Paleogene reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of high-quality reservoirs in Lufeng Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
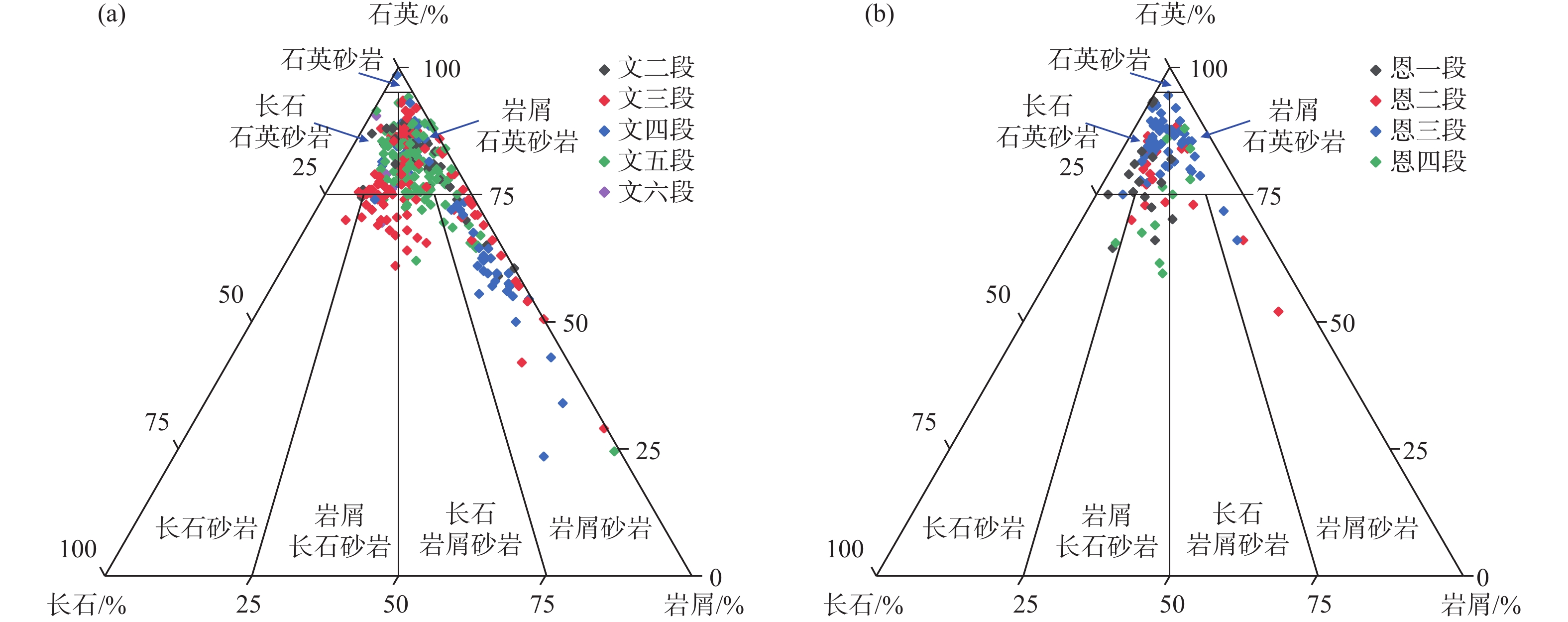
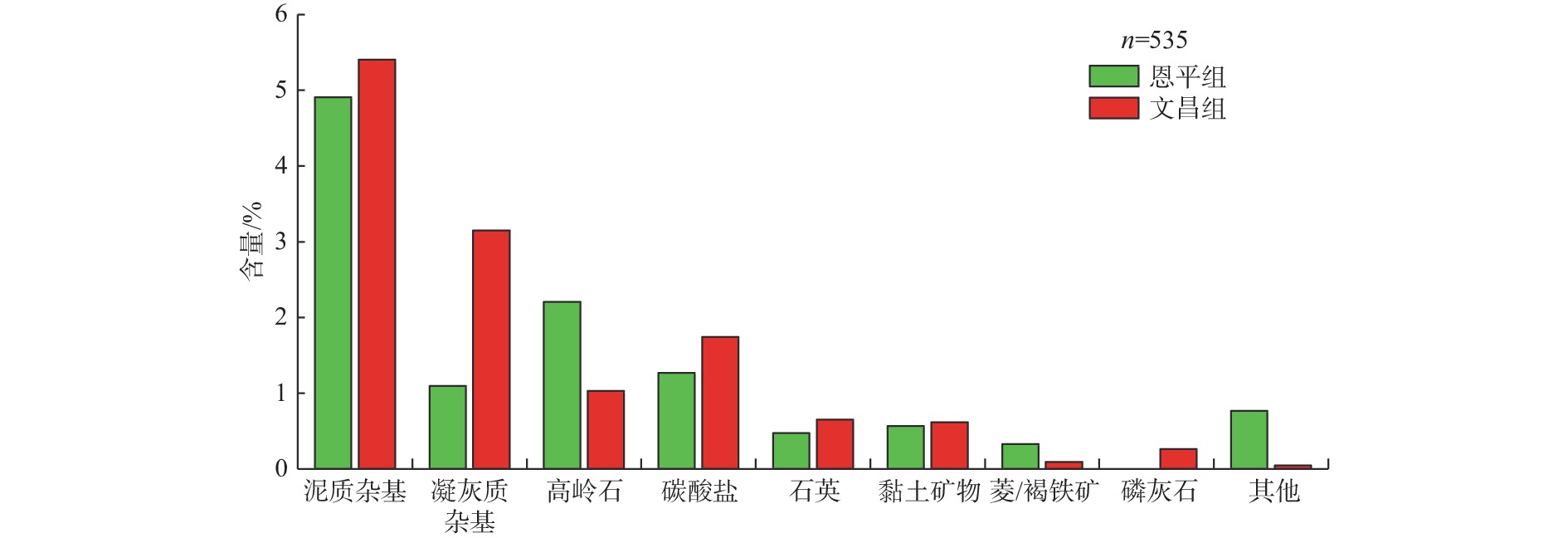
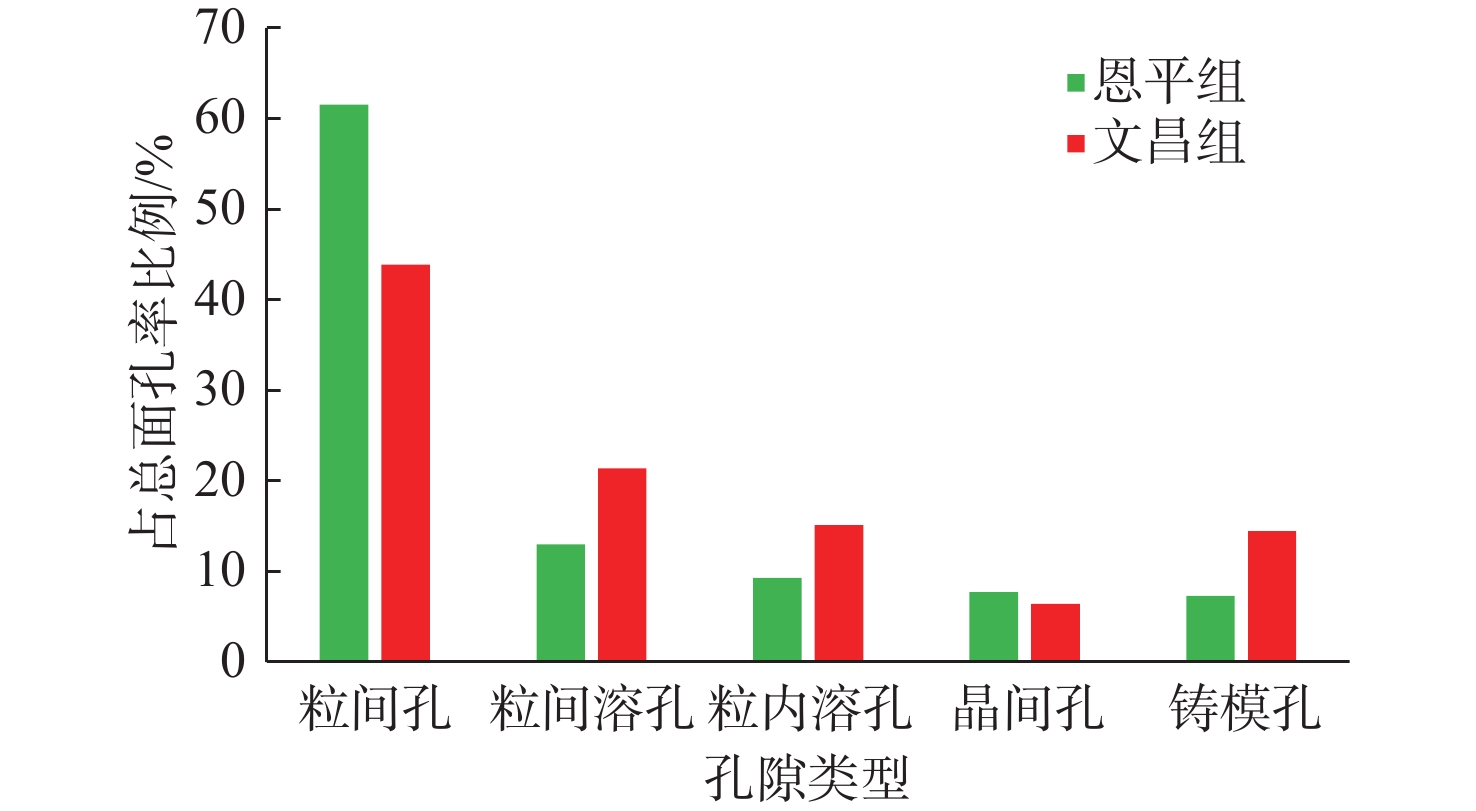
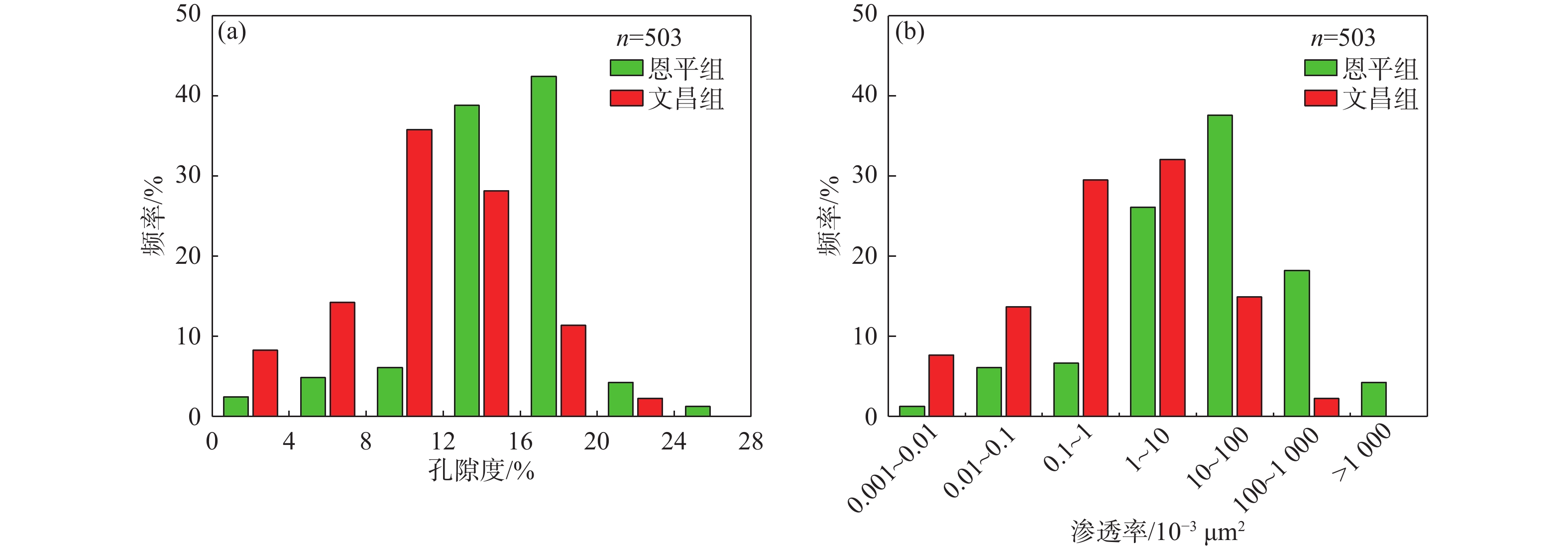
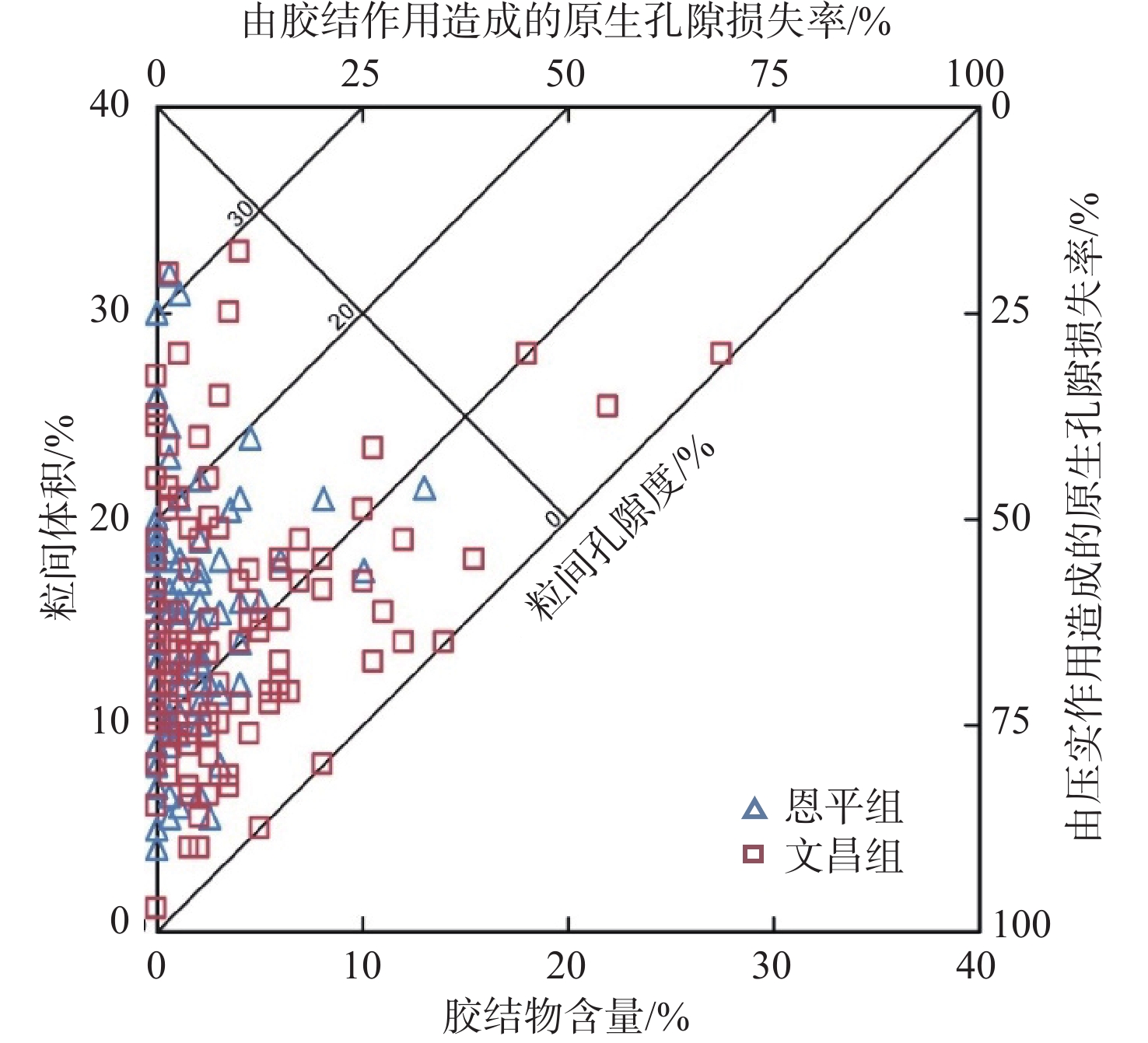
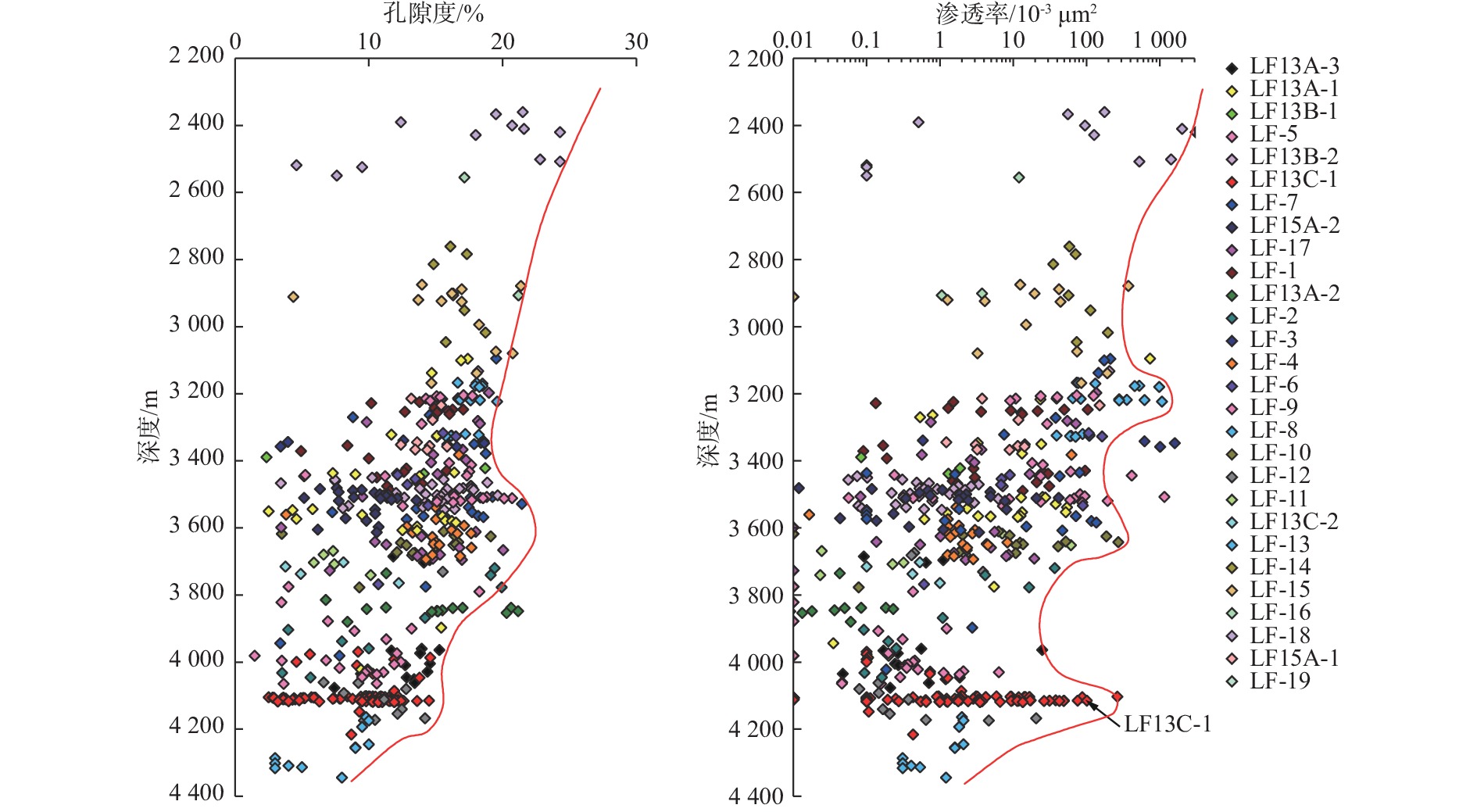
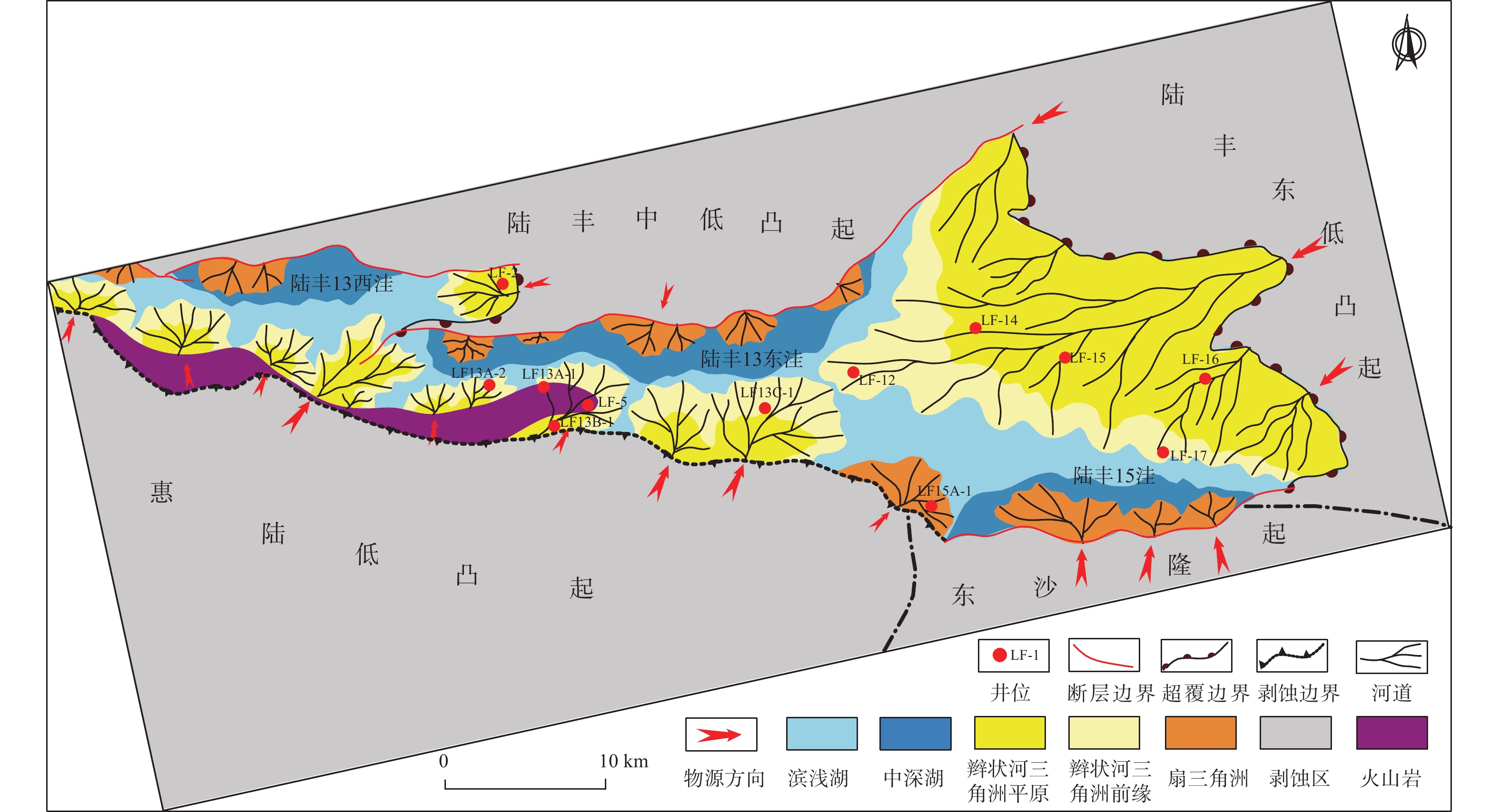
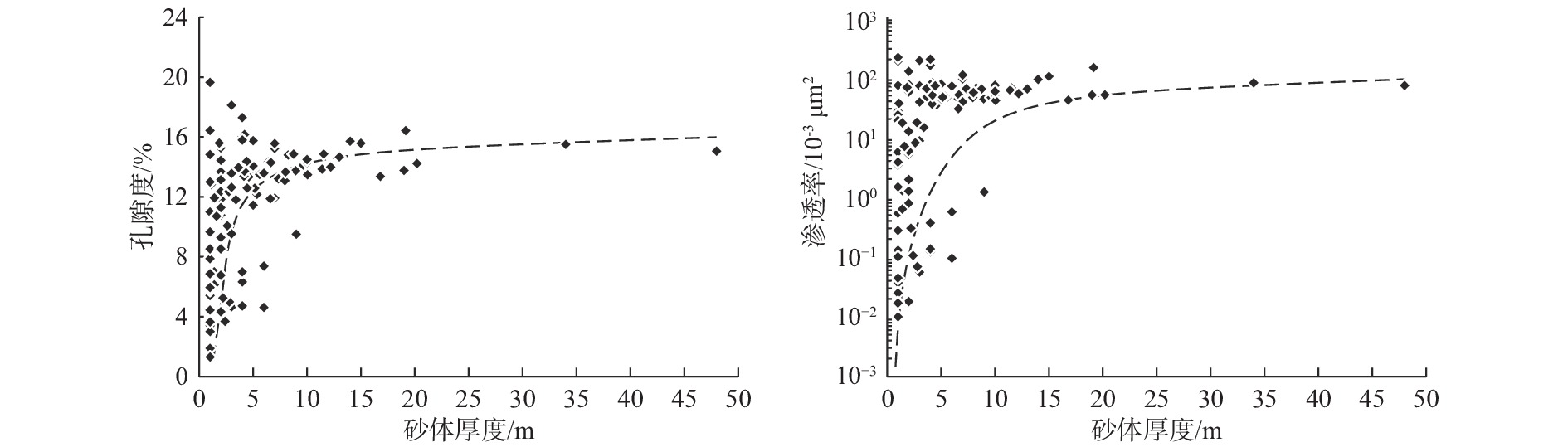
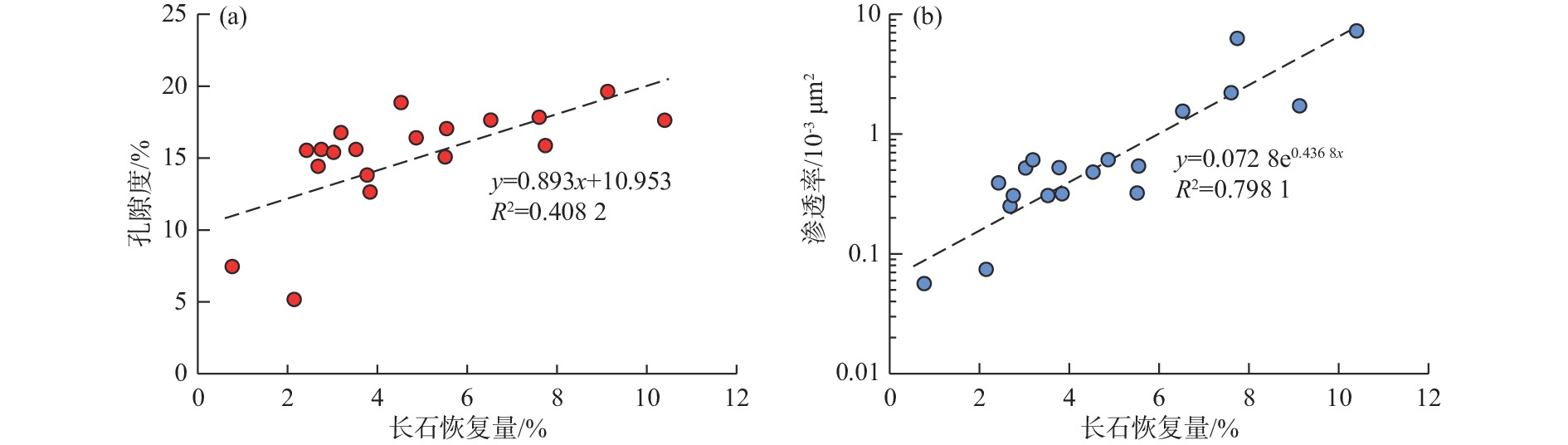
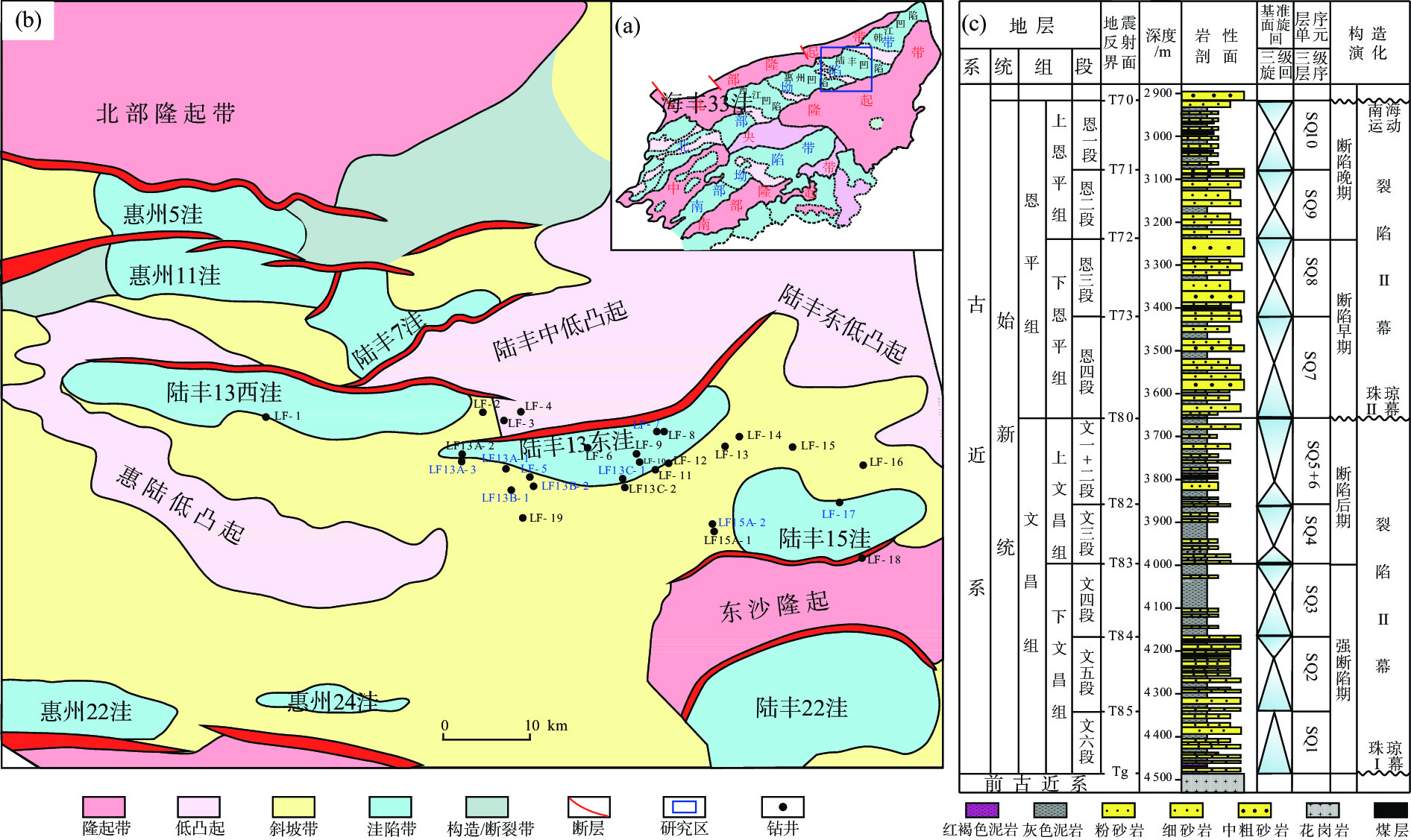
随着珠江口盆地勘探层系由浅层转向深层,古近系已成为陆丰凹陷油气“增储上产”的重要层系,但储层尚存在非均质性较强、产能释放难度大等问题,严重制约油气勘探进程。综合运用陆丰凹陷36口古近系钻井的铸体薄片、扫描电镜、物性分析、X衍射等分析化验数据,对文昌组和恩平组开展储层特征、成岩作用和优质储层主控因素研究。结果表明,陆丰凹陷古近系储层具有高石英、低长石和低岩屑含量的特征,文昌组主要发育岩屑石英砂岩,为特低—低孔隙度、超低—低渗透率储层,平均孔隙度为11.15%,平均渗透率10.93×10−3 μm2;恩平组主要发育长石石英砂岩,为低—中孔隙度、特低—中渗透率储层,平均孔隙度为15.23%,平均渗透率为139.53×10−3 μm2;储层孔隙类型以原生粒间孔为主,其次为粒间溶孔和粒内溶孔,但文昌组溶蚀孔占比高。古近系储层主要处于中成岩阶段A期,压实作用对减孔起决定性作用,胶结作用降低储层物性,溶蚀作用进一步改善储层物性。陆丰凹陷古近系优质储层形成条件包括:①母岩区石英含量高,搬运距离较远,高成分和结构成熟度,杂基含量低,单层砂体厚度大;②强流体改造改善储集空间,长石溶蚀对古近系尤其是文昌组储层改善明显,拥有良好断裂沟通源岩或临近源岩的砂岩储层溶蚀作用强;③凝灰质充填导致储层渗透率降低,低火山活动影响区更有利于优质储层发育。
Abstract:With the transformation of the exploration strata in the Pearl River Mouth Basin from shallow to deep, the Paleogene has become an important stratum to increase additional oil-gas reserves and production in the Lufeng Sag at present. However, some problems, such as strong heterogeneity and difficult productivity release, seriously restricts the oil-gas exploration. The reservoir characteristics, diagenesis, and main controlling factors of high-quality reservoirs in the Paleogene Wenchang Formation and Enping Formation were studied comprehensively using the casting thin section, scanning electron microscope, physical property analysis, X-ray diffraction and other analytical and testing data from 36 Paleogene wells in the sag. Results show that the Paleogene reservoir in the sag is rich in quartz but poor in feldspar and detritus. The Wenchang Formation is mainly composed of lithic quartz sandstone characteristic of ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability, in average porosity of 11.15% and average permeability of 10.93×10−3 μm2. The Enping Formation includes mainly feldspathic quartz sandstone characteristic of low-medium porosity and ultra-low-medium permeability reservoirs in average porosity of 15.23% and average permeability of 139.53×10−3 μm2. The reservoir pore types are mainly intergranular pores, followed by intergranular dissolution pores and intragranular dissolution pores, but the proportion of dissolved pores in Wenchang Formation is high. The Paleogene reservoir is mainly in the middle diagenetic stage A. Compaction plays a decisive role in reducing porosity, cementation reduces reservoir physical properties, and dissolution further improves reservoir physical properties. The formation conditions of the Paleogene high-quality reservoir in Lufeng Sag include: ① abundant quartz content in the parent rock area, reflecting a long transportation distance, high composition, and structural maturity, low matrix content, and large thickness of single sand body; ② strong fluid transformation that improved the reservoir space. Feldspar dissolution significantly improved the Paleogene reservoir, especially the Wenchang Formation reservoir, and the sandstone reservoir with good fracture communication source rock or adjacent source rock has strong dissolution; ③ tuffaceous filling reduced the reservoir permeability. The area less affected by volcanic activity is more conducive to the development of high-quality reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- main controlling factors /
- high-quality reservoirs /
- Paleogene /
- Lufeng Sag /
- Pearl River Mouth Basin
-

-
[1] 张向涛,汪旭东,舒誉,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷大中型油田地质特征及形成条件[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,48(11):2979-2989. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.11.021
[2] 陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
[3] 汪旭东,张向涛,何敏,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷南部文昌组储层发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2017,38(6):1147-1155.
[4] 吕正祥,文艺,赵福,等. 珠一坳陷陆丰地区文昌组成岩作用特征及孔隙发育成因[J]. 特种油气藏,2019,26(3):18-23.
[5] 朱筱敏,葛家旺,吴陈冰洁,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷深层砂岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(S1):69-80.
[6] 施和生. 论油气资源不均匀分布与分带差异富集:以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(5):1-8.
[7] 朱伟林,崔旱云,吴培康,等. 被动大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新进展与展望[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(10):1099-1109. doi: 10.7623/syxb201710001
[8] 高阳东,汪旭东,林鹤鸣,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷恩平组内部构造:沉积转换面识别及意义[J]. 天然气地球科学,2021,32(7):961-970.
[9] 张向涛,刘培,王文勇,等. 珠一坳陷古近系文昌期构造转变对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(5):1797-1813.
[10] 柳广弟,牛子铖,陈哲龙,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷在洼陷迁移控制下的油气成藏规律[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(S1):26-40.
[11] 代一丁,牛子铖,汪旭东,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷古近系与新近系油气富集规律的差异及其主控因素[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(S1):41-52.
[12] 朱定伟,张向涛,雷永昌,等. 陆丰北地区构造特征及恩平组勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(2):44-53.
[13] 葛家旺,朱筱敏,雷永昌,等. 多幕裂陷盆地构造-沉积响应及陆丰凹陷实例分析[J]. 地学前缘,2021,28(1):77-89.
[14] 何雁兵,肖张波,郑仰帝,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰13洼转换带中生界陆丰7—9潜山成藏特征[J]. 岩性油气藏,2022,35(3):1-11.
[15] 刘锐娥,李文厚,陈孟晋,等. 鄂尔多斯东部下二叠统山西组2段储层评价及勘探前景[J]. 古地理学报,2006,8(4):531-538.
[16] HOUSEKNECHT D W. Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones: Reply[J]. AAPG Bulletin. 1989, 73(10): 1277-1279.
[17] 黄思静,黄培培,王庆东,等. 胶结作用在深埋藏砂岩孔隙保存中的意义[J]. 岩性油气藏,2007,19(3):7-13.
[18] 丁琳,李晓艳,周凤娟,等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系优质储层差异发育特征及主控因素:以陆丰地区和惠州地区文昌组为例[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2022,41(1):75-86.
[19] 周凤娟,丁琳,马永坤,等. 陆丰13东洼文昌组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄特征及其物源示踪意义[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(4):46-55.
[20] 葛家旺,朱筱敏,张向涛,等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷文昌组构造-沉积演化模式[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(2):308-322.
-



 下载:
下载: