Characteristics of hydrocarbon distribution and analysis of the main controlling factors for reservoir formation in the central and southern anticline zone of XH Depression
-
摘要:
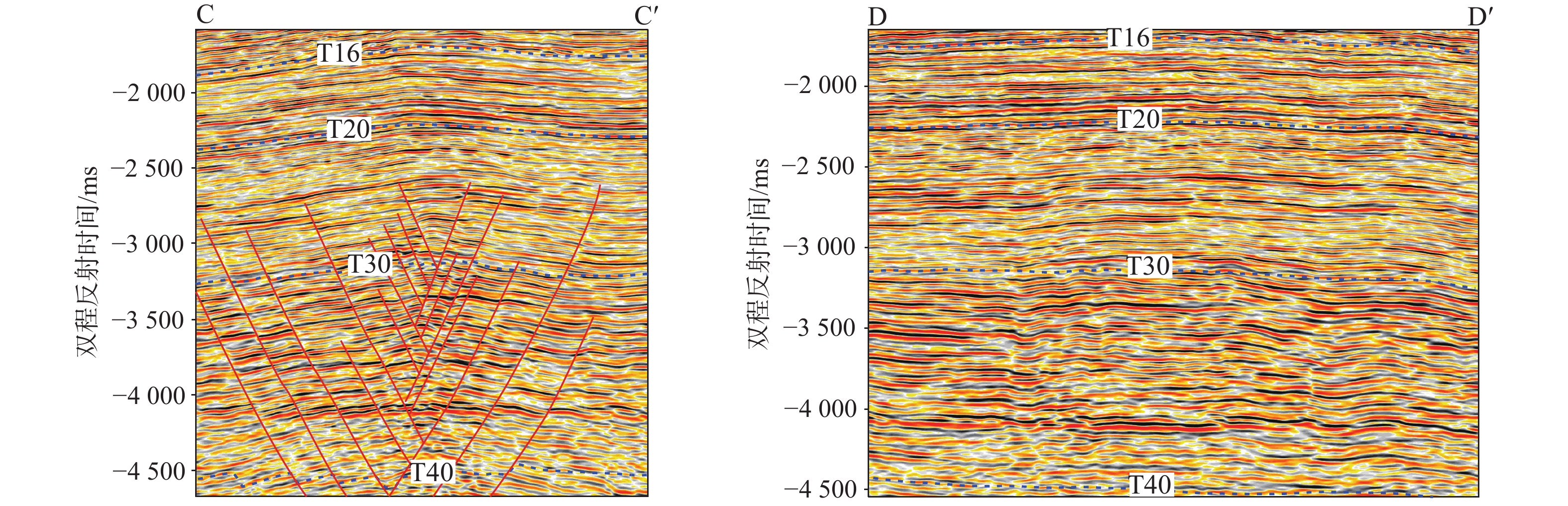
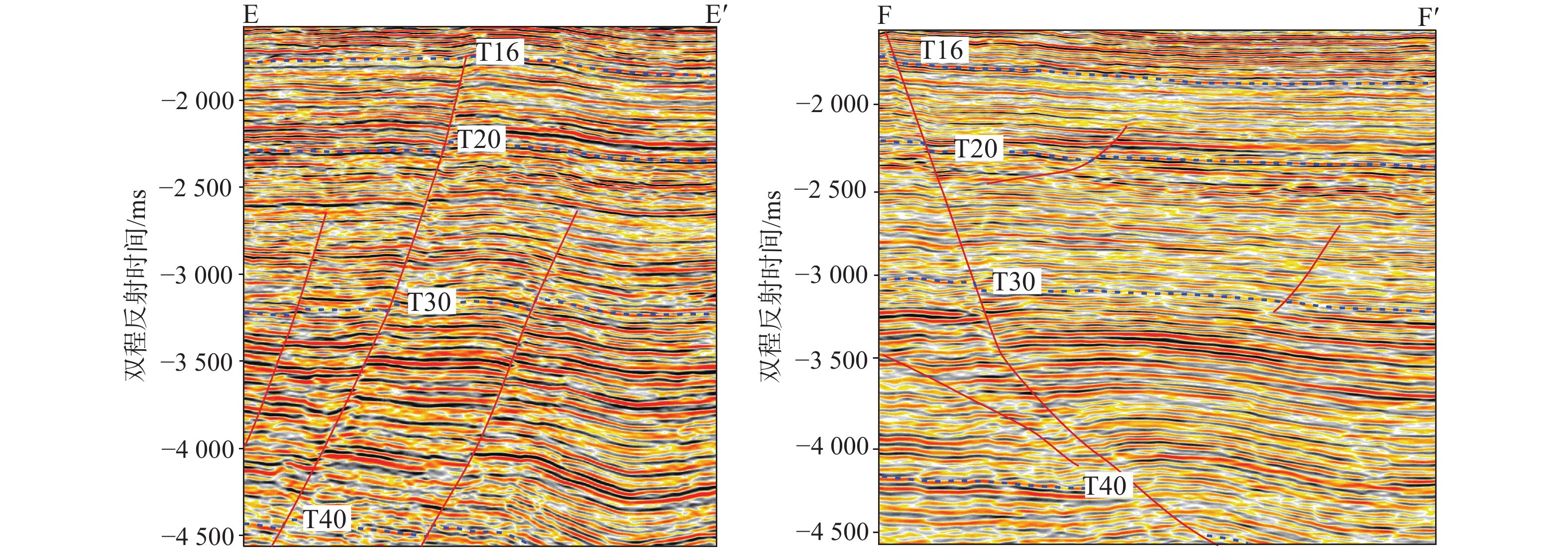
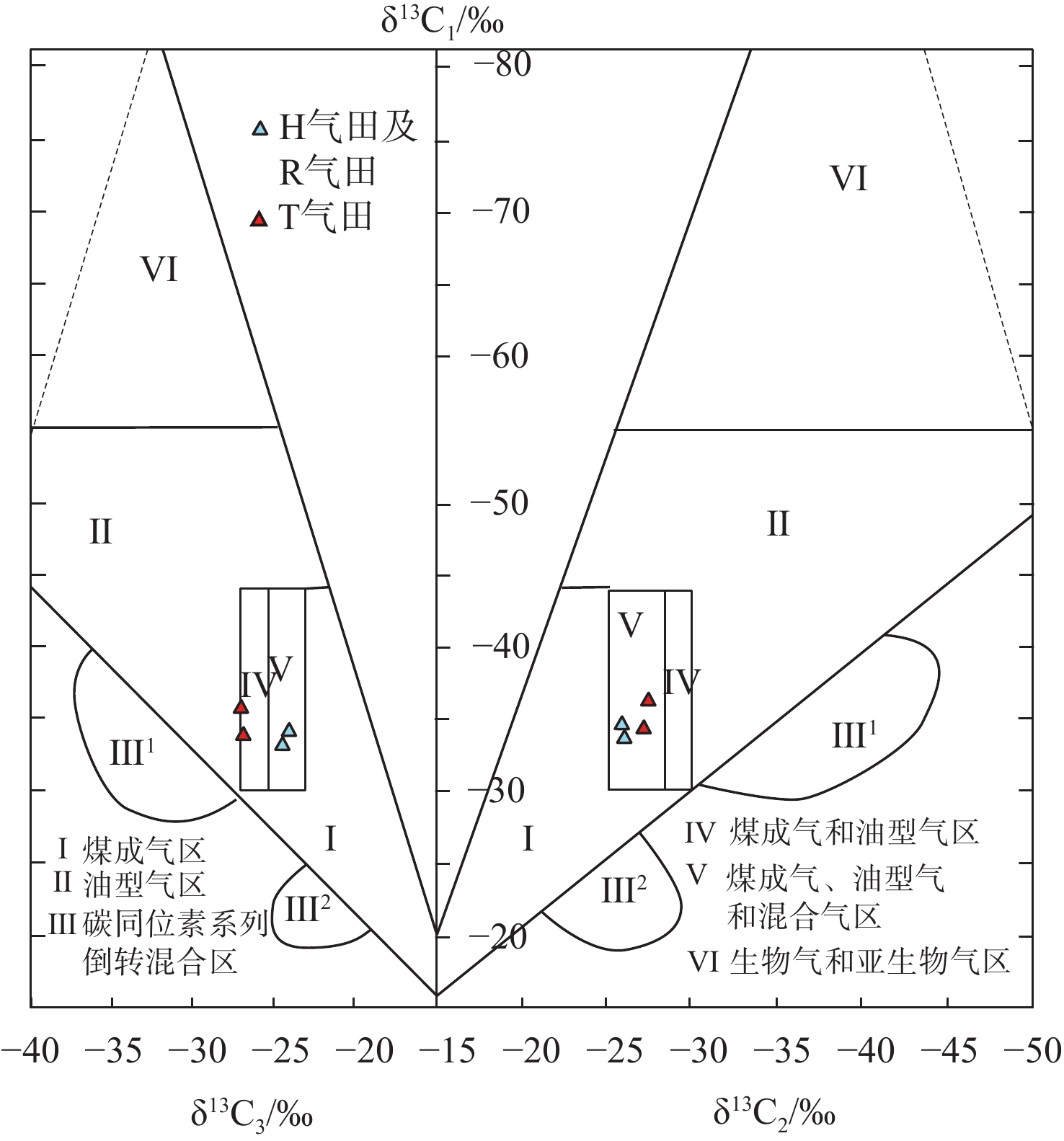
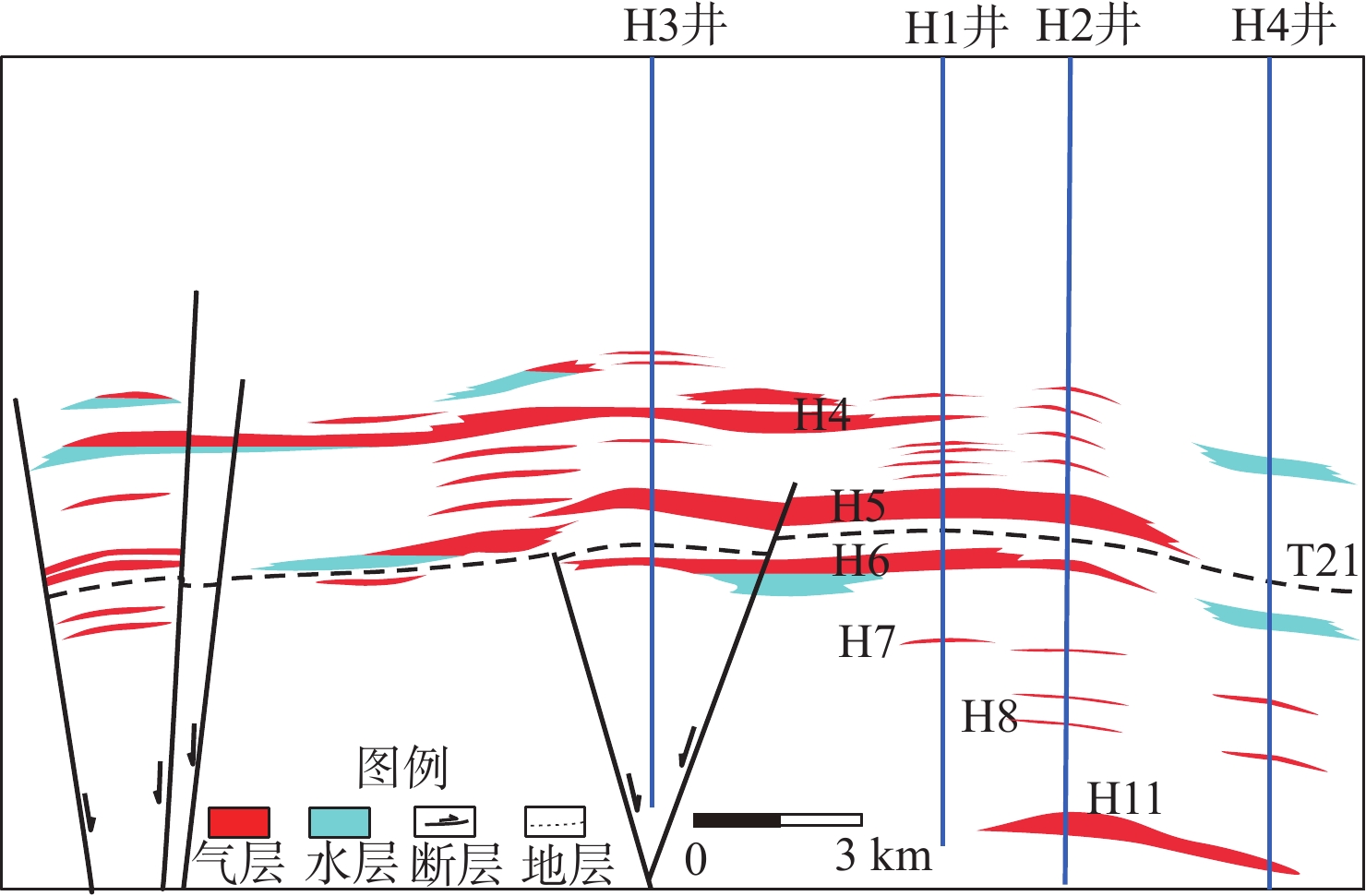
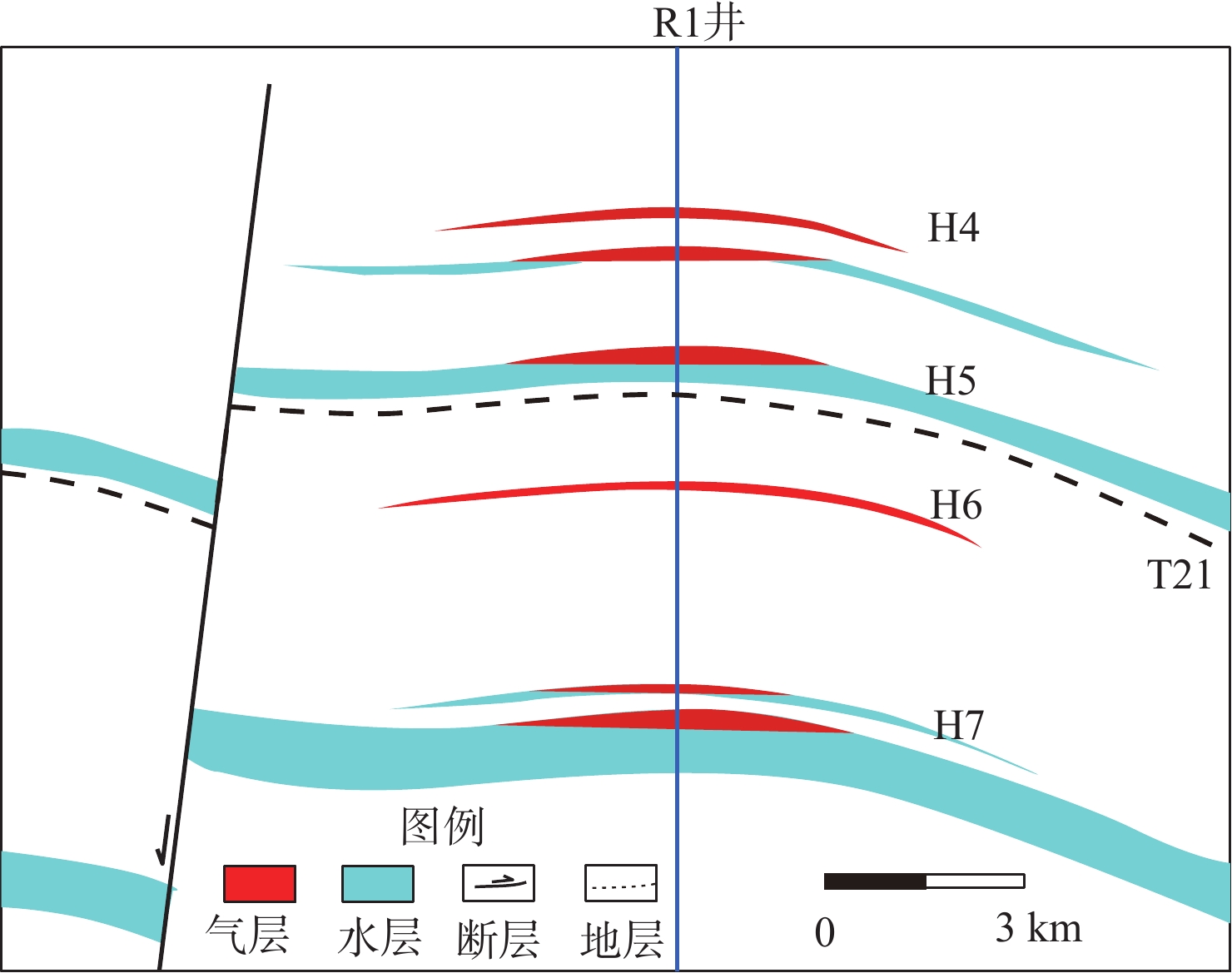
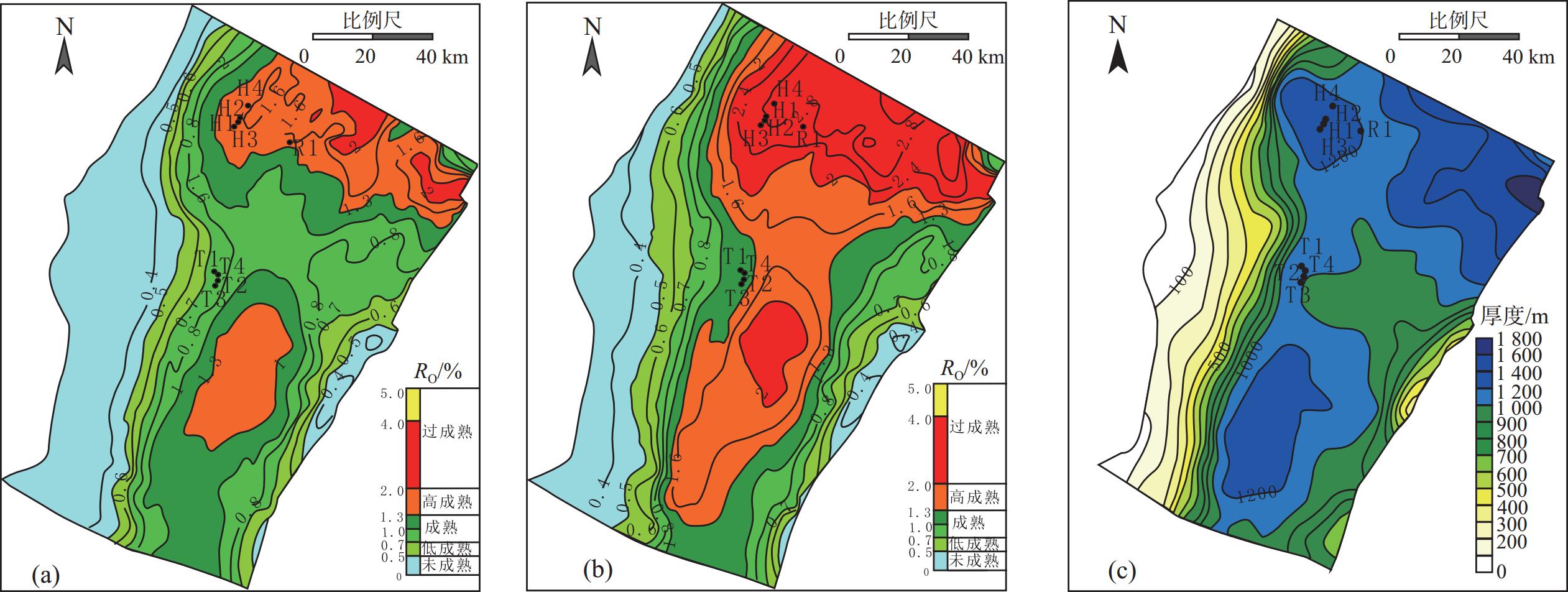
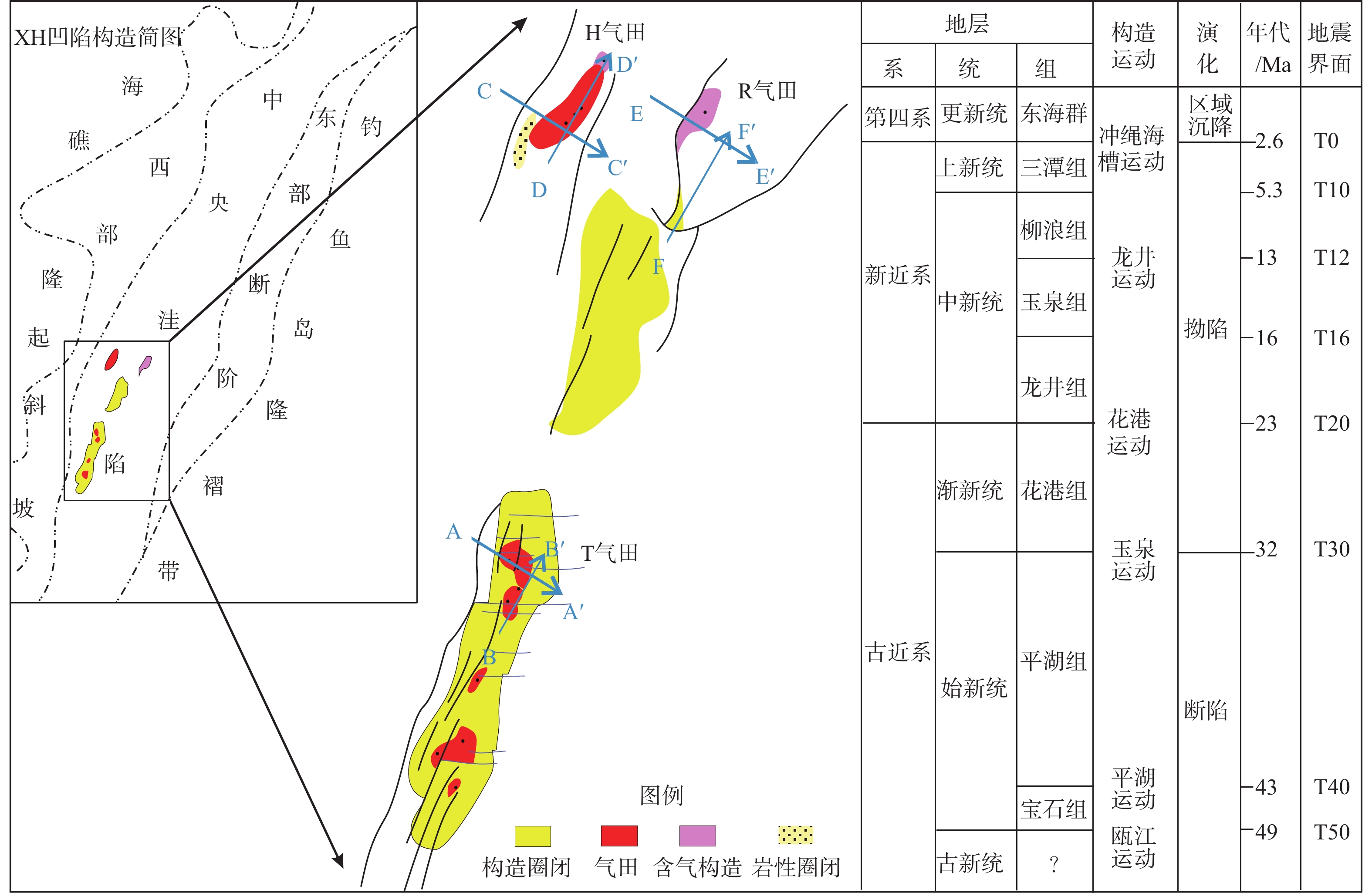
为了厘清XH凹陷中南部背斜带的油气成藏主控因素,解剖了中南部T气田、H气田、R气田等3个典型油气田。研究表明:中南部背斜带油气成因、来源和成藏期次一致,但油气分布却存在显著差异性,主要表现在富集程度、纵向分布层位和平面赋存位置3个方面。分析认为,造成油气分布差异性的主控因素为断裂系统、烃源岩分布、源-储构造叠合关系和断-砂耦合关系。断裂系统的差异性决定纵向上油气分布层位以及构造内部的差异化富集程度;平湖组煤系烃源岩成熟度和厚度分布的差异性决定区域油气富集程度;花港组源外成藏背景下,成藏期平湖组烃源层顶面构造与花港组储集层构造叠合关系决定局部构造汇烃强度;中南部花港组强水道化背景下,断层与砂体耦合关系决定单层油气成藏规模。
Abstract:In order to clarify the main controlling factors for reservoir formation in the central and southern anticline zone of XH Depression, three typical oil and gas fields in the central and southern part, including T Gas Field, H Gas Field, and R Gas Field, were dissected. The results showed that the source and accumulation stage of hydrocarbons in the central and southern anticline belt were consistent, but there were significant differences in hydrocarbon distribution, mainly manifesting in three aspects: enrichment degree, vertical distribution horizon and plane occurrence location. The analysis believed that the main controlling factors causing the differences in hydrocarbon distribution were fault system, hydrocarbon source rock distribution, source-reservoir structural overlap relationship, and fault-sand coupling relationship. The difference of fault system determined the vertical distribution horizon of hydrocarbons and the differential enrichment degree inside the structure; the difference of maturity and thickness distribution of coal measure source rocks in Pinghu Formation determined the regional hydrocarbon enrichment degree; under the background of hydrocarbon accumulation outside the source rocks in Huagang Formation, the overlap relationship between the top surface structure of Pinghu Formation source rocks and the reservoir structure of Huagang Formation determined the local structural hydrocarbon accumulation intensity; and under the background of strong waterway in Huagang Formation in the central and southern part, the coupling relationship between faults and sand bodies determined the hydrocarbon accumulation scale of single layer.
-

-
[1] 苏奥,陈红汉,胡飞,等. 西湖凹陷中央构造带中南部油气成藏条件、特征及富集规律[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(2):129-135.
[2] 谢月芳,陈敏娟,王坚勇. 东海西湖凹陷浙东中央背斜带中南部油气成藏规律与晚期剪切断层的关系探讨[J]. 海洋石油,2002(112):9-14.
[3] 苏程,李春峰,葛和平. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷渐-中新世异常反射体的特征与成因[J]. 海洋学研究,2010,28(4):16-23.
[4] 周心怀,徐国盛,崔恒远,等. 东海西湖凹陷中央反转构造带古近系花港组致密砂岩储集层裂缝发育特征与油气成藏关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):462-475.
[5] 于兴河,李顺利,曹冰,等. 西湖凹陷渐新世层序地层格架与沉积充填响应[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(2):299-314.
[6] 周荔青,江东辉,张尚虎,等. 东海西湖凹陷大中型油气田形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(5):159-168.
[7] 徐发,张建培,张田,等. 西湖凹陷输导体系特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(7):28-33.
[8] 刘亚茹,高顺莉,周平,等. 西湖凹陷转换断裂发育特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,36(10):44-51.
[9] 周心怀,蒋一鸣,唐贤君. 西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J]. 中国海上油气,2019,31(3):1-10.
[10] 邹玮,余一欣,刘金水,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中央反转构造带发育主控因素及宁波背斜形成过程[J]. 石油学报,2021,42(2):176-185.
[11] 戴金星. 各类烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学(B辑),1992,22(2):185-193.
[12] 徐陈杰,叶加仁,刘金水,等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖组Ⅲ型干酪根暗色泥岩生排烃模拟[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(2):359-366.
[13] 沈伟锋,于仲坤,刁慧,等. 西湖凹陷热流演化史模拟及成藏意义[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(1):42-53.
[14] 钱门辉. 西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩生烃特征研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2010:1-99.
[15] 朱扬明,周洁,顾圣啸,等. 西湖凹陷始新统平湖组煤系烃源岩分子特征[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(1):32-39.
[16] 贾健谊,须雪豪,孙伯强. 东海西湖凹陷原油与天然气的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋石油,2000,20(2):1-7.
[17] EADINGTON P J,LISK M,KRIEGER F W. Identify oil wellsites [P]. USA,Ptent No. 5543616.1996-08-06.
[18] 郝雪峰,陈红汉,高秋丽,等. 东营凹陷牛庄砂岩透镜体油气藏微观充注机理[J]. 地球科学,2006,31(2):44-52.
[19] 赵彦德,齐亚林,罗安湘,等. 应用流体包裹体和自生伊利石测年重构鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系油藏烃类充注史[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2016,46(6):43-54.
[20] 傅宁,杨树春,贺清,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴—神府区块致密砂岩气高效成藏条件[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(1):115-124.
[21] 蒋海军,胡明毅,胡忠贵,等. 西湖凹陷古近系沉积环境分析:以微体古生物化石为主要依据[J]. 岩性油气藏,2011,23(1):74-78.
[22] 蔡佳,祁鹏,宋双. 东海盆地西湖凹陷花港组下段沉积相分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(2):56-65.
[23] 张彦振,刘金水,覃军,等. 西湖凹陷中央洼陷带中部花港组岩性油气藏主控因素及形成模式[J]. 中国海上油气,2021,33(2):36-46.
[24] 姜雪,肖晓光,王宇. 多手段厘定东海西湖凹陷花港组物源体系[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(6):57-66.
-



 下载:
下载: