Application of quantitative reservoir prediction technology based on high frequency sequence framework in sand body
-
摘要:
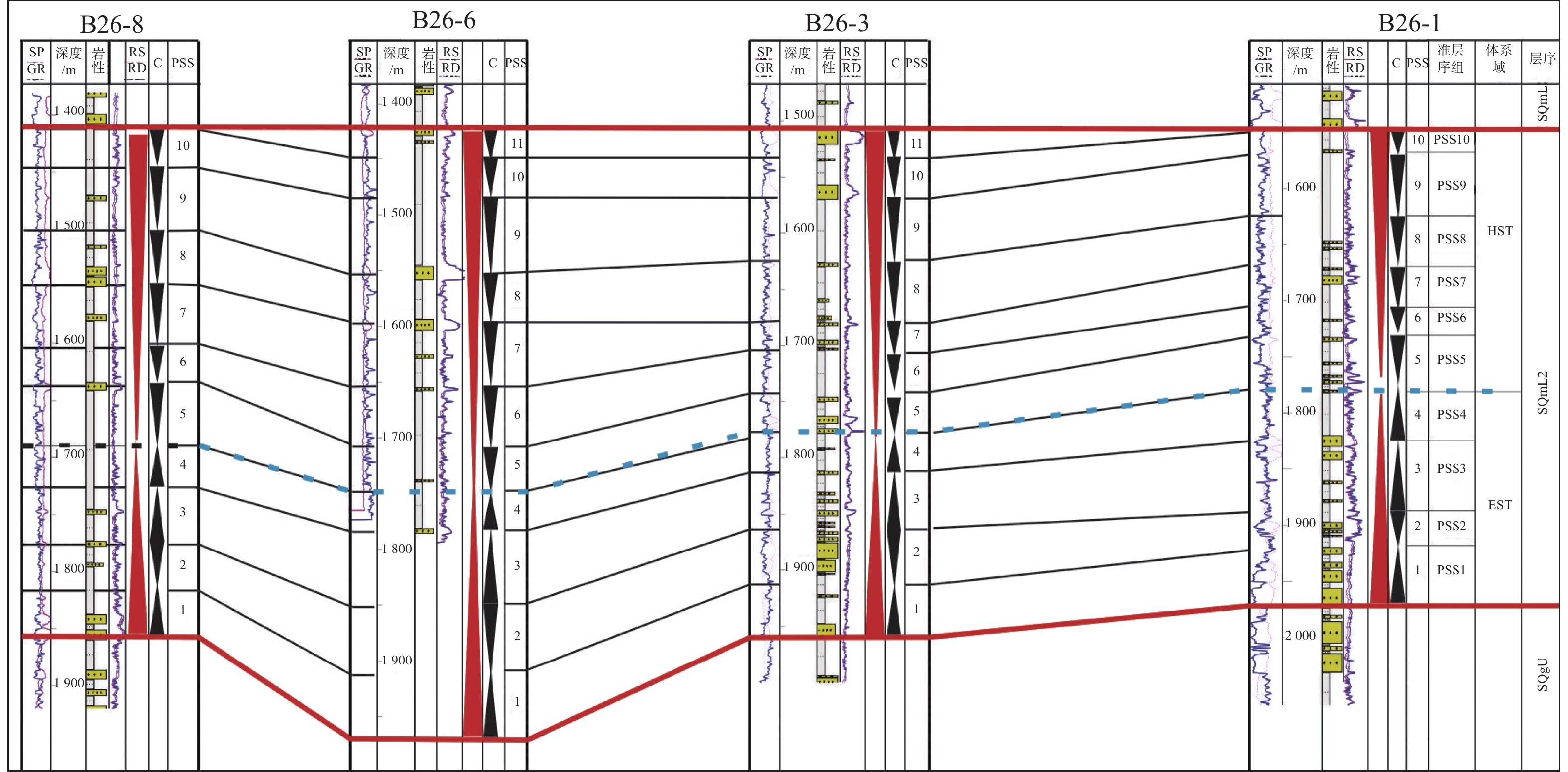
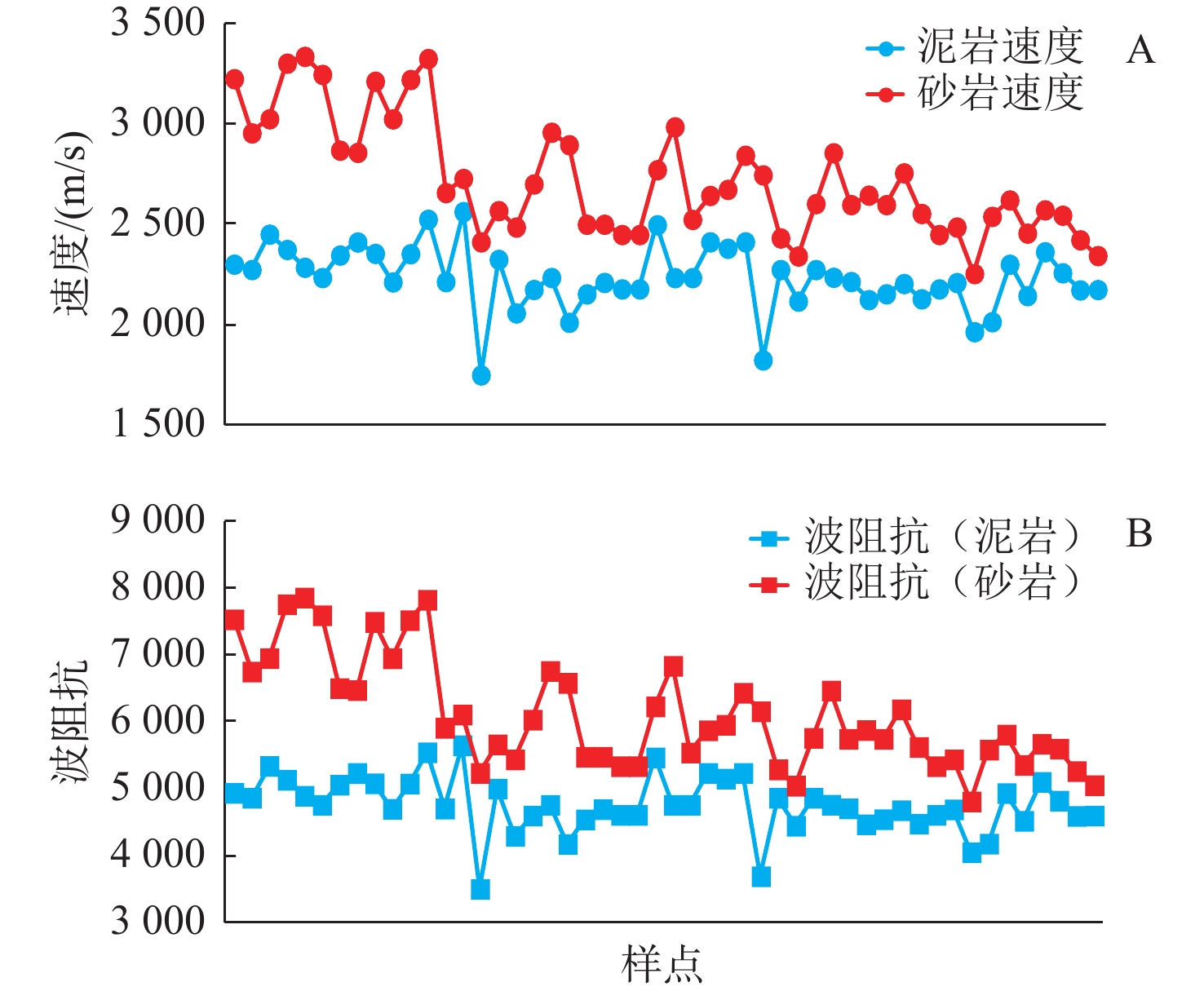
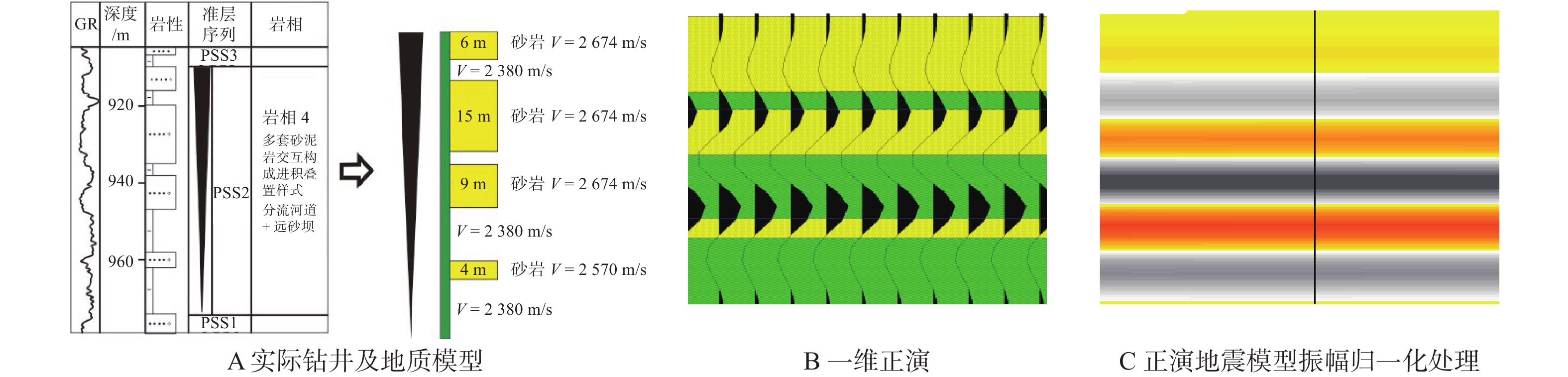
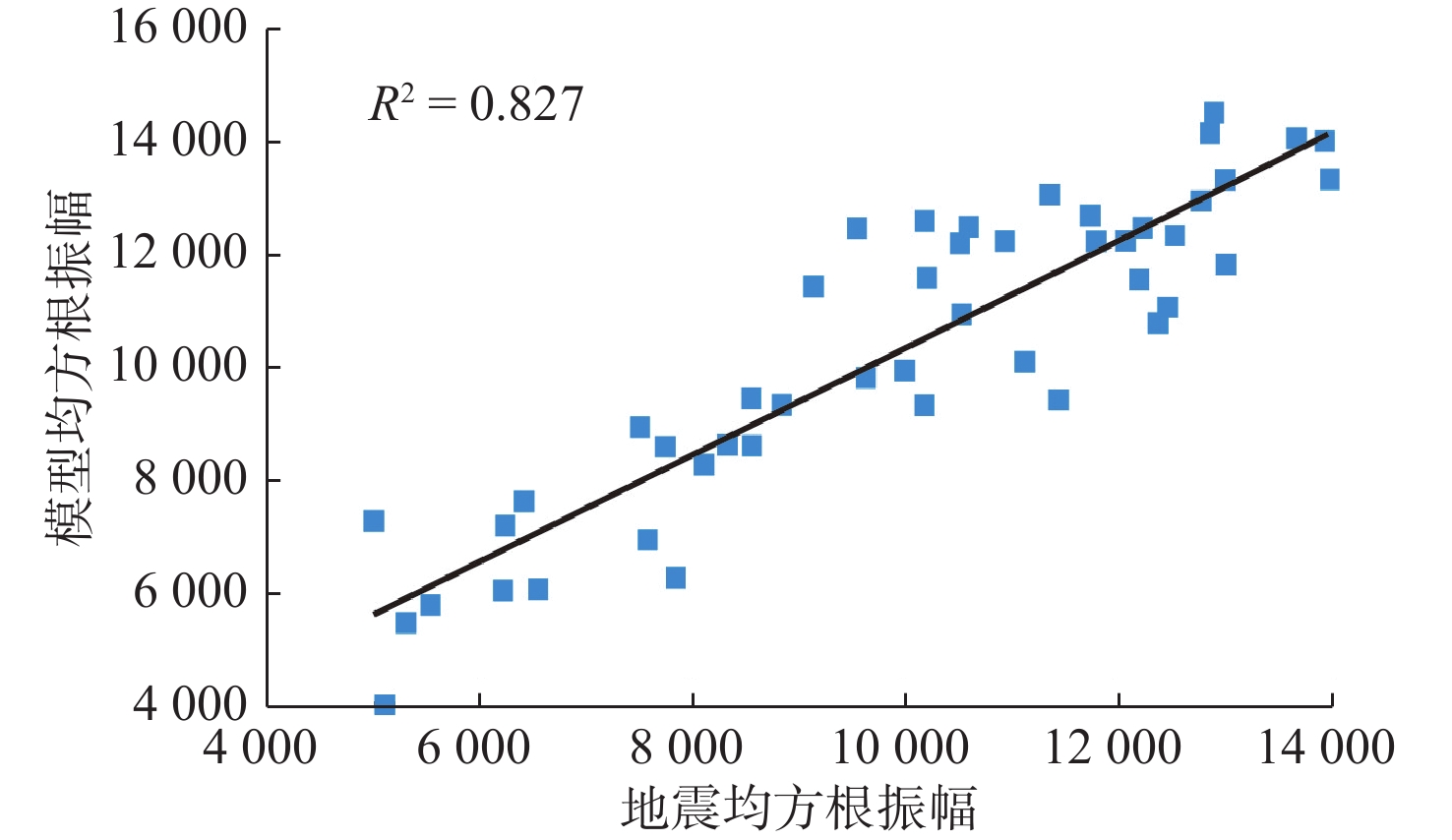
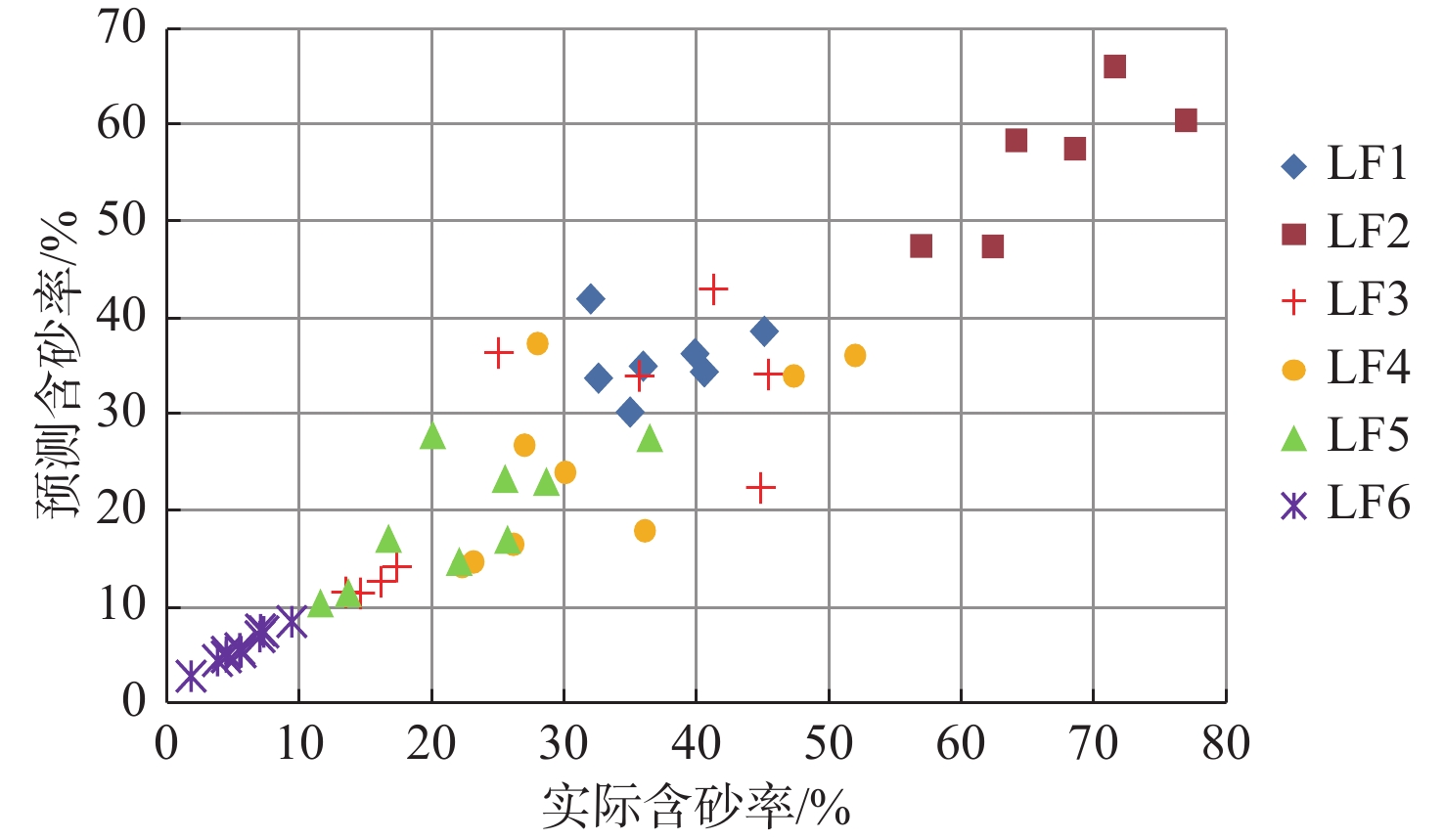
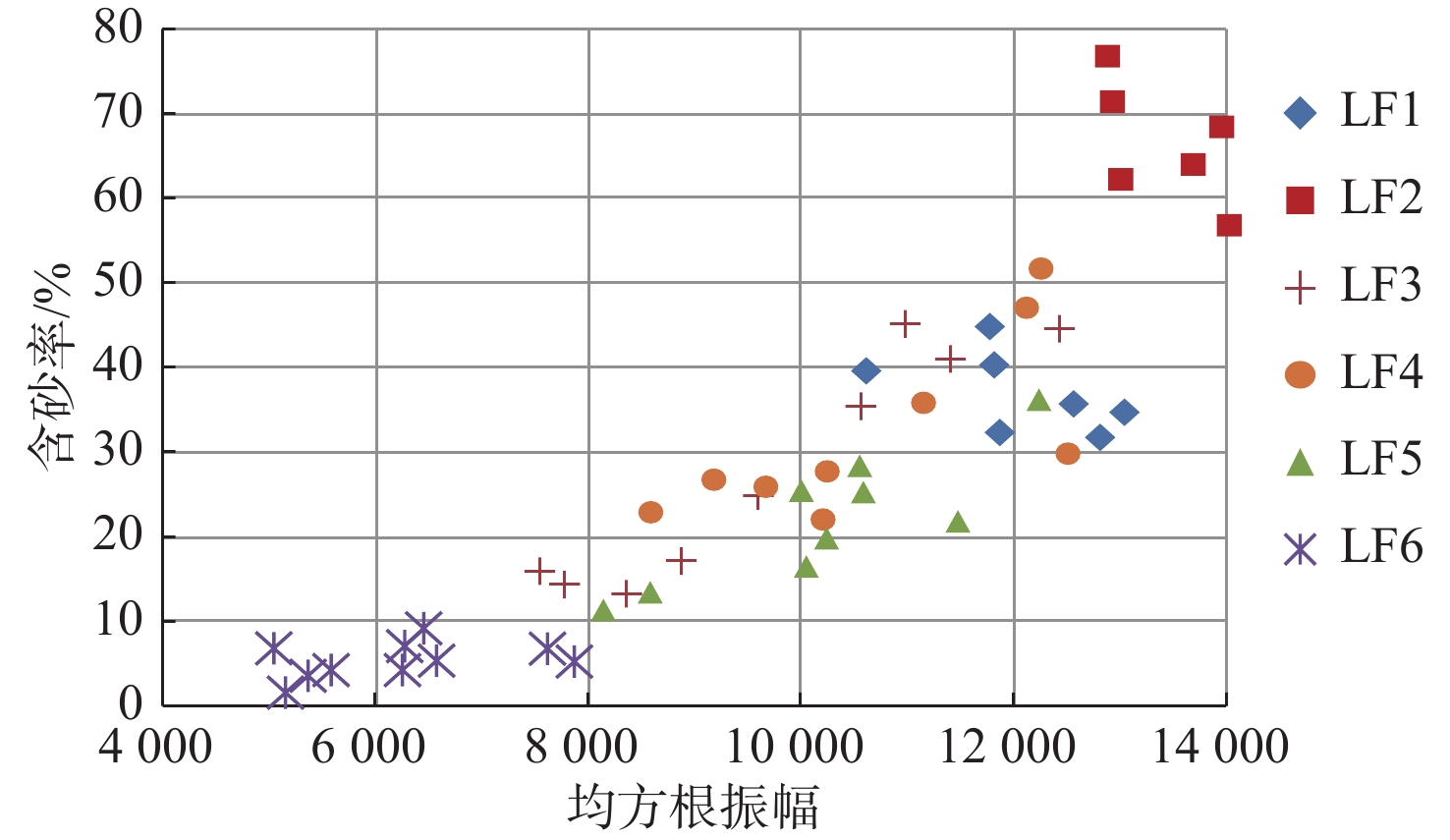
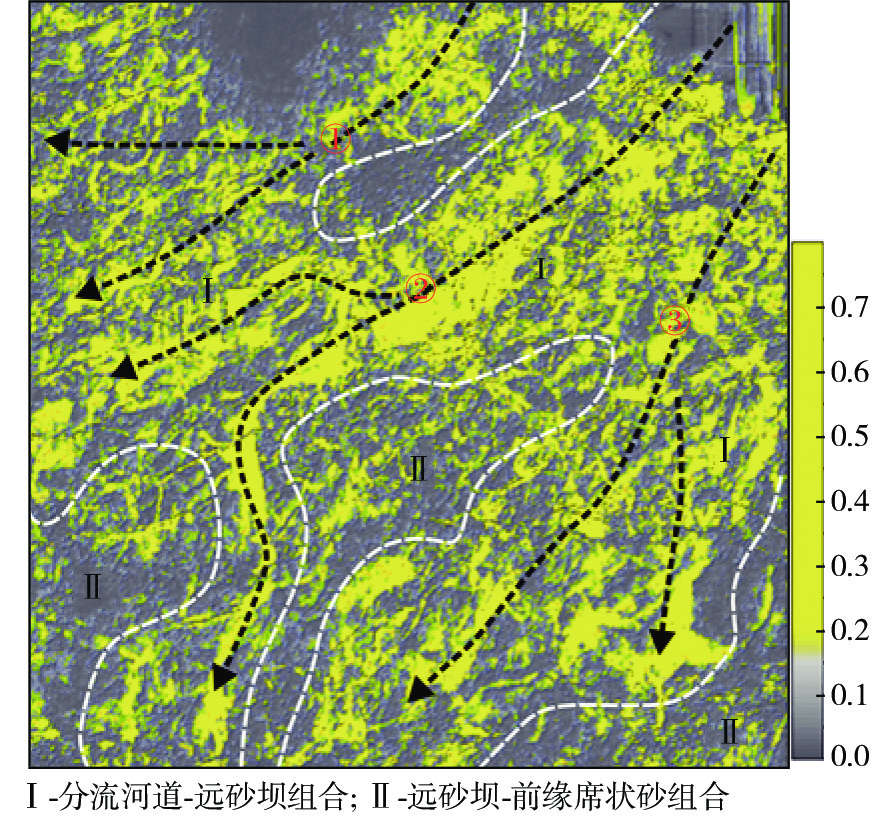
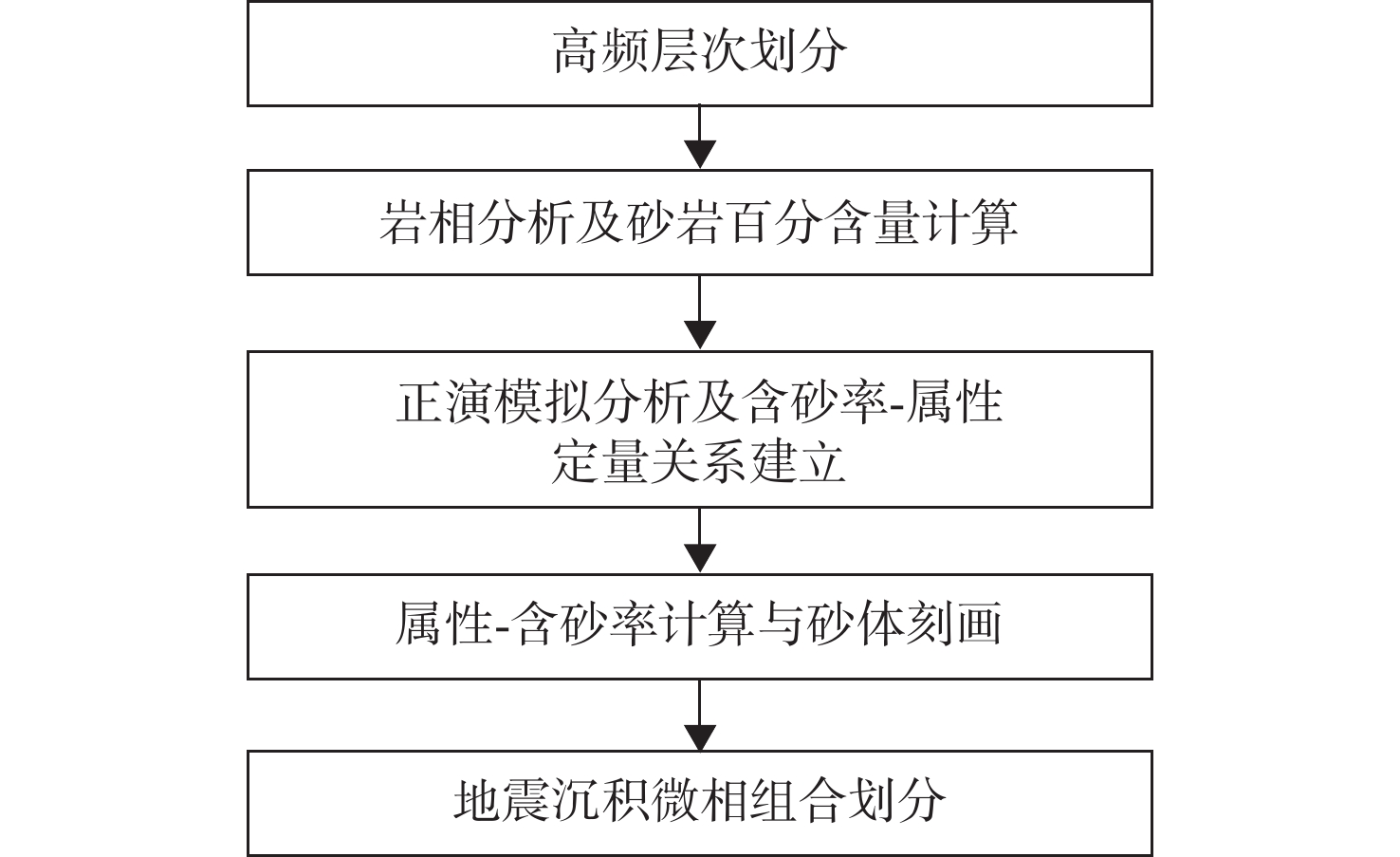
新近系浅水三角洲油气藏勘探在渤海海域油气藏勘探中占据重要地位。以渤南地区新近系明化镇组下段浅水三角洲为例,通过钻井、测井、岩芯以及地震资料综合分析,共划分了17个准层序组,并建立了高频层序地层格架,选取典型岩相提取合适参数,进行地震正演模拟建立均方根振幅与含砂率的定量关系,最终基于地震沉积学方法以砂岩百分含量与振幅的定量关系为线索进行砂岩定量化预测。结果表明,含砂率与振幅具有明显的正相关关系,采用三维地震数据振幅定量岩性解释具有较高的可靠性。利用含砂率与模型振幅的定量关系,将均方根振幅转换为含砂率值后,可以预测研究区高频层序下的含砂率分布,为沉积地貌和沉积学解释提供了更加直观的证据。该研究思路和技术方法在浅水三角洲储层研究中可以进行推广和应用。
Abstract:Exploration of the Neogene shallow-water delta plays an important role in the exploration of oil and gas reservoirs in Bohai Sea. The shallow-water delta of the lower member of Neogene Minghuazhen Formation in Bonan area was studied, from which 17 paresequencce sets were recognized based on the comprehensive analysis of drilling, logging, cores, and seismic data; and a high-frequency sequence stratigraphic framework was established. Typical lithofacies were selected to extract appropriate parameters, and seismic forward modeling was conducted to establish the quantitative relationship between amplitude and sand content. Finally, based on the seismic sedimentology method, the quantitative prediction of sandstone was carried out based on the quantitative relationship between sandstone percentage and amplitude. Results revealed an obvious positive correlation between sand content and amplitude, and it has high reliability for quantitative lithology interpretation using amplitude of 3D seismic data. By using the quantitative relationship between sand content and model amplitude, the distribution of sand content under high frequency sequences in the study area can be predicted by converting root mean square amplitude into sand content value, which provides more intuitive evidence for sedimentary geomorphology and sedimentology interpretation. This research idea and technique can be extended and applied to shallow-water delta reservoir exploration.
-
Key words:
- high-frequency sequence framework /
- amplitude /
- forward modeling /
- Neogene /
- Bonan area
-

-
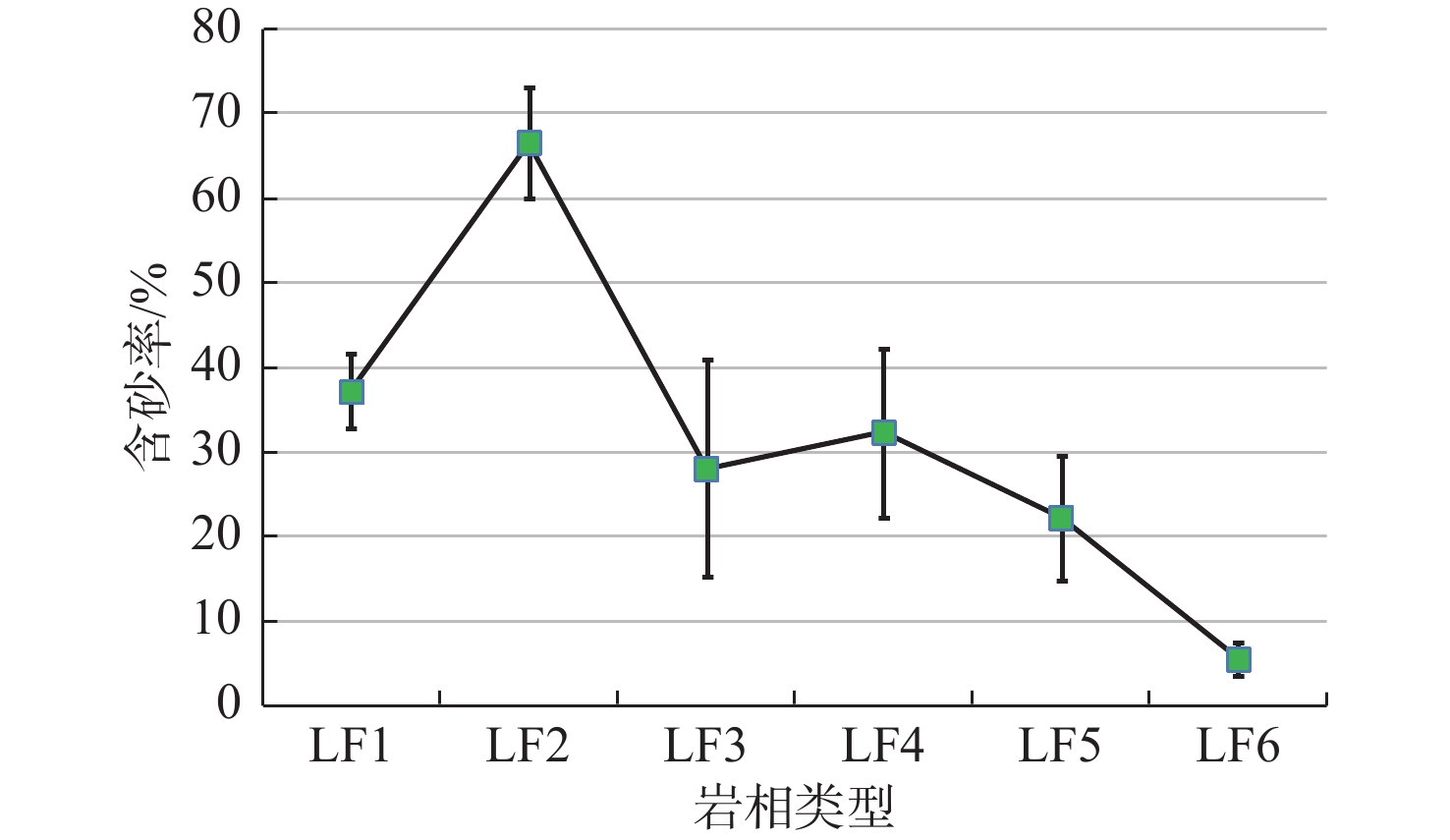
表 1 准层序组框架下岩相、岩性及沉积相特征统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of lithofacies, lithology and sedimentary facies under the framework of parasequence group
岩相类型 岩相 岩性描述 准层序组 沉积相解释 样品点 岩相1 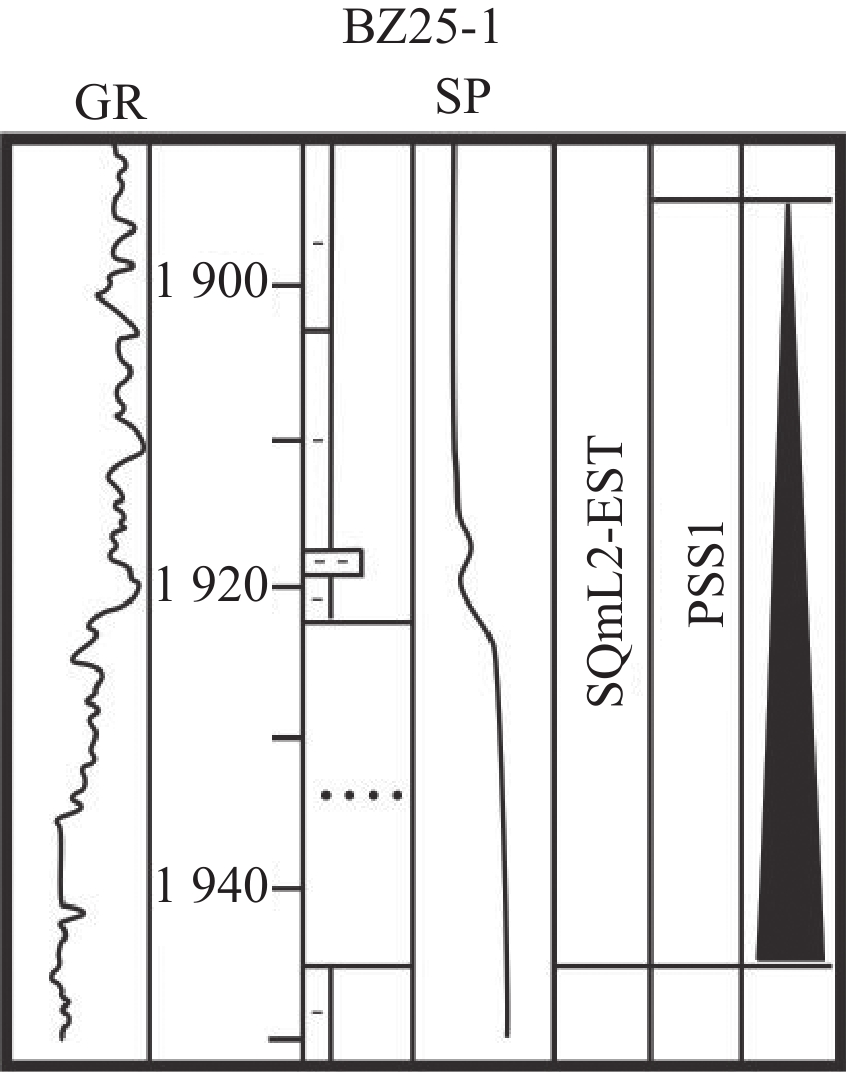
单一厚的泥岩和粗-中细砂岩组成,砂岩厚度13~22.5 m,泥岩厚度为23~27.5 m 高位域中晚期进积湖侵域早中期退积 分流河道 M1—M7 岩相2 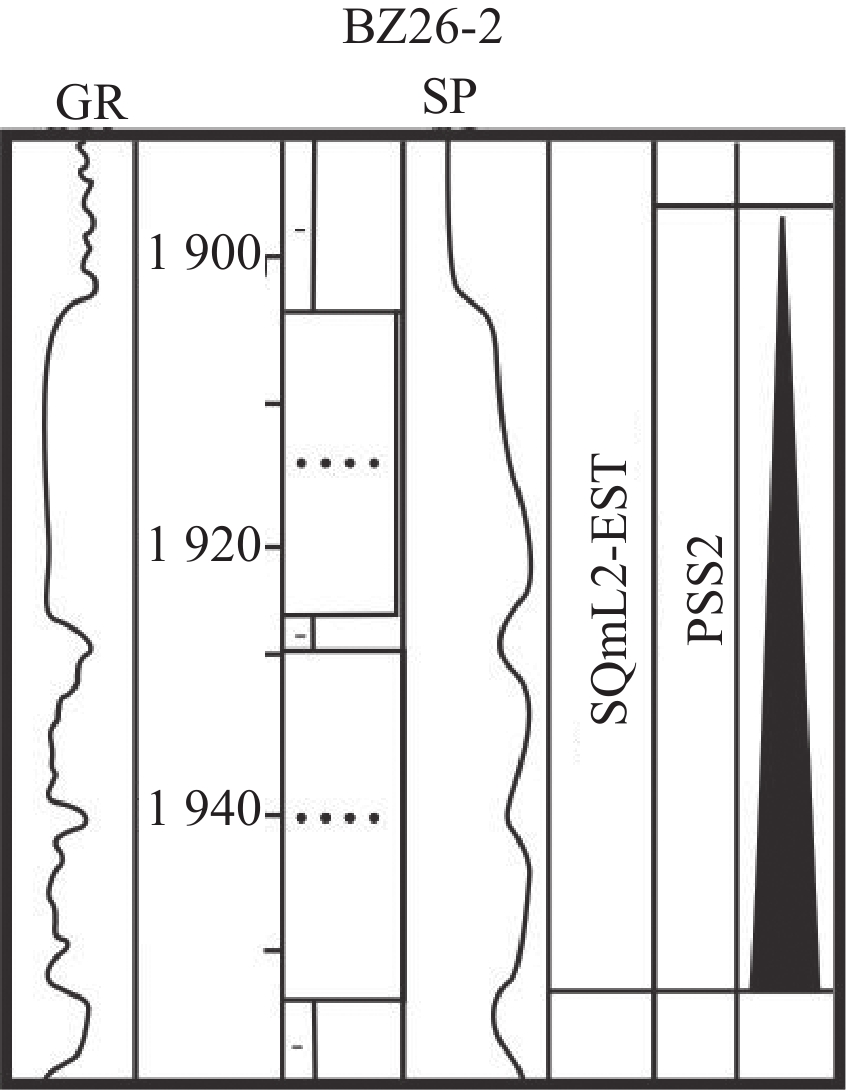
多套较厚的砂泥岩互层组合,砂岩多为中细砂岩,厚度6~15 m,大多>10 m,泥岩厚度3~7 m 湖侵域早期退积湖侵域早期加积 分流河道 M8—M13 岩相3 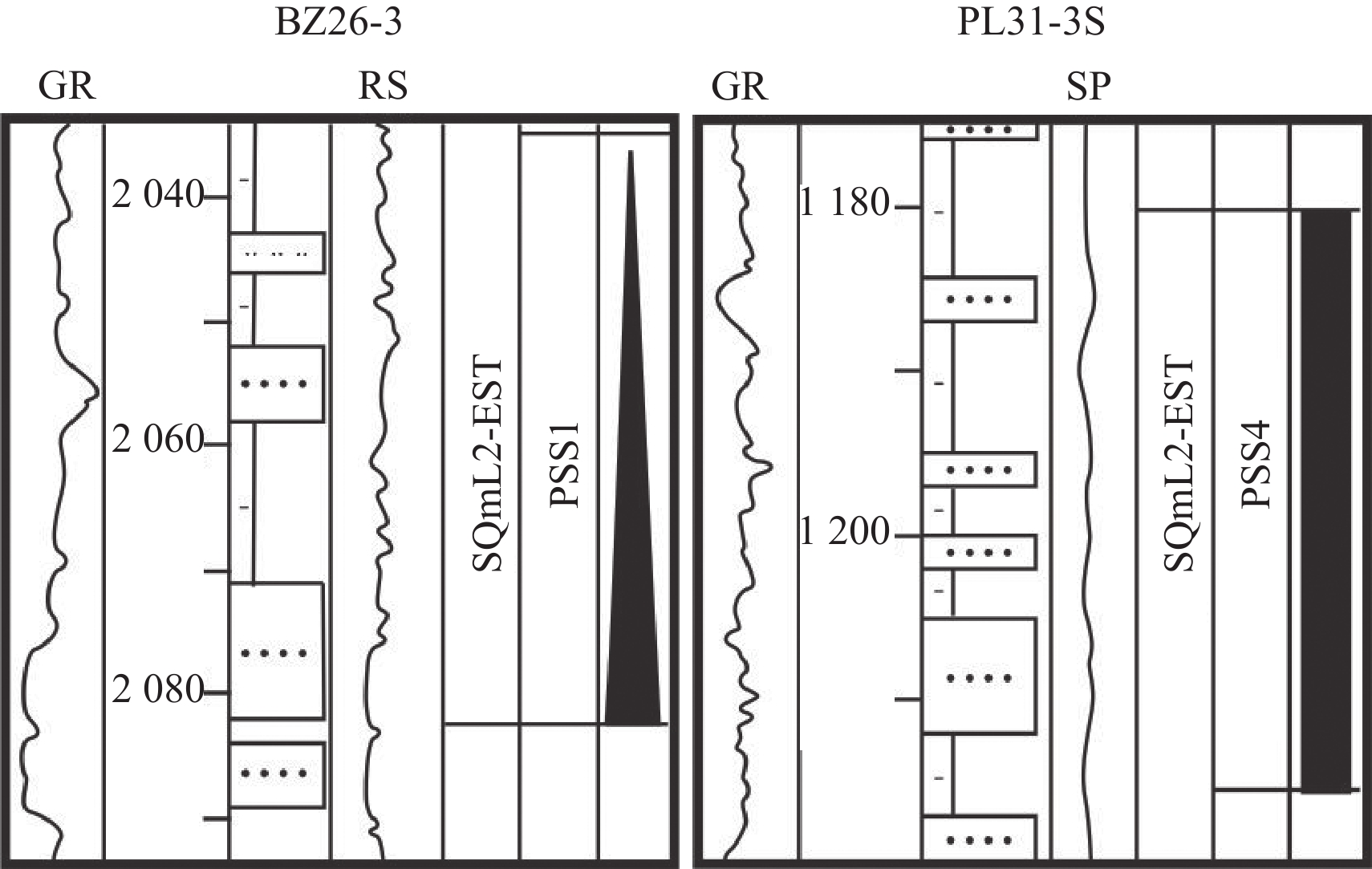
多套砂泥岩交互组合,砂岩多为中细砂岩,一般介于2~15 m,下部砂岩平均为5~15 m砂岩,最厚25 m,向上厚度减薄,泥岩厚度3~30 m,向上厚度增加 湖侵域中期退积 分流河道、远砂坝 M14—M22 岩相4 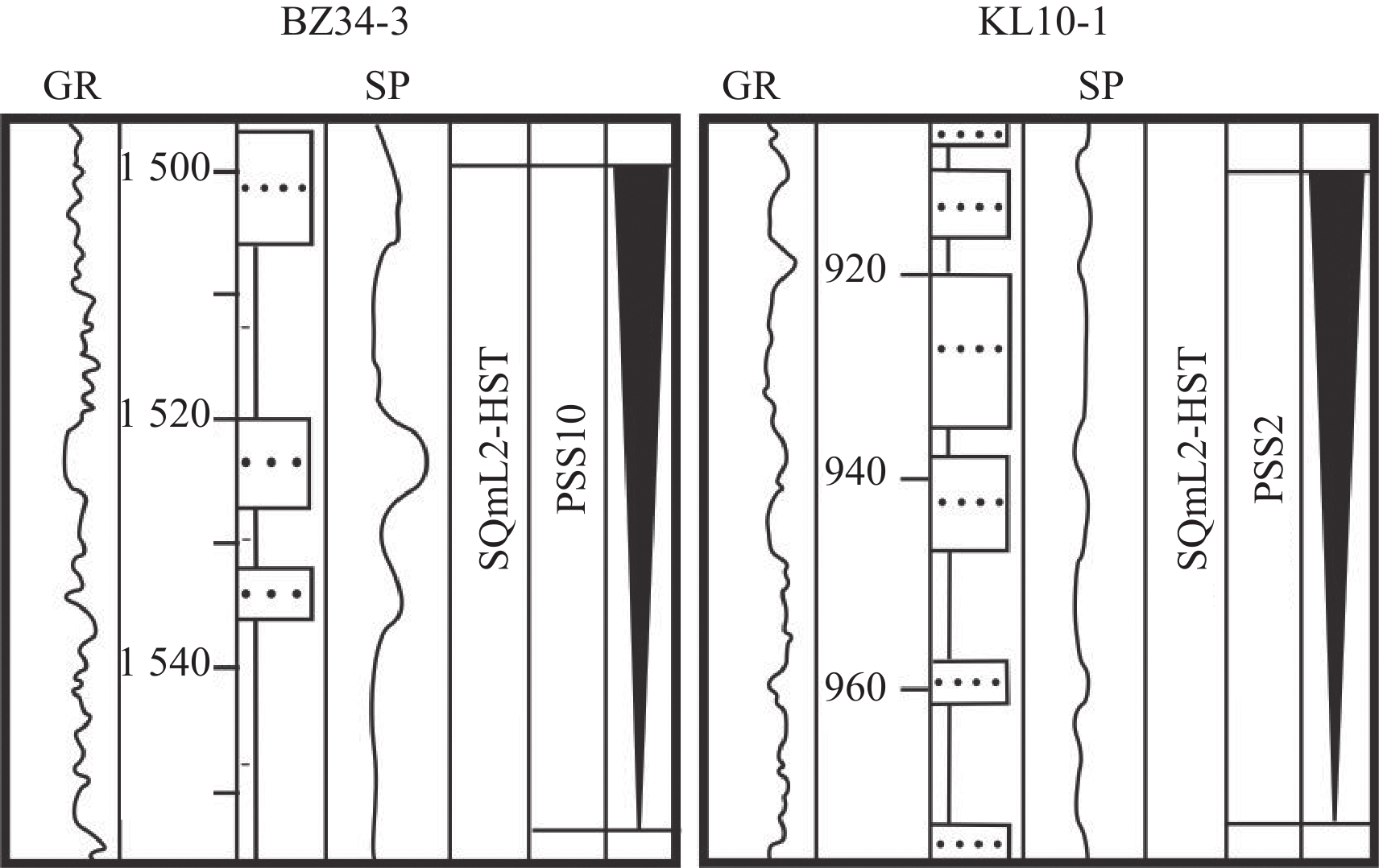
多套砂泥岩交互构成的进积叠置样式岩相组合,砂岩多为中细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,厚度介于1~15 m,上部砂岩较厚,最厚可达15 m,向下厚度减薄;泥岩厚度一般为3~20 m,向下厚度增加 高位域中晚期进积 分流河道、远砂坝 M23—M31 岩相5 
砂泥岩互层组合,砂岩岩性较细,多为细砂岩-粉砂岩,厚度不大(1~4 m),泥岩颜色较深,厚度一般为3~12 m 湖侵域晚期加积高位域早中期加积 湖水较深环境下的分流河道、远砂坝、席状砂 M32—M40 岩相6 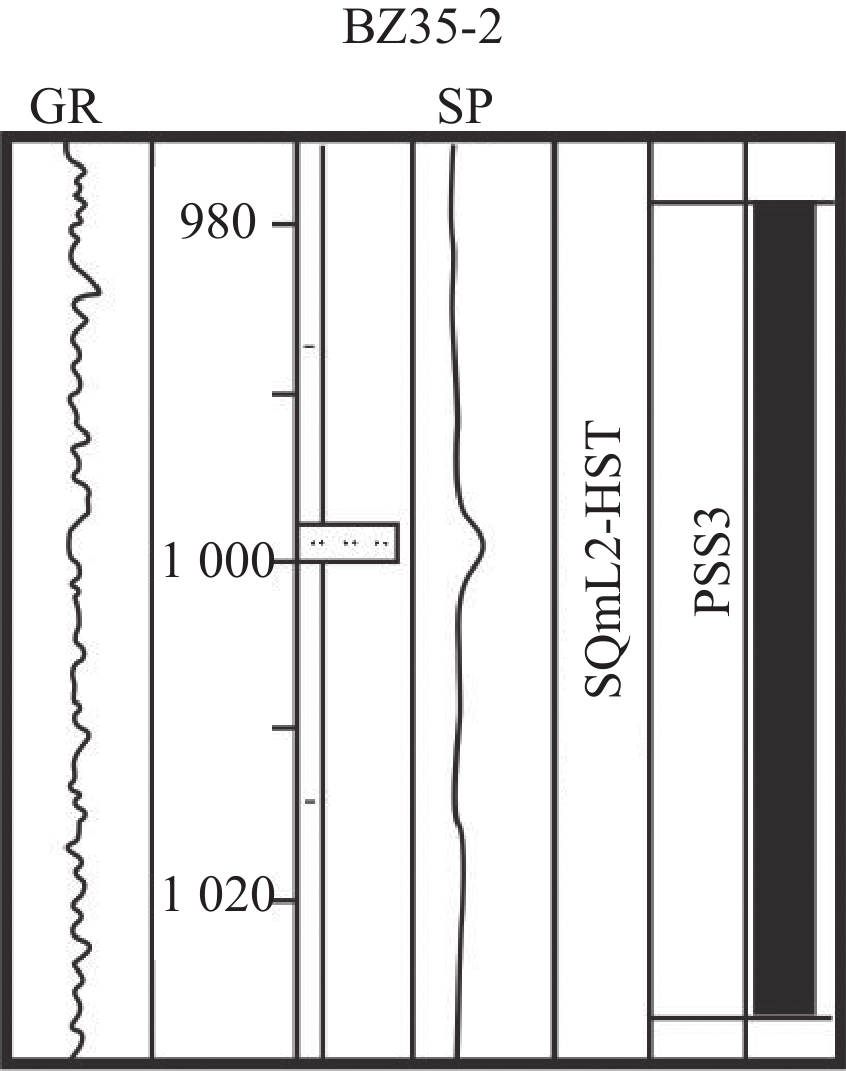
厚泥岩夹薄砂岩,砂岩以粉细砂-泥质粉砂岩为主,厚度1~4 m,泥岩厚度>25 m,最厚可达55 m 湖侵域晚期退积高位域早期进积 席状砂、砂滩 M41—M50 表 2 各岩相模型振幅统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of amplitude of each lithofacies model
岩相类型 最大振幅 最小振幅 平均振幅 岩相1 13 025 7 524 9 708 岩相2 14 025 11 004 12 628 岩相3 12 414 7 524 9 708 岩相4 12 493 8 569 10 641 岩相5 12 221 8 123 10 190 岩相6 7 850 5 023 6 245 表 3 储层预测结果与已有探井对比
Table 3. Comparison table of reservoir prediction results with existing exploration wells
钻井 预测含砂率/% 实际含砂率/% 误差率/% 预测微相 实际微相 W1 76.79 82.86 7.32 分流河道 分流河道 W2 45.31 8.26 6.11 分流河道 分流河道 W3 22.22 21.23 −4.66 远砂坝 远沙坝 W4 7.27 7.89 7.86 席状砂 席状砂 -
[1] 朱伟林,李建平,周心怀,等. 渤海新近系浅水三角洲沉积体系与大型油气田勘探[J]. 沉积学报,2008,26(4):575-582.
[2] 王德英,余宏忠,于海波,等. 渤海海域新近系层序地层格架约束下岩性圈闭发育特征分析及精细刻画-以石臼坨凸起明下段为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2012,24(S1):23-27.
[3] 张新涛,周心怀,李建平,等. 敞流沉积环境中“浅水三角洲前缘砂体体系”研究[J]. 沉积学报,2014,32(2):260-269.
[4] 陈斌,邓运华,郝芳,等. 黄河口凹陷BZ34断裂带油气晚期快速成藏模式[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(1):37-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.008
[5] 代黎明,李建平,周心怀,等. 渤海海域新近系浅水三角洲沉积体系分析[J]. 岩性油气藏,2007,19(4):75-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.04.013
[6] 邹才能,赵文智,张兴阳,等. 大型敞流坳陷湖盆浅水三角洲与湖盆中心砂体的形成与分布[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(6):813-825. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.06.011
[7] 孙和风,周心怀,彭文绪,等. 黄河口凹陷新近系浅水三角洲岩性油气藏成藏模式[J]. 大庆石油学院学报,2010,34(2):11-15.
[8] 张昌民,尹太举,朱永进,等. 浅水三角洲沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报,2010,28(5):933-944.
[9] 王德英,于海波,王启明,等. 渤海海域湖盆萎缩期浅水三角洲岩性油气藏差异成藏模式[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2018,42(3):16-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.03.002
[10] 曾洪流. 地震沉积学在中国:回顾和展望[J]. 沉积学报,2011,29(3):417-425.
[11] 曾洪流,朱筱敏,朱如凯,等. 陆相坳陷型盆地地震沉积学研究规范[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2012,39(3):75-284.
[12] 李超,廖新武,侯东梅,等. 地震沉积学在BZ19-4油田中的应用[J]. 断块油气田,2013,20(1):47-50.
[13] 王玉秀,汪利兵,韩芮,等. 地震沉积学在渤海蓬莱油田中的应用研究[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版),2014,16(6):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1980.2014.06.002
[14] 高磊,江涛,王明春,等. “富砂型”浅水三角洲储层预测及其油气成藏模式分析-以渤海西部沙垒田凸起明下段为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术,2018,40(1):27-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2018.01.05
[15] 付鑫,杜晓峰,官大勇,等. 地震沉积学在河流-浅水三角洲沉积相研究中的应用:以渤海海域蓬莱A构造区馆陶组为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):96-108.
[16] 刘豪,周心怀,田立新,等. 高频层序格架下的地质地球物理模型与砂体预测[J]. 地学前缘,2012,19(1):209-220.
[17] ZENG H L,WANG W,LIANG Q S. Seismic expression of delta to deep-lake transition and its control on lithology,total organic content,brittleness,and shale-gas sweet spots in Triassic Yanchang Formation,southern Ordos Basin,China[J]. Interpretation,2017,5(2):1-14.
[18] VAN WAGONER J C,MIT CHUM R M,CAMPION K M,et al. Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy in well logs,cores and outcrops:concepts for high-resolution correlation of time and facies[J]. AAPG Methods in Exploration Series,1990,7:1-55.
[19] CHARVIN K,HAMPSON G J,GALLAGHER K L,et al. Characterization of controls on high-resolution stratigraphic architecture in wave-dominated shoreface-shelf parasequence using inverse numeriacal modeling[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2011,81(8):562-578.
-



 下载:
下载: