Development and distribution of carbonate ramp reservoir in the Persian Gulf Basin
-
摘要:
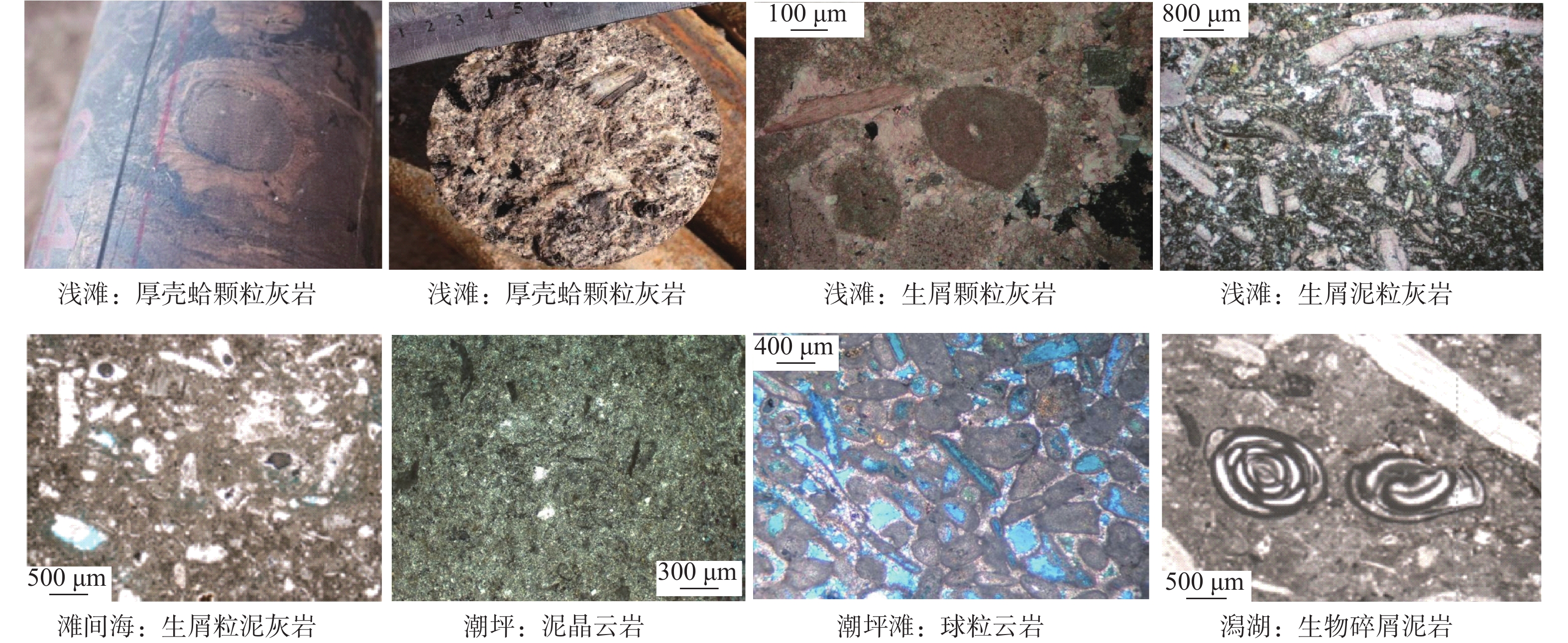
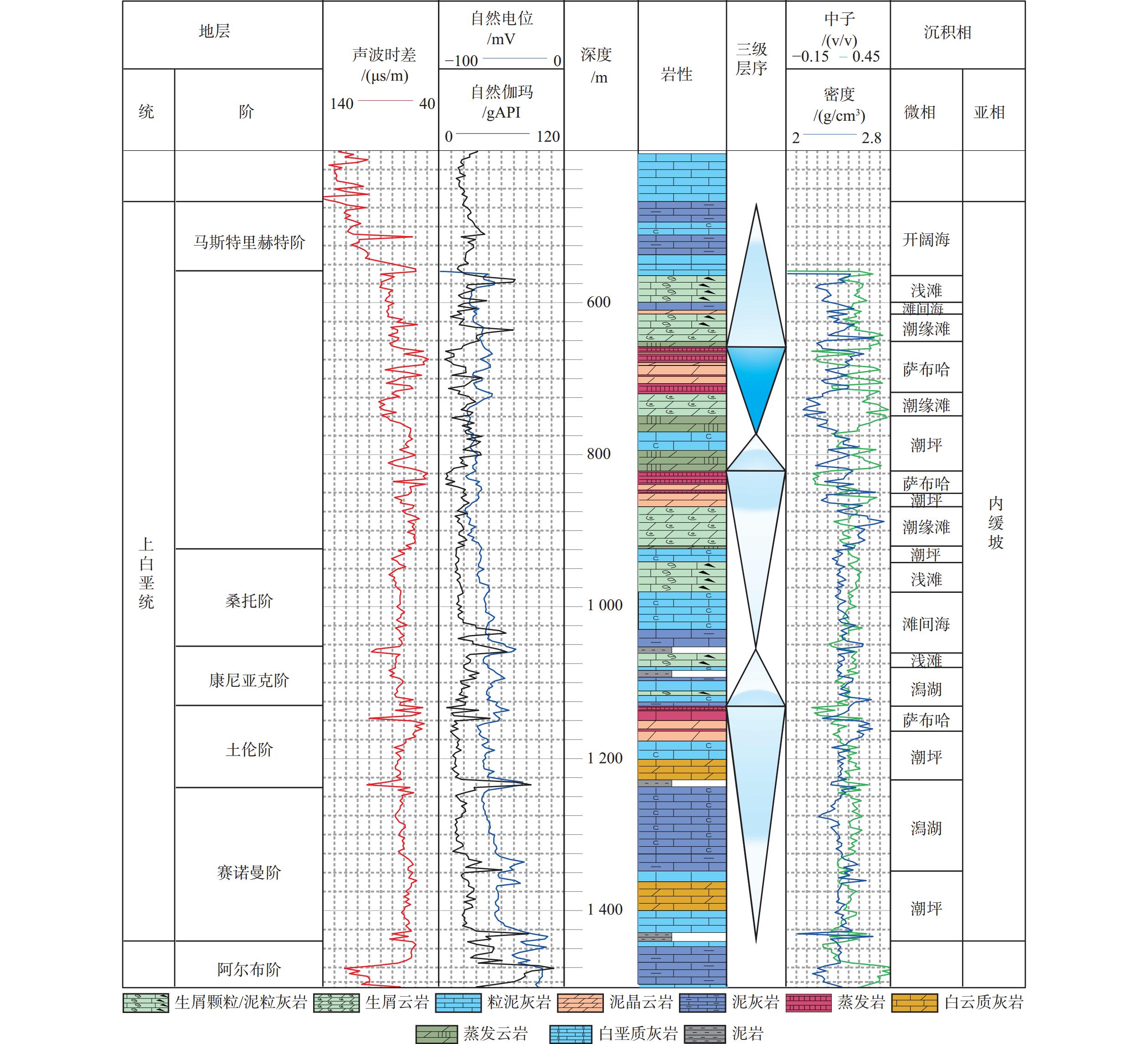
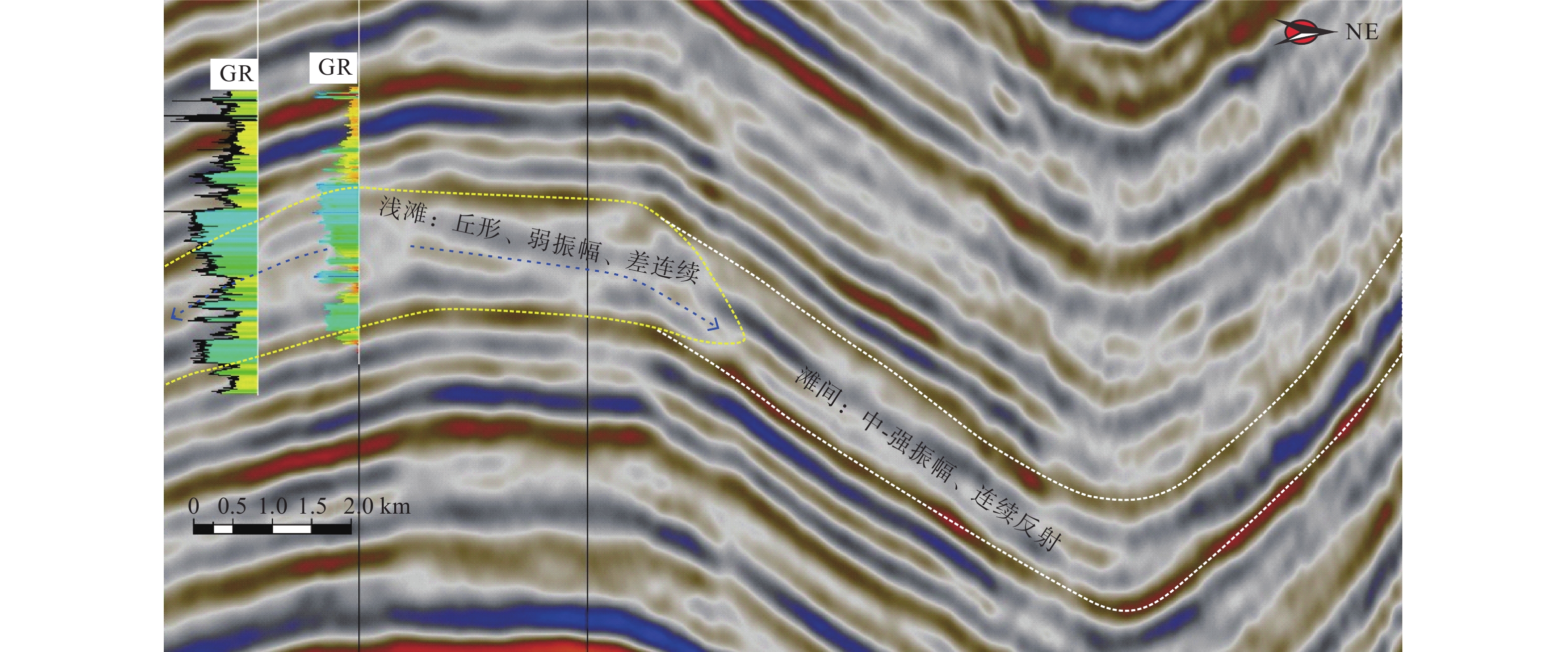
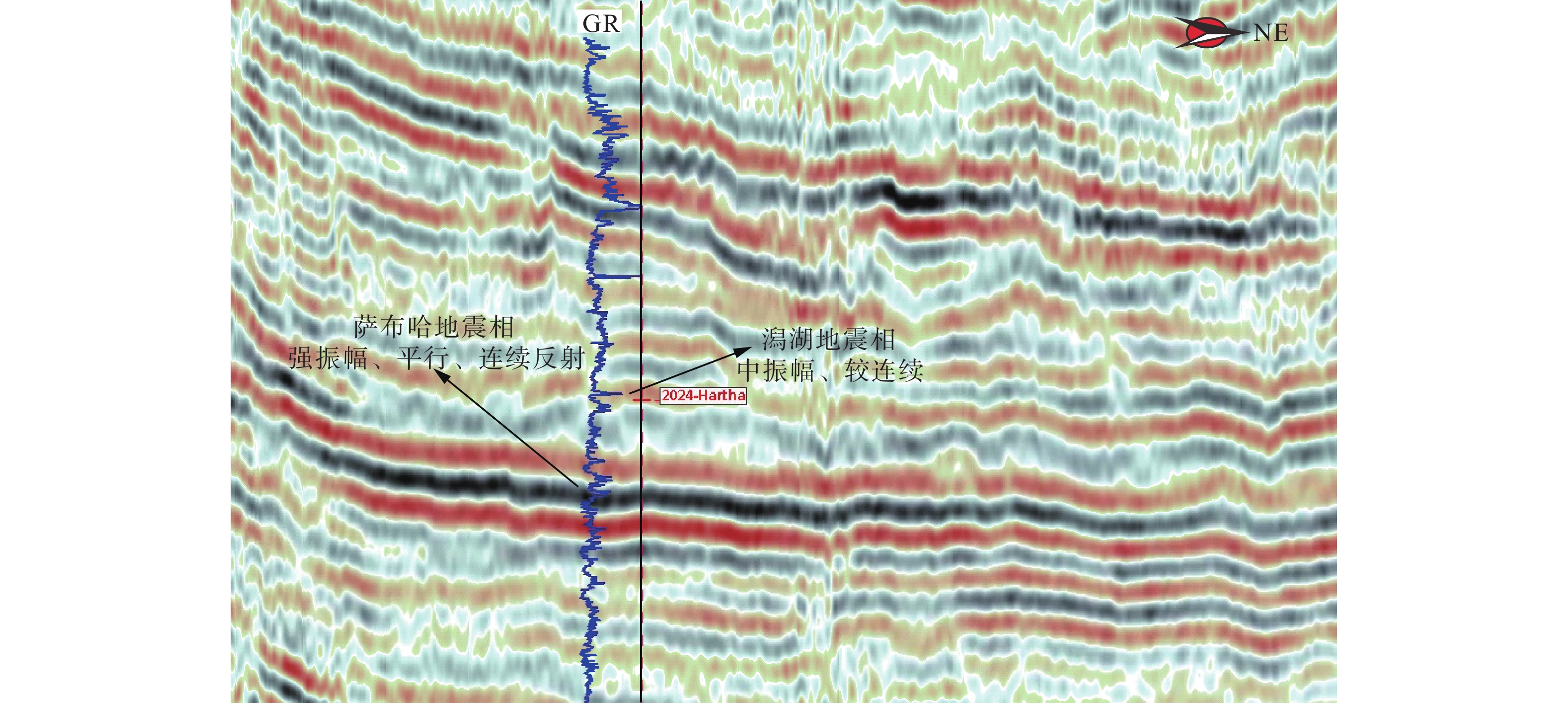
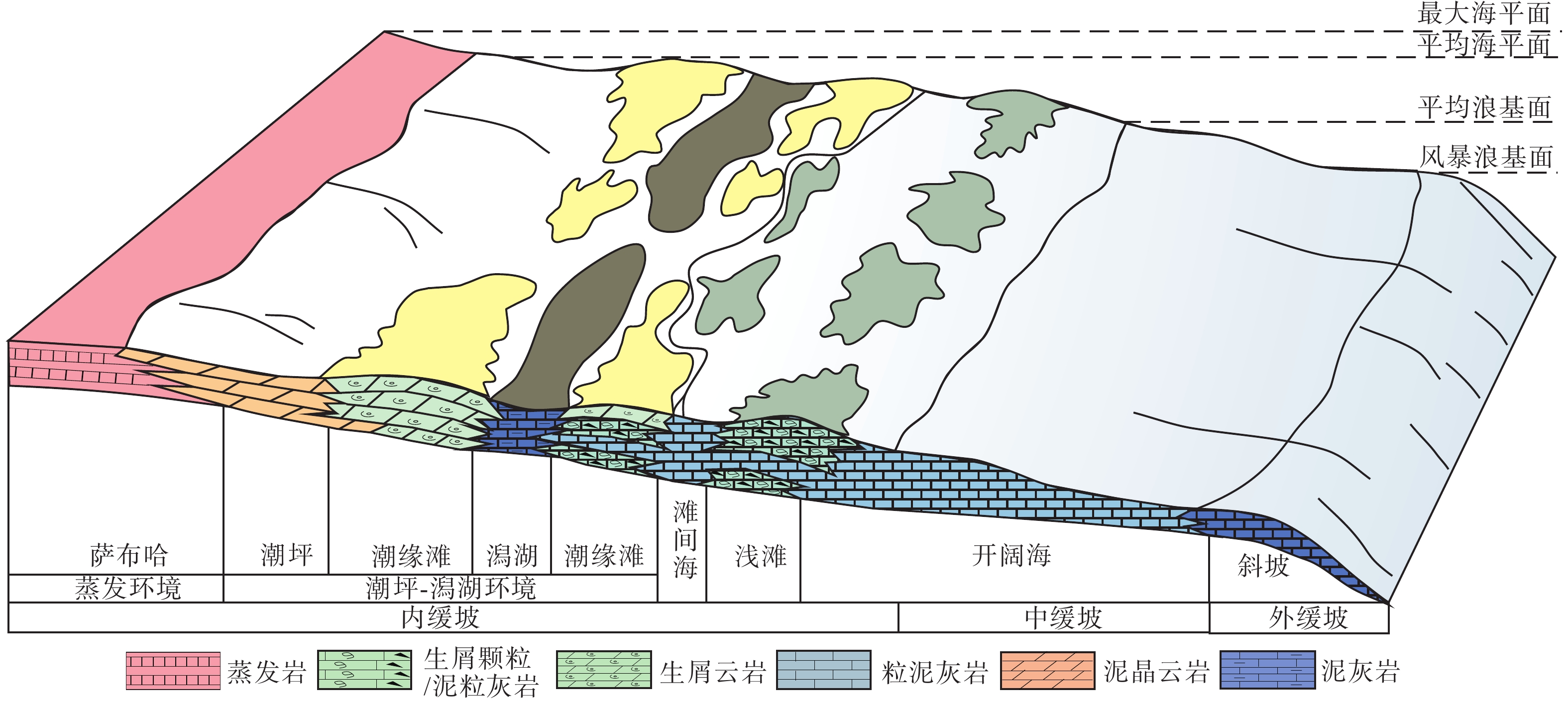
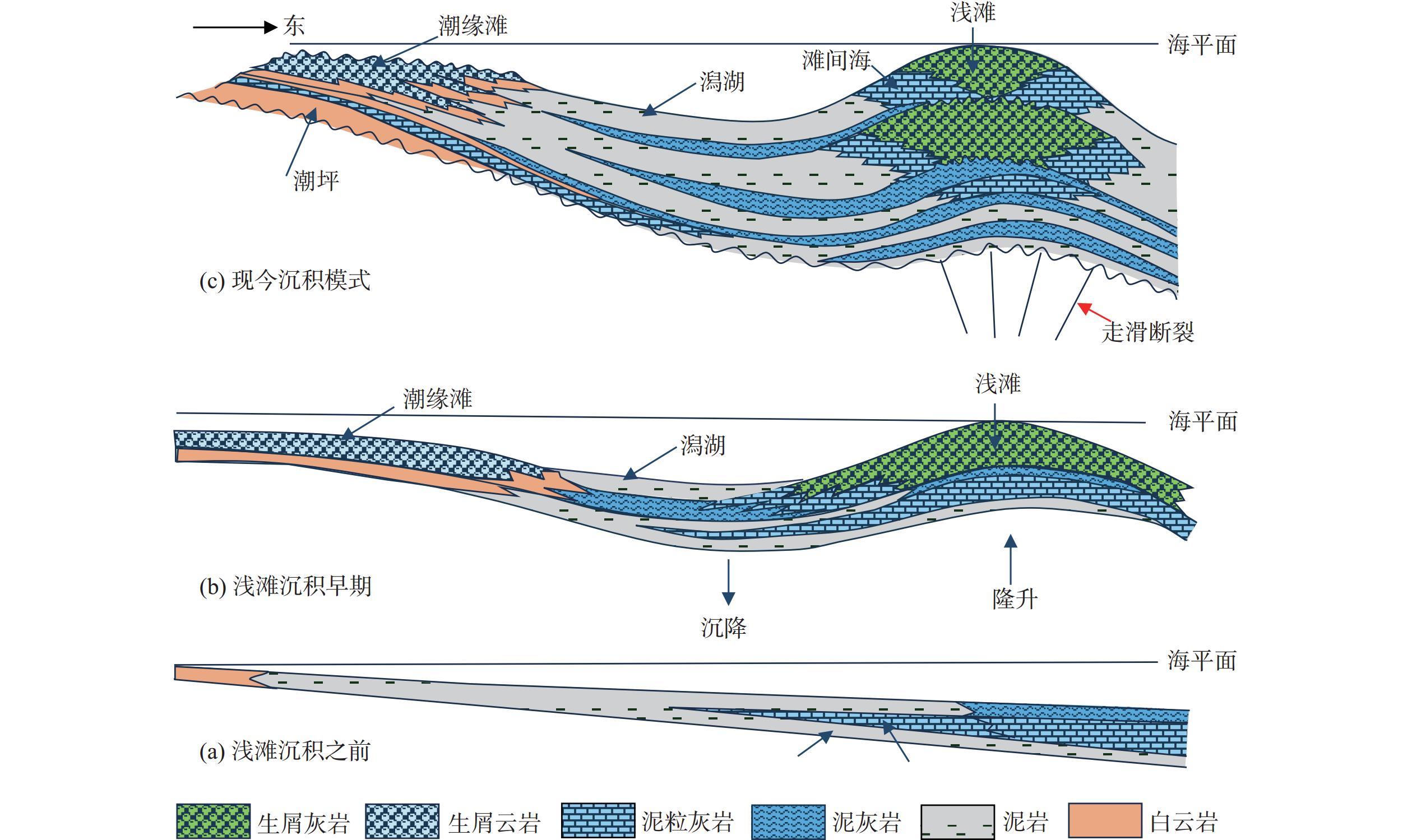
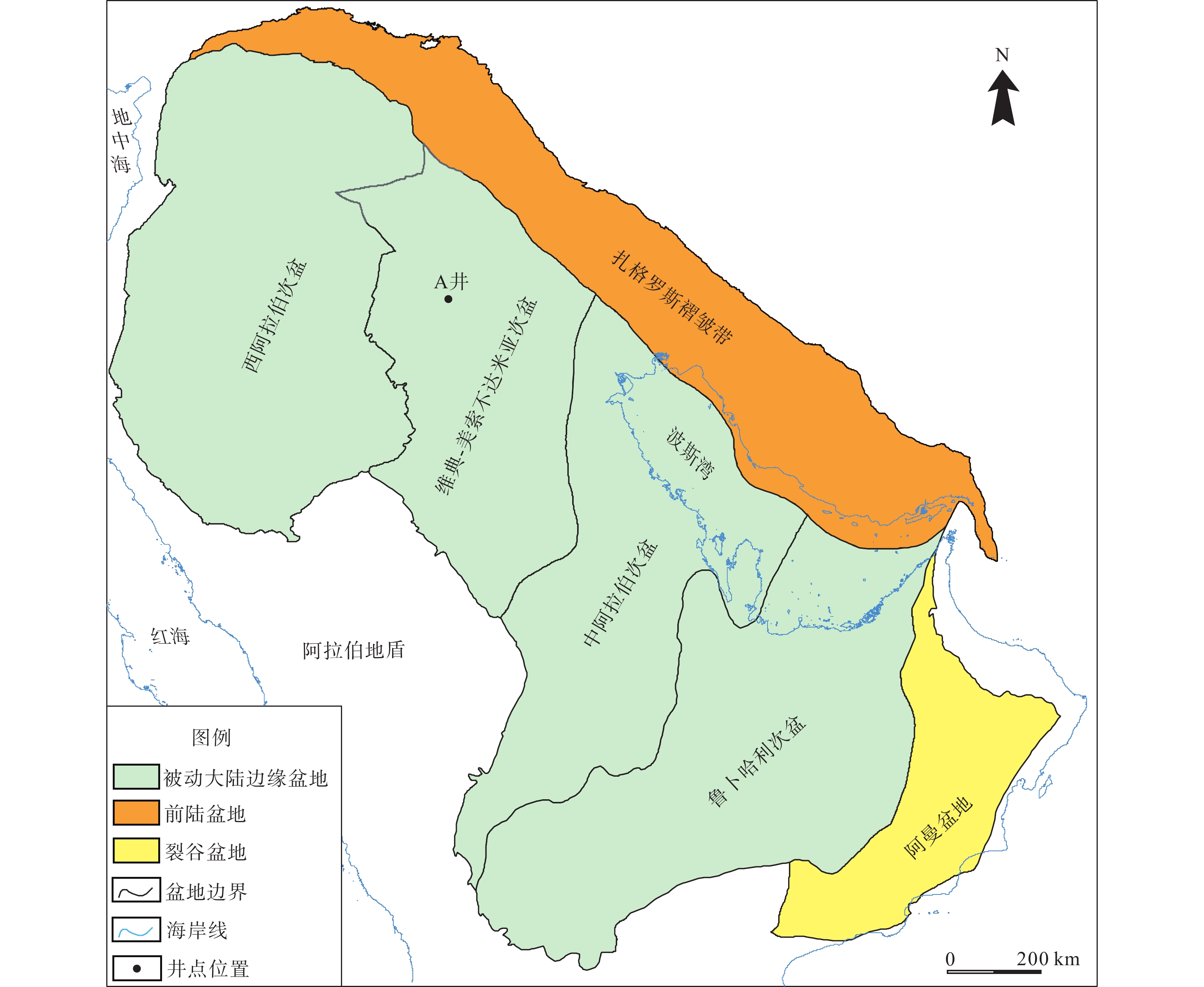
通过井震资料分析,对波斯湾盆地上白垩统碳酸盐岩缓坡储层发育模式与分布规律进行了研究,确定了研究区碳酸盐岩缓坡的沉积模式、储层发育的优势相带及发育控制因素。研究认为,波斯湾盆地上白垩统发育碳酸盐岩缓坡沉积,划分为内缓坡、中缓坡与外缓坡,内缓坡可进一步划分为萨布哈、潮坪、潟湖、潮缘滩、浅滩、滩间海沉积微相。浅滩相与潮缘滩相为有利储层发育带,其滩体的识别与预测对该区油气勘探至关重要。浅滩岩相主要为生屑灰岩,潮缘滩岩相主要为生屑云岩。地震相方面,碳酸盐岩滩体呈透镜状,地震反射具一定的前积结构,一般为弱振幅。测井相上,滩体表现“三高两低”特征。波斯湾盆地晚白垩世挤压形成的古地貌高控制了碳酸盐岩储层展布及发育程度,该认识可为波斯湾盆地碳酸盐岩领域油气勘探提供参考。
Abstract:On the basis of regional study, combined with drilling, logging, and seismic profiling, the development and distribution of the Upper Cretaceous carbonate ramp reservoir in the Persian Gulf Basin were studied, and the depositional pattern, favorable reservoir development facies, and distribution control factors were clarified. The Upper Cretaceous carbonate ramp sediments could be divided into inner ramp, middle ramp, and outer ramp; and the inner ramp could be sub-divided into the sedimentary microfacies of Sabha, tidal flat, lagoon, tidal shoal, shoal, and intershoal. The shoal facies and tidal shoal facies are favorable for reservoir development. The identification and prediction of shoal bodies are very important for oil and gas exploration in the area. The shoal lithofacies are mainly bioclastic limestone and the tidal shoal lithofacies are mainly bioclastic dolomite. In seismic profiles, the shoal body is lenticular in shape, and the seismic reflections have a certain clinoform structure and generally have weak amplitudes. The logging pattern of the shoal body is characterized by “three high and two low”, namely, high acoustic time difference, high neutron, and high porosity or permeability; and low gamma and low density. In the Persian Gulf Basin, the palaeogeomorphic high formed by extrusion in the Late Cretaceous controlled the distribution characteristics and development degree of reservoir. This study provided a good reference for the exploration onto carbonate oil and gas to clarify the development and distribution of the reservoir in shoal and tidal shoal facies.
-
Key words:
- Persian Gulf Basin /
- carbonate ramp /
- shoal /
- depositional model /
- main controlling factors
-

-
[1] AHR W M. Sedimentary and tectonic controls on the development of an Early Mississippian carbonate ramp,Sacramento Mountains area,New Mexico[M]//CREVELLO P,WILSON J,SARG F,et al. Controls on Carbonate Platforms and Basin Development. Tulsa:SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology,1989.
[2] 曾允孚,王成善. 海洋碳酸盐沉积相模式[J]. 矿物岩石,1991,11(3):107-117.
[3] BÁBEK O,KALVODA J,COSSEY P,et al. Facies and petrophysical signature of the Tournaisian/Viséan (Lower Carboniferous) sea-level cycle in carbonate ramp to basinal settings of the Wales-Brabant massif,British Isles[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2013,284/285:197-213.
[4] 杜金虎,张宝民,汪泽成,等. 四川盆地下寒武统龙王庙组碳酸盐缓坡双颗粒滩沉积模式及储层成因[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(6):1-10.
[5] KAKEMEM U,JAFARIAN A,HUSINEC A,et al. Facies,sequence framework,and reservoir quality along a Triassic carbonate ramp:Kangan Formation,South Pars Field,Persian Gulf Superbasin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,198:108166.
[6] 李扬, 刘波,田昌炳, 等. 伊拉克Y油田上白垩统Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层及其测井响应特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016,23(6):8-15.
李扬, 刘波, 田昌炳, 等. 伊拉克Y油田上白垩统Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层及其测井响应特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(6):8-15.
[7] HUSEINI M I. Tectonic and deposition model of late Precambrian-Cambrian Arabian and adjoining plates[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1989,73(9):1117-1131.
[8] ALSHARHAN A S,NAIRN A E M. Sedimentary basin and petroleum geology of the Middle East[M]. Amsterdam:The Netherlands,Elservier Science B V,2003:559-574.
[9] GHABEISHAVI A,VAZIRI-MOGHADDAM H,TAHERI A,et al. Microfacies and depositional environment of the Cenomanian of the Bangestan anticline,SW Iran[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2010,37(3):275-285.
[10] SADOONI F N. The nature and origin of Upper Cretaceous basin-margin rudist buildups of the Mesopotamian Basin,southern Iraq,with consideration of possible hydrocarbon stratigraphic entrapment[J]. Cretaceous Research,2005,26(2):213-224.
[11] AL-QAYIM B. Sequence stratigraphy and reservoir characteristics of the Turonian-Coniacian Khasib Formation in central Iraq[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology,2010,33(4):387-403.
[12] 高计县,田昌炳,张为民,等. 波斯湾盆地中白垩统Mishrif组碳酸盐岩储层特征及其发育模式[J]. 地质科学,2013,48(1):304-316.
[13] 黄茜,伏美燕,赵丽敏,等. 伊拉克HF油田上白垩统碳酸盐缓坡相储层发育特征[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(2):371-378.
[14] 杨永才,孙玉梅,李友川,等. 波斯湾盆地烃源岩地球化学特征与油气分布规律[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(5):36-46,70.
[15] 信石印,谢楠,张鑫,等. 波斯湾盆地烃源岩特征及对油气成藏的控制[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2017,33(5):45-51.
[16] 张鑫,苗顺德,刘小龙,等. 阿联酋地区碳酸盐礁滩体沉积特征与主控因素[J]. 中国海上油气,2022,34(5):87-93.
[17] SOK R,KNACKSTEDT M,GHOUS A,et al. Integrating Petrographic,Petrophysical and 3-D Pore Scale Measurements of Core Material from the Shuaiba Reservoir in Al Shaheen,Qatar[R]. Denver,Colorado:AAPG Annual Convention,2009:1-3.
[18] ALSHARHAN A S,AL-AASM I S,SALAH M G. Stratigraphy,stable isotopes,and hydrocarbon potential of the Aptian Shuaiba Formation,U. A. E. [M]// ALSHARHAN A S,SCOTT R W. Middle East Models of Jurassic/Cretaceous Carbonate Systems. Tulsa,United States:SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology,2000:299-314.
[19] SHARLAND P R,ARCHER R,CASEY D M,et al. Arabian plate sequence stratigraphy[M]. Bahrain:Gulf PetroLink,2001:83-95.
[20] 郑磊,金之钧,张哨楠. 中东鲁卜哈利盆地古生界致密砂岩储层特征及评价[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2013,34(4):475-482.
[21] 赵学钦,杨海军,马青,等. 塔北奥陶系碳酸盐岩沉积演化特征及台地发育模式[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2014,34(2):36-42.
[22] 刘艺妮,胡明毅,张三,等. 碳酸盐缓坡沉积微相特征及其对储集层发育的制约:以塔里木盆地古城地区中—下奥陶统为例[J]. 石油勘探与开放,2022,49(1):93-105.
[23] 王建坡,李越,程龙,等. 华南板块古生代生物礁及其古地理控制因素[J]. 古生物学报,2014,53(1):121-131.
-



 下载:
下载: