DISTRIBUTION PATTERN AND RISK ASSESSMENT FOR HEAVY METALS IN THE SURFACE SEDIMENTS OF JIAOZHOU BAY
-
摘要:
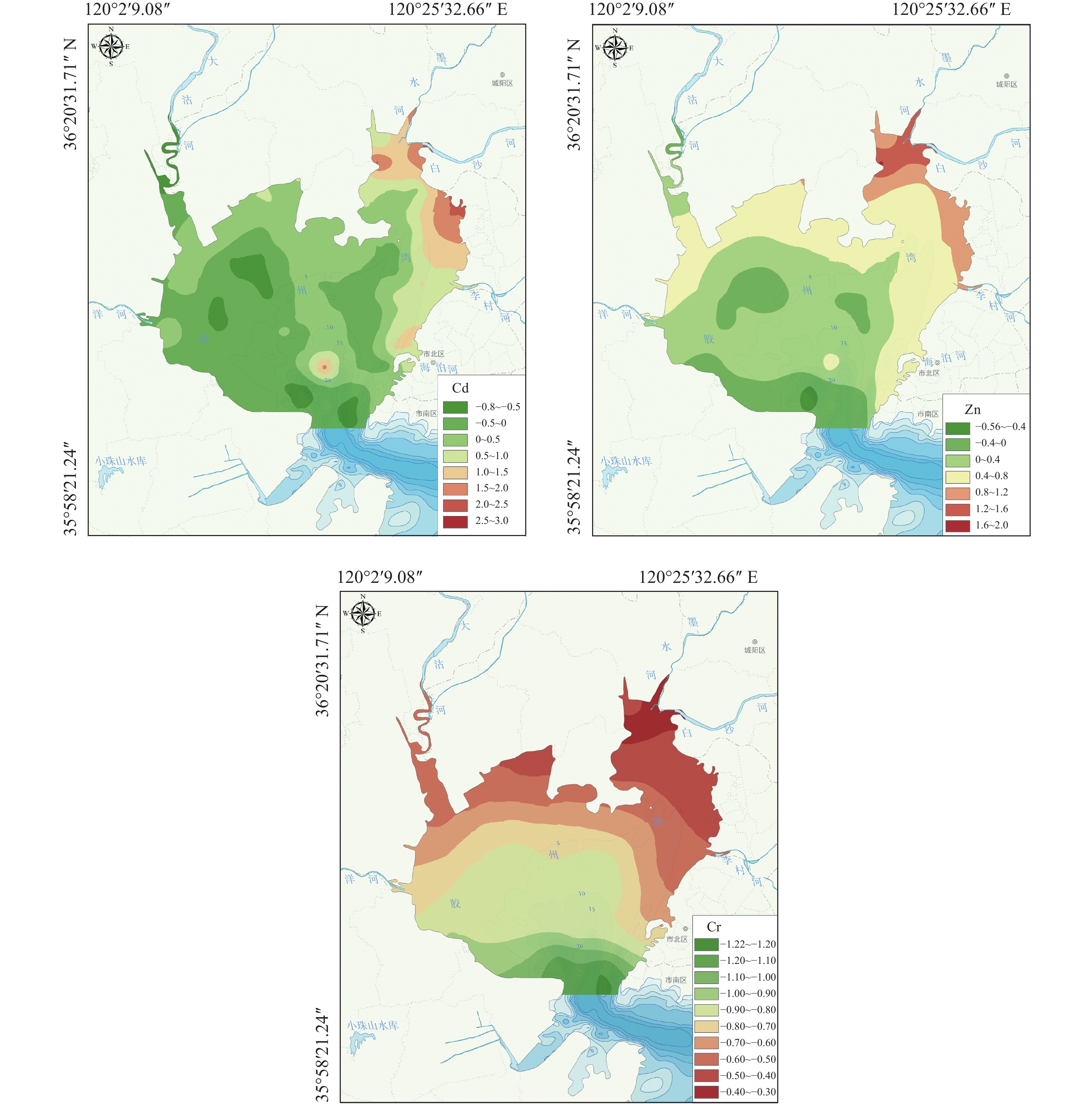
分析了胶州湾海域150个站位表层沉积物Hg、Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu、Cr、As等7种重金属元素的分布特征,对海洋沉积物质量进行标准分类,利用地质积累指数法和潜在生态风险指数法,对重金属元素的污染程度和生态风险等级进行评价。结果表明,研究区表层沉积物重金属元素呈现由岸向海逐渐减少的分布特征,且胶州湾东部近岸区域高于西部区域。经计算评价,胶州湾内表层沉积物7种重金属元素平均含量均未超过《海洋沉积物质量(GB 18668—2002)》规定的第一类沉积物标准,研究区东侧部分站位达到二类和三类标准。研究区表层沉积物重金属总体污染程度属清洁—轻度污染,综合潜在生态风险程度低。自20世纪80年代以来,人类活动已成为影响胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素分布的主要因素。
Abstract:In this paper, the distribution patterns of heavy metals of Hg, Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu, Cr and As taken from 150 surface sediment samples of Jiaozhou Bay are analyzed for assessment of environment qualities. The pollution level and ecological risk of the heavy metals are evaluated with the geological accumulation index and the potential ecological risk index. The results show that the amount of heavy metal elements in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay gradually decrease from coast towards the sea in general, and is relatively higher in the eastern nearshore area comparing to the western. According to our evaluation, the overall quality of sediments in Jiaozhou Bay is quite good, and the sediment quality according to average content of heavy metal elements belongs to the first type of sediments stipulated in Specifications of Marine Sediment Quality (GB 18668—2002), except for the sediments in the eastern part, which may reach the second or even the third type of sediment according to the standards. The overall heavy metals pollution levels of the sediments are clean to light polluted, and the integrated potential ecological risk is low. Since 1980s, human activities have become the main factor affecting the distribution of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay.
-
Key words:
- Jiaozhou Bay /
- surface sediment /
- heavy metals /
- distribution pattern /
- risk assessment
-

-
表 1 地质积累指数法污染程度分级
Table 1. Index of geoaccumulation and pollution levels
Igeo Igeo≤0 0<Igeo≤1 1<Igeo≤2 2<Igeo≤3 3<Igeo≤4 4<Igeo≤5 Igeo>5 级别 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 污染程度 清洁 轻度 偏中度 中度 偏重度 重度 严重 表 2 重金属的背景参照值和毒性系数
Table 2. Background reference values and toxicity coefficient of heavy metals
重金属元素 Hg Cd Pb Zn Cu Cr As 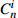 /(mg/kg)
/(mg/kg)0.25 1 70 175 50 90 15 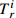
40 30 5 1 5 2 10 表 3 潜在生态风险指数法污染程度分级
Table 3. Potential ecological risk index and pollution levels
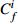
单因子污染程度 
综合污染程度 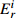
单因子潜在生态风险程度 RI 综合潜在生态风险程度 <1 低 <8 低 <40 低 <150 低 1~3 中等 8~16 中等 40~80 中等 150~300 中等 3~6 重 16~32 重 80~160 较重 300~600 重 ≥6 严重 ≥32 严重 160~320 重 ≥600 严重 ≥320 严重 表 4 表层样重金属元素含量
Table 4. Heavy metal contents in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay
/(mg/kg) 重金属元素 Hg Cd Pb Zn Cu Cr As 平均值(n=150) 0.11 0.10 30.58 85.50 30.15 62.94 8.54 最大值 1.83 0.67 70.30 829.00 114.00 169.00 15.50 最小值 0.0092 0.04 18.50 18.30 6.00 13.90 4.10 标准差 0.17 0.10 8.50 73.79 16.11 20.36 2.19 国家标准Ⅰ/Ⅱ/Ⅲ类[25] 0.2/0.5/1 0.5/1.5/5 60/130/250 150/350/600 35/100/200 80/150/270 20/65/93 胶州湾外海平均值[26] 0.04 0.09 25.25 47.51 17.57 48.58 8.44 中国泉州湾[27] 0.40 0.59 67.70 179.60 71.40 82.00 21.70 北部湾[28] 0.06 0.16 27.99 67.28 58.26 53.65 9.53 美国加利福尼亚湾[29] 0.05 0.33 10.90 59.00 15.00 39.0 5.10 爱琴海(莱斯沃斯岛)[30] — 0.15 46.00 85.90 30.00 97.60 — 表 5 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素Igeo值
Table 5. Geoaccumulation index(
Igeo) of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay 重金属元素 Hg Cd Pb Zn Cu Cr As Igeo最大值 2.41 3.19 1.27 3.79 1.98 0.76 0.72 Igeo最小值 −5.23 −0.88 −0.66 −1.71 −2.27 −2.85 −1.20 Igeo平均值 −2.17 0.13 0.02 0.31 −0.10 −0.75 −0.19 总体污染程度 清洁 轻度 轻度 轻度 清洁 清洁 清洁 表 6 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素生态风险评价
Table 6. Potential ecological risk assessments of heavy metals in surface sedimentsof Jiaozhou Bay
Hg Cd Pb Zn Cu Cr As 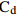
RI 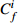
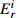
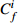
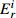
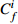
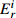
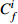
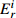
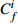
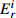
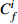
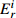
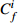
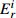
最大值 7.32 292.80 0.67 20.10 1.00 5.02 4.74 4.74 2.28 11.40 1.88 3.76 1.03 10.33 18.23 344.08 最小值 0.04 1.47 0.04 1.20 0.26 1.32 0.10 0.10 0.12 0.60 0.15 0.31 0.27 2.73 1.17 9.90 平均值 0.45 18.03 0.10 2.92 0.44 2.18 0.49 0.49 0.60 3.01 0.70 1.40 0.57 5.69 3.35 33.74 表 7 胶州湾沉积物主要来源
Table 7. Main sources of Jiaozhou Bay sediments
/(104 t/a) 时段 1952—1959年 1960—1969年 1970—1979年 1980—1989年 沿岸河流输沙 215.3 140.8 41.5 2.94 固体垃圾排放 60 100 100 161.15 海岸侵蚀 1 1 1 1 大气沉降 6.5 6.5 6.5 6.5 -
[1] 李玉, 闫国旺, 张亚亚. 近海重金属污染调查与分析[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2019: 1-17.
[2] 张珂,王朝晖,冯杰,等. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 分析测试学报,2011,30(12):1406-1411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2011.12.015
[3] FORSTNER U. Metal pollution in the aquatic environment[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1979: 110-192.
[4] LIVETT E A. Geochemical monitoring of atmospheric heavy metalpollution:theory and applications[J]. Advances in Ecological Research,1988,18:65-177.
[5] 马德毅,王菊英. 中国主要河口沉积物污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学,2003,23(5):521-525. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2003.05.016
[6] 殷效彩,杨永亮,余季金,等. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属分布研究[J]. 青岛大学学报(自然科学版),2001,14(1):76-80.
[7] 李玉,俞志明,曹西华,等. 重金属在胶州湾表层沉积物中的分布与富集[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2005,36(6):580-589. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.06.013
[8] 李玉,俞志明,宋秀贤. 运用主成分分析(PCA)评价海洋沉积物中重金属污染来源[J]. 环境科学,2006,27(1):137-141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.01.026
[9] 刘飞,钟少军,蒲晓强,等. 胶州湾李村河口沉积物中重金属分布特征及其控制因索[J]. 海洋科学,2006,30(4):30-35.
[10] 徐晓达,林振宏,李绍全. 胶州湾重金属污染研究[J]. 海洋科学,2005,29(1):48-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2005.01.010
[11] 陈正新,王保军,黄海燕,等. 胶州湾底质痕量元素污染研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2006,37(3):280-288. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2006.03.013
[12] 何书锋,李广雪,史经昊. 胶州湾表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(4):41-48.
[13] 王红晋,叶思源,杜远生,等. 胶州湾东部和青岛前海表层沉积物重金属分布特征及其对比研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2007(4):80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2007.04.012
[14] 肖彩玲,陈路锋,李雁宾. 胶州湾沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国科技论文,2017,12(9):1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2017.09.019
[15] 董贺平,邹建军,李广雪,等. 胶州湾西北部沉积物中重金属元素分布特征及评价[J]. 海洋地质动态,2007,23(8):4-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2007.08.002
[16] 刘珊珊,张勇,毕世普,等. 青岛近海底质沉积物重金属元素分布特征及环境质量评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2015,34(6):891-897.
[17] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. Geojournal,1969,2:108-118.
[18] 何书锋. 胶州湾沉积物重金属元素地球化学特征及其环境记录[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.
[19] 青岛海洋地质研究所. 青岛市1: 5万环境地质调查与评价报告[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2004.
[20] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research,1980,14(8):975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[21] 周凤霞. 从海岸带到深海部分化学参数的环境特征与指示意义[D]. 北京: 中国科学院, 2016: 1-20.
[22] 徐争启,倪师军,庹先国,等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术,2008,31(2):112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[23] 徐刚,刘健,孔祥淮. 南黄海西部陆架区表层沉积物重金属污染评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2012,31(2):181-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2012.02.007
[24] 丁喜桂,叶思源,高宗军. 近海沉积物重金属污染评价方法[J]. 海洋地质动态,2005,21(8):31-36,38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2005.08.009
[25] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局GB 18668—2002, 海洋沉积物质量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
[26] 青岛海洋地质研究所. 青岛市地质环境质量评价和生态与经许可持续发展报告[R]. 青岛: 青岛海洋地质研究所, 2006.
[27] YU R L,YUAN X,ZHAO Y H,et al. Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay,China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2008,20(6): 664-669. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62110-5
[28] DOU Y G,LI J,ZHAO J T,et al. Distribution,enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay,South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2013,67(1/2):137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.11.022
[29] SCHIFF K C,WEISBERG S B. Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in Southern California coastal shelf sediments[J]. Marine Environmental Research,1999,48(2):161-176. doi: 10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00033-1
[30] ALOUPI M,ANGELIDIS M O. Geochemistry of natural and anthropogenic metals in the coastal sediments of the island of Lesvos,Aegean Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution,2001,113(2):211-219. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00173-1
[31] 戴纪翠,宋金明,李学刚,等. 人类活动影响下的胶州湾近百年来环境演变的沉积记录[J]. 地质学报,2006,80(11):1770-1778. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.11.017
[32] 戴纪翠,宋金明,郑国侠. 胶州湾沉积环境演变的分析[J]. 海洋科学进展,2006,24(3):397-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2006.03.020
[33] 张拂坤. 胶州湾入海污染物容量研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2007.
-




 下载:
下载: