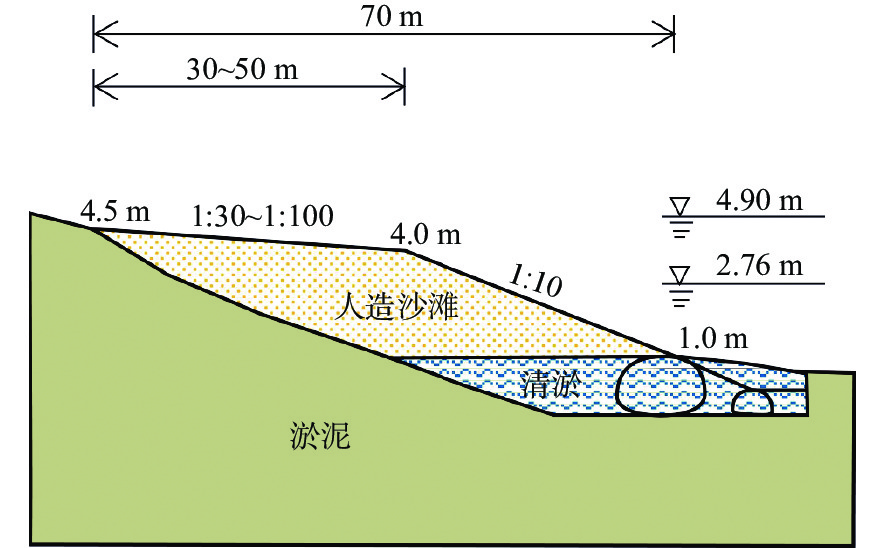
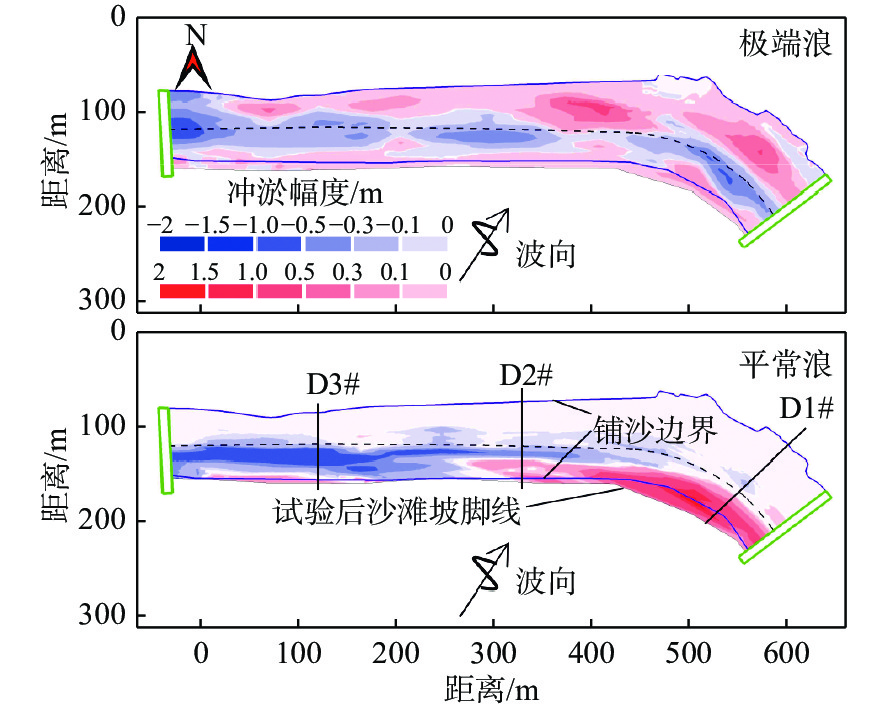
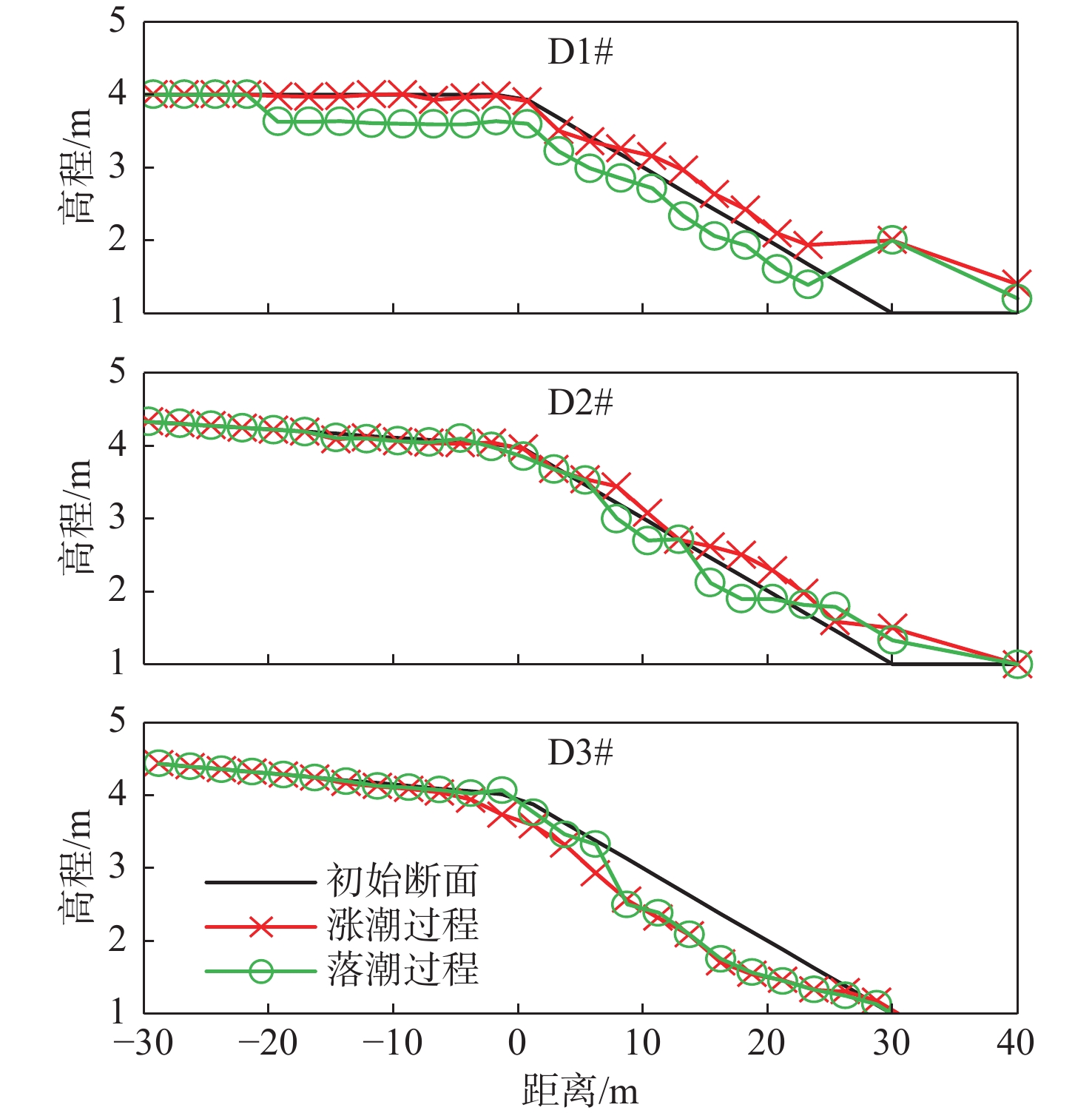
The influence of flood and ebb tide on the stability of an artificial beach
-
摘要:
为提高海湾内人造沙滩稳定性,以宁波西沪港北岸人造沙滩为研究对象,结合已有试验段人造沙滩退化过程,分析了沙源流失原因,并以此优化拟建段人造沙滩的位置,再通过波浪-泥沙物理模型试验,研究了不同强度波浪和潮位过程对拟建段人造沙滩稳定性的影响。结果表明:波浪和人造沙滩存在夹角时,沙滩前会存在明显的纵向沿岸输沙;人造沙滩建造后首年,平常浪作用1年对人造沙滩稳定性影响可能会大于单次台风浪对沙滩的作用;常浪作用下涨落潮引起的沙滩前沿水下沙坝发育过程不同,落潮水位过程波浪对沙滩的侵蚀大于涨潮水位过程;人造沙滩前落潮流和波生沿岸流方向一致,会加速沙滩侵蚀,当落潮流作用大于涨潮流,则会进一步导致沙滩严重退化。
Abstract:To improve the stability of artificial beaches, an artificial beach in the Xihu Harbor, Ningbo, Zhejiang was studied. Combined with the degradation process of the test section of the artificial beach, the reasons of sand loss were analyzed considering which section of the proposed artificial beach had been optimized. The influence of different intensity waves and tidal processes on the stability of the proposed artificial beach were studied by wave-sediment physical modelling experiment. Results indicate that when there is an angle between waves and artificial beaches, there will be significant longitudinal coastal sediment transport in front of the beach. In the first year after the construction of artificial beaches, the impact of normal wave action on the stability of artificial beaches for one year may be greater than that of a single typhoon wave on the beach. The development of underwater sand bars at the beach front caused by flood and ebb tides under normal wave action is different, and the wave erosion on the beach during ebb tide water level is greater than that during flood tide. When the directions of the ebb tide and the wave generated coastal current in front of the artificial beach are the same, the erosion of the beach will accelerate. If the effect of the ebb tide is greater than the flood tide, the degradation of the beach will further deteriorate.
-
Key words:
- artificial beach /
- stability /
- flood tide and ebb tide /
- wave /
- physical model
-

-
表 1 试验潮位和波浪组次
Table 1. Specifications of the tidal level and wave cases
组次 潮位工况 波浪工况 潮位/m 波高Hs/m 平均波周期T/s 试验时长/h 试验Ⅰ 定水位 台风浪 4.90 1.54 4.6 3 试验Ⅱ 定水位 常浪 2.76 0.49 3.5 66 试验Ⅲ 涨潮 常浪 1.76 0.49 3.5 30 2.76 0.49 3.5 30 3.76 0.49 3.5 6 试验Ⅳ 落潮 常浪 3.76 0.49 3.5 6 2.76 0.49 3.5 30 1.76 0.49 3.5 30 -
[1] 蔡锋. 中国海滩养护技术手册[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.
[2] 徐啸, 佘小建, 毛宁. 人造沙滩研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.
[3] 滕雨辰,刘爽,庄振业,等. 淤泥质海岸人造沙滩工程评估:以启东碧海银沙沙滩为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(1):77-83.
[4] 陈文超,庄振业,曹立华,等. 人工岬角对龙口市月亮湾浴场的影响机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(3):80-86.
[5] 陈海洲,谢琳. 莺歌海三莺村岸段人工沙滩工程岸线数值模拟以及模型的验证方法[J]. 海洋科学,2020,44(4):44-51.
[6] 刘建涛,王刚,陈文超,等. 北戴河西海滩潜堤岬头养滩功效研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2018,40(3):113-119.
[7] 孙连成. 天津港东疆港区人造沙滩冲淤稳定性试验研究[J]. 水运工程,2009(2):7-12.
[8] 吴明阳,张瑞波,解鸣晓,等. 潍坊滨海水城人造沙滩防护工程效果物理模型试验研究[J]. 水道港口,2015,36(6):467-473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2015.06.002
[9] 董伟良,邵杰,王卫远,等. 超强台风对沙滩侵蚀及其防护研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2021,46(4):42-47.
[10] 高峰,唐友刚,彭程,等. 港口扩建影响下近岸沙滩稳定防护三维水动力模型试验研究[J]. 海岸工程,2018,37(3):14-24.
[11] WILLIAMS J J,ROSE C P. Measured and predicted rates of sediment transport in storm conditions[J]. Marine Geology,2001,179(1/2):121-133.
[12] FRITZ H M,BLOUNT C,SOKOLOSKI R,et al. Hurricane Katrina storm surge distribution and field observations on the Mississippi Barrier Islands[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2007,74(1):12-20.
[13] FIORE M M E,ONOFRIO E E D,POUSA J L,et al. Storm surges and coastal impacts at Mar del Plata,Argentina[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2009,29(14):1643-1649. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.05.004
[14] 蔡锋,雷刚,苏贤泽,等. 台风“艾利”对福建沙质海滩影响过程研究[J]. 海洋工程,2006,24(1):98-109.
[15] 范红霞,王建中,朱立俊. 象山县西沪港海洋生态环境修复工程物理模型试验研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2015,32(3):86-90.
[16] 高佳,陈学恩,于华明. 黄河口海域潮汐、潮流、余流、切变锋数值模拟[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2010,40(S1):41-48.
[17] 刘家驹. 海岸泥沙运动研究及应用[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2009.
[18] 张宏,高涛,马杰,等. 威海湾海域治理工程物理模型试验研究[J]. 中国港湾建设,2018,38(11):41-45.
[19] 付波,张婷,黄健东,等. 广钢自备电厂取排水工程波浪泥沙试验研究[J]. 广东水利水电,2013(11):13-16.
[20] 郑金海,张弛. 海滩养护动力地貌基础理论与关键技术研究述评[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2022,53(4):791-796.
-




 下载:
下载: