Grain size characteristics and transport trends of surface sedimentin the bays of northern Hainan Island
-
摘要:
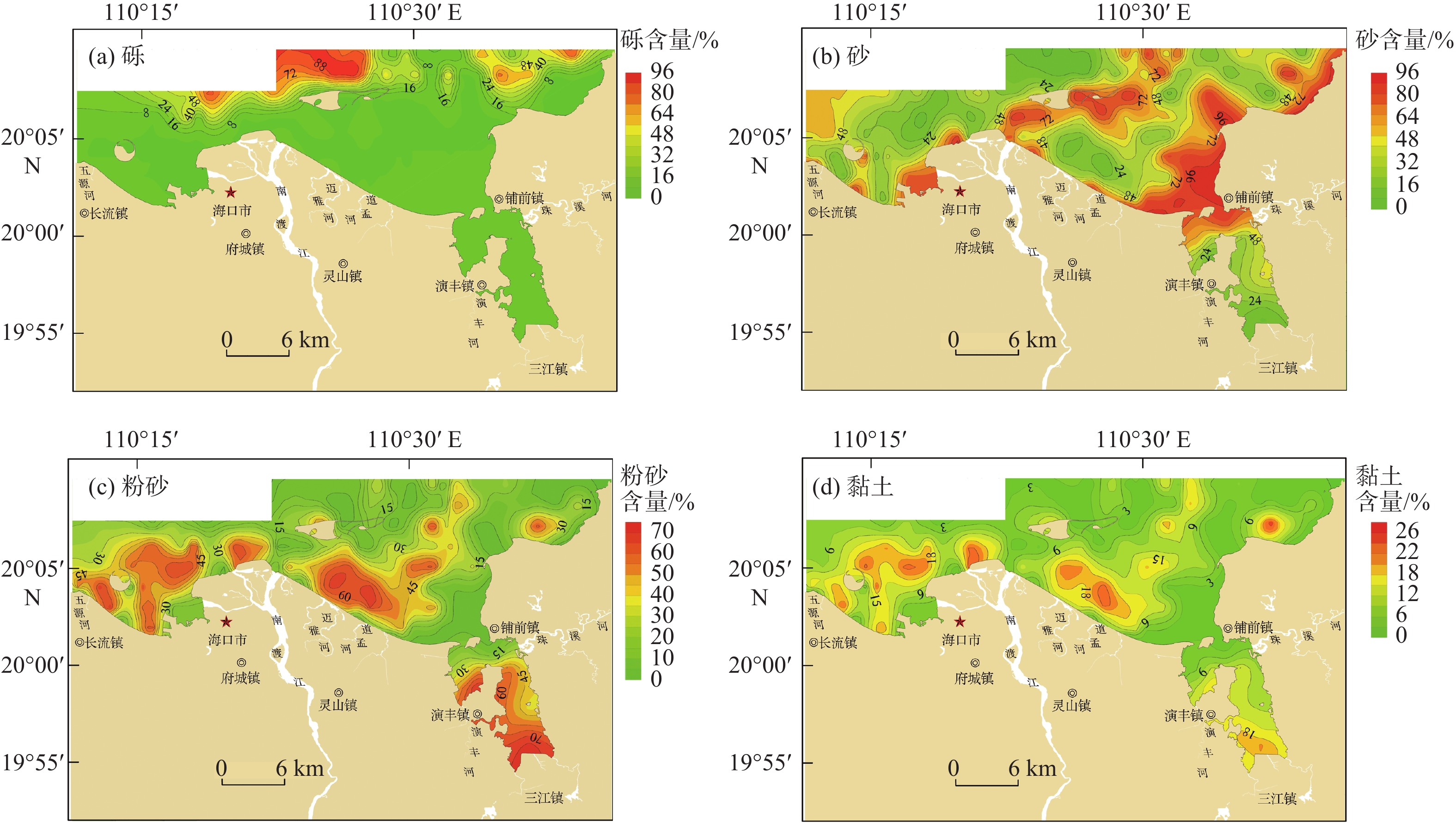
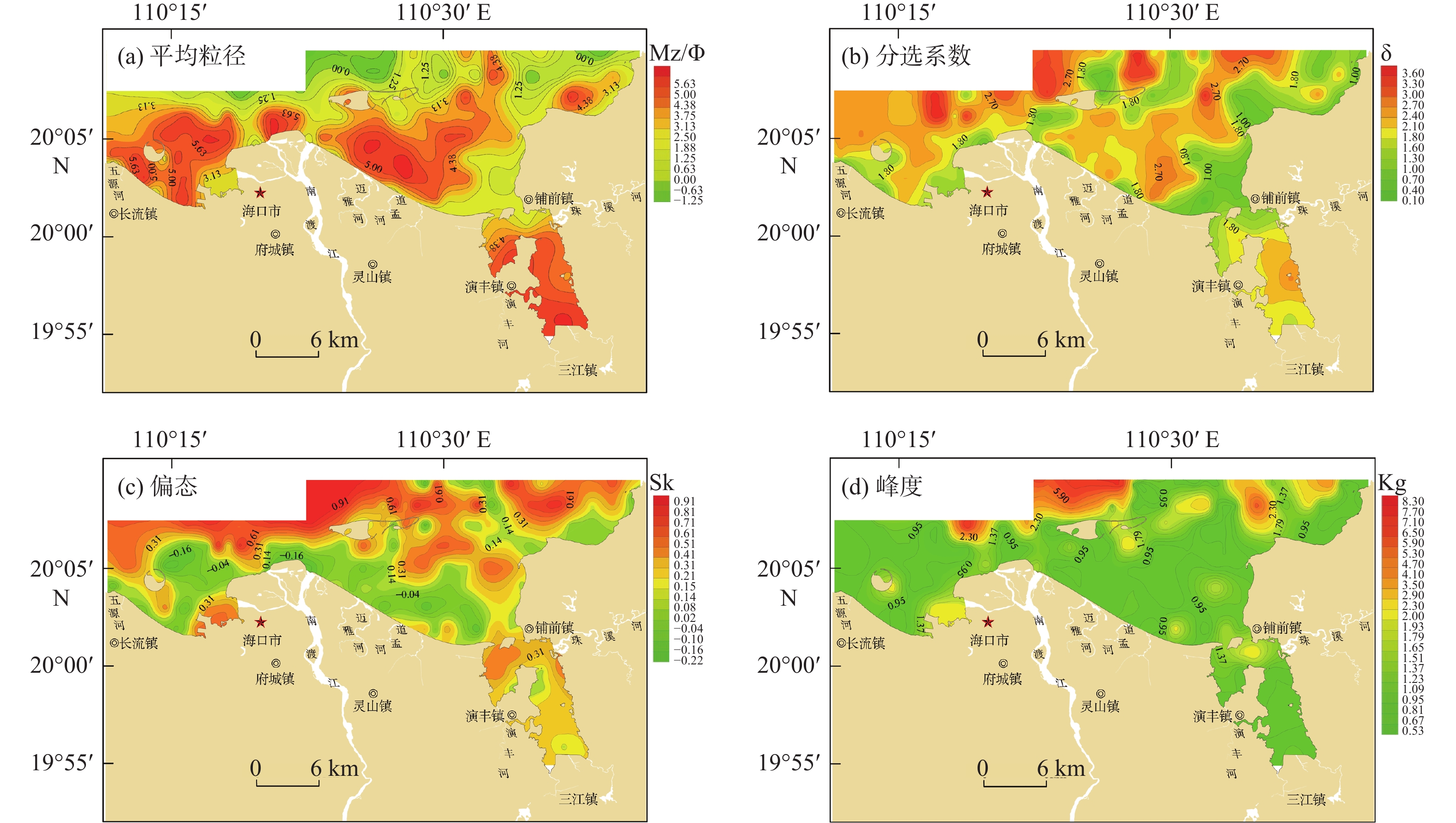
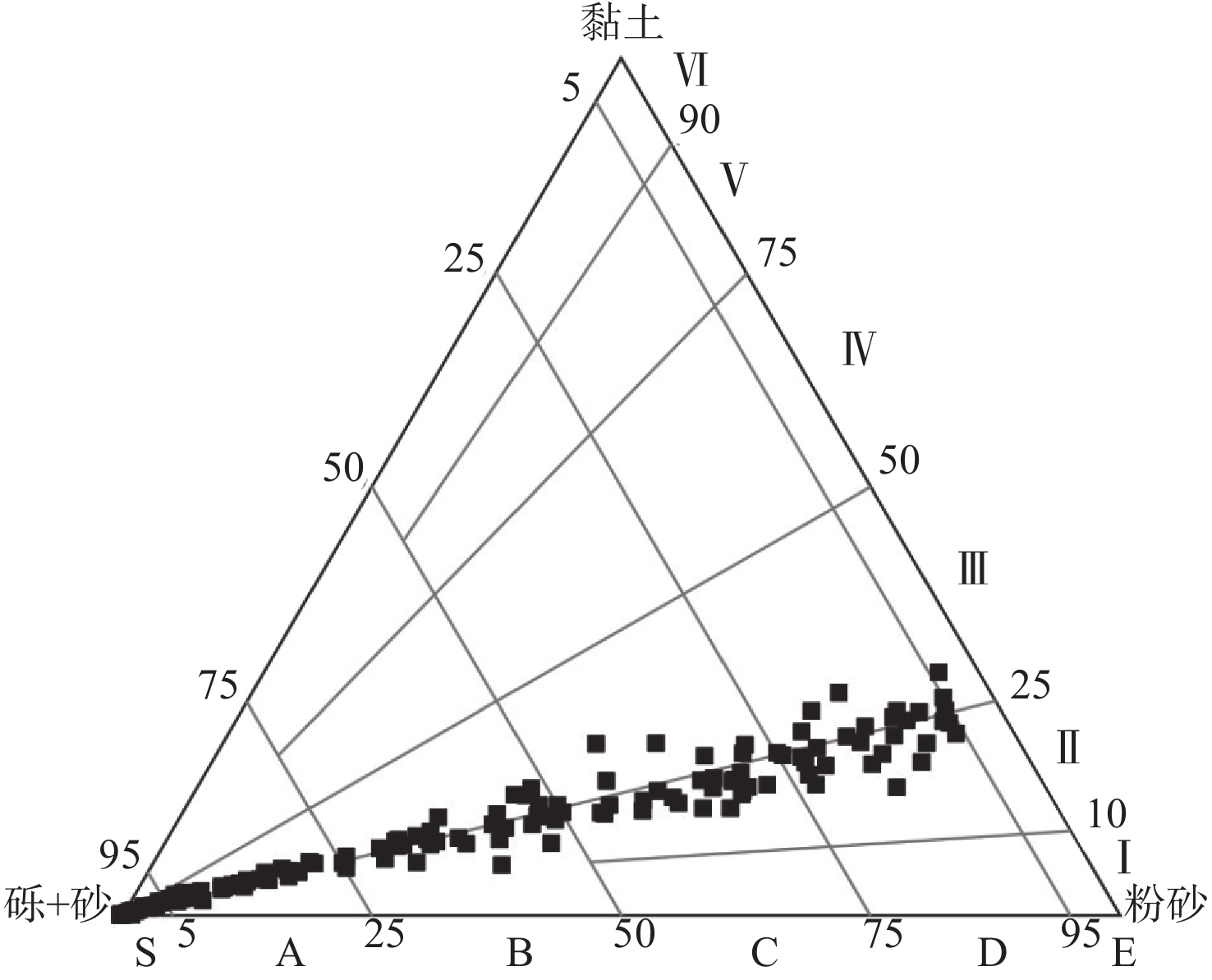
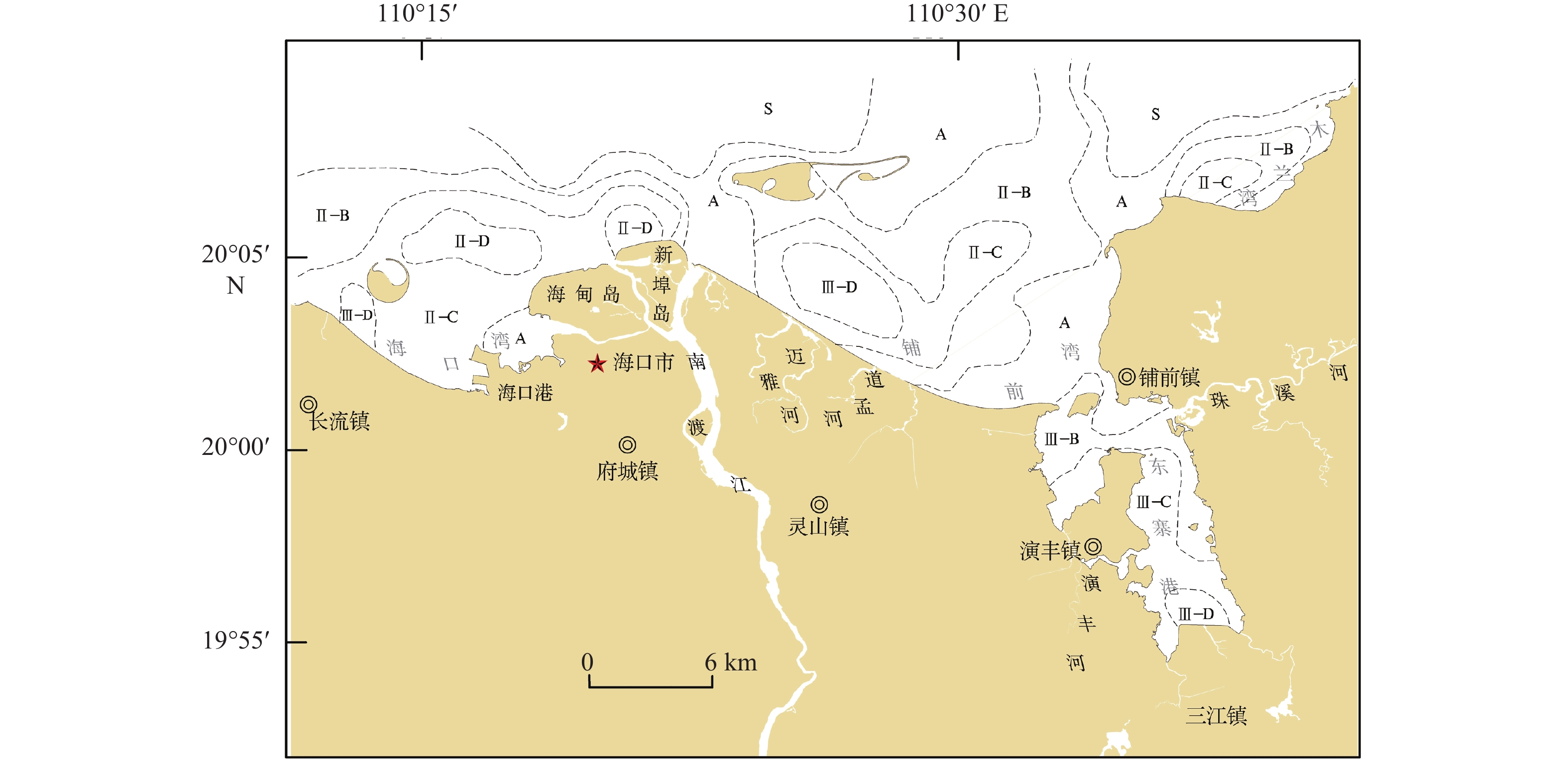
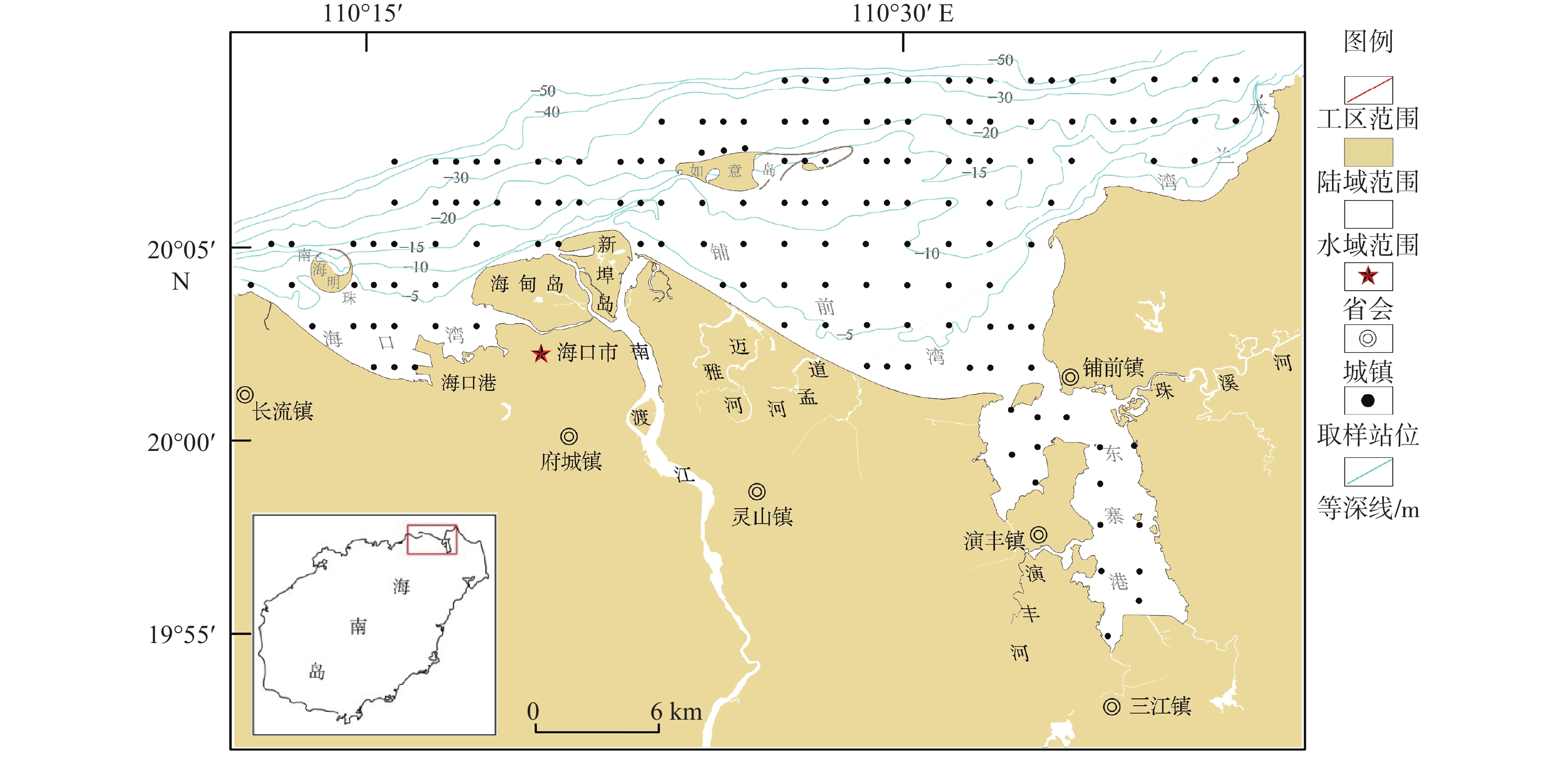
对海南岛北部海湾(海口湾、铺前湾、木兰湾和东寨港)192站位的表层沉积物样品进行粒度分析,基于粒级组分划分沉积物类型,利用Flemming三角图式法进行沉积动力分区,采用二维粒径趋势分析模型(GSTA)分析沉积物输运趋势。结果表明:研究区表层沉积物类型包括砾、砂质砾、砂、粉砂质砂、砂质粉砂和粉砂,其中,砂分布面积最广,其次为粉砂质砂,沉积物粒度由南往北依次呈“细—粗”旋回式变化,近岸和口门外砂体分选性较好,东寨港内湾和琼州海峡中部沉积物分选性差。研究区整体以偏高能环境为主,物质输运方式包括河流输沙、海岸侵蚀、沿岸输沙和底床剥蚀,其中,北部海峡潮余流作用强劲,表层沉积物存在EW向输运趋势;海湾中部受波浪和潮流的共同影响,于白沙浅滩处(如意人工岛)形成一个沉积汇聚中心;河口区受波浪、径流和潮流季节交替性作用控制,洪季时口门形成的堆积沙体,在NE向浪和W向沿岸流的侵蚀搬运作用下,向西输运至海口湾;近岸区主要受波浪改造作用影响,其中,铺前湾和木兰湾海域沉积物由海向岸搬运,趋势与波浪和涨潮流作用方向一致;东寨港水动力条件较弱,沉积物无明显输运趋势。研究结果揭示了本区海湾现代沉积特征及陆海交互作用,可为海岸侵蚀防护、航道安全保障和海洋环境治理提供科学依据。
Abstract:Characteristics of grain size distribution from 192 surface sediment samples collected in the bays of northern Hainan Island (Haikou Bay, Puqian Bay, Mulan Bay, and Dongzhai Port) were analyzed and the types of sediment were classified. The depositional dynamics were analyzed using Flemming triangle diagram, GSTA model was utilized to identify sediments transport trends. The modern sedimentary characteristics and land sea interaction in this area were revealed , and the scientific basis was provided for coastal erosion protection, channel safety assurance, and marine environment governance. Results show that the main types of surface sediments in the study area are gravel, sandy gravel, sand, silty sand, sandy silt, and silt. The distribution areas of sand were the widest, followed by silty sand. From south to north, the grain sizes of sediments changed cyclically. The sorting of surface sediments in estuary and seacoast was good, while it was poor in Dongzhai Harbor and middle of Qiongzhou Strait. The study area was dominated by high-energy environments. Sediment transport modes included river transport, coastal erosion, coastal transport, and seabed erosion. The trend of surface sediments transport in the northern part of study area was east to west, which was mainly influenced by the strong tidal residual current in Qiongzhou Strait. Baisha Shoal was a sedimentary convergence center, which was formed by the combined effects of waves and currents. The dominant sedimentary dynamics of estuary, included waves, runoff and tidal current, were alternated seasonally. The accumulated sand body that formed at estuary during flood season was eroded by northeastern waves and western coastal current, and then the eroded sediments were transported westward to Haikou Bay. Sediments of the nearshore area were transformed by wave. Sediments in the Puqian Bay and Mulan Bay were transported from sea to shore in a trend consistent with the directions of wave action and flood currents. The hydrodynamic of Dongzhai Port was weak, with no obvious trend of sediment transport. There was no obvious transport trend of sediment in the Dongzhai Port.
-
Key words:
- Hainan Island /
- northern bay /
- sediment /
- grain size /
- transport trend
-

-
表 1 表层沉积物粒级组分及粒度参数统计
Table 1. Grain size fraction and parameter of surface sediment
粒级组分/ % 粒度参数 砾 砂 粉砂 黏土 平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 偏态 峰度 最小值 2.40 3.03 0.60 0.02 −1.29 0.12 −0.22 −0.60 最大值 95.30 100.00 73.04 28.24 6.98 3.89 0.92 8.66 平均值 47.13 56.96 29.40 9.39 3.05 1.78 0.26 1.31 检出率 22.92 100 85.42 83.33 100 100 100 100 -
[1] 瞿洪宝,苟鹏飞,孙龙飞,等. 海南岛崖州湾表层沉积物空间分布特征及其受控机制[J]. 海洋学报,2021,43(12):70-81.
[2] 徐方建,李安春,黄敬利. 东海陆架浙-闽沿岸泥质沉积研究进展[J]. 海洋通报,2012,31(1):97-104.
[3] 王雪木,瞿洪宝,熊元凯,等. 海南昌化江入海口底表沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势[J]. 现代地质,2022,36(1):88-95.
[4] 项立辉,安成龙,张晓飞,等. 连云港近岸海域表层沉积物沉积特征及粒径趋势分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2015,34(3):317-325.
[5] 高抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析:原理与应用条件[J]. 沉积学报,2009,27(5):826-836.
[6] 石学法. 海洋沉积环境的基本参数和研究流程[J]. 海洋科学,1992,6:30-33.
[7] 肖晨曦,李志忠. 粒度分析及其在沉积学中应用研究[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2006,3:118-123.
[8] MCLAREN P,BOWLES D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1985,55:457-470.
[9] ASSELMAN,NATHALIE E M. Suspended sediment dynamics in a large drainage basin:the River Rhine[J]. Hydrological Processes,1999,13(10):1437-1450. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(199907)13:10<1437::AID-HYP821>3.0.CO;2-J
[10] POIZOT E,MEAR Y,THOMAS M,et al. The application of geostatistics in defining the characteristic distance for grain size trend analysis[J]. Computers and Geosciences,2006,32(3):360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2005.06.023
[11] GAO S,COLLINS M. A critique of the McLaren method for defining sediment transport paths:discussion[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1991,61(1):143-146. doi: 10.1306/D42676A9-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[12] GAO S,COLLINS M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends,based upon definition of "transport vectors"[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1994,90(1/2):47-60.
[13] GAO S,COLLINS M. Analysis of grain-size trends,for defining sediment transport pathways in marine environments[J]. Coastal Research,1994,10(1):70-78.
[14] 林纪江,王平,胡日军,等. 海南日月湾海域表层沉积物分布特征与运移趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(6):11-21.
[15] 陈斌,印萍,徐刚,等. 浙江内陆架表层沉积物粒度分布特征及运移趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(6):95-100.
[16] 张连杰,赵博,王鹏,等. 大连湾海域沉积动力环境与物质输运[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(6):12-19.
[17] PULLEY S,GOUBET A,MOSER I,et al. The sources and dynamics of fine-grained sediment degrading the freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) beds of the River Torridge,Devon,UK[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2019,657(20):420-434.
[18] 徐方建,李安春,李铁刚,等. 东海内陆架EC2005孔沉积物粒度分形特征[J]. 地质学报,2011,85(6):1038-1044.
[19] 王奎博,张丽,王瑞琪,等. 海南岛海岸侵蚀脆弱性评价[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2022,37(5):1149-1158.
[20] 周晗宇,陈沈良,钟小菁,等. 海口湾西海岸海滩沉积物与海滩稳定性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报,2013,32(1):26-34.
[21] 曾维特,杨永鹏,张东强,等. 海南岛北部海湾沉积物重金属来源、分布主控因素及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(3):1085-1094.
[22] 滕学春,吴秀杰. 琼州海峡的波浪特征[J]. 黄渤海海洋,1993,4:1-8.
[23] 陈达森,陈波,严金辉,等. 琼州海峡余流场季节性变化特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2006,2:12-17.
[24] 谢华亮,戴志军,吴莹,等. 海南岛南渡江河口动力沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报,2014,32(5):884-892.
[25] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志:第十一分册,海南省海湾[M]. 青岛:海洋出版社,1999.
[26] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫局. 海洋监测规范 第3部分:样品采集、贮存与运输:GB 17378.3—2007 [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2007.
[27] FOLK R L,WORD W. Brasor rivers bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1957,27:3-27. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[28] FOLK R L,ANDREWS P B,LEWIS D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[ J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13:937-968.
[29] FLEMMING B W. A revised textural classification of gravel-free muddy sediments on the basis of ternary diagrams[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2000,20(10/11):1125-1137.
[30] 贾建军,高抒,薛允传. 图解法与矩法沉积物粒度参数的对比[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2002,33(6):577-582.
[31] 陈亮,张玉芬,李团结,等. 琼州海峡及周边海域沉积环境及近万年以来沉积演化[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2014,39(6):696-704.
[32] 陈宜展,曹永港,黄艳松,等. 海口湾海域波浪特征分析[J]. 海洋工程,2019,37(2):96-103.
[33] 戴志军,陈子燊,欧素英. 海南岛南渡江三角洲海岸演变的波浪作用分析[J]. 台湾海峡,2000,4:413-418.
[34] 胡泰桓,李志强,朱士兵,等. 琼州海峡南岸海滩剖面动态变化特征分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2021,40(4):678-687.
[35] 吴创收,杨世伦,罗向欣,等. 近四十年南渡江水下三角洲的冲淤变化及其主控原因[J]. 海洋科学进展,2011,29(3):339-345.
[36] 陈海洲,王宝灿,谢琳. 海口白沙浅滩的形成与演变[J]. 海岸工程,2011,30(4):37-45.
[37] 林尤文,于淼,朱丽蓉,等. 南渡江水沙变化特征及其趋势分析[J]. 人民珠江,2020,41(12):15-20.
-



 下载:
下载: