Inversion structure and its application in petroleum exploration in Santos Basin, Brazil
-
摘要:
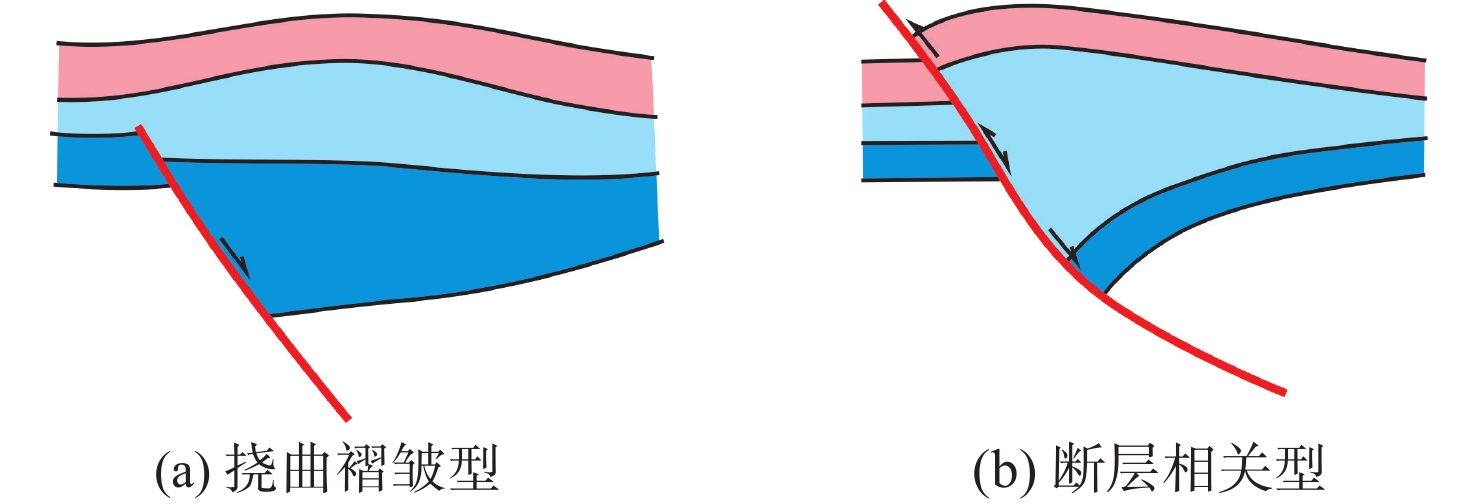
为了揭示反转构造的成藏特征,系统总结了反转构造的类型特征、构造样式及形成机制,并对桑托斯盆地的勘探实例开展了分析。研究表明,正反转构造是一种重要的含油气圈闭,其发育演化与所受的挤压应力强度相关,在轻微、中等反转阶段,主要发育挠曲褶皱反转构造,在强烈和全部反转阶段,主要表现为断层强烈逆冲反转,发育断层相关型构造;反转构造是区域构造事件的响应,热体制变化和区域构造体制变化是2种主要的构造反转动力机制。正反转构造具有近源供烃,断裂-裂缝等运移通道发育以及圈闭可靠、规模大等特征,油气“生-汇-聚”时空匹配关系良好,是一种重要的油气藏类型。
Abstract:To reveal the hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of inversion structures, the types, styles, and formation mechanism of inversion structures are summarized, and exploration examples of the Santos Basin, Brazil, were analyzed. Results show that positive-inversion structures are important hydrocarbon-bearing traps. Their development and evolution are related to compressive stress intensity. In slight or intermediate inversion stage, they mainly develop flexural fold inversion structures. In strong or full inversion stages, they mainly show strong thrusting and develop fault-related inversion structures. Inversion structures are the response of regional tectonic events. Thermal regime change and regional tectonic regime change are two main tectonic counter-rotational force mechanisms. Positive inversion structures are characterized by near-source hydrocarbon supply, development of migration channels such as faults and fractures, and reliable and large-scale traps. In addition, positive inversion structures provide a good condition in which hydrocarbon generation, migration, and accumulation are well-matched in space and time, forming an important reservoir type.
-
Key words:
- Santos Basin /
- hydrocarbon accumulation /
- structural style /
- dynamic mechanism /
- inversion structure
-

-
[1] GLENNIE K W, BOEGNER P L E. Sole pit inversion tectonics[C]//Petroleum Geology of the Continental Shelf of North-West Europe. London: Institute of Petroleum, 1981: 110-120.
[2] BALLY A W. Tectogenese at seismique reflexion[J]. Bulletin Society. Geologique de France,1984,7(2):279-285.
[3] MITRA S. Geometry and kinematic evolution of inversion structures[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1993,77(7):1159-1191.
[4] WILLIAMS G D,POWELL C M,COOPER M A. Geometry and kinematics of inversion tectonics[J]. London:Geological Society,Special Publications,1989,44(1):3-15. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.044.01.02
[5] ULIANA M A,ARTEAGA M E,LEGARRETA L,et al. Inversion structures and hydrocarbon occurrence in Argentina[J]. London:Geological Society,Special Publications,1995,88(1):211-233. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.088.01.13
[6] 漆家福, 夏义平, 杨桥. 油区构造解析[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2007.
[7] MCCLAY K R. Glossary of thrust terms [M ]//MCCLAY K R. Thrust Tectonic. London: The Geological Society. 1991: 419-433.
[8] TURNER J P,WILLIAMS G A. Sedimentary basin inversion and intra-plate shortening[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2004,65(3):277-304.
[9] COOPER M,WARREN M J. The geometric characteristics,genesis and petroleum significance of inversion structures[J]. Geological Society,London:Special Publications,2010,335:827-846. doi: 10.1144/SP335.33
[10] 姜华,王华,肖军,等. 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷构造反转与油气聚集[J]. 石油学报,2008,29(3):372-377. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.03.011
[11] 唐大卿,陈红汉,江涛,等. 伊通盆地新近纪差异构造反转与油气成藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(6):682-691. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.06.06
[12] 张宙,赵洪,罗仁春,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组盖层特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(10):50-56.
[13] 郭真,刘池洋,田建锋. 东海盆地西湖凹陷反转构造特征及其形成的动力环境[J]. 地学前缘,2015,22(3):59-67. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.03.005
[14] 陈昭年,陈发景. 反转构造与油气圈闭[J]. 地学前缘,1995,2(3/4):96-102.
[15] 强昆生,吕修祥,周心怀,等. 渤海辽东湾坳陷JX1-1 反转构造与油气成藏史[J]. 矿物岩石,2012,32(4):31-40.
[16] 陈哲龙,柳广弟,卢学军,等. 二连盆地反转构造反转程度定量研究及对油气成藏的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,46(11):4136-4145.
[17] 陈树光,张以明,崔永谦,等. 二连盆地巴音都兰凹陷反转构造及成因机制[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(4):559-569.
[18] 李明刚. 桑托斯盆地盐下裂谷系构造特征及圈闭发育模式[J]. 断块油气田,2017,24(5):608-612. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201705003
-




 下载:
下载: