The phase control modeling of porous carbonate reservoir by machine learning for the Cretaceous Mishrif Formation reservoir of H Oilfield in the Middle East
-
摘要:
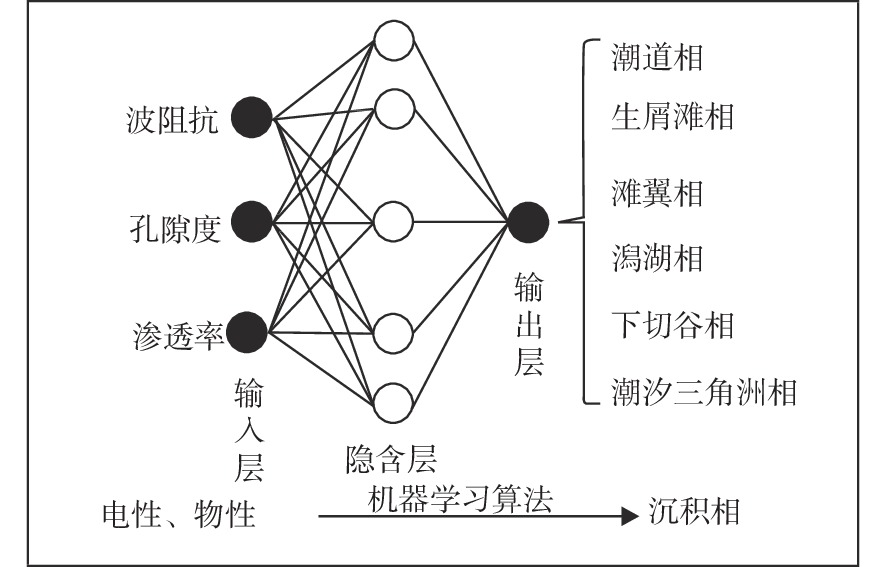
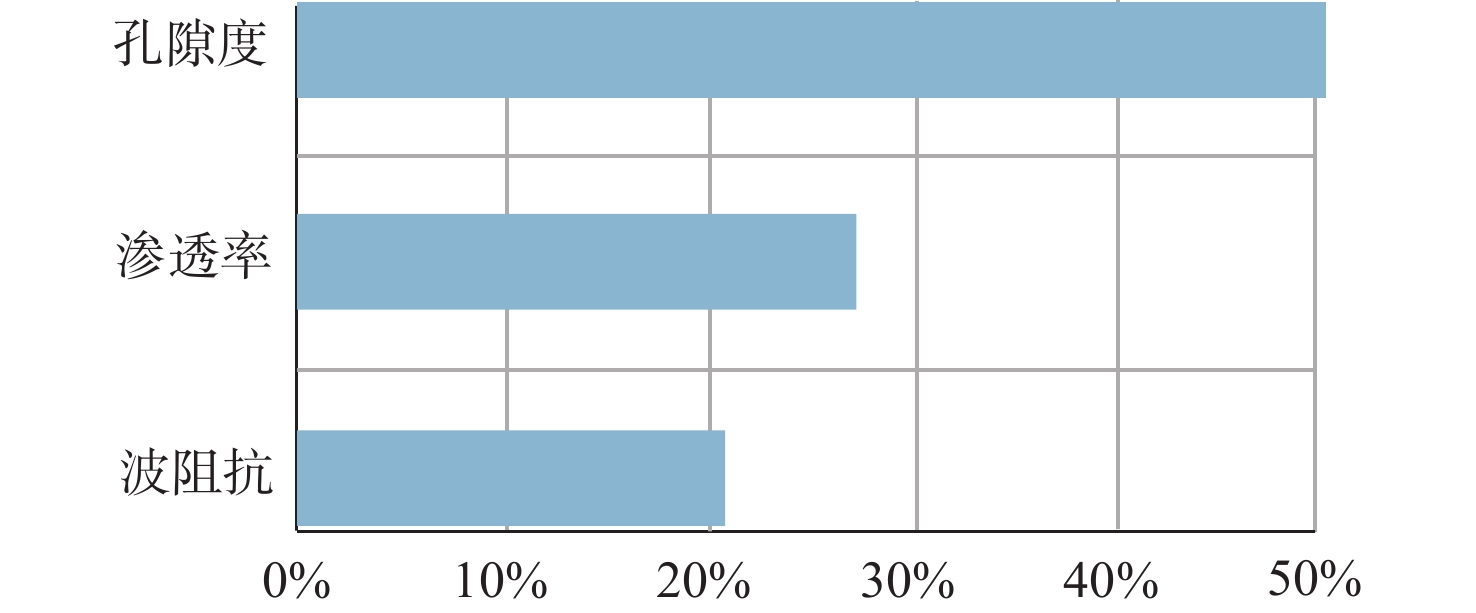
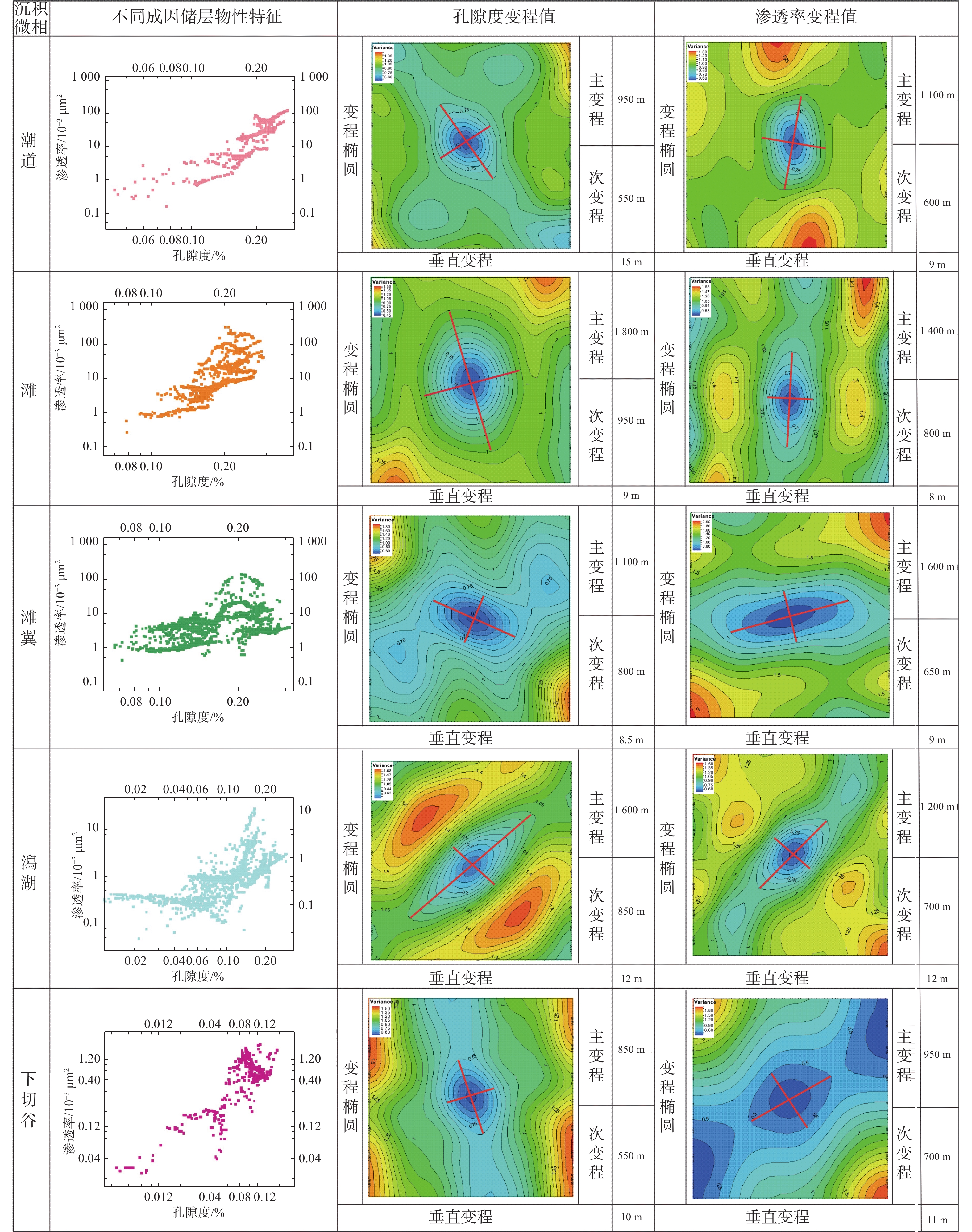
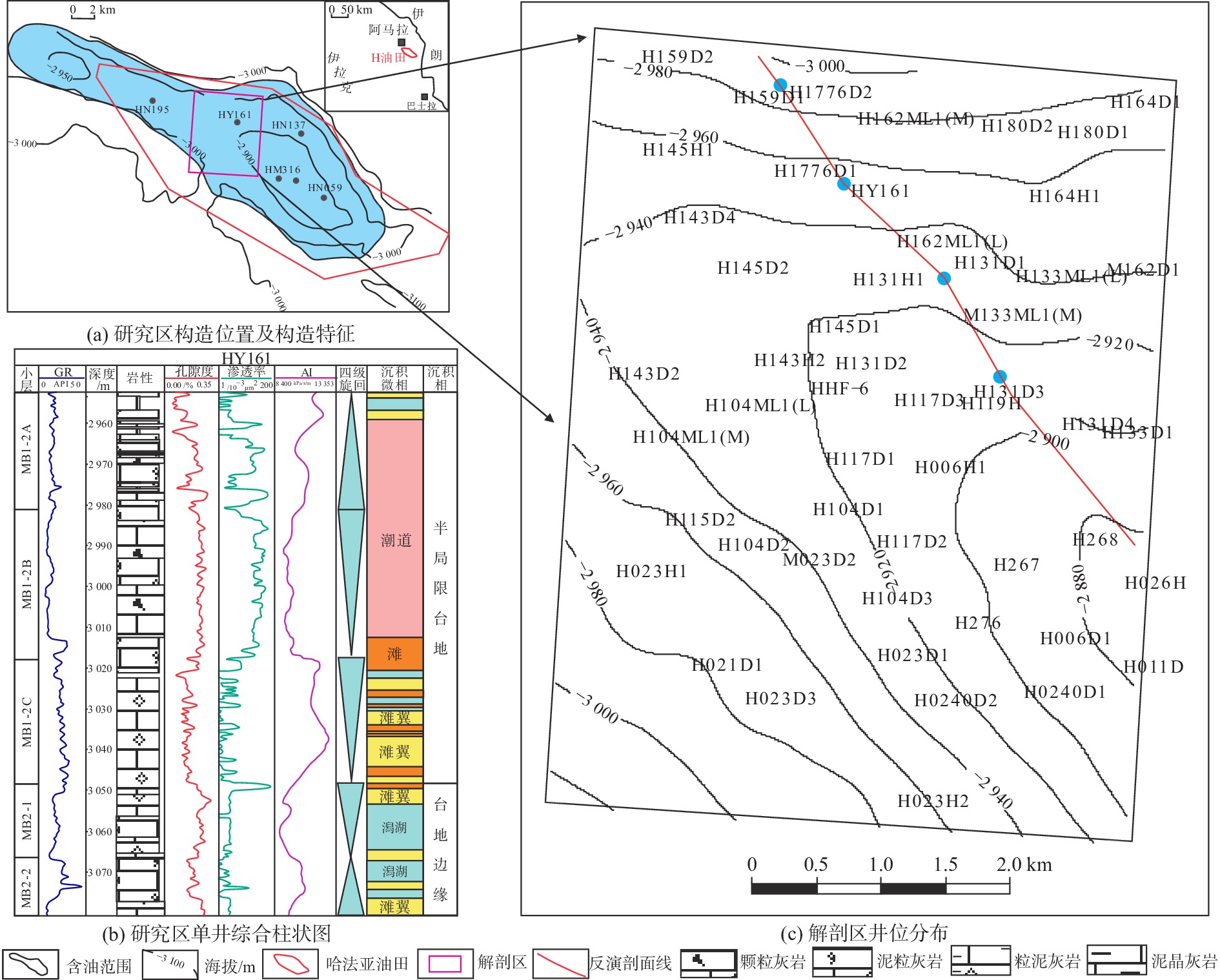
孔隙型碳酸盐岩储层的化学及机械沉积作用使得各沉积微相空间上不具备碎屑岩储层沉积微相明确的几何形态和外部结构,且不同成因储层的物性差异明显。依据常规的沉积微相建模方法难以如实地再现不同微相复杂的空间展布规律,进而也降低了相控属性建模的精度。本文以中东H油田白垩系Mishrif组生物碎屑灰岩为研究对象,通过开展波阻抗、孔隙度和渗透率的反演,利用机器学习的方法建立研究区的三维沉积微相模型。在此基础上,通过不同微相的变差函数分析,开展相控属性建模。结果表明,利用机器学习方法建立的沉积微相模型符合海相碳酸盐岩台地相序变化规律,充分体现了微相的空间形态和各微相间的接触关系,以沉积微相为约束条件建立的储层属性模型不仅满足了模拟结果与已知数据的概率一致性问题,又能分相带反映储层的空间变化特征。
Abstract:The chemical and mechanical sedimentation of porous carbonate reservoir blurs geometric shape and external structure of clastic reservoir sedimentary microfacies in space, and complicated the physical properties of reservoirs of different origins. Conventional sedimentary microfacies modeling methods are difficult to reproduce objectively the complex spatial distribution of different microfacies, thereby the accuracy of facies control attribute modeling could be reduced. Therefore, taking the Cretaceous Mishrif Formation bioclastic limestone in the Middle East H Oilfield as the research object, we established a three-dimensional sedimentary microfacies model in the study area by carrying out wave impedance inversion, porosity inversion, and permeability inversion, using machine learning methods. The phase-controlled attribute modeling was performed through the variogram analysis of different microfacies. The sedimentary microfacies model established using machine learning methods conforms to the changes in facies sequence of marine carbonate platforms, fully reflecting the spatial morphology of microfacies and the contact relationship among microfacies. The reservoir attribute model that established with the sedimentary microfacies as a constraint not only meets the requirement of probability consistency between simulation results and known data, but also reflects the spatial variation characteristics of the reservoir by phase zones.
-

-
表 1 基于机器学习沉积微相建模训练数据
Table 1. Training data of sedimentary microfacies modeling based on machine learning
I方向 J方向 K方向 沉积微相
类型孔隙度/% 渗透率/10−3 μm2 波阻抗/(g/cm3)•(m/s) 井网格 191 89 330 潮道 0.312 4 110.265 8 764.254 13 171 93 330 滩翼 0.182 6 12.456 1 1234.265 9 94 95 330 滩 0.281 4 46.325 9 165.4990 18 114 98 330 潮道 0.294 7 98.567 9 123.3808 2 134 101 330 潮道 0.334 5 89.365 7 057.1318 43 158 107 330 滩翼 0.212 4 8.362 10 476.5800 46 216 107 330 潟湖 0.144 2 5.324 10 084.6972 44 53 126 330 滩翼 0.128 2 10.362 9 208.2089 23 161 127 330 潟湖 0.180 7 7.486 9 904.0917 19 215 131 330 滩 0.286 1 45.368 8 664.0966 7 241 132 330 滩 0.262 5 14.256 8 959.1630 49 188 136 330 滩翼 0.171 9 25.321 9 057.4794 26 128 137 330 滩翼 0.226 4 13.425 9 213.25 8 207 155 330 滩 0.275 4 35.467 9 417.1972 27 137 161 330 潟湖 0.175 0 8.456 9 435.1845 20 116 166 330 潟湖 0.118 6 5.346 8 504.6259 10 68 170 330 潟湖 0.147 1 10.12 9 982.4414 34 100 170 330 滩翼 0.242 8 12.365 8 389.2607 25 44 173 330 潟湖 0.134 0 3.251 9 711.0238 33 35 137 330 潮道 0.323 9 230.536 7 435.6258 25 -
[1] 尹楠鑫,国殿斌,李中超,等. 沉积微相-岩石相随机模拟及其控制下的属性建模:以苏里格气田苏49-01加密试验区为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2015,45(3):92-98.
[2] 王大鹏. 全球古生界海相碳酸盐岩油气富集规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.
[3] 高建文. 深埋藏阶段碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程及其储层意义[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2016.
[4] 孙文举,乔占峰,邵冠铭,等. 中东H油田中白垩统Mishrif组MB1-2亚段沉积与储集层构型[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(4):713-722.
[5] GRÉLAUD C,RAZIN P,HOMEWOOD P. Channelized systems in an inner carbonate platform setting:differentiation between incisions and tidal channels (Natih Formation,Late Cretaceous,Oman)[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications,2010,329(1):163-186. doi: 10.1144/SP329.8
[6] 赵丽敏,周文,钟原,等. 伊拉克H油田Mishrif组储集层含油性差异主控因素分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(2):302-311.
[7] 云美厚,李晓斌,冯磊. 地震波速度影响因素剖析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2021,56(6):1448-1458,1204.
[8] 杨彬. 地震波阻抗反演合成记录测试分析及处理应用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014.
[9] 张海翔,李占东,李阳,等. “双控”地质建模技术的实践与认识:以渤海湾盆地SZ36-1油田为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2021,56(3):603-611,415-416.
[10] 赵鹏飞,倪军娥,李敬功,等. 渤海MN油田南区相控地质建模[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(12):33-40.
[11] 罗建民,张旗. 大数据开创地学研究新途径:查明相关关系,增强研究可行性[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(4):6-12.
[12] 王有涛. 特低渗砂砾岩储层油水层判别方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学, 2010.
[13] 李玉君,邓宏文,田文,等. 波阻抗约束下的测井信息在储集层岩相随机建模中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2006,33(5):569-571.
[14] 吴键,曹代勇,邓爱居,等. 三维地质建模技术在油田基础地质研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2005,27(2):52-55.
[15] 张淑娟. 复杂断块油藏相控储层建模研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2009.
-



 下载:
下载: