Early prediction of source rocks in Zhongjiannan Basin in low exploration area
-
摘要:
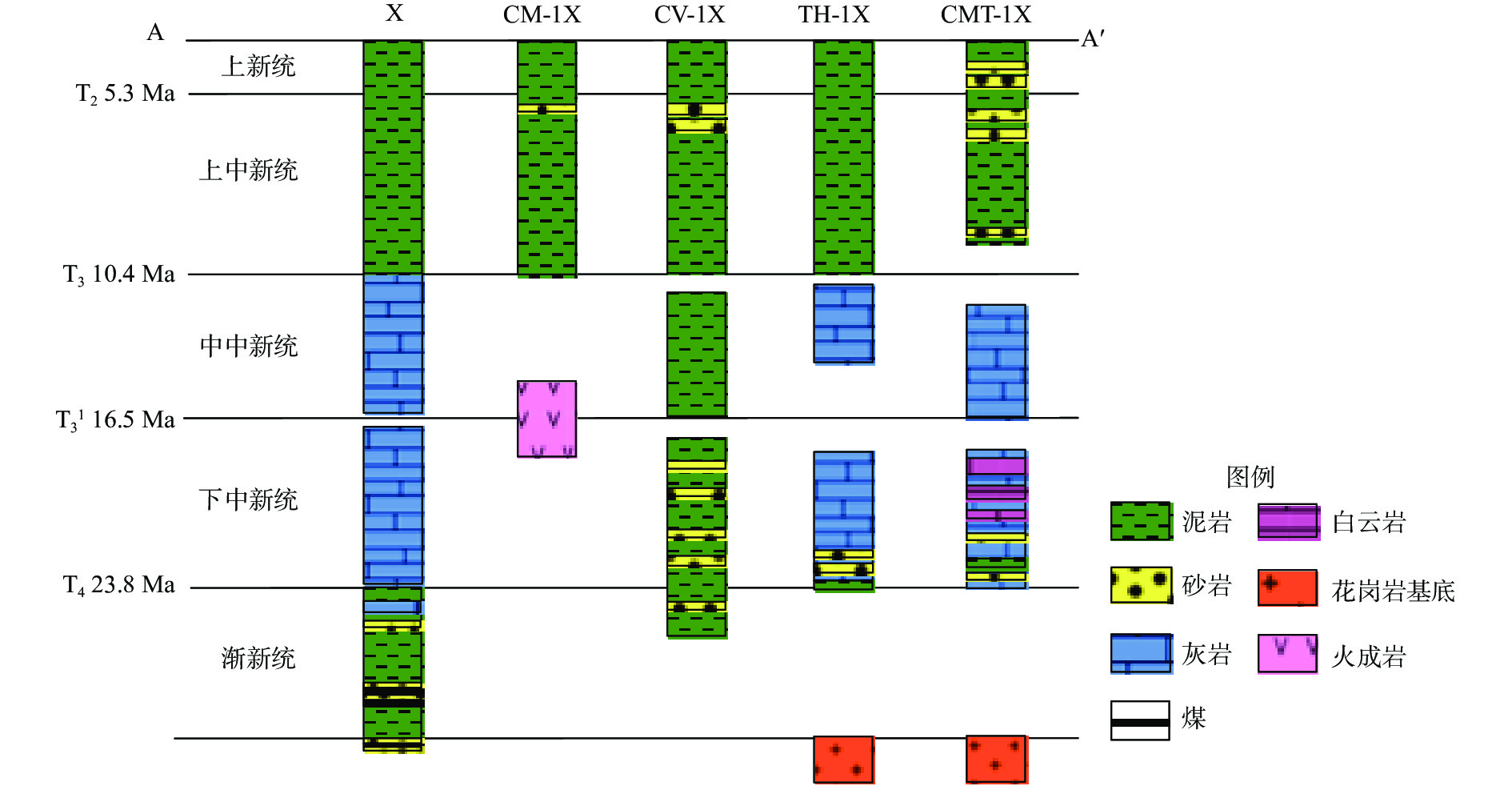
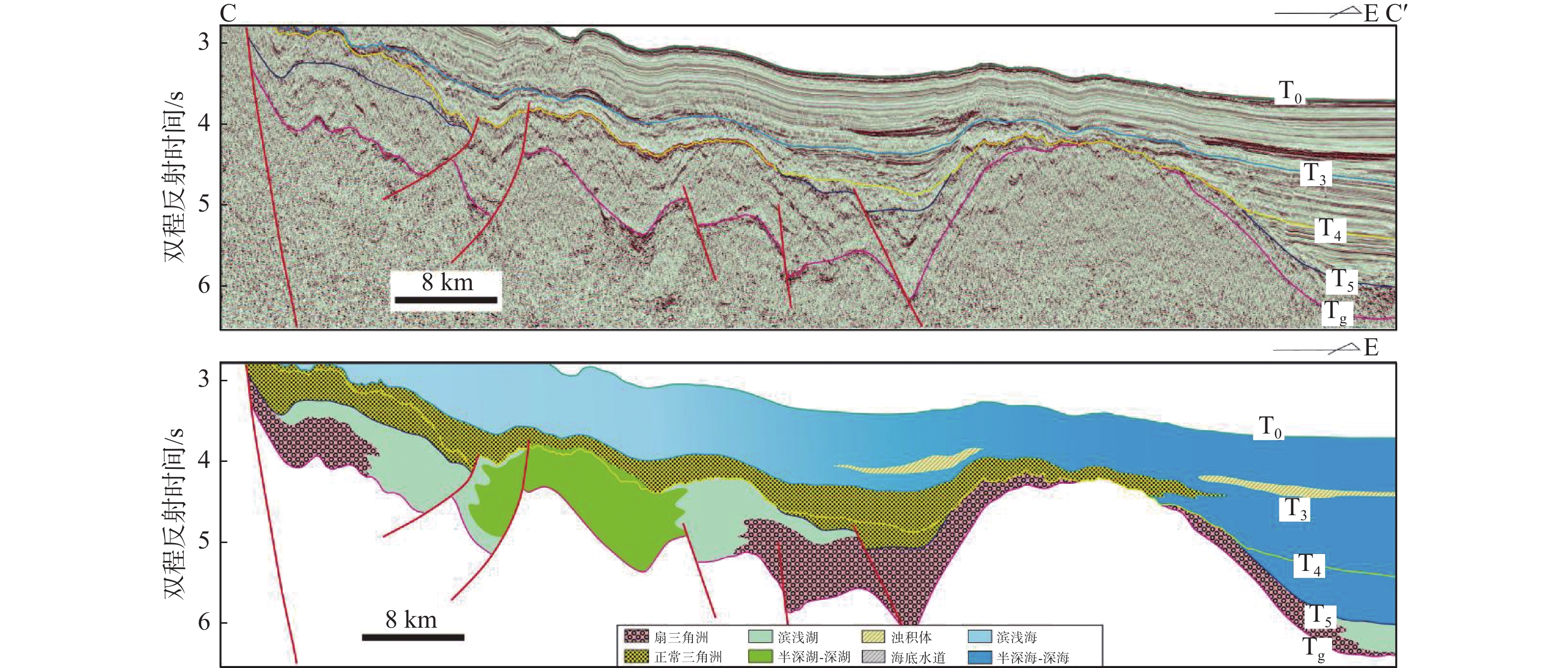
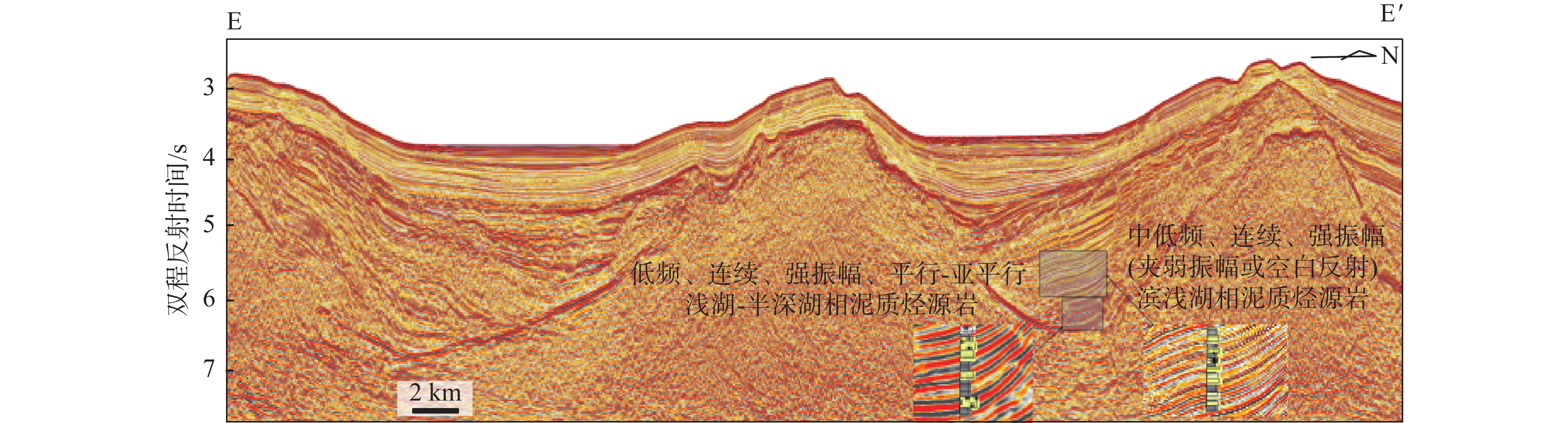
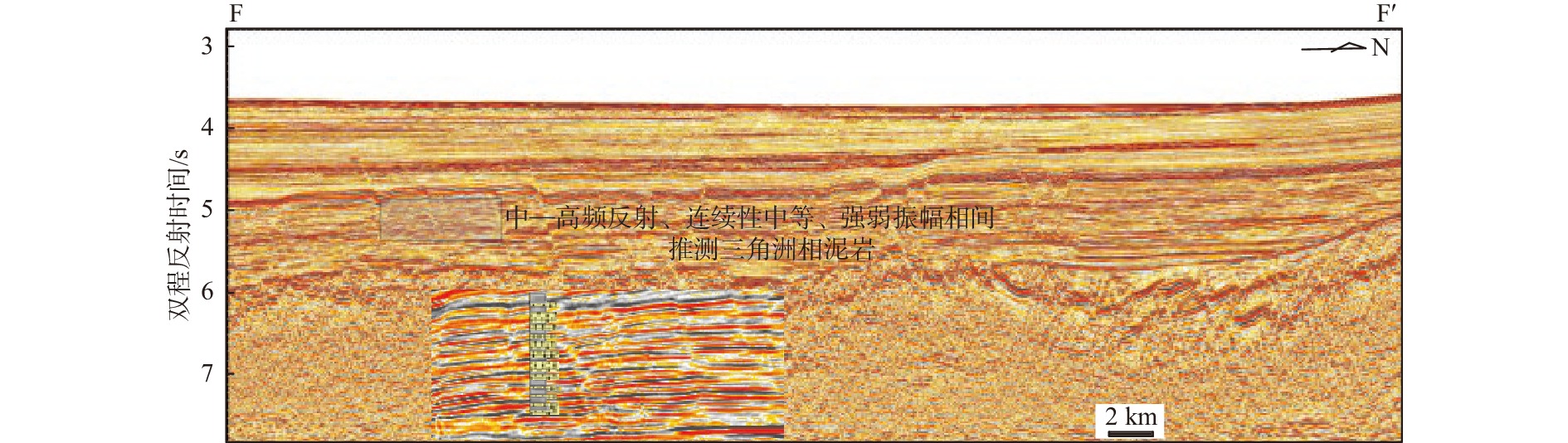
烃源岩是油气生成的物质基础。利用最新采集的高品质二维地震资料和综合研究成果,在中建南盆地内划分出4套地震层序,识别了5个不整合地震反射界面。通过分析盆地沉积演化特征,推测中建南盆地发育3套烃源岩,分别为中始新统湖相烃源岩、上始新统—渐新统湖相和海陆交互相烃源岩以及下—中中新统海相烃源岩。通过对其周边盆地进行类比分析,厘定了3套烃源岩的地震相特征;对不同沉积相带泥岩百分含量进行赋值,最终判识推测了中建南盆地新生代3套烃源岩泥岩厚度及分布特征。本研究可为盆地下一步油气资源评价、有利二级构造带分析和勘探部署提供参考。
Abstract:Source rocks are the material basis for oil and gas generation. Based on newly acquired high-quality two-dimensional seismic data and comprehensive research results, we recognized four sets of seismic sequences and five stratigraphic units controlled by unconformity in seismic reflection interface in the Zhongjiannan Basin, and analyzed the sedimentary evolution characteristics of the basin. It is speculated that three sets of main source rocks were developed in the Zhongjiannan Basin, i.e. Middle Eocene lacustrine source rocks, Upper Eocene-Oligocene lacustrine source rocks and ocean-land facies source rocks, and Lower Miocene to Upper Miocene marine source rocks. Through analogical analysis of the surrounding basins, the seismic facies characteristics of the three sets of source rocks were determined. The thickness and distribution of mudstone in the three sets were estimated in the percentage of mud in different sedimentary facies zones. This study provided a reference for evaluating oil and gas resources, analyzing favorable secondary structural zones, and exploration planning.
-
Key words:
- Zhongjiannan Basin /
- low exploration area /
- source rock /
- seismic facies /
- analogy method
-

-
表 1 中建南盆地不同沉积相烃源岩地质参数表
Table 1. Geological parameters of source rocks in different sedimentary facies in Zhongjiannan Basin
地 层 沉积相类型 泥岩含量/% 参考区 中始新统—渐新统 (Tg—T4) 中深湖 60~85 珠一坳陷、白云凹陷 滨浅湖 40~60 其他相带 20~50 滨浅海-半深海(陆源海相) 30~50 珠二坳陷(珠海组) 5~99 琼东南盆地(崖城组) 下中新统—中中新统 (T4—T3) 滨浅海 50~70 万安盆地 -
[1] 张强,吕福亮,王彬,等. 南海油气分布特征及主控因素探讨[J]. 海相油气地质,2012,17(3):1-8.
[2] 张强,吕福亮,贺晓苏,等. 南海近 5 年油气勘探进展与启示[J]. 中国石油勘探,2018,23 (1):54-61.
[3] 高红芳,白志琳,郭依群. 南海西部中建南盆地新生代沉积相及古地理演化[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),2000,14(6):411-416.
[4] 陈玲. 南海中建南盆地构造样式分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,1(26):53-58.
[5] 姚伯初,邱燕,吴能友,等. 南海西部海域地质构造特征和新生代沉积[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1999.
[6] 金庆焕. 南海地质与油气资源[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1989.
[7] 解习农,张成,任建业,等. 南海南北大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性对油气成藏条件控制[J]. 地球物理学报,2011,54(12):3280-3291.
[8] 高红芳,王衍棠,郭丽华. 南海西部中建南盆地油气地质条件和勘探前景分析[J]. 中国地质,2007,34(4):592-598.
[9] FYHN M B W,NIELSENB L H,BOLDREELA L O. Geological evolution,regional perspectives and hydrocarbon potential of the northwest Zhongjiannan Basin,offshore Central Vietnam[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2009,26 :1–24.
[10] 钟广见,高红芳. 中建南盆地新生代层序地层特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学[J]. 2005,106(3):403-409.
[11] 孙珍,赵中贤,周蒂,等. 南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2011,36(5):798-806.
[12] BOJESEN-KOEFOED J A,NIELSEN L H,NYTOFT H P,et al. Geochemical characteristics of oil seepages from Dam Thi Nai,Central Vietnam:implications for hydrocarbon exploration in the offshore Phu Khanh Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology,2005,28(1):3-18.
[13] VU A T,FYHN M B W,XUAN C T,et al. Cenozoic tectonic and stratigraphic development of the Central Vietnamese continental margin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,86:386-401.
[14] 吴克强,姜雪,孙和风,等. 近海富生油凹陷湖相烃源岩发育模式:以黄河口凹陷古近系为例[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(2):63-70.
[15] 吴克强,刘志峰,王升兰,等. 珠一坳陷北部洼陷带始新统半深—深湖相烃源岩综合判识[J]. 中国海上油气,2015,(27)3:10-15.
[16] 吴宇翔,舒誉,丁琳,等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼文昌组基于层序地层格架约束下的优质烃源岩预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(3):41-49.
[17] 甘军,张迎朝,梁刚,等. 琼东南盆地深水区烃源岩沉积模式及差异热演化[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(8):2627-2635.
[18] 张义娜,张功成,杨海长等. 白云南洼恩平组海相烃源岩空间展布规律及发育模式[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(12):17-23.
[19] 王子嵩,刘震,孙志鹏,等. 琼东南深水区乐东-陵水凹陷渐新统烃源岩早期预测及评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(3):876-888.
[20] 李晓唐,何家雄,张伟. 莺歌海盆地古新近系烃源岩条件与有利油气勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(2):129-142.
[21] 张义娜,张功成,杨海长,等. 琼东南盆地长昌凹陷渐新统崖城组沉积特征研究[J]. 海洋石油,2013,33(2):15-21.
[22] DUNG B V,TUAN H A,KIEU N V,et al. Depositional environment and reservoir quality of Miocene sediments in the central part of the Nam Con Son Basin,southern Vietnam shelf[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2018,97:672-689.
[23] 张厚和,赫栓柱,刘鹏,等. 万安盆地油气地质特征及其资源潜力新认识[J]. 石油实验地质,2017,39(5):625-632.
[24] 王元,李贤庆,王刚,等. 莺琼盆地中新统海相烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):500-510.
-



 下载:
下载: