Controlling factors and development patterns of fractures in deep tight sandstone in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin: a case study from W Structure in south central region of Central Depression Belt
-
摘要:
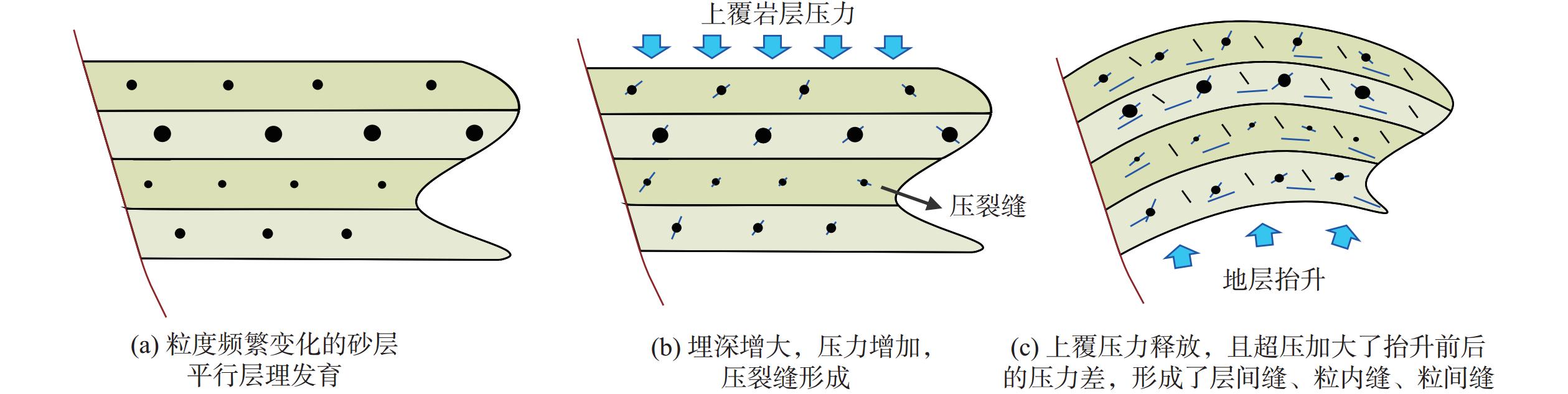
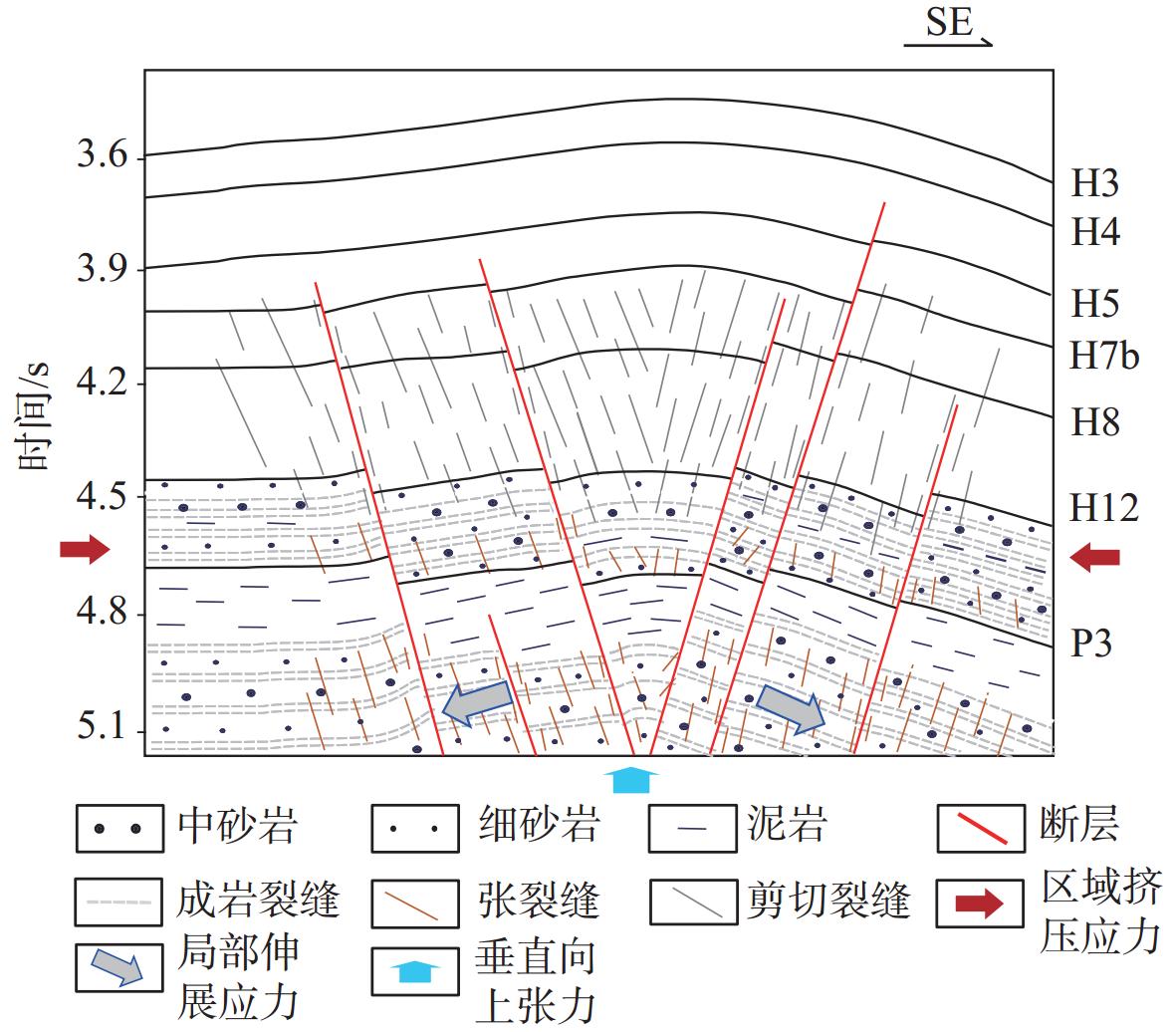
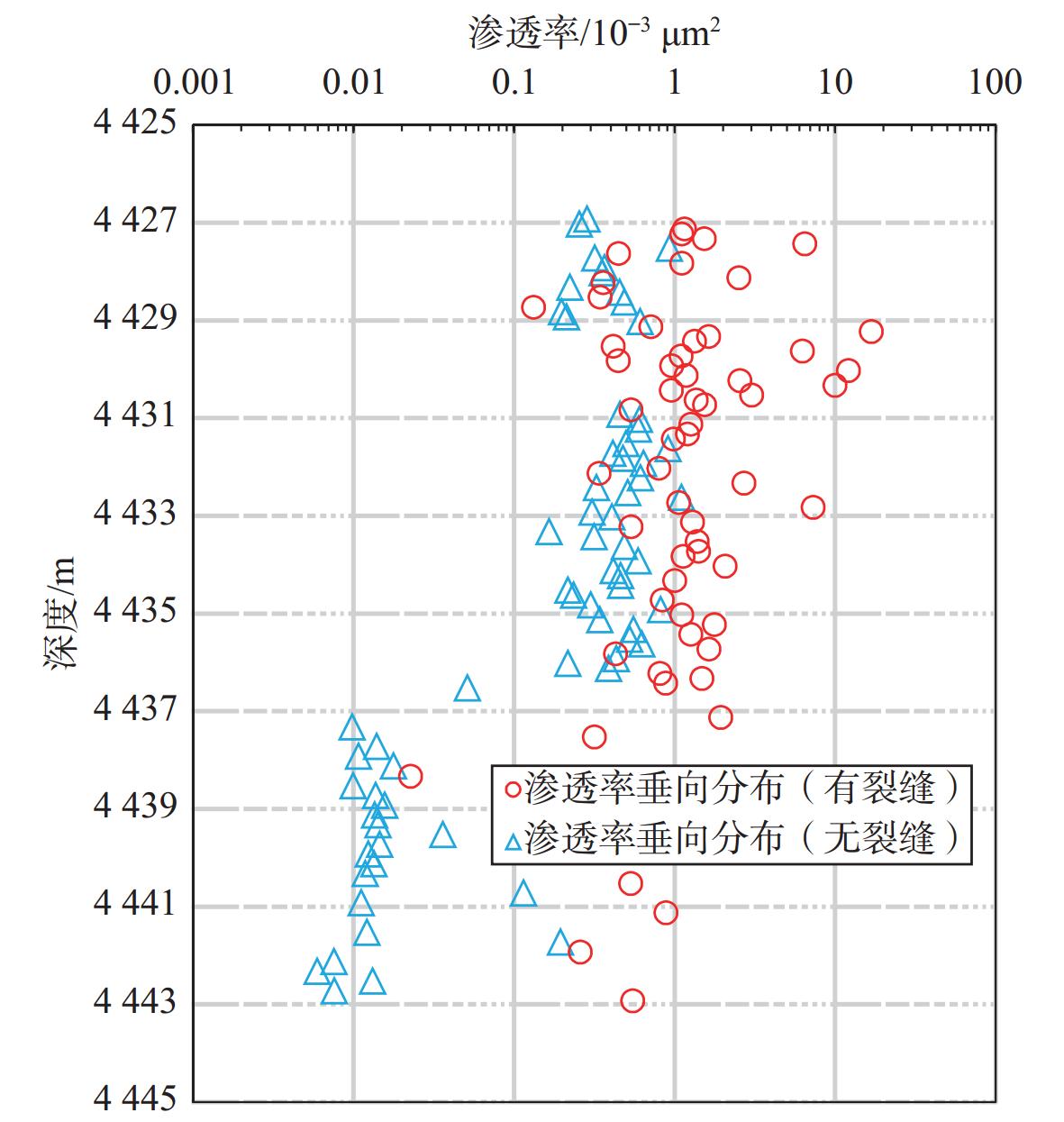
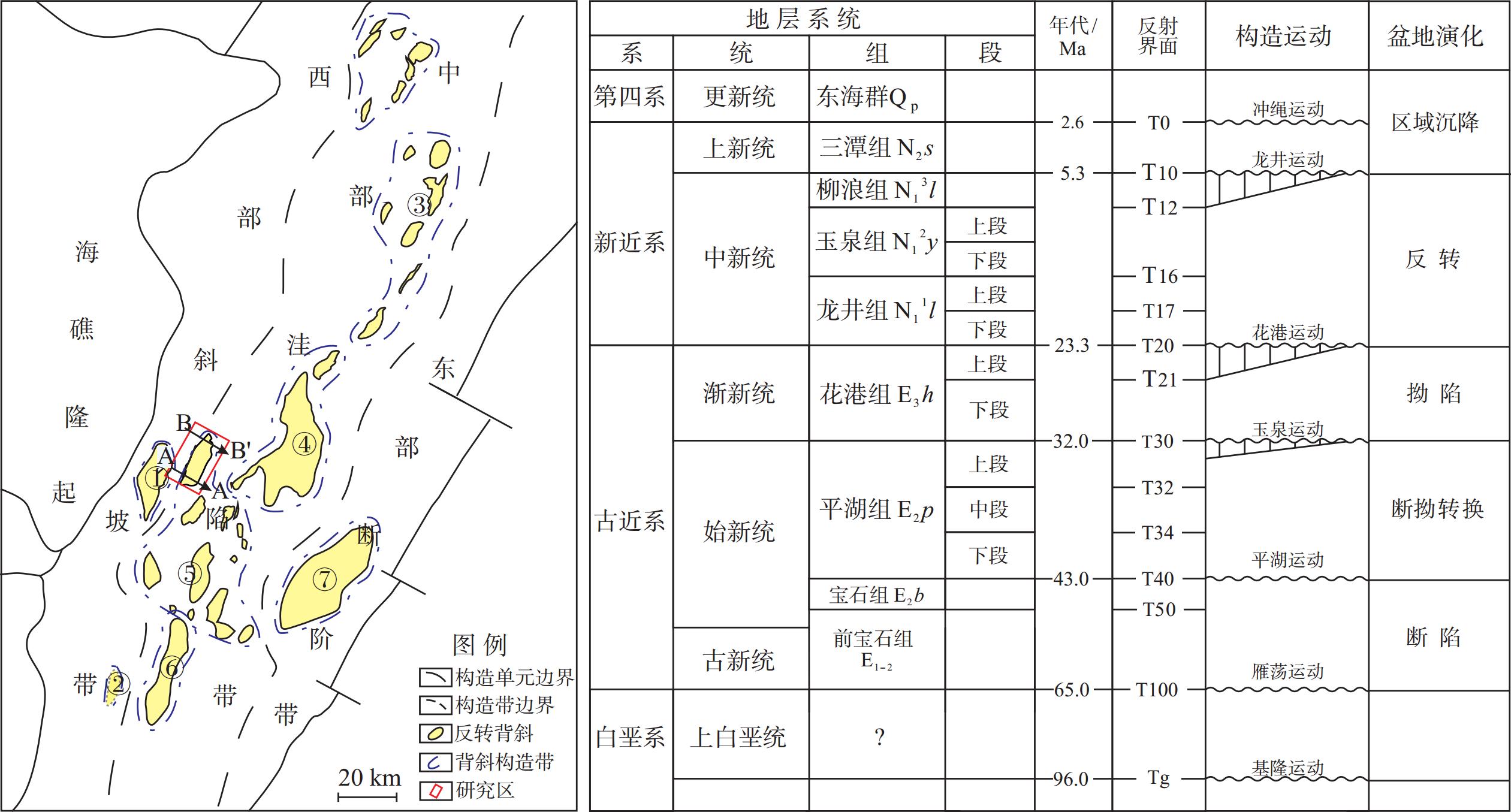
西湖凹陷大部分油气资源量集中在3 500 m之下的深层低孔渗储层中,前人对该区深层裂缝型“甜点”储层的研究相对较少。以中部洼陷带W构造为重点研究靶区,总结裂缝预测方法,研究深层裂缝形成的控制因素及发育模式。研究结果表明,按裂缝成因类型划分,W构造深层低孔渗砂岩储层裂缝包括成岩缝、剪切缝和张裂缝。其中,成岩缝的发育受沉积层理与压力释放的共同控制;剪切缝受地层变形强弱的控制,主要发育于花港组地层变形较强的部位;张裂缝与地层上隆后产生的水平伸展应力有关。结合储层物性条件分析认为,深层裂缝发育是控制致密砂岩气藏“甜点”储层的重要因素之一。通过构造应力场模拟研究并结合单井岩芯及薄片综合分析,可有效预测裂缝的集中发育区,为深层裂缝型“甜点”储层的预测提供依据。
Abstract:Most of the oil and gas resources in the Xihu Sag are concentrated in deep low-porosity and permeability reservoirs below
3500 m. Previous studies on deep fractured "sweet spot" reservoirs in this area are relatively rare. Taking the W structure in the central depression belt as the research target area, the fracture prediction method is summarized, and the controlling factors and development patterns of deep fracture formation are studied. Results show that the fractures in the deep tight sandstone reservoir of the W structure could be classified into diagenetic fractures, shear fractures, and tension fractures in fracture genesis type. Among them, the diagenetic fractures is controlled by sedimentary bedding and pressure release. The shear fractures are controlled by the intensity of stratum deformation and are mainly developed in the parts with strong deformation of the Huagang Formation. The tension fractures are related to the horizontal extension stress generated after the stratum uplift. After analyzing the reservoir physical properties, we believe that the development of deep fractures is one of the important factors controlling the "sweet spot" reservoirs of tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Through tectonic stress field simulation combined with single well core and thin section analysis, the concentrated development area of fractures can be effectively predicted, providing a basis for the prediction of deep fractured "sweet spot" reservoirs. -

-
表 1 岩芯裂缝发育特征
Table 1. Characteristics of fractures seen in drilling cores
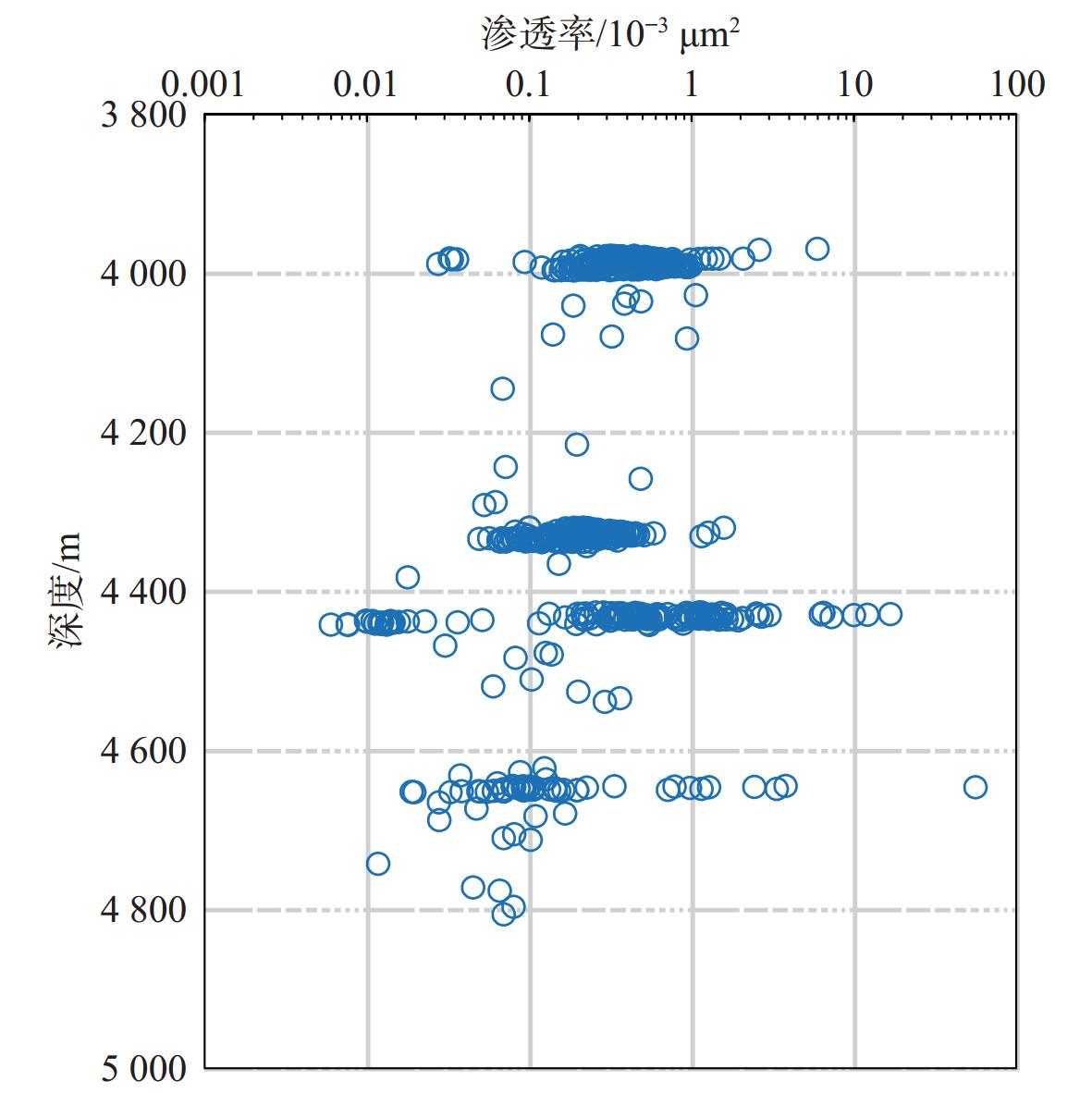
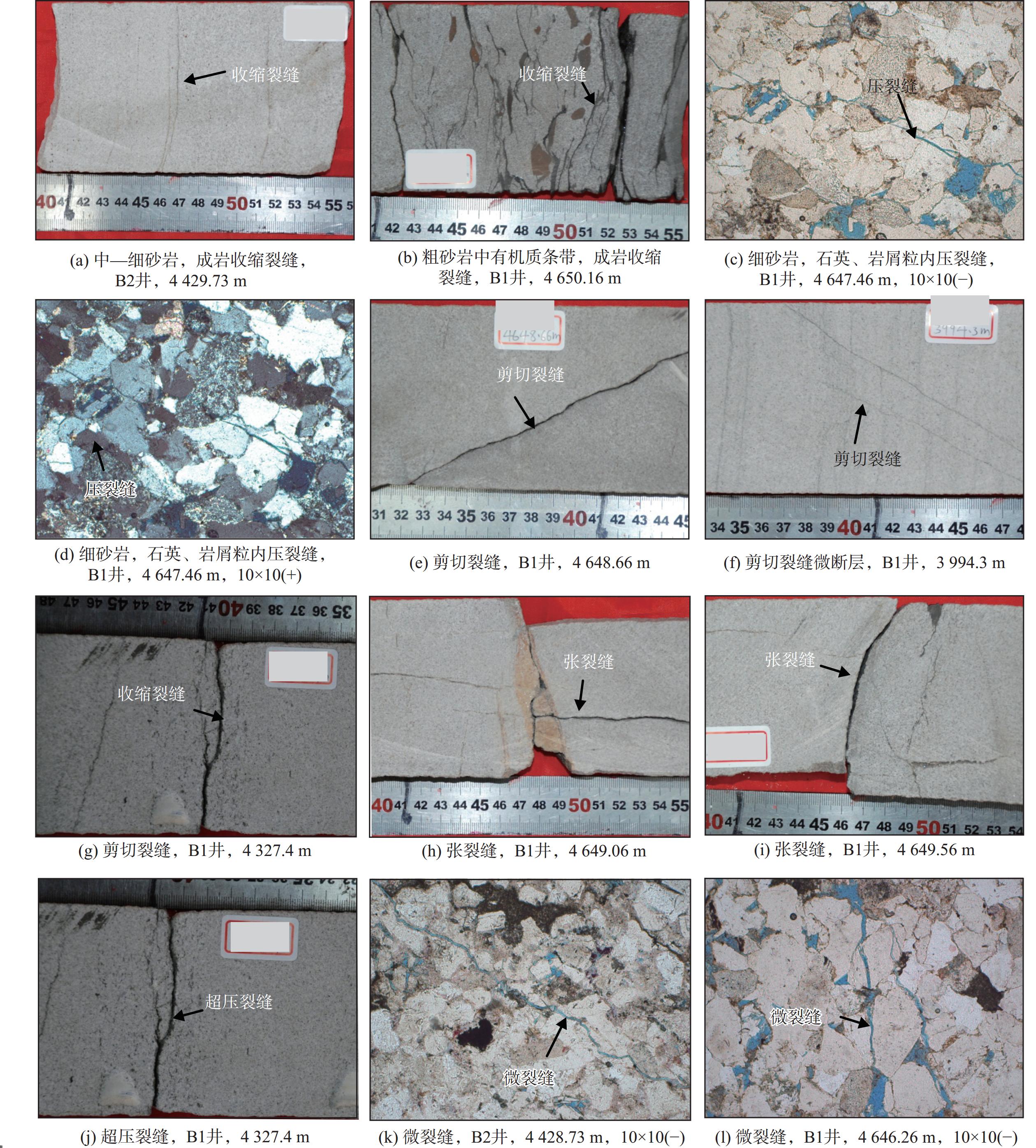
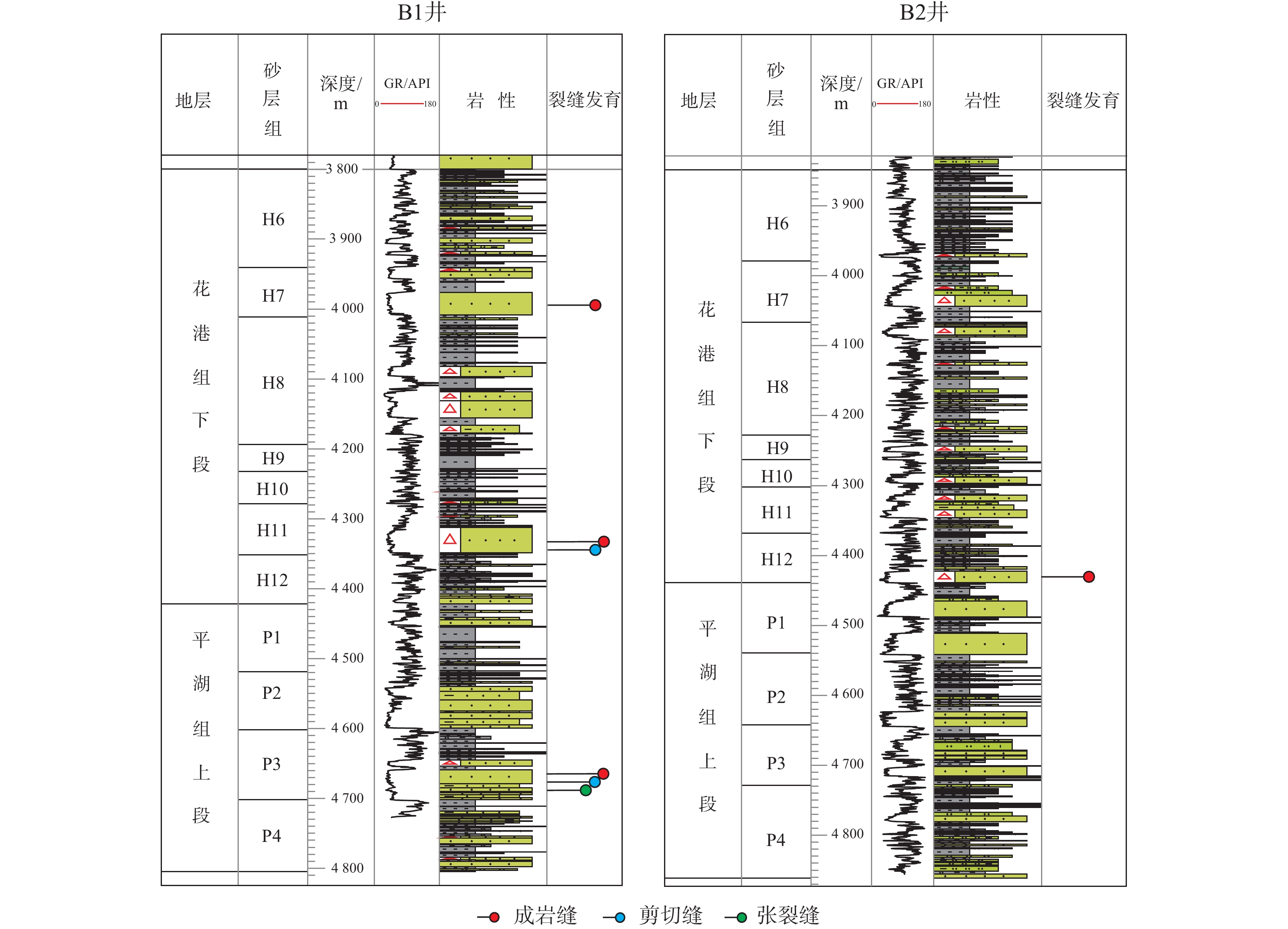
井位 起止深度/m 条数 类型 充填 发育特征 砂层组 组 3 992 1 剪切缝 未被充填 斜交缝,缝面平直,岩芯内缝长13 cm,宽0.5 mm H7 3 994.3 2 剪切缝 被充填 2条近平行斜交缝,缝宽1 mm,充填物难以识别 H7 3 986.23~3 986.6 3 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H7 3 982~3 982.5 5 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H7 花港组 4 325.72 1 剪切缝 未被充填 斜交缝,剪切裂缝,缝宽0.5 mm ,充填物难以识别,缝长>15 cm H11 4 335.8 1 剪切缝 被充填 H11 4 327.1~4 327.4 4 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H11 B1 4 328.4~4 328.6 6 成岩(脱水收缩) 被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行粉砂岩夹碳屑条带裂缝面上见沥青 H11 4 645.06~4 646.06 38 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 P3 4 646.06~4 647.16 25 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 P3 4 647.16~4 648.36 21 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 P3 4 648.66 1 剪切缝 未被充填 斜交缝,缝面平滑,缝宽1 mm P3 平湖组 4 649.06 1 张裂缝 未被充填 垂直缝,缝面不平滑,缝宽1.5 mm,缝长19 cm P3 4 649.56 1 张裂缝 未被充填 垂直缝,缝面不平滑,缝宽1.5 mm,缝长15 cm P3 4 651.56 1 张裂缝 部分被充填 斜交缝,缝面不平滑,缝宽1.5 mm,缝长10 cm P3 4 426.93~4 427.93 15 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 427.93~4 428.93 11 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 428.93~4 429.83 14 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 428.83~4 430.83 17 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 B2 4 430.83~4 431.83 8 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 花港组 4 431.83~4 432.83 14 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 432.83~4 433.83 17 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 433.83~4 434.83 10 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 434.83~4 435.83 16 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 4 434.83~4 436.83 8 成岩(脱水收缩) 未被充填 层理发育处,与层理近平行 H12 -
[1] 薛永安. 渤海海域深层天然气勘探的突破与启示[J]. 天然气工业,2019,36(1):17-26. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.01.002
XUE Yong'an. The breakthrough of the deep-buried gas exploration in the Bohai Sea area and its enlightenment[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2019,36(1):17-26. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.01.002
[2] 秦德文,高红艳,钟韬,等. 东海低渗气藏储层改造区“甜点”预测技术研究与应用[J]. 海洋石油,2017,37(2):45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.02.045
QIN Dewen,GAO Hongyan,ZHONG Tao,et al. Study and application of “sweet spot”prediction technique in the reservoir reconstruction of gas reservoir with low permeability in East China Sea[J]. Offshore Oil,2017,37(2):45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.02.045
[3] TAYLOR T R,GILES M R,HATHON L A,et al. Sandstone diagenesis and reservoir quality prediction:models,myths,and reality[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2010,94(8):1093-1132. doi: 10.1306/04211009123
[4] 宋子齐,成志刚,孙迪,等. 利用岩石物理相流动单元“甜点”筛选致密储层含气有利区:以苏里格气田东区为例[J]. 天然气工业,2013,33(1):41-48. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.01.006
SONG Ziqi,CHENG Zhigang,SUN Di,et al. Identification of tight gas play fairways according to flow unit sweet spots of petrophysical facies:a case study from the eastern Sulige Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2013,33(1):41-48. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2013.01.006
[5] 司朝年,邬兴威,夏东领,等. 致密砂岩油“甜点”预测技术研究:以渭北油田延长组长3油层为例[J]. 地球物理学进展,2015,30(2):664-671. doi: 10.6038/pg20150225
SI Chaonian,WU Xingwei,XIA Dongling,et al. The research of “sweet spot”prediction technology for tight sandstone reservoir:a case study of Chang 3 reservoir of Yanchang Formation in Weibei Oilfield[J]. Progress in Geographics,2015,30(2):664-671. doi: 10.6038/pg20150225
[6] 杨晓萍,赵文智,邹才能,等. 低渗透储层成因机理及优质储层形成与分布[J]. 石油学报,2007,28(4):57-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.011
YANG Xiaoping,ZHAO Wenzhi,ZOU Caineng,et al. Origin of low-permeability reservoir and distribution of favorable reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2007,28(4):57-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.011
[7] 祝海华,钟大康,李其荣,等. 四川盆地蜀南地区上三叠统须家河组低孔低渗透储层特征及形成机理[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(1):167-175.
ZHU Haihua,ZHONG Dakang,LI Qirong,et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of Upper Triassic Xujiahe tight sandstone reservoir in Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2013,31(1):167-175.
[8] 田景春,吴琦,王峰,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地下石盒子组盒8 段储集砂体发育控制因素及沉积模式研究[J]. 岩石学报,2011,27(8):2403-2412.
TIAN Jingchun,WU Qi,WANG Feng,et al. Research on development factors and the deposition model of large area reservoir sandstones of He8 section of Xiashihezi Formation of Permian in Ordos basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011,27(8):2403-2412.
[9] 赵仲祥,董春梅,林承焰,等. 低渗-致密砂岩储层“甜点”成因机制研究:以西湖凹陷X气田花港组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(5):995-1007.
ZHAO Zhongxiang,DONG Chunmei,LIN Chengyan,et al. Formation mechanism of “sweet spot” in low permeability and tight gas reservoirs:a case study of Huagang Formation in X Gas Field,Xihu Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology,2018,47(5):995-1007.
[10] 吴克强,谢晓军,廖计华,等. 中国近海古近纪碎屑岩储层特征与溶蚀作用规律[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(2):5-17.
WU Keqiang,XIE Xiaojun,LIAO Jihua,et al. The rules of reservoir characteristics and dissolution of paleogene clastic rocks in offshore China[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(2):5-17.
[11] 周心怀,徐国盛,崔恒远,等. 东海西湖凹陷中央反转构造带古近系花港组致密砂岩储集层裂缝发育特征与油气成藏关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):462-475. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.03
ZHOU Xinhuai,XU Guosheng,CUI Hengyuan,et al. Fracture development and hydrocarbon accumulation in tight sandstone reservoirs of the Paleogene Huagang Formation in the central reversal tectonic belt of the Xihu Sag,East China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2020,47(3):462-475. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.03
[12] 赵志兴,徐国盛,赵林海,等. 西湖凹陷西部斜坡带花港组、平湖组储层裂缝发育特征及有效裂缝测井识别[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(3):337-346 .
ZHAO Zhixing,XU Guosheng,ZHAO Linhai,et al. Characteristics of fracture development in the Huagang Formation and Pinghu Formation tight sandstone reservoirs and effective fracture logging identification and prediction in the western slope zone of Xihu Sag,East China Sea[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2021,48(3):337-346.
[13] 王允诚. 裂缝性致密储集层[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1992.
WANG Yuncheng. The Fracture-Controlled Stimulated Reservoir [M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1992.
[14] 曾联波,漆家福,王永秀. 低渗透储层构造裂缝的成因类型及其形成地质条件[J]. 石油学报,2007,28(4):52-56.
ZENG Lianbo,QI Jiafu,WANG Yongxiu. Origin type of tectonic fractures and geological conditions in low-permeabil ity reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2007,28(4):52-56.
[15] 曾大乾,张世民,卢立泽. 低渗透致密砂岩气藏裂缝类型及特征[J]. 石油学报,2003,24(4):36-39.
ZENG Daqian,ZHANG Shimin,LU Lize. Types and characteristics of fractures in tigh tsandstone gas reservoirs with low permeability[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2003,24(4):36-39.
[16] 袁静,曹宇,李际,等. 库车坳陷迪那气田古近系裂缝发育的多样性与差异性[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2017,38(5):840-850. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170502
YUAN Jing,CAO Yu,LI Ji,et al. Diversities and disparities of fracture systems in the Paleogene in DN Gas Field,Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology,2017,38(5):840-850. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170502
[17] 王振宇,刘超,张云峰,等. 库车坳陷K区块冲断带深层白垩系致密砂岩储层裂缝发育规律、控制因素与属性建模研究[J]. 岩石学报,2016,32(3):865-876.
WANG Zhengyu,LIU Chao,ZHANG Yunfeng. A study of fracture development controlling factor and property modeling of deep-lying tight sandstone in Cretaceous thrust belt K region of Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2016,32(3):865-876.
[18] 王春梅,黄思静,孙治雷,登. 川西坳陷须家河组致密砂岩储层裂缝发育特征及其成因:以孝泉-新场-合兴场地区为例[J]. 天然气工业,2011,31(8):43-47. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.08.010
WANG Chunmei,HANG Sijing,SUN Zhilei,et al. Characteristics and origin of fractures in tight sandstone reservoirs of the Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichun Depression:a case study in the Xiaoquan-Xinchang-Hexingchang area[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2011,31(8):43-47. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.08.010
[19] 巩磊,高铭泽,曾联波,等. 影响致密砂岩储层裂缝分布的主控因素分析:以库车前陆盆地侏罗系—新近系为例[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(2):199-208. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.12.003
GONG Lei,GAO Mingze,ZENG Lianbo,et al. Controlling factors on fracture development in the tight sandstone reservoirs:a case study of Jurassic-Neogene in the Kuqa foreland basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(2):199-208. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.12.003
[20] 季宗镇,戴俊生,汪必峰. 地应力与构造裂缝参数间的定量关系[J]. 石油学报,2010,33(1):68-72. doi: 10.7623/syxb201001011
JI Zonezhen,DAI Junsheng,WANG Bifeng. Quantitative relationship between crustal stress and parameters of tectonic fracture[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2010,33(1):68-72. doi: 10.7623/syxb201001011
[21] HOOPER E C D. Fluid migration along growth faults in compacting sediments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology,1991,14(2):161-180 .
[22] BARTON C A,ZOBACK M D,MOOS D. Fluid flow along potentially active faults in crystalline rock[J]. Geology,1995,23(4):683-686 .
-



 下载:
下载: