Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and their magnetic indicators in beach surface sediments in Rizhao City
-
摘要:
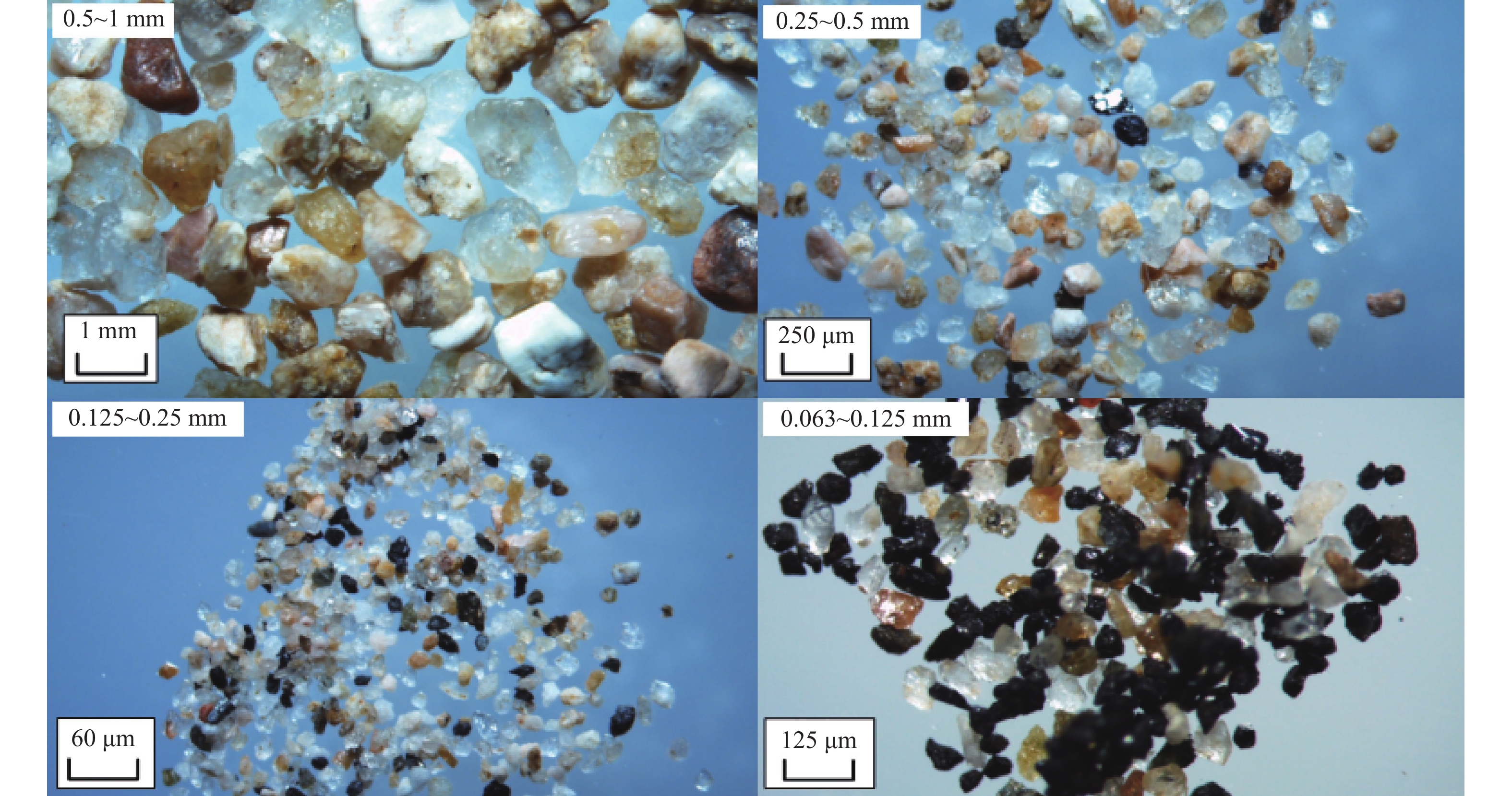
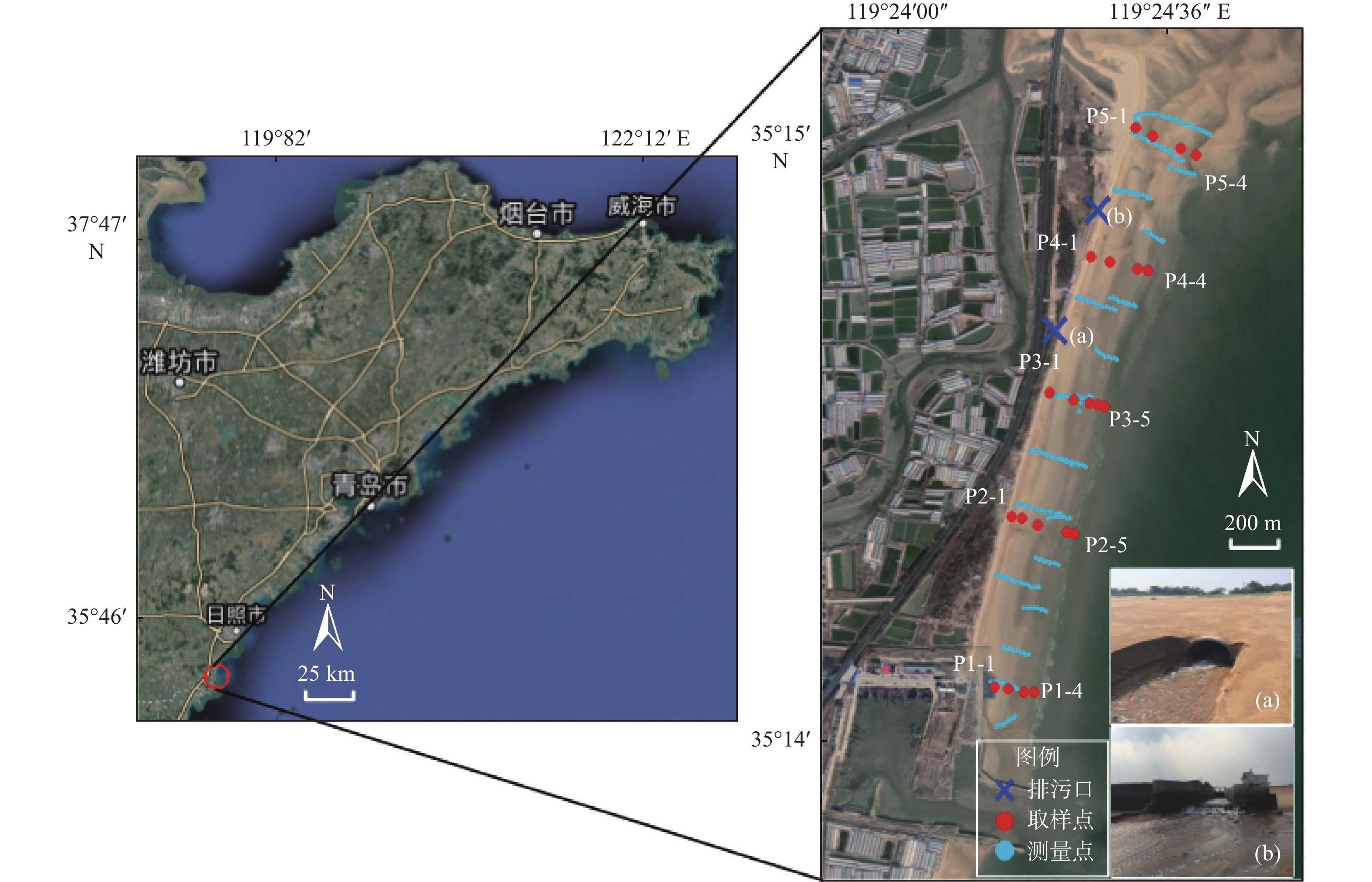
研究区域为山东省南部日照市涛雒镇海滩,对其表层沉积物中7种重金属元素(Cr、Ni、V、Fe、Zn、Co、Pb)的含量进行测试,并使用地累积指数法对其污染状况进行了评估;同时对表层沉积物的磁学参数进行原位磁化率和室内磁学参数测试。结果表明,研究区域整体污染情况较轻,各重金属元素均轻度污染或无污染,重金属污染源主要为河口及海滩排污口。野外体积磁化率和室内质量磁化率分布特征与重金属含量分布特征一致,磁性颗粒的晶粒类型为多畴(MD),磁性矿物类型为亚铁磁性矿物。通过室内质量磁化率与重金属含量的高度正相关性,建立了研究区域重金属污染的磁学诊断方法。
Abstract:Seven heavy metal elements (Cr, Ni, V, Fe, Zn, Co, Pb) are tested for the surface sediments of the Taoluo Town beach, Rizhao City, southern Shandong Province. The geoaccumulation index method is adopted to evaluate the pollution status by heavy metals. At the same time, Both the in-situ magnetic susceptibility (
$ \mathrm{\kappa } $ $ \mathrm{\chi } $ -
Key words:
- environmental magnetism /
- heavy metals /
- pollution assessment /
- surface sediment /
- beach /
- Rizhao City
-

-
表 1 重金属污染程度分级
Table 1. Heavy metal pollution degree classification
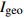 范围
范围污染程度 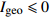
无污染 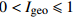
轻度污染 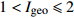
偏中度污染 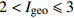
中度污染 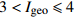
偏重污染 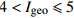
重污染 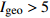
严重污染 表 2 重金属污染评价背景值
Table 2. Background value for heavy metal pollution evaluation
重金属名称 Cr Ni V Fe Zn Co Pb 背景值/(μg/g) 57.1 24.3 74.7 29120 64.6 12.1 26.8 表 3 涛雒镇海滩表层沉积物重金属含量
Table 3. Heavy metal contents in surface sediments of Taoluo Beach
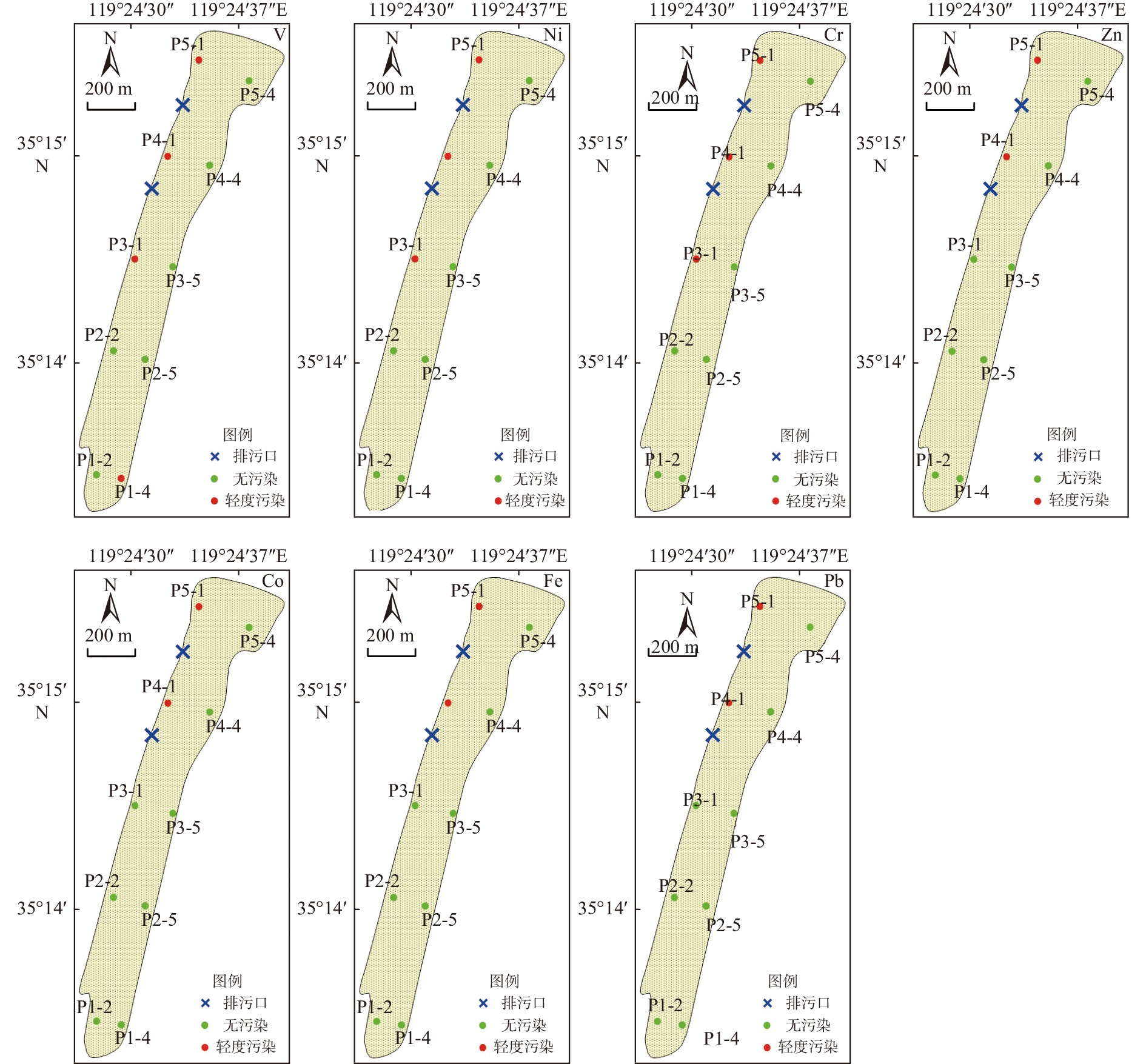
点位 重金属含量/(μg/g) Cr Ni V Fe Zn Co Pb 日照涛雒镇海滩 P1-2 92 36 118 39501 88 15.5 26 P1-4 95 38 127 41339 90 14.7 27 P2-2 90 34 105 37574 87 14.7 25 P2-5 90 35 107 37795 86 14.7 25 P3-1 102 46 154 48817 94 18.2 33 P3-5 90 35 109 38187 90 14.3 26 P4-1 120 62 195 67327 103 19.3 46 P4-4 89 35 113 38755 88 15.9 26 P5-1 112 55 187 57567 100 20.9 42 P5-4 94 38 121 41024 90 17.9 27 平均值 97 41 134 44789 91 16.6 30 评价标准 一类标准 80 - - - 150 - 60 二类标准 150 - - - 350 - 130 表 4 重金属含量Pearson相关性分析
Table 4. Pearson correlation analysis for heavy metal content
Cr Ni V Fe Zn Co Pb Cr 1 Ni 0.99** 1 V 0.98** 0.98** 1 Fe 0.99** 0.99** 0.97** 1 Zn 0.98** 0.98** 0.98** 0.98** 1 Co 0.84** 0.86** 0.88** 0.83** 0.85** 1 Pb 0.99** 0.99** 0.97** 0.99** 0.98** 0.83** 1 注:** p<0.01, n=10。 表 5 取样点地累积指数
Table 5. Geoaccumulation index of the sampling point
点位 地累积指数( 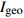 )
)Cr Ni V Fe Zn Co Pb P1-2 −0.1 −0.1 0.0 −0.3 −0.1 −0.2 −0.6 P1-4 0.0 0.0 0.2 −0.2 −0.1 −0.3 −0.6 P2-2 −0.1 −0.2 −0.1 −0.4 −0.1 −0.3 −0.7 P2-5 −0.1 −0.2 −0.1 −0.4 −0.1 −0.3 −0.7 P3-1 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.0 0.0 0.0 −0.3 P3-5 −0.1 −0.2 −0.1 −0.4 −0.1 −0.3 −0.6 P4-1 0.3 0.7 0.8 0.5 0.1 0.1 0.2 P4-4 −0.1 −0.2 0.0 −0.3 −0.1 −0.2 −0.6 P5-1 0.2 0.5 0.7 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.1 P5-4 0.0 0.0 0.1 −0.3 −0.1 0.0 −0.6 平均值 0.0 0.1 0.2 −0.2 0.0 −0.1 −0.4 表 6 研究区与其他地区海滩重金属含量的比较
Table 6. Comparison of heavy metal contents the study area and other beaches
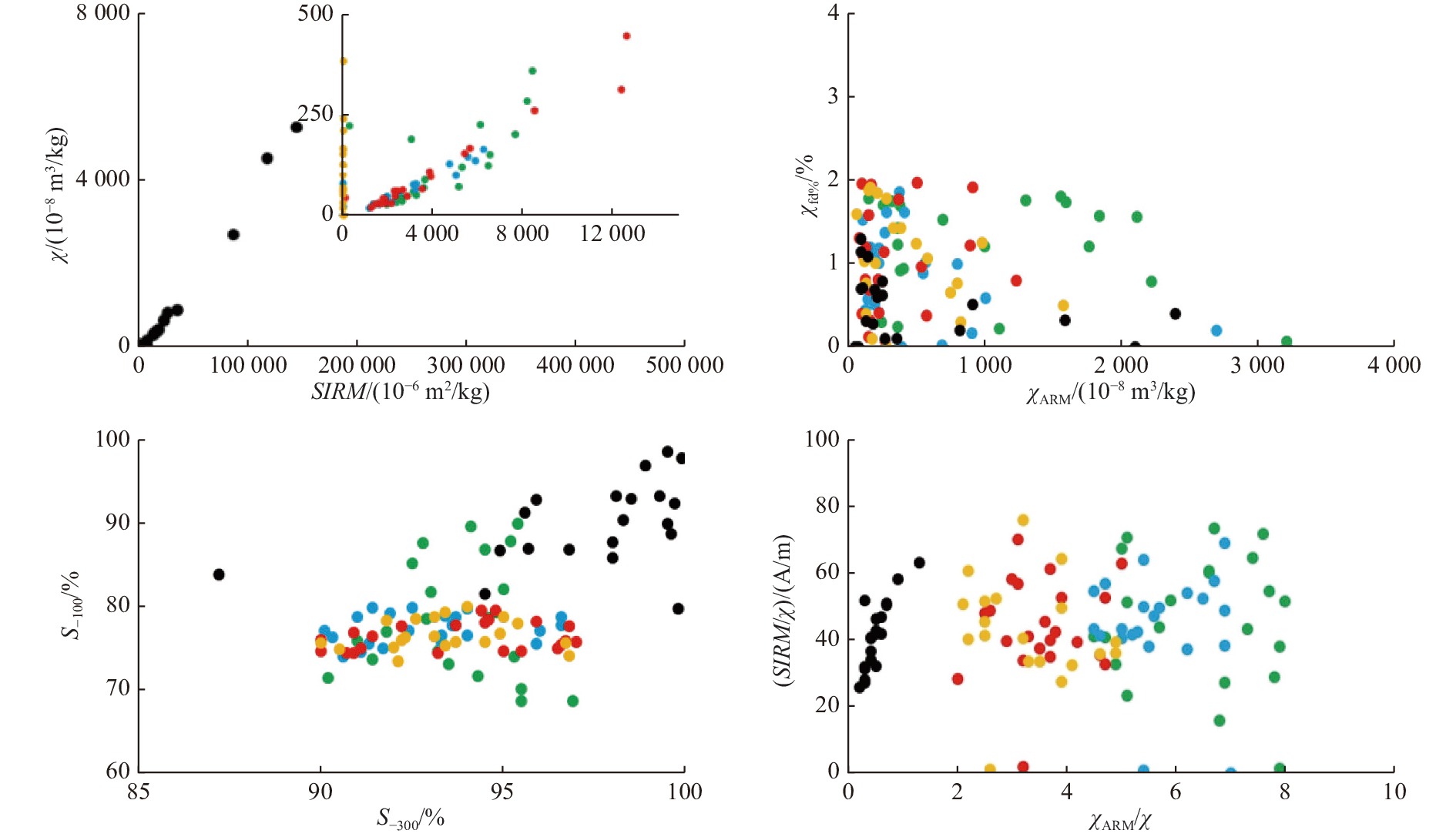
μg/g 海滩名称 重金属平均含量 Cr Ni V Fe Zn Co Pb 本次研究 涛雒镇海滩 97 42 134 45 142 92 16 31 其他地区 石老人海滩(夏季)[14](中国青岛) 69 15 - 50 000 41 - 34 石老人海滩(冬季)[14](中国青岛) 117 21 - 76 000 64 - 43 Huatulco[5](墨西哥) 150 12 - 82 296 29 13 11 Al-Khobar[6](沙特阿拉伯) 51 75 - 7 552 53 5 5 Sodwana Bay[7](南非) 426 15 - 7 784 3 7 1 Lutong[8](马来西亚) 85 - - 1 888 18 13 13 Bahia Solano[9](哥伦比亚) 269 - 143 30 964 126 109 410 Stratoni-lerrssos Gulf[10](希腊) - - - - 1 863 - 1146 Sulcis-Iglesiente[11](意大利) 6 - - - 3 272 - 203 表 7 磁学参数与重金属含量的相关性
Table 7. Correlation between magnetic parameters and heavy metal content
Cr Fe Ni V Zn Co Pb 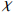
0.99** 0.99** 0.96** 0.99** 0.97** 0.80** 0.99** 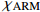
0.93** 0.94** 0.97** 0.92** 0.95** 0.90** 0.92** SIRM 0.98** 0.98** 0.95** 0.99** 0.97** 0.78** 0.99** 
−0.03 −0.02 −0.13 −0.01 −0.09 −0.11 0 S−100 −0.47 −0.48 −0.57 −0.43 −0.48 −0.64* −0.44 S−300 0.18 0.14 0.12 0.16 0.19 −0.05 0.16 注:* p<0.05,** p<0.01;样本数n=10。 表 8
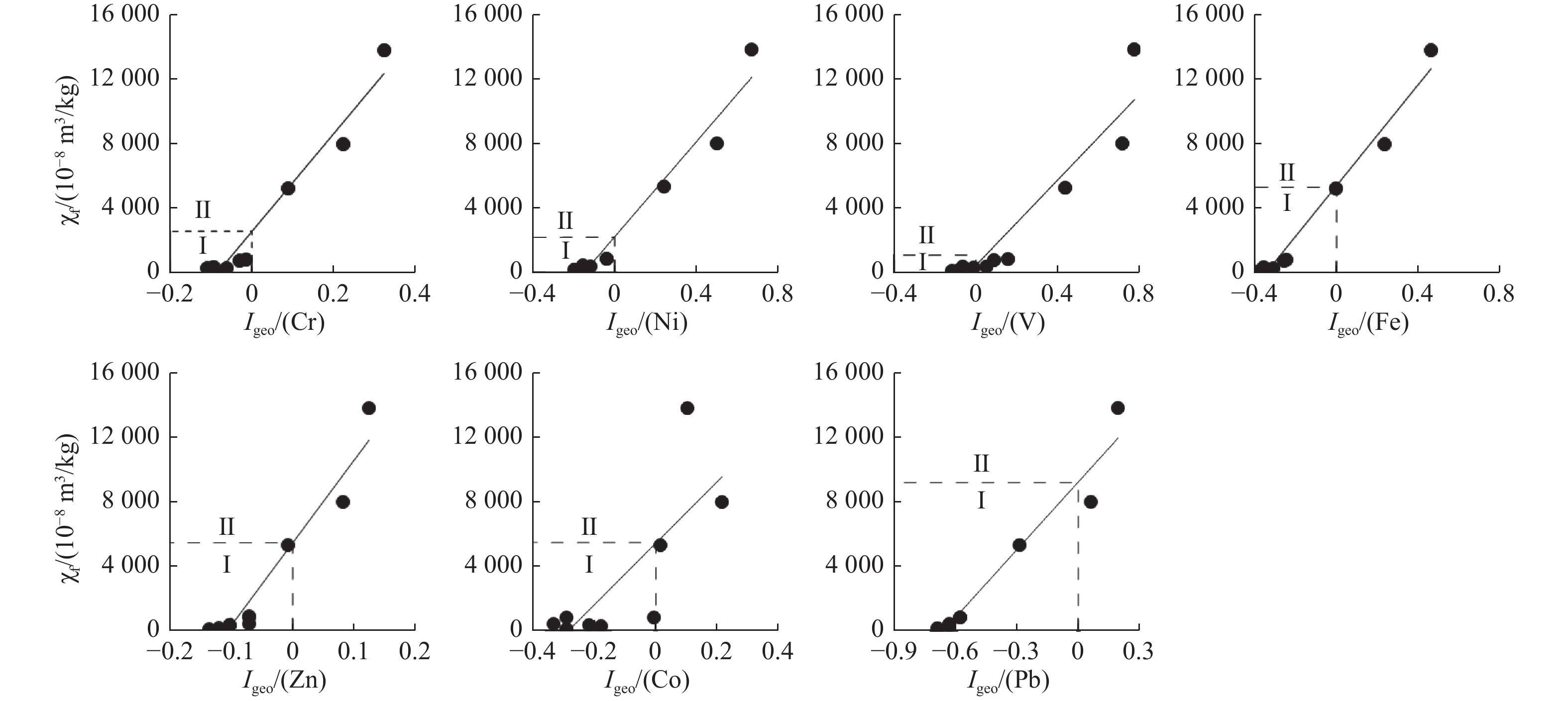
$ \mathrm{\chi } $ 与重金属地累积指数的线性拟合Table 8. Linear fitting between
$ \mathrm{\chi } $ and heavy metal geoaccumulation index线性拟合方程 R2 Igeo(Cr) = ( 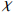 −2596.7) / 30290
−2596.7) / 302900.96 Igeo(Ni) = ( 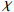 −2202.9) / 14771
−2202.9) / 147710.96 Igeo(V) = ( 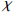 −465.5) / 13207
−465.5) / 132070.89 Igeo(Fe) = ( 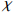 −5425.2) / 15676
−5425.2) / 156760.98 Igeo(Zn) = ( 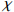 −5434) / 51163
−5434) / 511630.93 Igeo(Co) = ( 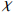 −5444.1) / 19031
−5444.1) / 190310.63 Igeo(Pb) = ( 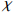 −9210.3) / 13990
−9210.3) / 139900.96 -
[1] 田金,李超,宛立,等. 海洋重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 水产科学,2009,28(7):413-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2009.07.013
[2] VALLEE B L,ULMER D D. Biochemical effects of Mercury,Cadmium,and Lead[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry,1972,41(10):91-128.
[3] BESSA A,NGUEUTCHOUA G,JANPOU A K,et al. Heavy metal contamination and its ecological risks in the beach sediments along the Atlantic Ocean (Limbe coastal fringes,Cameroon)[J]. Earth Systems and Environment,2021,5(2):433-444. doi: 10.1007/s41748-020-00167-5
[4] VETRIMURUGAN E,SHRUTI V C,JONATHAN M P,et al. Comprehensive study on metal contents and their ecological risks in beach sediments of KwaZulu-Natal Province,South Africa[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2019,149:110555.1-110555.11.
[5] RETAMA I,JONATHAN M P,SHRUTI V C,et al. Microplastics in tourist beaches of Huatulco Bay,Pacific coast of southern Mexico[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,113(1/2):530-535.
[6] EL-HAZEK M N,AL-SHIEKH A A. Pollution assessment and mining at Jazan coastline,Saudi Arabia[J]. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2019,10(12):609-620. doi: 10.4236/ajac.2019.1012042
[7] NTANGANEDZENI B,ELUMALAI V,RAJMOHAN N. Coastal aquifer contamination and geochemical processes evaluation in Tugela catchment,South Africa:geochemical and statistical approaches[J]. Water,2018,10(6):687. doi: 10.3390/w10060687
[8] ANANDKUMAR A,NAGARAJAN R,PRABAKARAN K,et al. Human health risk assessment and bioaccumulation of trace metals in fish species collected from the Miri coast,Sarawak,Borneo[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,133:655-663. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.033
[9] GUTIÉRREZ-MOSQUERA H,SHRUTI V C,JONATHAN M P,et al. Metal concentrations in the beach sediments of Bahia Solano and Nuquí along the Pacific coast of Chocó,Colombia:a baseline study[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,135:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.060
[10] PAPPA F K,TSABARIS C,IOANNIDOU A,et al. Radioactivity and metal concentrations in marine sediments associated with mining activities in Ierissos Gulf,North Aegean Sea,Greece[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2016,116:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.07.006
[11] ROMANO E,DE GIUDICI G,BERGAMIN L,et al. The marine sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic contribution from the Sulcis-Iglesiente mining district (Sardinia,Italy)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,122(1/2):331-343.
[12] DEVANESAN E,CHANDRASEKARAN A,SIVAKUMAR S,et al. Magnetic susceptibility as proxy for heavy metal pollution detection in sediment[J]. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology(Transaction A,Science),2020,44(3):875-888. doi: 10.1007/s40995-020-00865-9
[13] WANG S,LIU J,LI J,et al. Environmental magnetic parameter characteristics as indicators of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments off the Zhoushan Islands in the East China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,150:110642. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110642
[14] WANG Y,HUANG Q,LEMCKERT C,et al. Laboratory and field magnetic evaluation of the heavy metal contamination on Shilaoren Beach,China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,117(1/2):291-301.
[15] 宋明春, 王沛成. 山东省区域地质[M]. 济南: 山东地图出版社, 2003.
[16] 张增奇,刘书才,杜圣贤,等. 山东省地层划分对比厘定意见[J]. 山东国土资源,2011(9):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2011.09.002
[17] 宋红瑛,刘金庆,印萍,等. 日照近海表层沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2016,46(3):96-104.
[18] 孙磊,滕浩,金永发. 日照港岚山港区航行的安全操纵[J]. 青岛远洋船员职业学院学报,2021,42(3):43-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3747.2021.03.011
[19] 国家海洋局北海分局. 日照港海域水文气象资料汇编[R]. 青岛: 国家海洋局北海分局, 1997: 9.
[20] 李广雪, 丁咚, 曹立华, 等. 山东半岛滨海沙滩现状与评价[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.
[21] 程小会, 邓敬颂. ICP–MS法测定土壤中12种金属元素时的样品前处理方法[J]. 化学分析计量. 2019 (4): 115-118.
[22] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. Geojournal,1969,2(3):109-118.
[23] 迟清华, 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-148.
[24] 鄢明才, 迟清华, 顾铁新, 等. 中国东部地壳元素丰度与岩石平均化学组成研究[J]. 物探与化探. 1997, 21(6): 451-459.
[25] 庞绪贵,宋娟娟,代杰瑞,等. 日照市土壤地球化学元素分布规律及成因探讨[J]. 山东国土资源,2018,34(4):43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.04.008
[26] KING J,BANERJEE S K,MARVIN J,et al. A comparison of different magnetic methods for determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials:some results from lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1982,59(2):404-419. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90142-X
[27] BANERJEE S K,KING J,MARVIN J. A rapid method for magnetic granulometry with applications to environmental studies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,1981,8(4):333-336. doi: 10.1029/GL008i004p00333
[28] THOMPSON R. Environmental magnetism[M]. Berlin: Springer Science and Business Media, 2012.
[29] 卢升高. 中国土壤磁性与环境[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003.
[30] 陈生涛,苗安洋,温婷婷,等. 辽东湾表层沉积物重金属污染特征及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2019,38(2):256-262.
[31] 张昊,郝义,王惠,等. 日照市海岸带海滩沉积物粒度特征及物源分析[J]. 山东国土资源,2020,36(3):50-58.
[32] SHUWEI Z,CIOPPA M T,SHIHONG Z. Spatial variations in particle size and magnetite concentration on Cedar Beach:implications for grain-sorting processes,Western Lake Erie,Canada[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica‐English Edition,2010,84(6):1520-1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00345.x
[33] 耿婷婷,张敏,蔡五田. 北方某钢铁厂部分厂区土壤重金属污染的初步调查[J]. 环境科学与技术,2011,34(S1):343-346.
[34] 陈轶楠,马建华,张永清. 晋南某钢铁厂及周边土壤重金属污染与潜在生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报,2015,24(9):1540-1546.
[35] 张强,邹华,张涛,等. 无锡某钢铁厂土壤污染现状及评价[J]. 城市环境与城市生态,2012,25(6):25-30.
[36] 吴振,王松涛,刘金庆,等. 日照市海岸带土壤和海底沉积物重金属分布与环境质量评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(1):59-68.
[37] 周洪英. 徐州城市表层土壤重金属污染特征与环境磁学响应[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2016.
[38] STRZYSZCZ Z. Magnetic susceptibility of soils in the areas influenced by industrial emissions[M]. Soil Monitoring, Birkhäuser, Basel, 1993: 255-269.
[39] STRZYSZCZ Z,MAGIERA T. Magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals contamination in soils of southern Poland[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,1998,23(9/10):1127-1131.
[40] CHAN L S,NG S L,DAVIS A M,et al. Magnetic properties and heavy-metal contents of contaminated seabed sediments of Penny's Bay,Hong Kong[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2001,42(7):569-583. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00203-4
-





 下载:
下载: