Characteristics and main controlling factors of post-salt hydrocarbon accumulation in Espirito Santo Basin, Brazil
-
摘要:
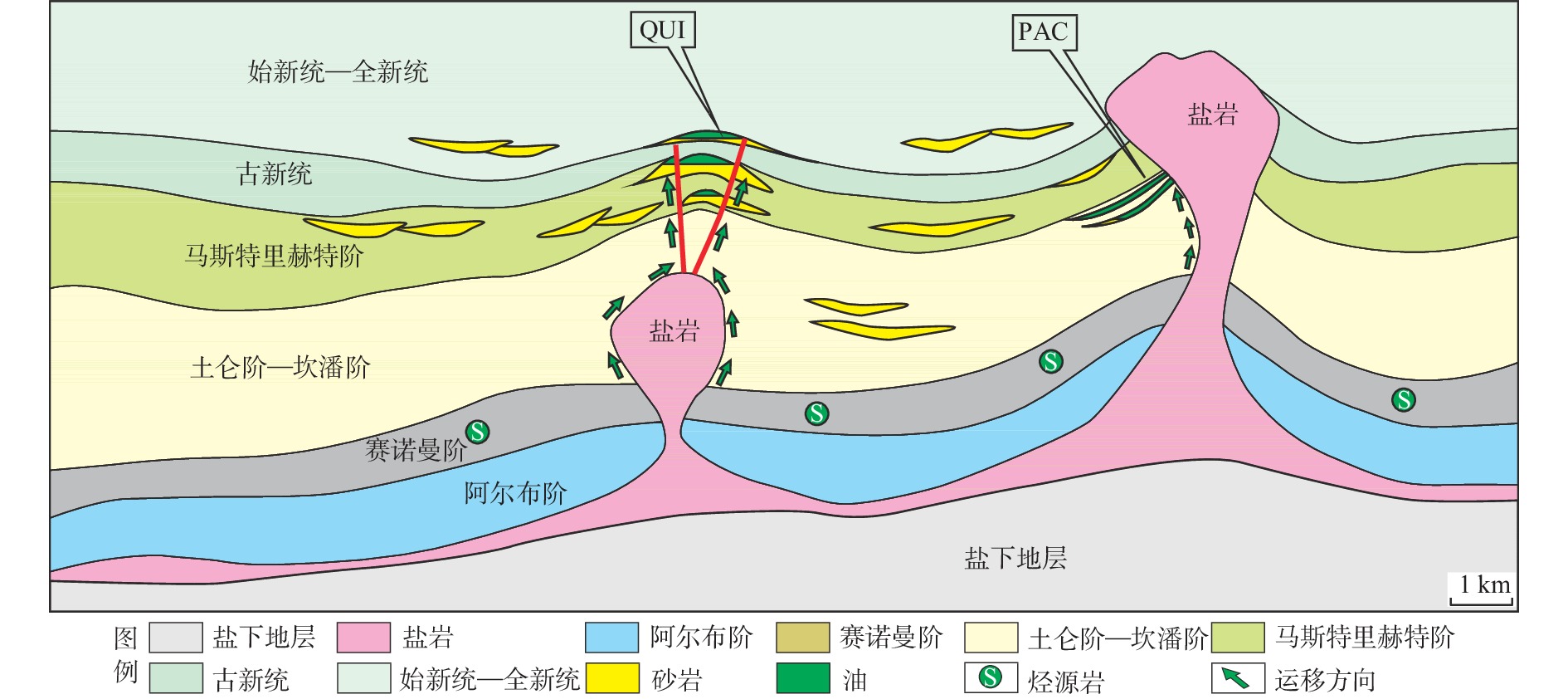
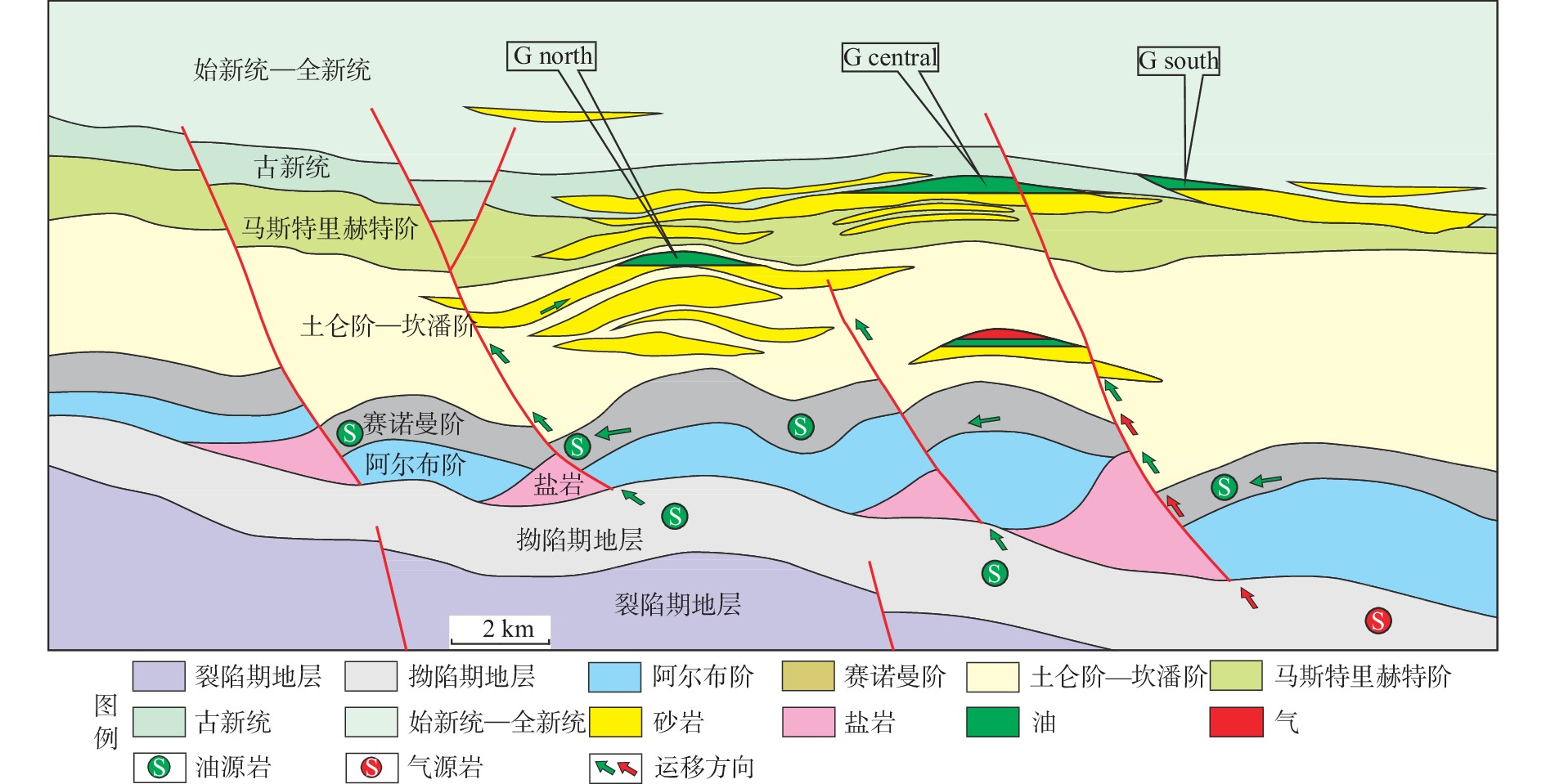
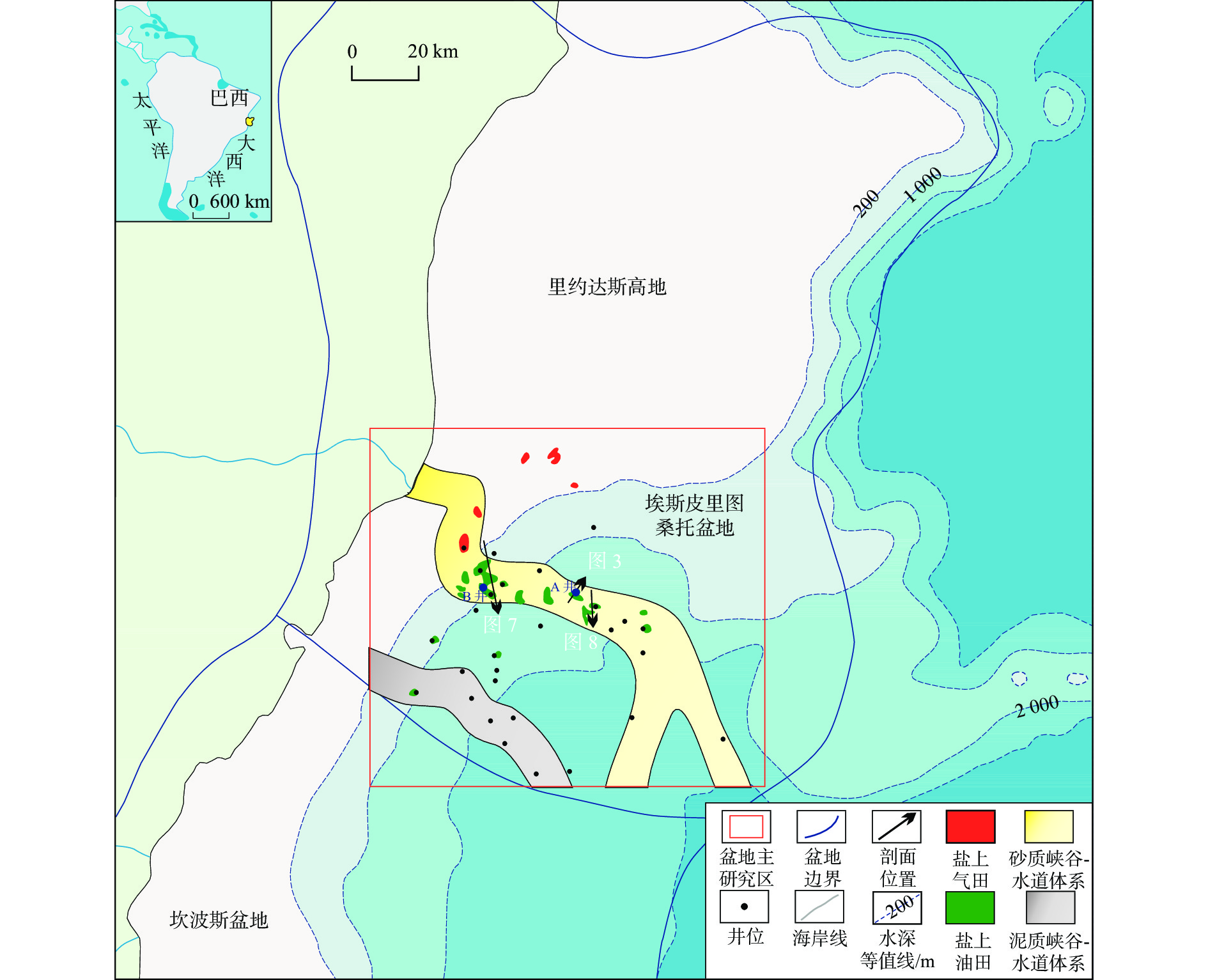
大坎波斯盆地是世界深水沉积勘探的热点盆地,但针对其北段的埃斯皮里图桑脱盆地盐上油气富集规律的系统研究尚未展开。为进一步指导埃斯皮里图桑脱盆地盐上的油气勘探,综合利用钻井、测井和地震资料,对该盆地的油气成藏特征和主控因素进行了综合分析。研究表明:①埃斯皮里图桑托盆地发育盐下湖相和盐上海相2套烃源岩,且储层主要为盆地北部上白垩统—新近系深水水道砂岩;②依据盐岩层滑脱变形的构造特征,可将盐上构造格局划分为盐滑脱带、盐底辟带和盐推覆带;③盐滑脱带成藏模式表现为盐下和盐上烃源岩生成的油气分别通过盐窗和盐相关断裂运移,最终在盐滑脱形成的滚动背斜等圈闭中成藏;④盐底辟带成藏模式表现为盐上烃源岩生成的油气通过盐相关断裂运移,最终在盐底辟相关背斜和盐侧翼遮挡的圈闭中成藏;⑤储层、盐相关铲式断层和盐岩活动是油气成藏的主控因素。
Abstract:The Campos Basin in Brazil is well-known of deep-water sedimentary exploration in the world. However, no systematic study has been carried out on the post-salt hydrocarbon accumulation in the Espirito Santo Basin (ESB) in the northern part of the Campos Basin. To advance the post-salt oil and gas exploration, the characteristics of oil-gas accumulation and the main controlling factors in the ESB were scrutinized using drilling, logging, and seismic profiling. Results bring up the following 4 conclusions: ① Two sets of source rocks including pre-salt lacustrine and post-salt marine source rocks are developed. The reservoir is mainly composed of the Upper Cretaceous to Tertiary deepwater channel sandstone in the north of the basin. ② According to the detachment deformation of salt rock, post-salt formation can be divided into detachment zone, diapir zone, and nappe zone. ③ The hydrocarbon accumulation model of salt detachment zone shows that the hydrocarbon generated by pre-salt and post-salt source rocks migrate through salt windows and salt related faults, respectively, and finally form reservoirs in rolling anticlines and other traps formed by salt detachment. ④ The hydrocarbon accumulation model of salt diapir zone is that hydrocarbon generated by post-salt source rocks migrate through salt-related faults, and finally accumulated in anticlines related with salt diapers and other traps blocked by salt flank. ⑤ Reservoir- and salt-related listric faults, and activities of salt-bearing rocks are the main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in the ESB.
-
Key words:
- Espirito Santo Basin /
- post-salt /
- pre-salt /
- structural zonality /
- hydrocarbon accumulation /
- main controlling factors
-

-
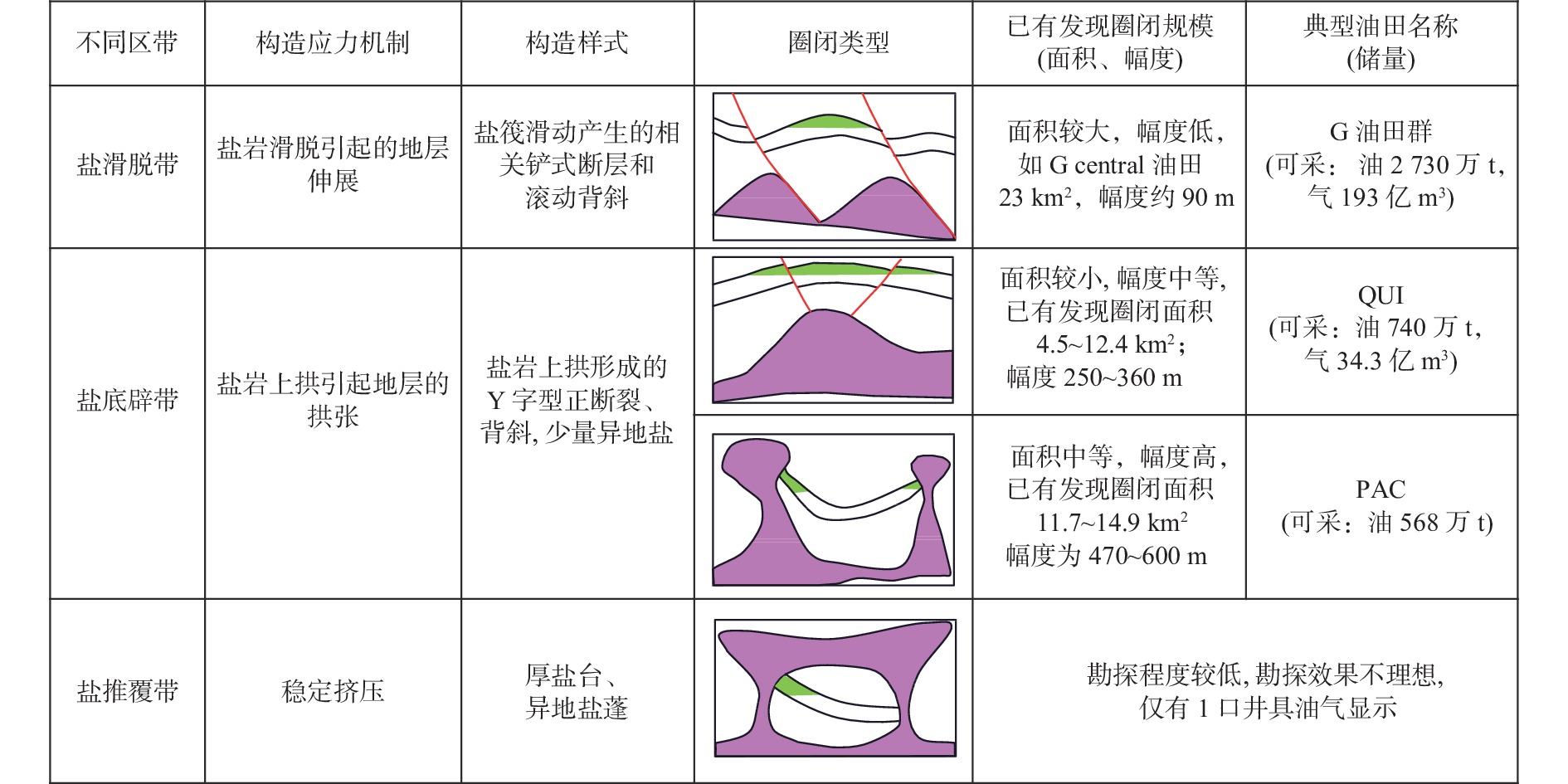
表 1 埃斯皮里图桑托盆地海域盐上主要油气田充满度统计
Table 1. Statistics of fullness of major post-salt oil and gas fields of the Espirito Santo Basin
油气田名称 盐岩
类型层位 圈闭面积/km2 圈闭高点 闭合幅度/m 烃柱高度/m 含烃面积/km2 充满系数/% TVDSS/m 垂向 面积 G Central 隐
伏
型马斯特里赫特阶 23.4 3 210 90 50 9.5 56 41 QUI 马斯特里赫特阶 8.93 4 320 360 144 2.52 40 28 COC 古新统 12.4 3 320 355 225 6.21 63 50 PDM 古新统 4.5 3 055 285 145 2.84 51 63 PAC 刺穿型 三冬阶 14.89 4 580 470 379 10.49 81 70 BRI 三冬阶 11.7 3 700 600 551 8.4 92 72 注:TVDSS(True Vertical Depth Sub-sea)为平均海平面下垂直深度。 -
[1] 李全. 巴西埃斯皮里图桑托盆地深水油气勘探潜力初探[J]. 科技视界,2014(27):277-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2014.27.220
[2] 谢华锋,周生友,惠冠洲. 巴西圣埃斯皮里图盆地油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质,2016,38(6):821-827. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606821
[3] 康洪全,孟金落,程涛,等. 巴西坎波斯盆地深水沉积体系特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(1):93-104. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.01.09
[4] 马中振,谢寅符,耿长波,等. 巴西坎波斯(Campos)盆地石油地质特征与勘探有利区分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(5):1389-1396.
[5] 张申,郭莉,林卫东. 巴西坎普斯盆地油气地质特征与隐蔽油气藏[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2012,33(5):705-712. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120506
[6] IHS Energy. Espinto Santo Basin[DB]. IHS database, 2018.
[7] 邬长武. 南大西洋含盐盆地油气富集规律及勘探潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质,2015,36(1):121-126.
[8] 陶崇智,殷进垠,陆红梅,等. 南大西洋被动陆缘盆地盐岩对油气成藏的影响[J]. 石油实验地质,2015,37(5):614-618. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201505614
[9] 康洪全,程涛,李明刚,等. 巴西桑托斯盆地油气成藏特征及主控因素分析[J]. 中国海上油气,2016,28(4):1-8.
[10] 杨永才,孙玉梅,李友川,等. 南大西洋被动陆缘共轭盆地烃源岩分布与油气富集规律:以巴西桑托斯盆地和西非纳米贝盆地为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(2):157-167.
[11] 汪新伟,孟庆强,邬长武,等. 巴西大坎波斯盆地裂谷体系及其对盐下成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(2):193-202. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150203
[12] 袁圣强,吴时国,马玉波,等. 南大西洋深水盆地的构造沉积演化及含油气系统[J]. 天然气地球科学,2008,19(2):216-221. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.02.216
[13] 刘子玉,吕栋,解东宁. 巴西东缘桑托斯盆地盐上碎屑岩系沉积特征及其演化规律[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(8):1-8.
[14] 孙旭东,郑求根,郭兴伟,等. 巴西桑托斯盆地构造演化与油气勘探前景[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(2):37-45.
[15] 程涛,陶维祥,康洪全,等. 下刚果盆地北部海域海相碳酸盐岩沉积储层特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(2):148-157. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018120401
[16] 戈红星,JACKSON M P A. 盐构造与油气圈闭及其综合利用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版),1996,32(4):640-649.
[17] 彭文绪,王应斌,吴奎,等. 盐构造的识别、分类及与油气的关系[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2008,43(6):689-698. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2008.06.014
[18] 贾承造,赵文智,魏国齐,等. 盐构造与油气勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2003,30(2):17-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.02.003
[19] 余一欣,周心怀,彭文绪,等. 盐构造研究进展述评[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2011,35(2):169-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.02.001
[20] 刘祚冬,李江海. 西非被动大陆边缘盆地盐构造对油气的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2011,38(2):196-202.
[21] 刘静静,邬长武,丁峰. 南大西洋两岸含盐盆地类型与油气分布规律[J]. 石油实验地质,2018,40(3):372-380. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201803372
[22] 刘深艳,胡孝林,常迈. 西非加蓬海岸盆地盐岩特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 海洋石油,2011,31(3):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2011.03.001
[23] 温志新,徐洪,王兆明,等. 被动大陆边缘盆地分类及其油气分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(5):678-688.
[24] 康洪全,贾怀存,程涛,等. 南大西洋两岸含盐盆地裂谷层序油气地质特征与油气分布特征对比[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(4):113-119.
[25] 孙自明,何治亮. 裂谷与被动陆缘叠合盆地的盐构造与油气成藏:以西非下刚果—刚果扇盆地和宽扎盆地为例[J]. 石油实验地质,2016,38(3):287-292. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201603287
[26] 陈亮,赵红岩,韩文明,等. 毛塞几比盆地外陆架-陆坡区阿尔比阶-土伦阶沉积特征及成藏体系[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(4):132-140.
[27] 孙涛,王建新,孙玉梅. 西非塞内加尔盆地深水区油气地球化学特征与油气成藏[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(6):1284-1292.
[28] Perez-Gussinye M. A tectonic model for hyperextension at magma-poor rifted margins:an example from the West Iberia-Newfoundland conjugate margins[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications,2013,369(1):403-427. doi: 10.1144/SP369.19
-



 下载:
下载: