Petroleum accumulation mode and potential in the eastern section of the southern slope of Dongying Sag
-
摘要:
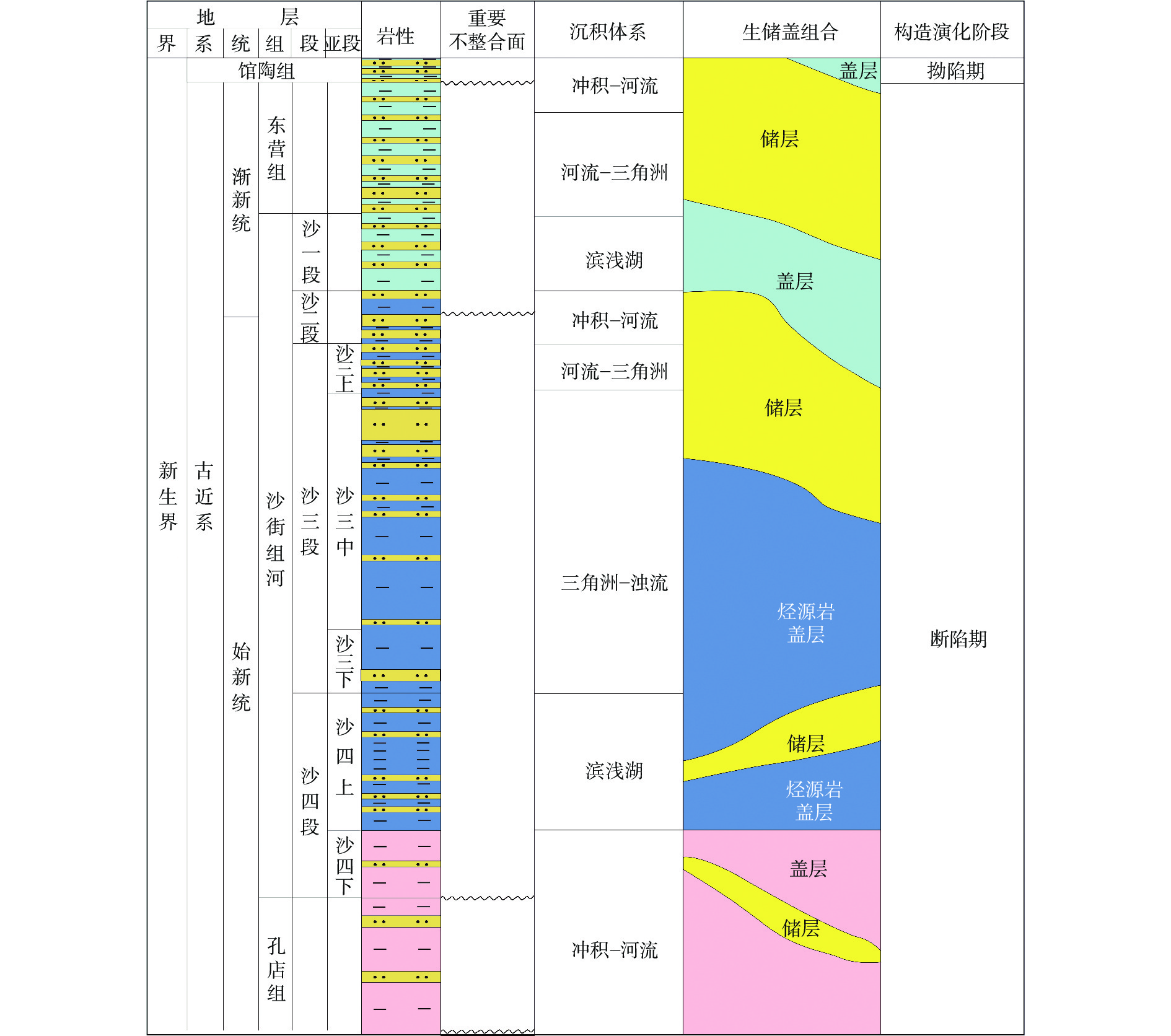
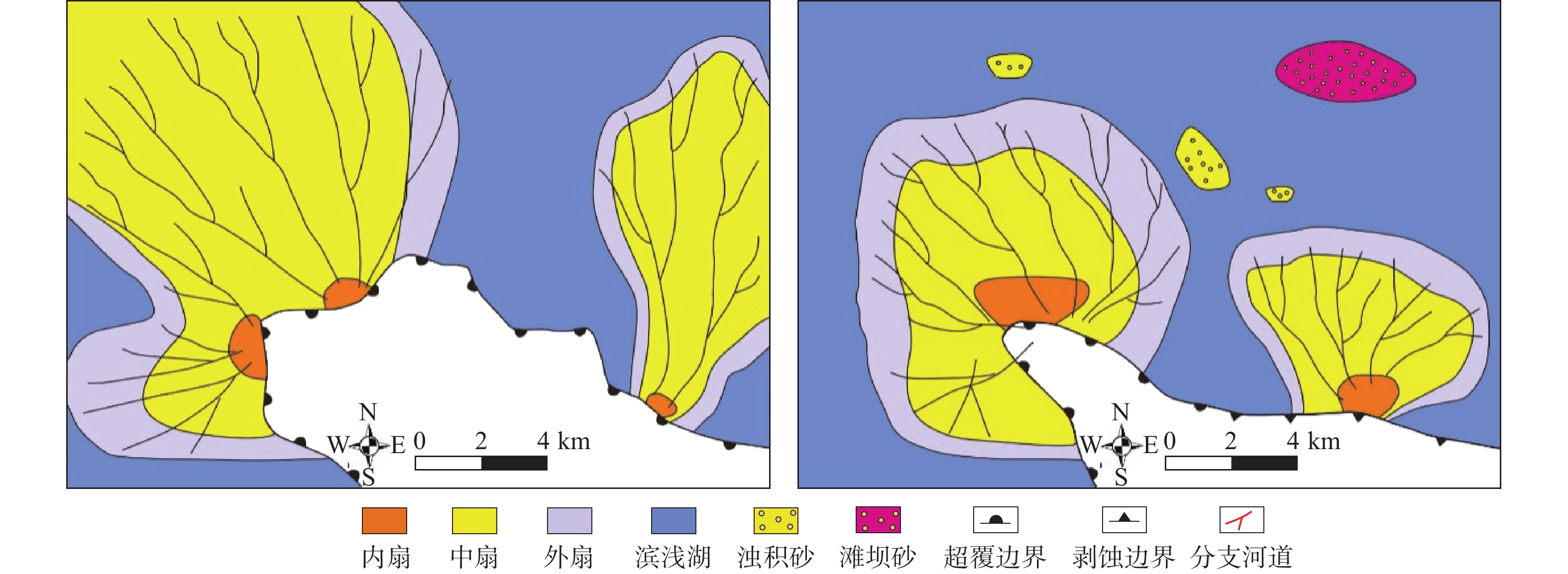
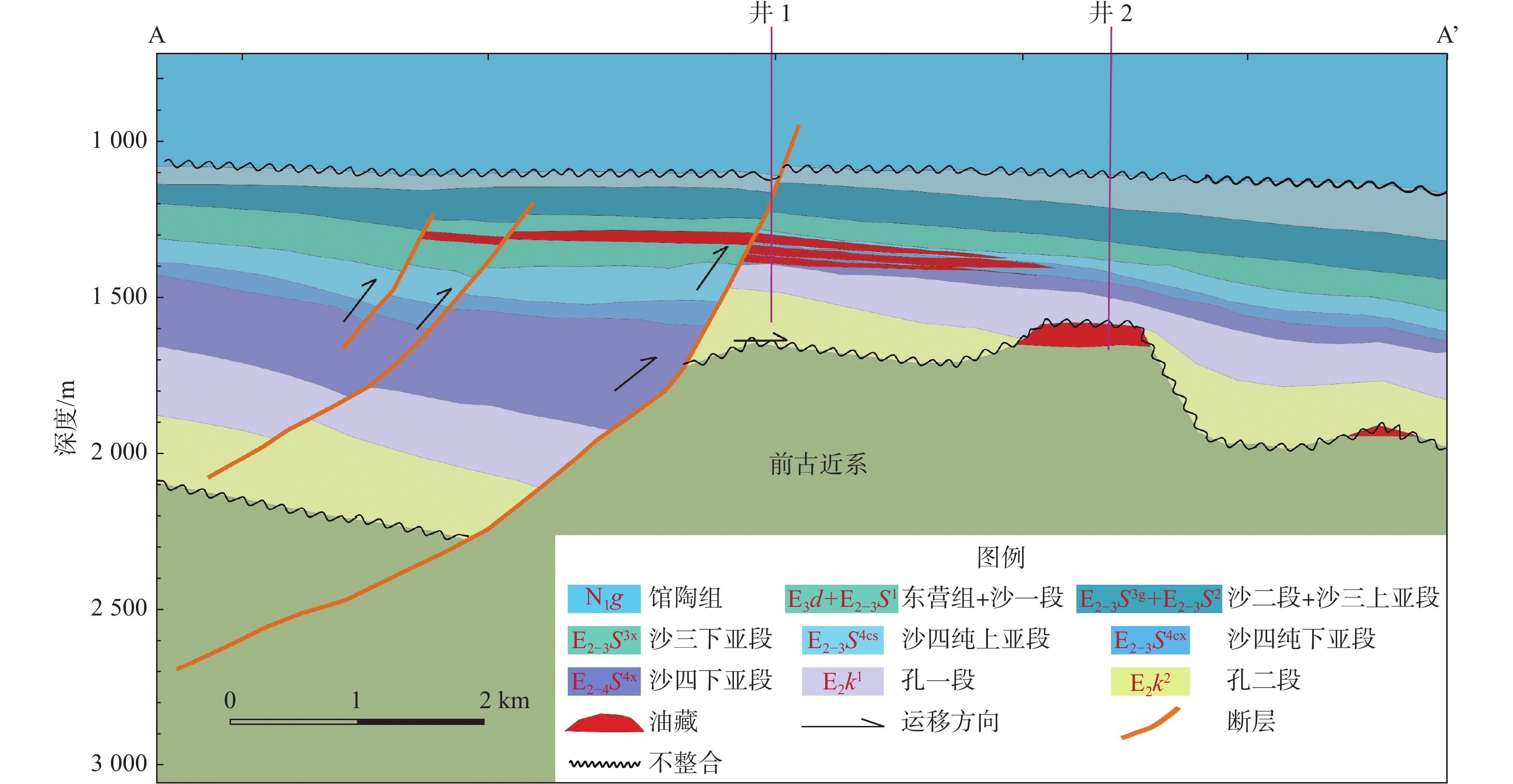
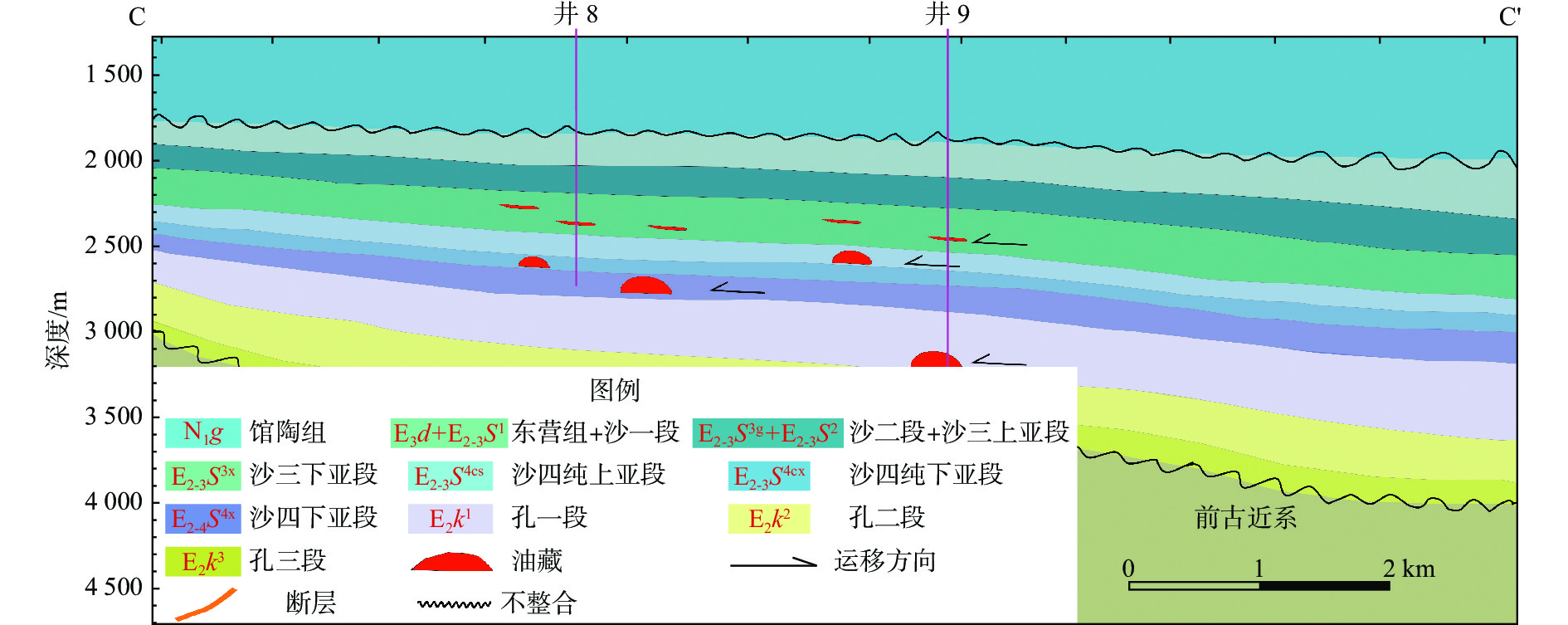
东营凹陷油气资源丰富,但油气分布差异大。东营凹陷南坡东段成藏及油气分布特征研究结果表明,研究区内凸起带、斜坡带和缓坡带的沉积环境和构造条件差异大,油气成藏模式不同。凸起带以不整合遮挡油藏为主,斜坡带以构造油气藏为主并含少量小规模地层超覆油藏,缓坡带以岩性油气藏为主。研究区内断层对油气运移、聚集和油气藏分布都有明显的控制作用。在断层发育区,通过断层、不整合和砂体的三维输导体系,油气可以发生长距离运移,形成构造和不整合油气藏;在断层稀少区,油气以近源运移为主,形成岩性油气藏。初步勘探开发结果显示,岩性油气藏的地层压力高、产量好、前景大,成藏模式为油田老区的“增储上产”指明了方向。
Abstract:The Dongying Sag is a rich reservoir, but the distribution of oil and gas is very uneven. The characteristics of oil accumulation and distribution in the eastern section of the southern slope of Dongying Sag are studied in detail. Results indicate that the uplift zone, slope zone, and gentle slope zone of the study area have diverse sedimentary environments and geological structures, thus different hydrocarbon accumulation modes exist. The uplift zone is dominated by stratigraphic oil pools overlain by unconformities; the slope zone dominated by structural pools with a small amount of stratigraphic oil pools onlapping on unconformities; and the gentle slope zone dominated by lithological oil pools. The faults in the study area have a key impact on the migration, accumulation, and distribution of petroleum pools. In the areas of dense faults, oil migrates over long distances to form structural and stratigraphic oil pools through 3-D conduit systems of faults, unconformities, and sand bodies. In the areas of sparse faults, oil migrates over very short distances to form lithological oil pools close to the source area. The preliminary exploration and development show that the lithological oil pools undergo high pressures, showing good production potential and direction of exploration for additional reserve and yield in a mature field.
-

-
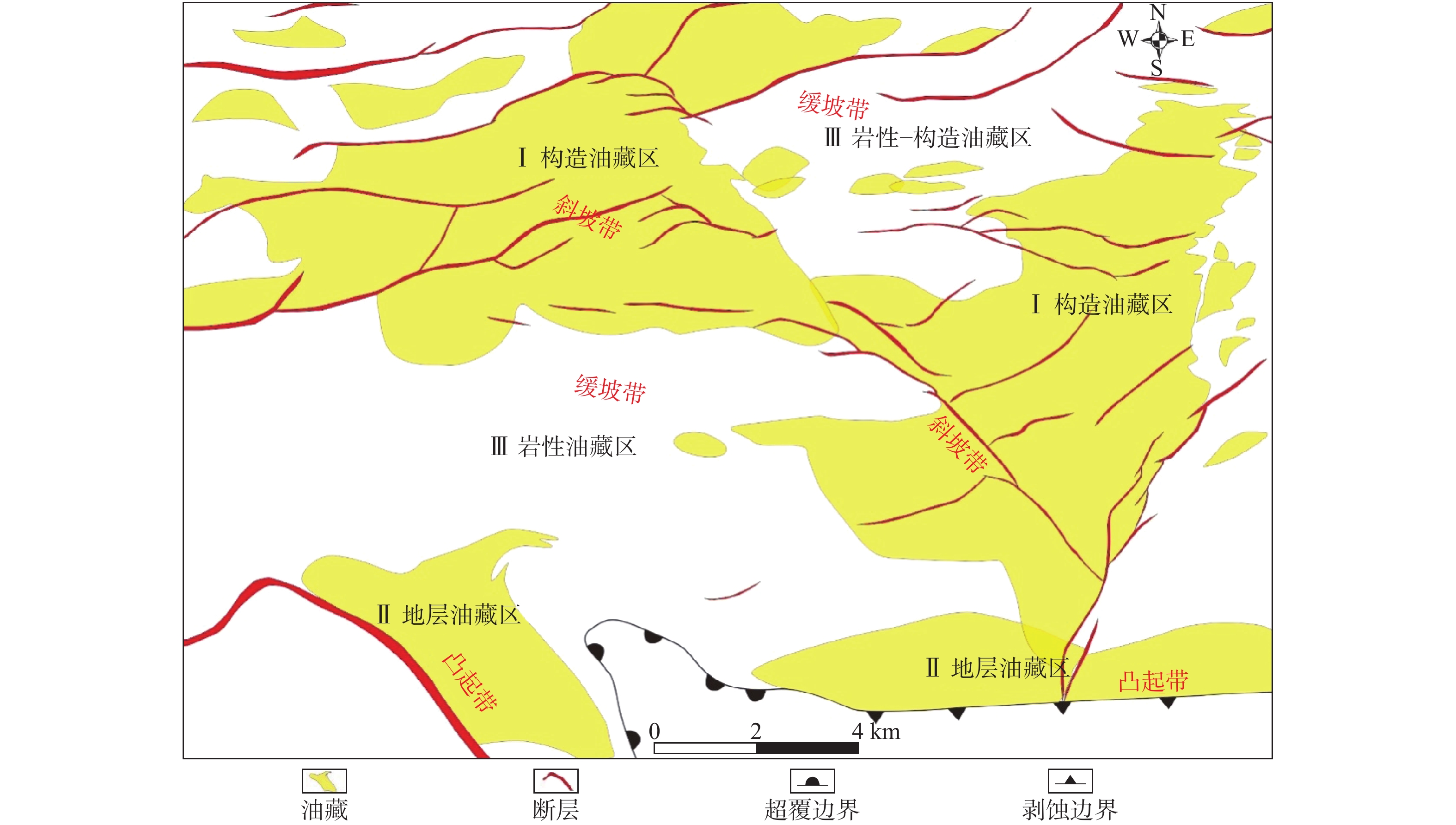
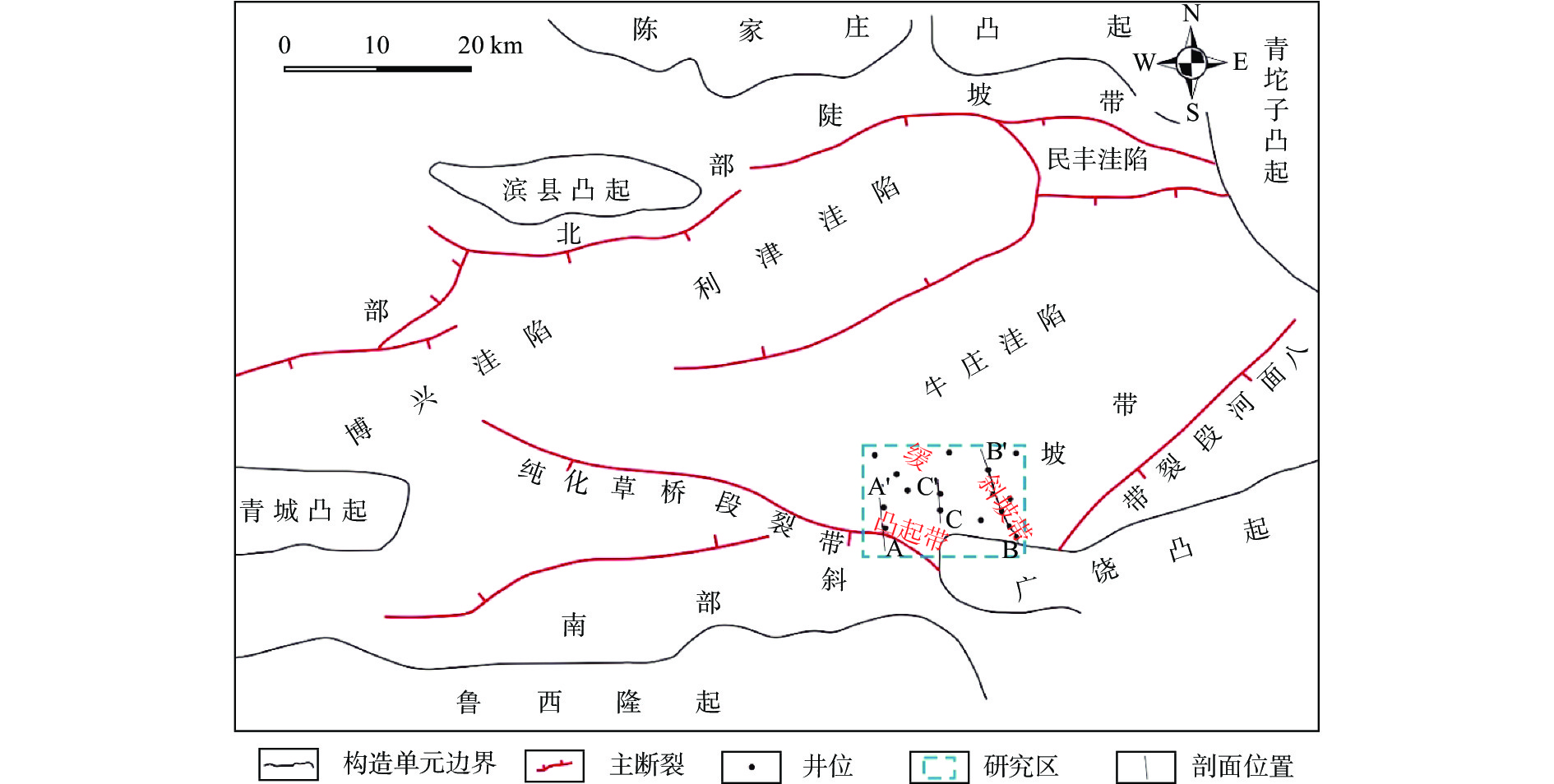
图 1 东营凹陷研究区构造区划图[9]
Figure 1.
-
[1] STERNBACH C A. Super basin thinking:methods to explore and revitalize the world’s greatest petroleum basins[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2020,104(12):2463-2506. doi: 10.1306/09152020073
[2] FRYKLUND B,STARK P P. Super basins:new paradigm for oil and gas supply[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2020,104(12):2507-2519. doi: 10.1306/09182017314
[3] 李鹭光,何海清,范土芝,等. 中国石油油气勘探进展与上游业务发展战略[J]. 中国石油勘探,2020,25(1):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.001
[4] 胡素云,李建忠,王铜山,等. 中国石油油气资源潜力分析与勘探选区思考[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(5):813-823. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005813
[5] 王建强,梁杰,陈建文,等. 中国海域基岩油气藏特征及未来勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(6):151-162.
[6] 陈建文,杨长清,张莉,等. 中国海域前新生代地层分布及其油气勘查方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(1):1-25.
[7] 尹太举,张昌民,李中超. 东营凹陷滑塌浊积岩沉积特征及油气藏勘探技术[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2006,27(1):93-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.01.015
[8] 宋国奇,宁方兴,郝雪峰,等. 骨架砂体输导能力量化评价:以东营凹陷南斜坡东段为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(1):4-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.01.002
[9] 赵琪. 东营凹陷南斜坡王家岗地区沙三段沉积体系与储层特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
[10] 李明忠,李云伟,耿绍宇,等. 东营凹陷南斜坡地层油藏成藏条件及分布规律[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2007,12:356-361.
[11] 雷裕红,罗晓容,张立宽,等. 东营凹陷南斜坡东段沙河街组砂岩输导层连通性量化表征[J]. 石油学报,2013,34(4):692-700. doi: 10.7623/syxb201304009
[12] 高亮,孙波,王延章. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷南坡沙四上亚段滩坝沉积特征及控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质,2018,40(5):669-675. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201805669
[13] 窦鲁星,侯加根,张莉,等. 断陷湖盆同生断层发育区三角洲砂体分布模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):534-546. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.09
[14] 张伟忠,查明,张云银,等. 东营凹陷新生代扭张构造样式及控藏规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2017,38(6):1052-1058. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170605
[15] 邱贻博,贾光华,刘晓峰,等. 东营凹陷古近系构造转换及其对盆地控制作用[J]. 中国石油勘探,2020,25(6):50-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.06.005
[16] 王永诗,郝雪峰,胡阳. 富油凹陷油气分布有序性与富集差异性:以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(5):785-794. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.05.04
[17] 宁方兴. 东营凹陷乐安油田不整合结构与油气聚集[J]. 中国石油勘探,2008,13(3):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2008.03.004
[18] 张参,阳宏,王飞龙,等. 渤中凹陷南洼东营组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(11):35-44.
[19] 隋佳铎,林承焰,任丽华,等. 基于地震沉积学方法的湖相浊积砂体识别:以东营凹陷牛20区块沙三中亚段为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(2):33-42.
-



 下载:
下载: