438.
[2] 张江勇,汪品先. 深海研究中的底栖有孔虫:回顾与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(4):545-551. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.009
[3] MIAO Q M,THUNELL R C. Late Pleistocene-Holcene distribution of deep-sea benthic foraminifera in the South China Sea and Sulu sea:paleoceanography implications[J]. Journal of Foraminifera Research,1996,26(1):9-23. doi: 10.2113/gsjfr.26.1.9
[4] WEI G J, HUANG C Y, WANG C C, et al. High-resolution benthic foraminifer δ13C records in the South China Sea during the last 150ka[J]. 2006, 232(3/4): 227-235.
[5] WEI G J,ZOU L,DENG W F,et al. Mn/Ca ratio in planktonic foraminifer from ODP Site 1144,the northern South China Sea:a possible paleoclimate indicator[J]. Geochemical Journal,2011,43(4):235-246.
[6] JIAN Z M, WANG L J, KIENAST M, et al. Benthic foraminiferal paleoceanography of the South China Sea over the last 40, 000 years[J]. 1999, 156(1/4): 159-186.
[7] WANG P X,LI Q Y,TIAN J,et al. Monsoon influence on planktic δ18O records from the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,142:26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.04.009
[8] 钮耀诚,张译元,杜江辉,等. 南海西部MIS 3期底栖有孔虫反映的生产力变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(1):85-92.
[9] 梁静之,黄宝琦,董轶婷,等. 南海北部MD12-3432站MIS11期以来底栖有孔虫反映的古环境变化[J]. 地学前缘,2016(4):292-300.
[10] 许慎栋,陈文煌,邓文峰,等. 南海北部沉积物中浮游有孔虫Globigerinoides ruber壳体氧同位素指示的冬季表层海水温度[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(2):101-107.
[11] 潘梦迪,邬黛黛,吴能友,等. 南海北部神狐海域晚末次冰期以来有孔虫特征及其对古海洋环境的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(2):127-138.
[12] YIN J,LIU C L,ZHANG J P,et al. Distribution and constraining factors of planktonic and benthic foraminifers in bottom sediments of the southern South China Sea[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2018,502:130-146.
[13] WANG P X,LI Q Y,TIAN J. Pleistocene paleoceanography of the South China Sea:progress over the past 20 years[J]. Marine Geology,2014,352:381-396. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.003
[14] 陈芳,苏新,陆红锋,等. 南海北部浅表层沉积底栖有孔虫碳同位素及其对富甲烷环境的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(4):1-7.
[15] 曹超,雷怀彦. 南海北部有孔虫碳氧同位素特征与晚第四纪水合物分解的响应关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2012,42(1):162-171.
[16] 庄畅,陈芳,程思海,等. 南海北部天然气水合物远景区末次冰期以来底栖有孔虫稳定同位素特征及其影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究,2015,35(2):422-432. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.17
[17] 庄畅,陈芳,程思海,等. 南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物分解释放成因的有孔虫碳同位素轻值事件[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2016,46(10):1334-1348.
[18] WALLER H O. Foraminiferal biofacies off the south China coast[J]. J Paleontology,1960,34(6):1164-1182.
[19] 涂霞. 南海东北部海区有孔虫的分布及其与海洋环境的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报,1983,2(1):11-19,85-89.
[20] 徐建,黄宝琦,陈荣华,等. 南海东北部表层沉积中有孔虫的分布及其环境意义[J]. 热带海洋学报,2001,20(4):6-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2001.04.002
[21] 李淑鸾. 珠江口底质中有孔虫埋葬群的分布规律[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1985,5(2):85-106.
[22] 李淑鸾. 珠江口底质沉积中浮游有孔虫的分布规律[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),1987,6:111-123.
[23] 李淑鸾. 珠江口底质沉积中胶结壳有孔虫的分布规律[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1988,19(2):187-196.
[24] 李涛,向荣,李团结. 珠江口表层沉积物底栖有孔虫分布及环境指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(6):91-98.
[25] 李涛,向荣,李团结. 珠江口外表层沉积物底栖有孔虫分布及环境指示[J]. 热带海洋学报,2011,30(4):51-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.04.008
[26] 舒业强,王强,俎婷婷. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2018,48(3):276-287.
[27] CHEN D Y,LIAN E G,SHU Y Q,et al. Origin of the springtime South China Sea Warm Current in the southwestern Taiwan Strait:evidence from seawater oxygen isotope[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2020,63(10):1564-1576. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9642-8
[28] 汪品先 . 海洋微体古生物论文集[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1980: 1-204.
[29] MURRY J W. Ecology and applications of benthic foraminifera[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006: 1-426.
[30] GUPTA B S. Modern Foraminifera[M]. New York, Boston, Dordrecht, London, Moscow, kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003.
[31] 李作明, 陈金华, 何国雄 等. 香港古生物和地层[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.
[32] 陈荣华,徐建,孟翊,等. 南海东北部表层沉积物中微体化石与碳酸盐溶跃面和补偿深度[J]. 海洋学报,2003,25(2):48-56.
[33] 胡松梅. 分异度、均衡度在动物考古中的应用[J]. 考古与文物,1999,2:94-98.
[34] 李亮,陈忠,刘建国,等. 南海北部表层沉积物类型及沉积环境区划[J]. 热带海洋学报,2014,33(1):54-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.007
[35] 于君,邱永松. 黑潮入侵对南海东北部初级生产力的影响[J]. 南方水产科学,2016,12(4):17-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.04.003
[36] NAN F,XUE H J,YU F. Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea:a review[J]. Progress in Oceanography,2015,137(1):314-333.
-




 下载:
下载: