“Sweet spot” prediction technique for mid-deep low permeability gas reservoirs in M Structure of East China Sea
-
摘要:
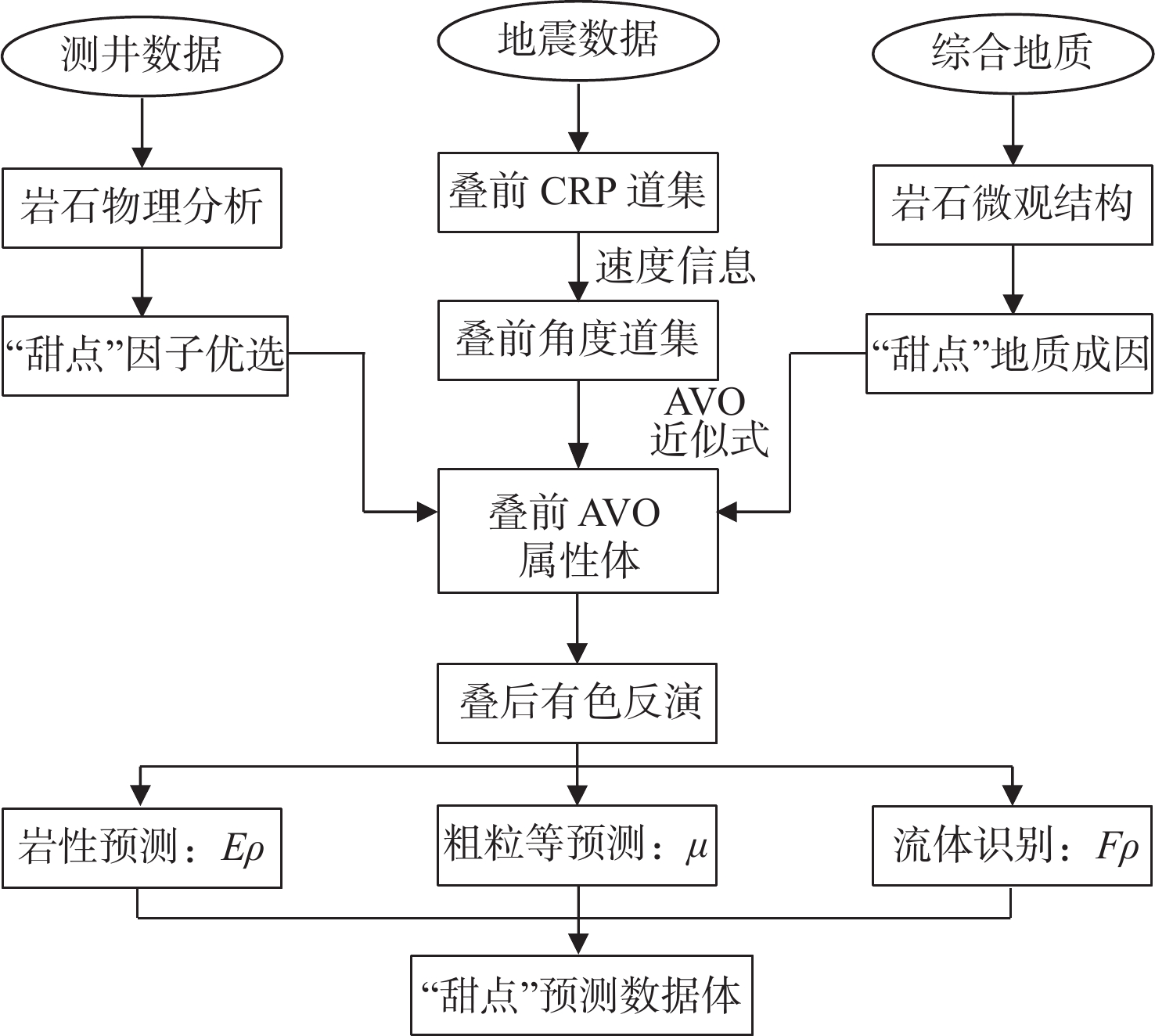
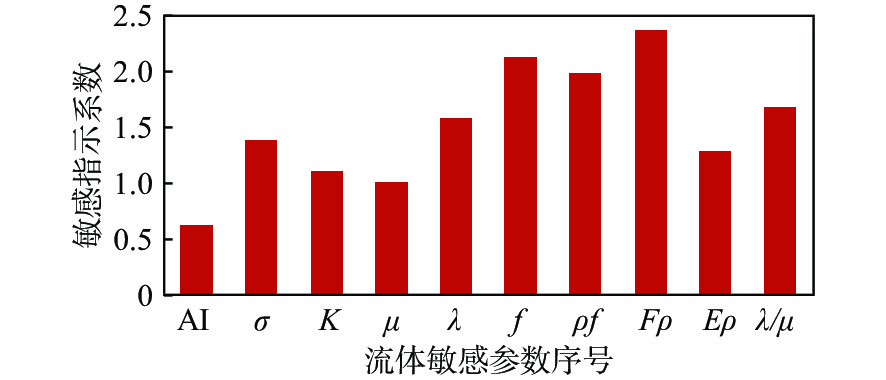
近年来,构造-岩性复合型油气藏已逐渐成为东海“扩储增产”的重要领域,提高“甜点”储层钻遇率对于勘探开发一体化设计的部署与落实具有重要意义。研究区低渗气藏储层厚、埋深大,内部非均质性强,孔渗关系复杂,地球物理响应特征差异小,亟待开展低渗气藏“甜点”储层的精细表征研究。以地震岩石物理为驱动,利用杨氏阻抗Eρ区分碎屑岩储层与非储层,通过分类寻优认为,剪切模量μ为洁净、粗粒、高渗透率优质储层的综合敏感弹性因子。为了削弱岩石骨架孔隙度的影响,采用高灵敏烃检因子Fρ开展烃类检测,最终结合岩性、“甜点”和烃检属性体以精细表征优质“甜点”储层富集区。应用效果证实:该方法的“甜点”预测吻合度达到86.07%,为井位部署和轨迹优化提供了重要依据,可推广至类似区块以供借鉴。
Abstract:In recent years, structural-lithological complex reservoirs have gradually become the key in reservoir expansion and production in the East China Sea. The low permeability gas reservoir in the middle and deep low-permeability gas reservoir in the M Structure of the East China Sea was studied. The study area has large burial depth, strong internal heterogeneity, and complex porosity-permeability relationship, but little difference in geophysical response characteristics. It is urgent to study the fine characterization of sweet spot reservoir in the reservoir. Seismic rock physics were analyzed, in which the Young’s impedance was used to distinguish clastic rock reservoir from non-reservoir. By classifying and optimizing parameters in seismological profiling, shear modulus was found and used as a comprehensive sensitive elastic factor, and combined with a high sensitivity hydrocarbon detection factor, clear clean, coarse-grained, and high-permeability high quality reservoirs could be detected. In addition, to reduce the influence of rock skeleton porosity, a highly sensitive fluid factor was used to detect hydrocarbons. Finally, combined with lithology and attributes of hydrocarbon detection, good sweet spot reservoir areas were finely characterized. Results show that the sweet spot prediction using this method reached a high successful prediction rate of 86.07%, which provided an important basis for well deployment and trajectory optimization and a reference for working on similar blocks.
-

-
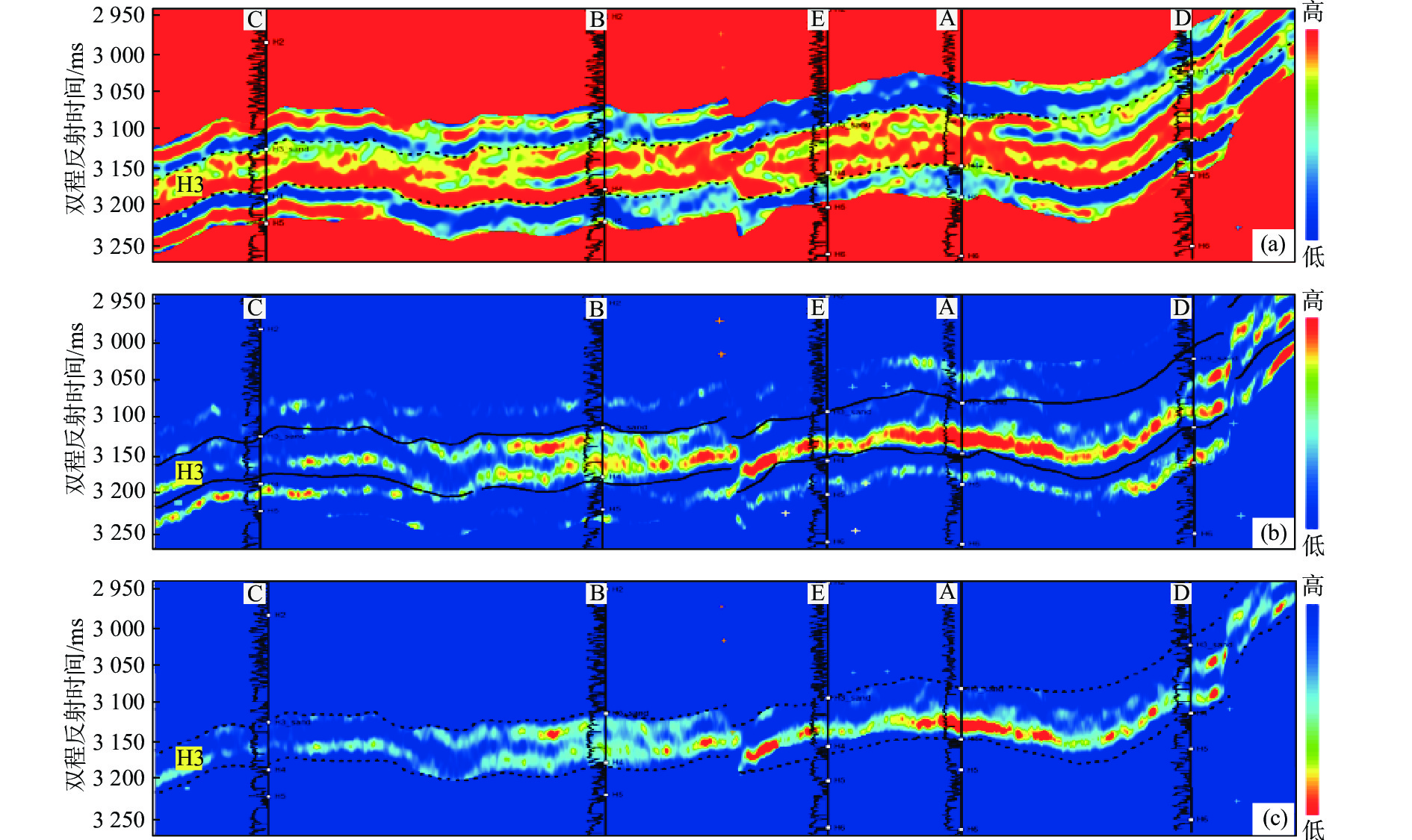
表 1 H3层储层“甜点”类型划分标准
Table 1. Classification criteria of reservoir sweet spot in H3 layer
储层类别 岩性 物性 含流体性 岩性 泥质含量/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率K/(10−3 μm2) 气饱和度Sg/% Ⅰ类“甜点” 中砂岩、粗砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 ≥10 >55 Ⅱ类“甜点” 中砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 1≤K≤10 ≥45 Ⅲ类“甜点” 细砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 ≥0.5 ≥40 Ⅳ类“甜点” 细砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 0.2≤K≤0.5 ≥35 气水同层 细砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 ≥0.2 20≤Sg≤35 含气水层 细砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 ≥0.2 10≤Sg<20 干层 细砂岩 ≤35 ≥7 <0.2 干层 表 2 H3储层“甜点”预测吻合度统计
Table 2. The coincidence statistics of H3 reservoir "sweet spot" prediction
地层 井名 地层厚度/m 井上“甜点”厚度/m 预测“甜点”厚度/m 相对误差 厚度符合率/% 符合率均值/% H3 A 158.75 43.3 46.5 3.2 93.1 86.07 B 155.95 46.6 38.2 9.4 78.01 C 154.80 0.0 0.0 0.0 100 D 164.36 13.0 18.0 5.0 72.22 E 158.00 41.8 37.0 4.8 87.02 -
[1] 谢玉洪. 中国海油“十三五”油气勘探重大成果与“十四五”前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探,2021,26(1):43-54.
[2] 杨勤勇,杨江峰,王咸彬,等. 中国石化物探技术新进展及发展方向思考[J]. 中国石油勘探,2021,26(1):121-130.
[3] OSTRANDER W J. Plane-wave reflection coefficients for gas sands at nonnormal angles of incidence[J]. Geophysics,1984,49:1637-1648. doi: 10.1190/1.1441571
[4] CHIBURIS E F. Analysis of amplitude versus offset to detected gas/oil contacts in the Arabian Gulf[C]//54th Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts, 1984: 669-670.
[5] SMITH G C,GIDLOW P M. Weighted stacking for rock property estimation and detection of gas[J]. Geophysical Prospecting,1987,35(9):993-1014. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1987.tb00856.x
[6] GOODWAY B, CHEN T, DOWNTON J. Improved AVO fluid detection and lithology discrimination using Lame petrophysical parameters[C]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1997, 16: 183-186.
[7] HEDLIN K, Pore space modulus and extraction using AVO[C]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2000, 19: 170-173.
[8] BATZLE M L. Optimal hydrocarbon indicators[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts,2001,20:1697-1700.
[9] RUSSELL B H,Hedlin K,Hilterman F J,et al. Fluid-property discrimination with AVO:a Biot-Gassmann perspective[J]. Geophysics,2003,68(1):29-39. doi: 10.1190/1.1543192
[10] MARK Q,BRUCE S,CHRIS T. Poisson impedance[J]. The Leading Edge,2006,45(3):239-242.
[11] 王栋,何振华,黄德济. 新流体识别因子的构建与应用分析[J]. 石油物探,2009,48(2):141-148.
[12] 印兴耀,张世鑫,张锋. 针对深层流体识别的两项弹性阻抗反演与Russell流体因子直接估算方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2013,56(7):2378-2390.
[13] 刘力辉,李建海,刘玉霞. 地震物相分析方法与“甜点”预测[J]. 石油物探,2013,52(4):432-437.
[14] 许翠霞,马鹏善,赖令彬,等. 致密砂岩含气性敏感参数:以松辽盆地英台气田营城组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(6):712-716.
[15] 李春宁. 多波联合AVA属性提取与油气预测[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014.
[16] 陈祖庆,杨鸿飞,王静波. 基于叠前反映的致密砂岩含气储层识别技术研究[J]. 天然气技术与经济,2015,9(4):18-22.
[17] 徐玥,张林清. 利用Russell流体因子进行致密砂岩气“甜点”预测[J]. 西部探矿工程,2016,12(2):20-23.
[18] 张林清,张会星,姜效典,等. 弹性参数反演与属性融合技术在“甜点”预测中的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(4):582-589.
[19] 曹冰,秦德文,陈践发. 西湖凹陷低渗储层“甜点”预测关键技术研究与应用:以黄岩A气田为例[J]. 石油学报,2018,36(1):188-197.
[20] 李久娣. 东海西湖N区块致密砂岩气藏甜点预测研究[J]. 石油物探,2019,58(3):444-452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.03.014
[21] 王迪,张益明,刘志斌,等. AVO定量解释模板在LX地区致密气“甜点”预测中的应用[J]. 石油物探,2020,59(6):936-948.
[22] 韩刚,高红艳,龙凡,等. 叠前反演在西湖凹陷致密砂岩储层“甜点”预测中的应用[J]. 石油物探,2021,60(3):471-478.
[23] 张岩,秦德文. 东海古近系致密碎屑岩“甜点”地震预测方法及应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(5):51-58.
[24] 尤丽,张迎朝,李才,等. 基于沉积成岩-储集相分析确定文昌9区低渗储层“甜点”分布[J]. 吉林大学学报,2014,44(5):1432-1440.
[25] RUSSELL B H,GRAY D,HAMPSON D P,et al. Linearized AVO and poroelasticity[J]. Geophysics,2011,76(1):19-29.
[26] 张岩,李键,侯志强. 基于叠前弹性信息直接提取的高灵敏烃类检测方法[J]. 地球物理学进展,2021,36(3):1187-1195.
[27] 李春宁, 杜启振, 陈刚. 一种新的流体指示因子[C]//中国地球物理学会第二十九届年会, 2013.
[28] 刘力辉,杨晓,丁燕. 基于岩性预测的CRP道集优化处理[J]. 石油物探,2013,52(5):482-488.
-



 下载:
下载: