The internal structure of Liaozhong No.1 strike slip fault and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Jinzhou A Structure
-
摘要:
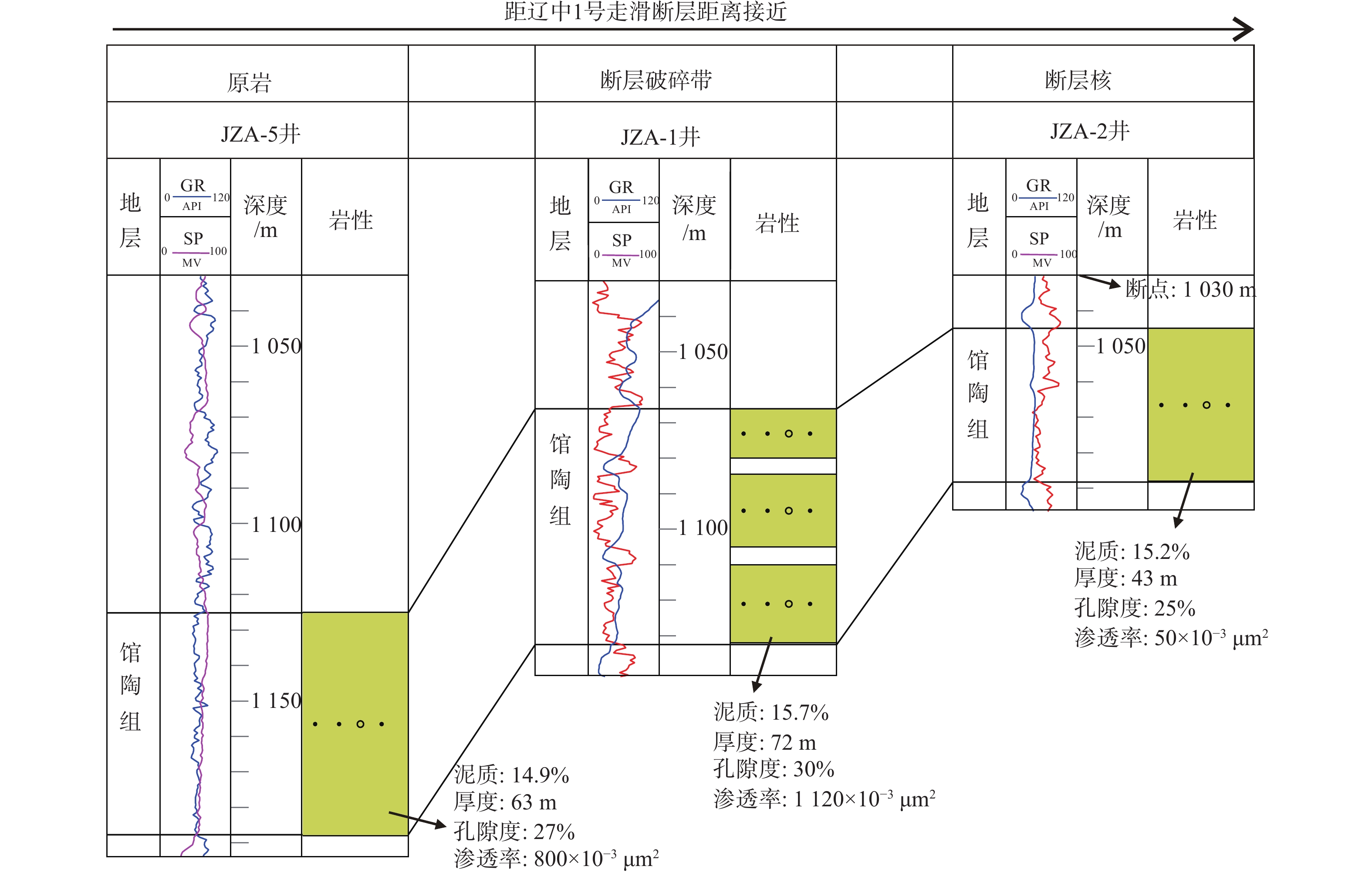
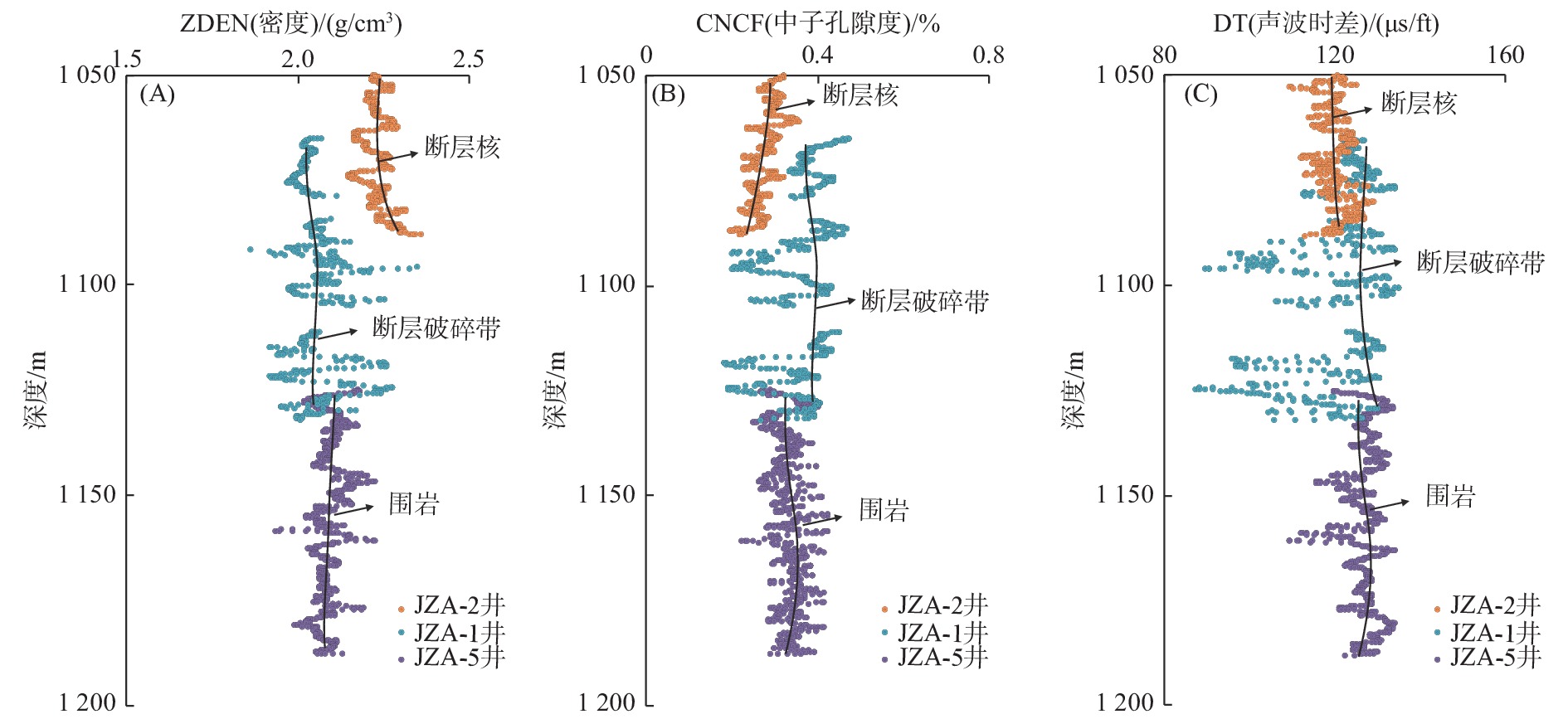
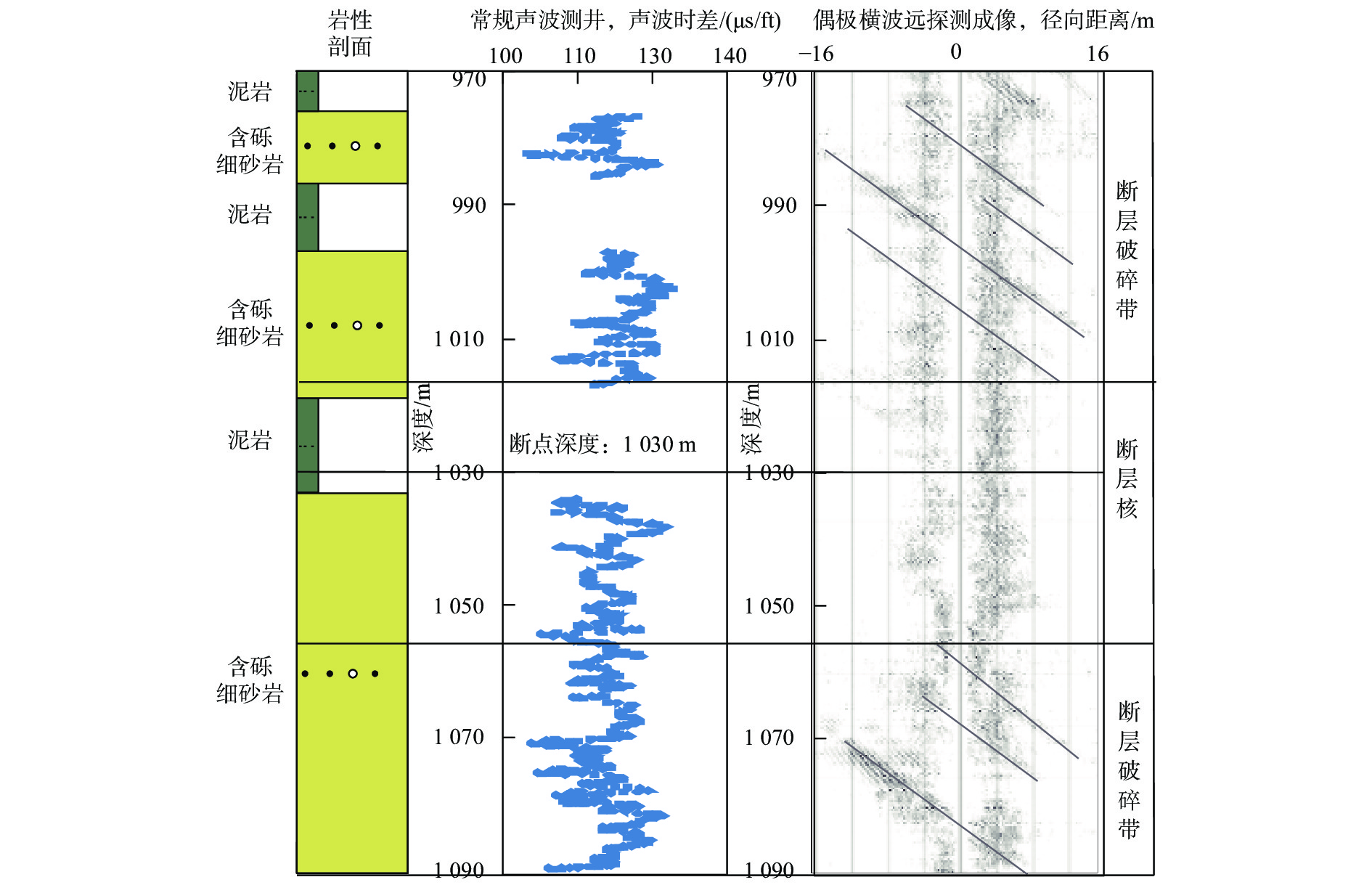
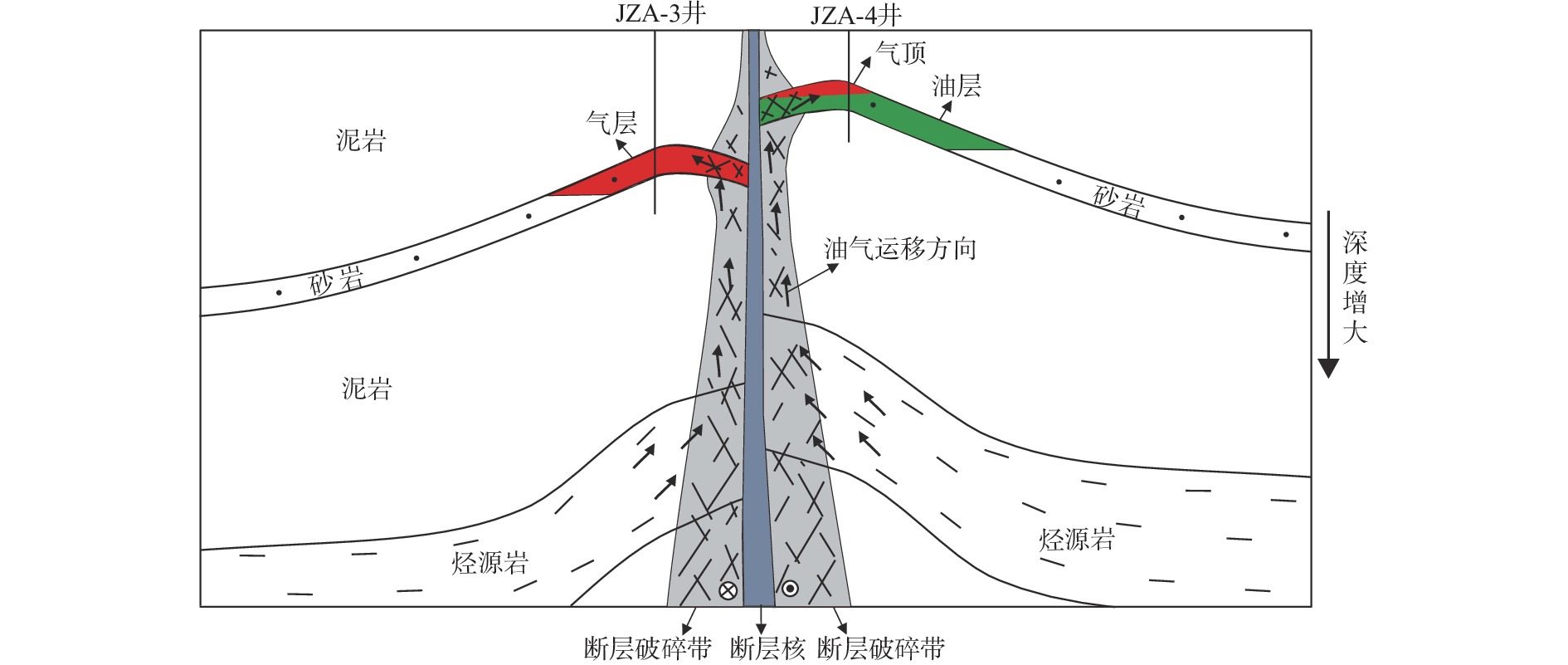
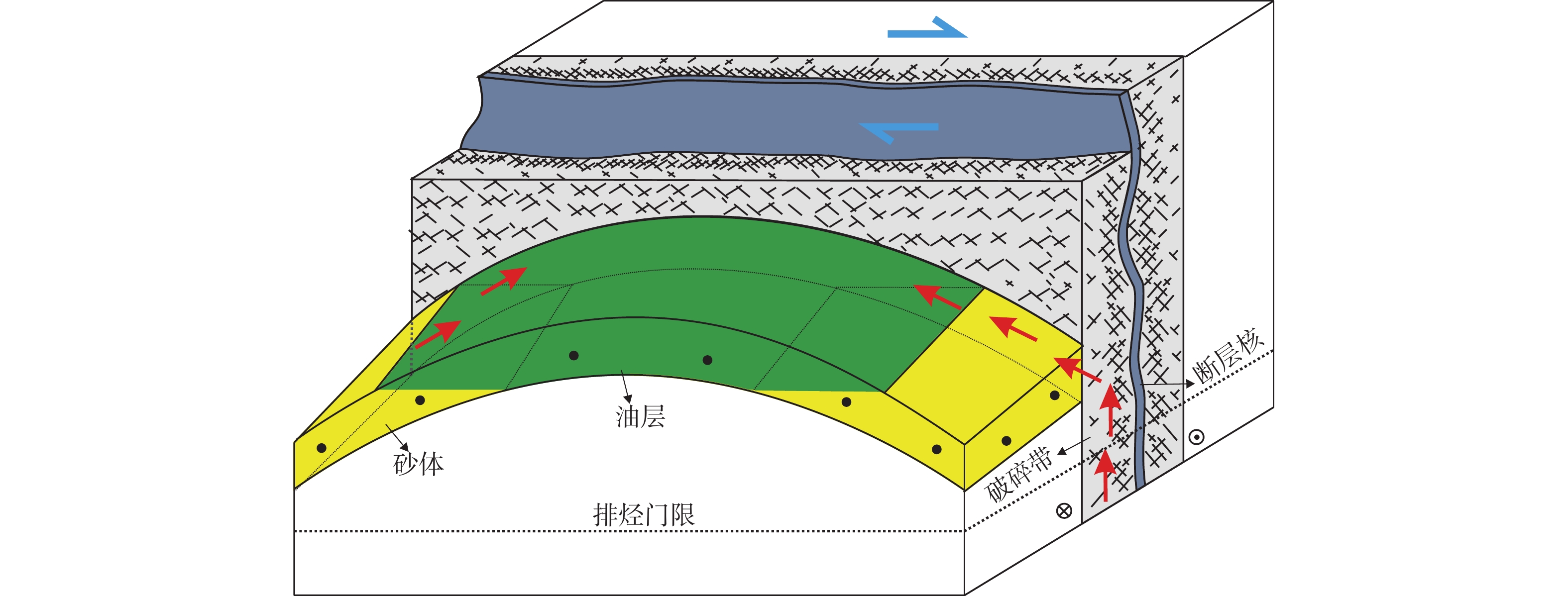
锦州A构造的发现是辽东湾海域走滑断裂带内调节断层欠发育区的首个勘探突破,为弄清该构造成藏的主控因素,利用钻井、测井、地震等资料,对锦州A 构造段辽中1号走滑断层及其内部结构开展研究,并明确其对油气成藏的控制作用。研究结果表明:地震振幅、纵波速度在走滑断层附近发生明显变化,这种变化的范围可以代表走滑断层内部结构发育的规模,从浅到深辽中1号走滑断层内部结构的发育规模变大。利用多井横向对比常规测井的密度、中子孔隙度和声波时差资料以及偶极声波远探测技术,可以识别走滑断层内部结构,随着距离走滑断层的接近, 密度资料会出现先减小再增大的趋势,中子孔隙度和声波时差资料则会出现先增大再减小的趋势,代表从围岩到断层破碎带再到断层核的发育趋势。锦州A 构造段辽中1号走滑断层发育由断层破碎带和断层核组成的二元结构,断层破碎带孔渗性好,是油气垂向运移的有利通道;断层核孔渗性差,有利于油气的侧向封堵。
Abstract:The discovery of Jinzhou A Structure (JAS) in the Liaodong Bay, NE China, marks a breakthrough of oil-gas exploration in less-developed area of accommodated fault in the Liaozhong No.1 strike-slip fault (No.1 SSF) zone. To determine the main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in the JAS, based on drilling, logging, and seismic data, the No.1 SSF and its internal structure were anatomized in the JAS, and its controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation was clarified. Results show that first, the amplitude and P-wave velocity changed obviously near No.1 SSF. The range of these changes showed that the internal structure and the scale of the No.1 SSF increased from shallow to deep. Secondly, the internal structure of the No.1 SSF was revealed by using multi-well lateral comparison in bulk density (as in ZDEN), neutron porosity (as in CNCF), and delta compression time (as in DT) data, and by using dipole acoustic reflection imaging technology. Approaching to the No.1 SSF, the ZDEN data decreased first and then increased, while the CNCF and DT data showed the opposite trend, indicating the transition from surrounding rock to fault fracture zone and then to the fault core. Thirdly, the JAS in the No.1 SSF developed a dual structure composed of fault fracture zone and fault core. The fracture zone has good porosity and permeability, which is a favorable channel for vertical migration of oil and gas, while the fault core has poor porosity and permeability, which is conducive to lateral sealing of oil and gas.
-

-
[1] BEN-ZION Y,SAMMIS C G. Characterization of fault zones[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics,2003,160(3):677-715. doi: 10.1007/PL00012554
[2] 付晓飞,肖建华,孟令东. 断裂在纯净砂岩中的变形机制及断裂带内部结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,13(1):25-35.
[3] 付晓飞. 张性断裂带内部结构特征及油气运移和保存研究[J]. 地学前缘,2012,6(2):200-210.
[4] RAWLING G C,GOODWIN L B,WILSON J L. Internal architecture,permeability structure,and hydrologic significance of contrasting fault-zone types[J]. Geology,2001,29(1):43-46. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0043:IAPSAH>2.0.CO;2
[5] 陈伟,吴智平,侯峰,等. 断裂带内部结构特征及其与油气运聚关系[J]. 石油学报,2010,31(5):84-90.
[6] 吴智平,陈伟,雪雁,等. 断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封闭性[J]. 地质学报,2010,84(4):570-578.
[7] 王孝彦,高强,孟令东,等. 低-非孔隙岩石中走滑断裂带内部结构的形成演化[J]. 断块油气田,2015,22(6):681-685.
[8] MENG L D,FU X F,WANG Y C,et al. Internal structure and sealing properties of the volcanic fault zones in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression,Songliao Basin,China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014,41(2):165-174.
[9] MITCHELL T M,FAULKNER D R. The nature and origin of off-fault damage surrounding strike-slip fault zones with a wide range of displacements:a field study from the Atacama fault system,northern Chile[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2009,31(8):802-816. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2009.05.002
[10] 周心怀,刘震,李潍莲. 辽东湾断陷油气成藏机理[M] . 北京:石油工业出版社,2009:24-26.
[11] 徐长贵. 渤海走滑转换带及其对大中型油气田形成的控制作用[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(9):1548-1560.
[12] 龚再升,蔡东升,张功成. 郯庐断裂对渤海海域东部油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油学报,2007,28(4):1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.001
[13] 吴奎,徐长贵,张如才,等. 辽中凹陷南洼走滑伴生构造带发育特征及控藏作用[J]. 中国海上油气,2016,28(3):54-60.
[14] 朱伟林,米立军,龚再升. 渤海海域油气成藏与勘探[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2009:41-44.
[15] 庆龙. 渤海海域构造形成演化与变形机制[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2012:76-78.
[16] NICOLAISEN E A. Seismic characterization of fault zones for use in fault facies reservoir models[J]. Procedia Engineering,2009,20(3):435-444.
[17] CSTCHINGS R D,RYMER M J,Goldman M,et al. High resolution seismic imaging of fault zones:methods and examples from the San Andreas Fault[C]. AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts,2011.
[18] BOTTER C,CARDOZO N,HARDY S,et al. Mechanical Modelling and Seismic Imaging of Fault Zones[C]// Fault and Top Seals 2012,EAGE,Session:Geomechanical modelling in Seal Evaluation. 2012.
[19] BOTTER C,CARDOZO N,HARDY S,et al. From mechanical modeling to seismic imaging of faults:a synthetic workflow to study the impact of faults on seismic[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2014,57:187-207. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.05.013
[20] BOTTER C,CARDOZO N,HARDY S,et al. Seismic characterisation of fault damage in 3D using mechanical and seismic modelling[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2016,77:973-990. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.002
[21] 刘伟,朱留芳,许东晖. 断裂带结构单元特征及其测井识别方法研究[J]. 测井技术,2013,37(5):495-498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2013.05.008
[22] ZHANG G,LI N,GUO H W,et al. Fracture identification based on remote detection acoustic reflection logging[J]. Applied Geophysics,2015,12(4):473-481. doi: 10.1007/s11770-015-0522-0
[23] 陈伟. 含油气盆地断裂带内部结构特征及其与油气运聚的关系[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东),2011.
[24] TANG X M,GLASSMAN H,PATTERSON D,et al. Single-well acoustic imaging in anisotropic formations[C]//SEG, San Antonio Annual Metting,2007:109-113.
[25] 唐晓明,魏周拓,苏远大,等. 偶极横波远探测测井技术进展及其应用[J]. 测井技术,2013,37(4):333-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2013.04.001
-




 下载:
下载: