Geological conditions and prospects for CO2 storage in the Cenozoic strata of the Yantai Depression, South Yellow Sea Basin
-
摘要:
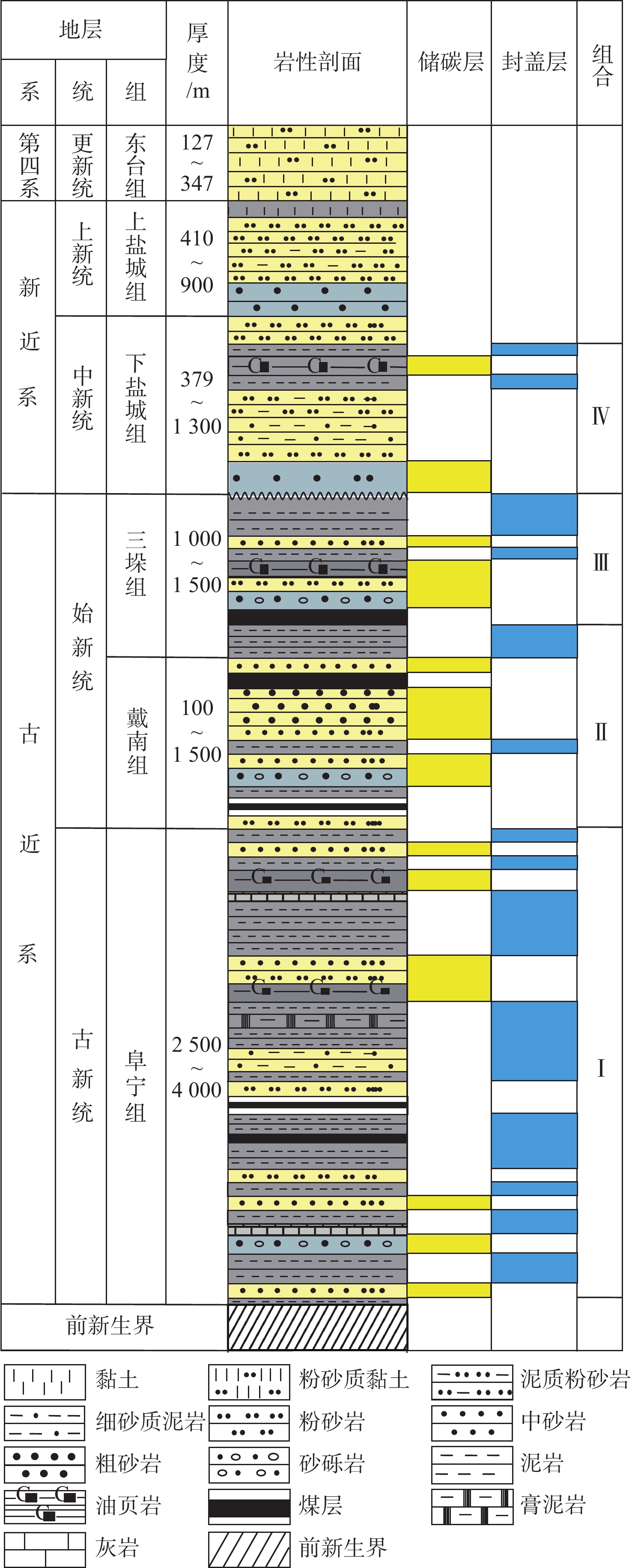
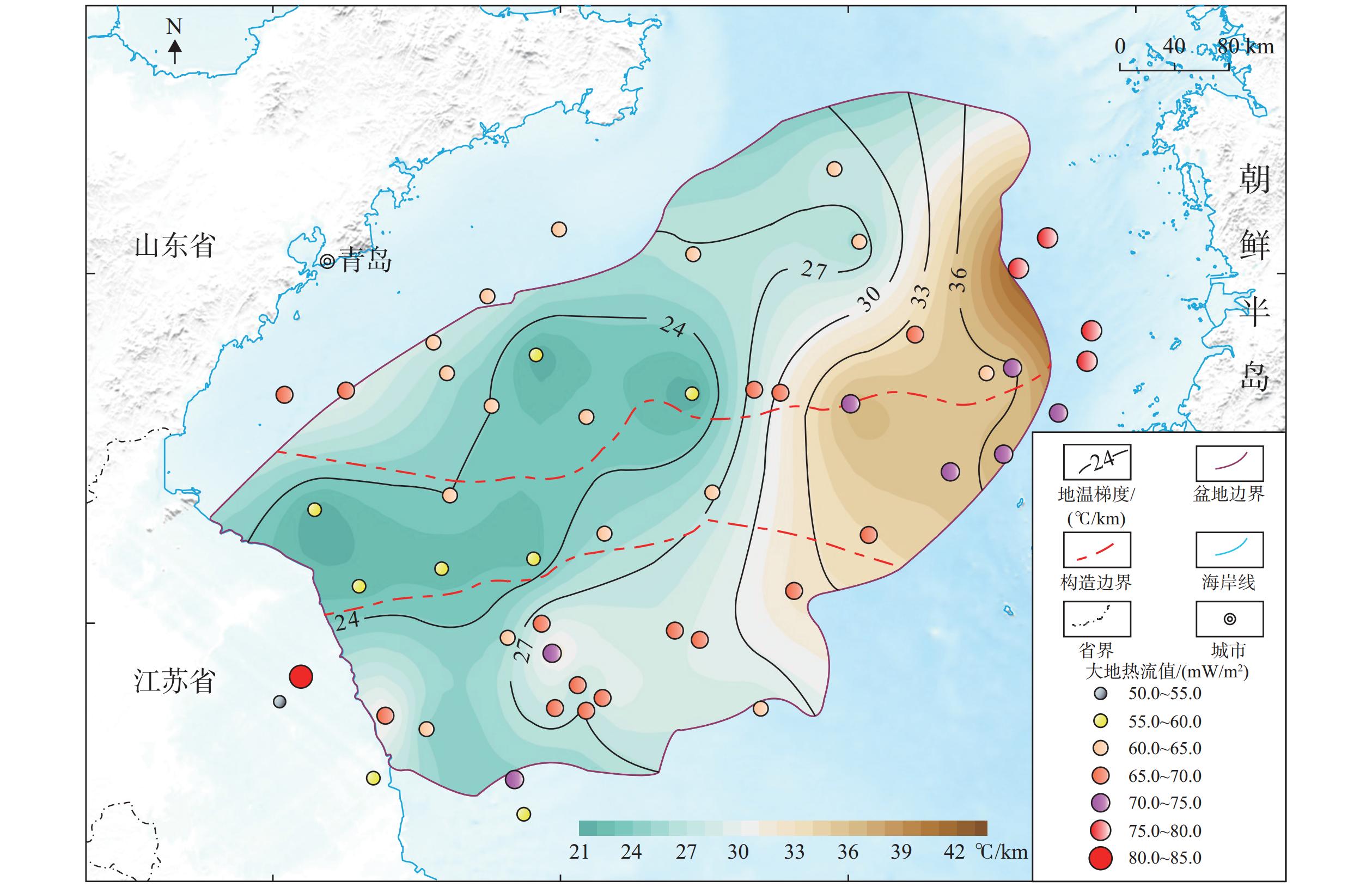
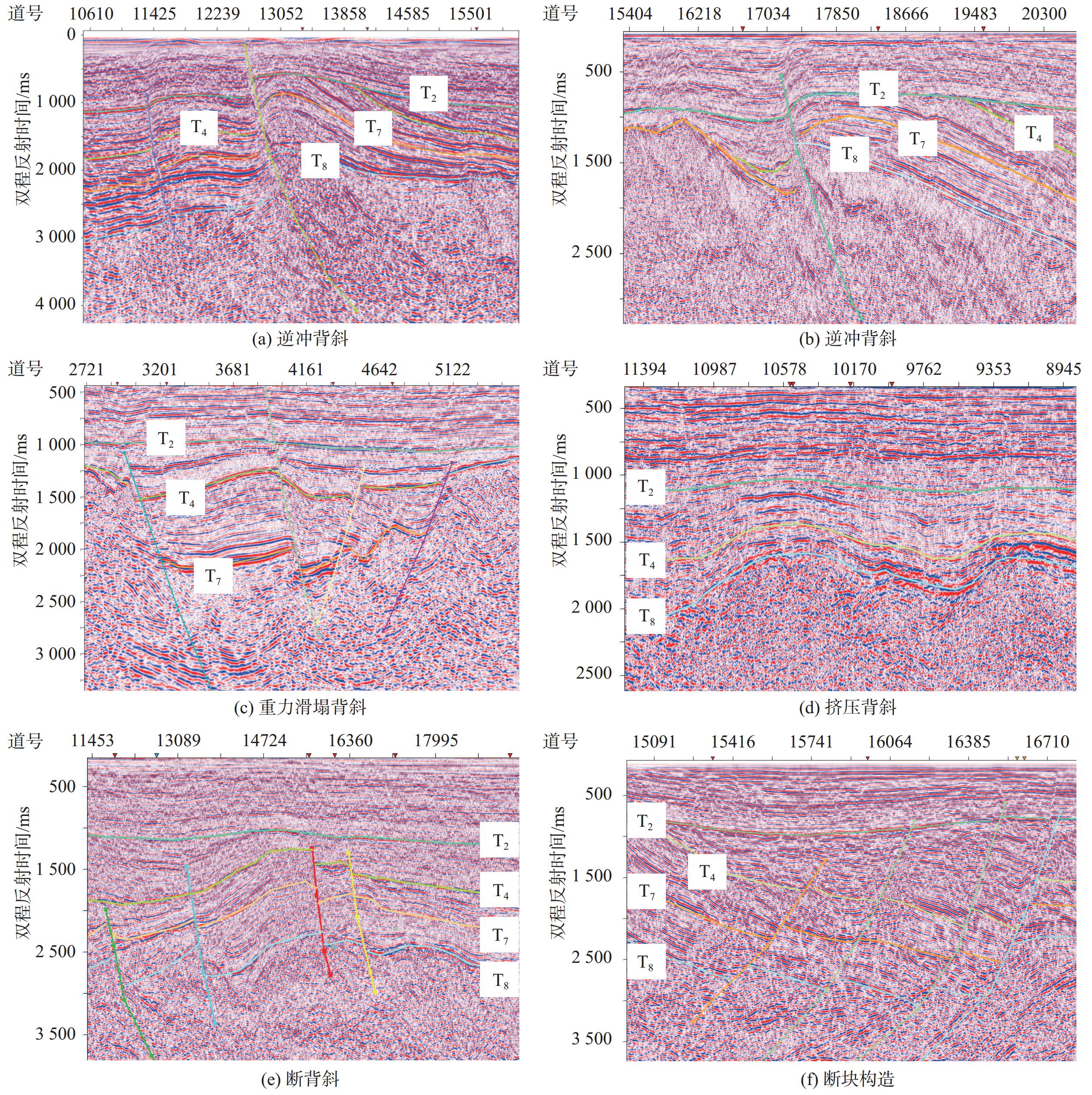
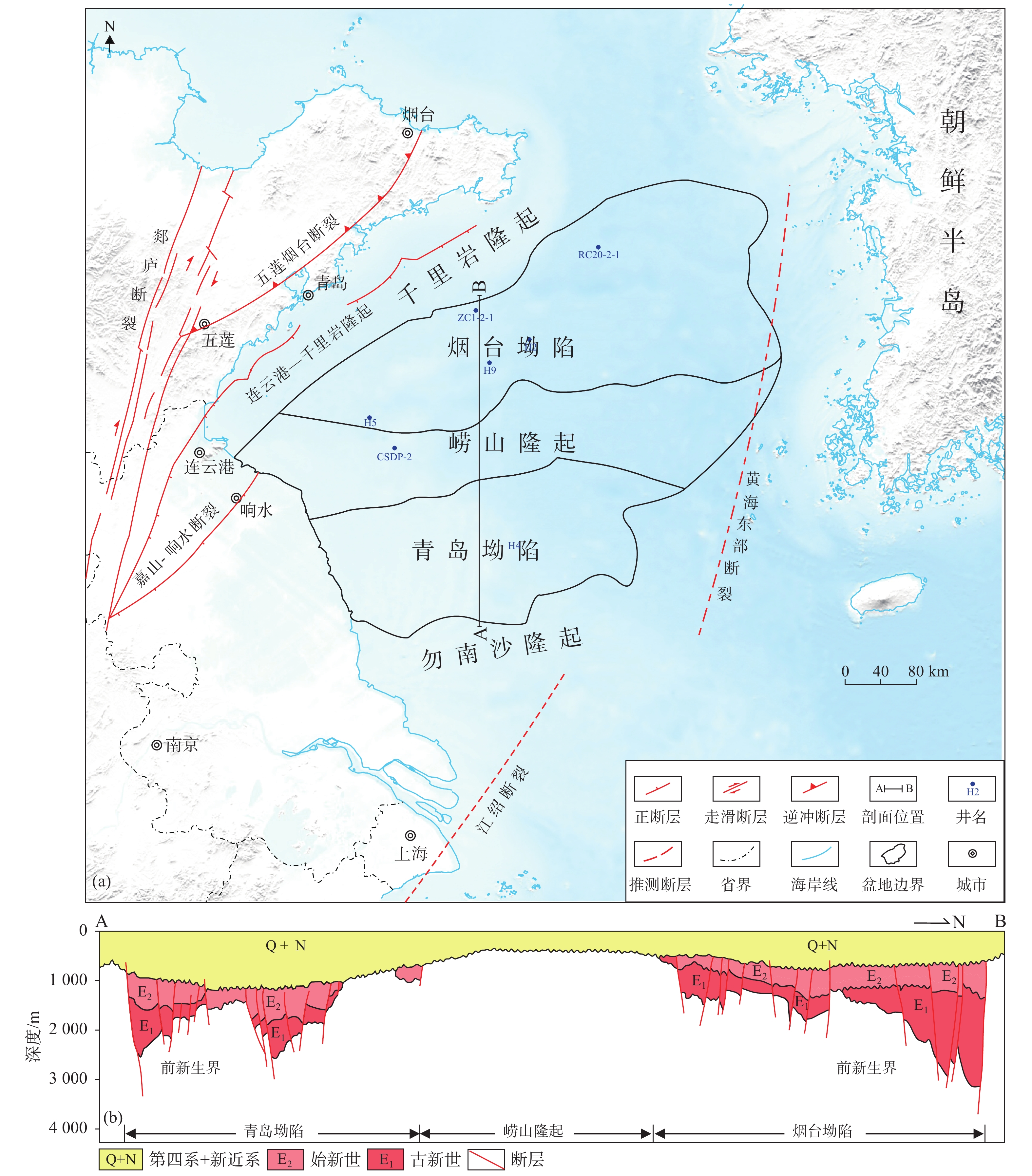
海域咸水层二氧化碳封存是碳减排的有效途径,可为沿海地区实现碳中和背景下的可持续发展提供技术支撑。南黄海盆地烟台坳陷与沿海碳源分布空间匹配较好,是潜在的二氧化碳封存区。本文分析了烟台坳陷二氧化碳封存地质条件,通过建立地层体积模型约束计算过程预测了新生界咸水层封存潜力,评价了该区二氧化碳封存前景。结果表明,烟台坳陷作为NEE向发育的地堑式或半地堑式的凹陷群,其新生界发育有4套储碳-封盖组合,地壳稳定性较好,具有较低的地温梯度与大地热流值,呈现“冷盆”特征,总体具有较好的二氧化碳封存地质条件;烟台坳陷800~3 200 m深度咸水层二氧化碳封存潜力平均为99 Gt,二氧化碳封存潜力巨大;烟台坳陷新生界主要发育逆冲背斜、重力滑塌背斜、挤压背斜、断背斜和断块构造等5种类型的构造圈闭,平面上发育有4个封存有利区,具有较好的二氧化碳地质封存前景。相关评价结果可为未来的二氧化碳离岸地质封存场地选址研究提供科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 海域咸水层封存 /
- 二氧化碳封存地质条件 /
- 潜力评价 /
- 烟台坳陷 /
- 南黄海盆地
Abstract:Offshore saline aquifer CO2 storage is an effective approach for reducing carbon emissions and offers technical support for the sustainable development of coastal regions within the framework of carbon neutrality. The Yantai Depression in the South Yellow Sea Basin aligns well with the distribution of coastal carbon sources, making it a promising area for potential CO2 storage. This study analyzes the geological conditions for CO2 storage in the Yantai Depression of the basin. A stratigraphic volume model was established, and constraint calculations were applied to predict the storage potential of the Cenozoic saline aquifers, followed by an evaluation of CO2 storage prospects in the region. The results show that the Yantai Depression, which comprises a series of NE-trending graben and half-graben depressions, contains four carbon storage-caprock assemblages in the Cenozoic. The region exhibits strong crustal stability, a low geothermal gradient, and low heat flow, characteristic of a "cold basin." These factors contribute to favorable geological conditions for CO2 storage. The storage potential of CO2 in the 800~3 200 m deep saline aquifers of the Yantai Depression averages 99 Gt, indicating a substan tial storage capacity. Structurally, the Cenozoic strata of the Yantai Depression is defined by five types of traps: thrust anticlines, gravity-sliding anticlines, compressive anticlines, faulted anticlines, and fault blocks. Four favorable storage zones have been identified, highlighting the strong geological potential for CO2 sequestration. These findings provide a scientific basis for future site selection studies for offshore CO2 geological storage.
-

-
[1] International Energy Agency. Exploring clean energy pathways:the role of CO2 storage[R]. Paris: International Energy Agency,2019.
[2] International Energy Agency. Net zero by 2050:a roadmap for the global energy sector[R]. Paris:International Energy Agency,2021.
[3] 蔡博峰,李琦,张贤,等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)年度报告(2021):中国CCUS路径研究[R]. 北京:生态环境部环境规划院,中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所, 中国21世纪议程管理中心,2021.
CAI B F,LI Q,ZHANG X, et al. Annual Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture,Utilization and Storage (CCUS) in China (2021) : China CCUS Pathways Study[R].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, the Administrative Center for China's Agenda 21, 2021.
[4] 张贤,杨晓亮,鲁玺,等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)年度报告(2023)[R]. 北京:中国21世纪议程管理中心,全球碳捕集与封存研究院,清华大学,2023.
ZHANG X,YANG X L,LU X, et al. Annual Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture,Utilization and Storage (CCUS) in China (2023)[R]. Beijing:The Administrative Center for China's Agenda 21,The Global CCS Institute,Tsinghua University,2023.
[5] SCHRAG D P. Storage of carbon dioxide in offshore sedi-ments[J]. Science,2009,325(5948):1658-1659. doi: 10.1126/science.1175750
[6] 米立军. 全球海上CO2封存现状及中国近海机遇与挑战[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(1):123-135.
MI L J. Current status of global CO2 ocean sequestration and opportunities and challenges in China offshore areas[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2023,35(1):123-135.
[7] 周守为,李清平,朱军龙,等. CO2海洋封存的思考与新路径探索[J]. 天然气工业,2024,44(4):1-10,199. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.04.001
ZHOU S W,LI Q P,ZHU J L, et al. Consideration on CO2 marine storage and exploration of new paths[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2024,44(4):1-10,199. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.04.001
[8] 陈建文,王嘹亮,王平康,等. 中国海域沉积盆地咸水层二氧化碳地质封存潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2024,44(3):98-114.
CHEN J W,WANG L L,WANG P K, et al. Carbon dioxide geological storage potential in saline aquifer of sedimentary basins in China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2024,44(3):98-114.
[9] 曹默雷,陈建平. CO2深部咸水层封存选址的地质评价[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(5):1868-1882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.05.022
CAO M L,CHEN J P. The site selection geological evaluation of the CO2 storage of the deep saline aquifer[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(5):1868-1882. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.05.022
[10] SAWADA Y,TANAKA J,SUZUKI C, et al. Tomakomai CCS demonstration project of Japan,CO2 injection in progress[J]. Energy Procedia,2018,154:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.002
[11] AKAI T,KURIYAMA T,KATO S, et al. Numerical modelling of long-term CO2 storage mechanisms in saline aquifers using the Sleipner benchmark dataset[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2021,110:103405. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2021.103405
[12] Global CCS Institute. Global Status of CCS Report 2020[R]. Global CCS Institute,2020.
[13] XIE H P,LI X C,FANG Z F, et al. Carbon geological utilization and storage in China:current status and perspectives[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2014,9(1):7-27. doi: 10.1007/s11440-013-0277-9
[14] United States Department of Energy. Carbon sequestration atlas of the United States and Canada (Third edition)[R]. Washington, DC: United States Department of Energy,2010.
[15] United States Department of Energy. Carbon storage atlas(Fifth edition)[R]. Washington, DC: United States Department of Energy,2015.
[16] GOODMAN A,HAKALA A,BROMHAL G, et al. U. S. DOE methodology for the development of geologic storage potential for carbon dioxide at the national and regional scale[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(4):952-965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.03.010
[17] BRENNAN S T,BURRUSS R C,MERRILL M D, et al. A probabilistic assessment methodology for the evaluation of geologic carbon dioxide storage[J]. US Geological Survey open-file report, 2010, 1127(2010): 31.
[18] United States Geological Survey Geologic Carbon Dioxide Storage Resources Assessment Team. USGS ircular 1386:national assessment of geologic carbon dioxide storage resources-results (ver. 1.13)[R].United States Geological Survey, 2013.
[19] 郭建强,文冬光,张森琦,等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存潜力评价与示范工程[J]. 中国地质调查,2015,2(4):36-46.
GUO J Q,WEN D G,ZHANG S Q, et al. Potential evaluation and demonstration project of CO2 geological storage in China[J]. Geological Survey of China,2015,2(4):36-46.
[20] BACHU S,BONIJOLY D,BRADSHAW J, et al. Estimation of CO2 storage capacity in geological gedia - Phase 2[R]. Washington, DC: Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum,2007.
[21] BACHU S,BONIJOLY D,BRADSHAW J,et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation:methodology and gaps[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2007,1(4):430-443. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00086-2
[22] ZHOU Q,BIRKHOLZER J T,TSANG C F, et al. A method for quick assessment of CO2 storage capacity in closed and semi-closed saline formations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2008,2(4):626-639. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.02.004
[23] 沈平平,廖新维,刘庆杰. 二氧化碳在油藏中埋存量计算方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2009,36(2):216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2009.02.012
SHEN P P,LIAO X W,LIU Q J. Methodology for estimation of CO2 storage capacity in reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2009,36(2):216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2009.02.012
[24] SZULCZEWSKI M L,MACMINN C W,HERZOG H J, et al. Lifetime of carbon capture and storage as a climate-change mitigation technology[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2012,109(14):5185-5189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115347109
[25] 李阳,王锐,赵清民,等. 含油气盆地咸水层二氧化碳封存潜力评价方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(2):424-430. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220851
LI Y,WANG R,ZHAO Q M, et al. A CO2 storage potential evaluation method for saline aquifers in a petroliferous basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2023,50(2):424-430. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220851
[26] SHAN Y L,HUANG Q,GUAN D, et al. China CO2 emission accounts 2016-2017[J]. Scientific Data,2020,7(1):54. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0393-y
[27] GUAN Y R,SHAN Y L,HUANG Q, et al. Assessment to China's recent emission pattern shifts[J]. Earth's Future,2021,9(11):e2021EF002241.
[28] SHAN Y L,LIU J H,LIU Z, et al. An emissions-socioeconomic inventory of Chinese cities[J]. Scientific Data,2019,6(1):190027. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2019.27
[29] SHAN Y L,GUAN Y R,HANG Y, et al. City-level emission peak and drivers in China[J]. Science Bulletin,2022,67(18):1910-1920. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.08.024
[30] 霍传林. 我国近海二氧化碳海底封存潜力评估和封存区域研究[D]. 大连:大连海事大学,2014.
HUO C L. Study on the potential evaluation and the storage areas of the carbon dioxide seabed storage in offshore China[D]. Dalian:Dalian Maritime University,2014.
[31] 陈建文,梁杰,张银国,等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(6):1-29.
CHEN J W,LIANG J,ZHANG Y G, et al. Regional evaluation of oil and gas resources in offshore China and exploration of marine Paleo-Mesozoic oil and gas in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2019,39(6):1-29.
[32] 高战武,缑亚森,钟慧,等. 中国东部海域断裂构造格架与地震活动研究[J]. 震灾防御技术,2021,16(1):11-18. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210102
GAO Z W,GOU Y S,ZHONG H, et al. Fault structure frame and seismicity in the sea on the eastside of Chinese mainland[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention,2021,16(1):11-18. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20210102
[33] 陈建文,杨长清,张莉,等. 中国海域前新生代地层分布及其油气勘查方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(1):1-25.
CHEN J W,YANG C W,ZHANG L, et al. Distribution of Pre-Cenozoic strata and petroleum prospecting directions in China seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2022,42(1):1-25.
[34] YUAN Y,CHEN J W,ZHANG Y G, et al. Sedimentary system characteristics and depositional filling model of Upper Permian–Lower Triassic in South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University,2018,25(12):2910-2928. doi: 10.1007/s11771-018-3962-x
[35] 陈建文,张异彪,陈华,等. 南黄海盆地海相中—古生界地震探测技术攻关历程及效果[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(4):1-17.
CHEN J W,ZHANG Y B,CHEN H, et al. Research experiences and application of seismic exploration technology to the Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2021,37(4):1-17.
[36] YUAN Y,CHEN J W,ZHANG Y X, et al. Tectonic evolution and geological characteristics of hydrocarbon reservoirs in marine Mesozoic–Paleozoic strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2018,17(5):1075-1090. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3583-x
[37] YUAN Y,CHEN J W,LIANG J, et al. Hydrocarbon geological conditions and exploration potential of Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2019,18(6):1329-1343. doi: 10.1007/s11802-019-3853-2
[38] 雷宝华,陈建文,梁杰,等. 印支运动以来南黄海盆地的构造变形与演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(3):45-54.
LEI B H,CHEN J W,LIANG J, et al. Tectonic deformation and evolution of the South Yellow Sea Basin since Indosinian movement[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2018,38(3):45-54.
[39] 张银国,陈建文,龚建明,等. 青岛海洋地质研究所45年来海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2024,44(3):1-22.
ZHANG Y G,CHEN J W,GONG J M, et al. Progress in marine oil and gas survey in Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology over the past 45 years[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2024,44(3):1-22.
[40] 朱伟林,陈春峰,张伯成,等. 南黄海古生代盆地原型演变与烃源岩发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(5):728-741. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005728
ZHU W L,CHEN C F,ZHANG B C, et al. Paleozoic basin prototype evolution and source rock development in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2020,42(5):728-741. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005728
[41] 雷宝华,张银国,王明健,等. 南黄海盆地崂山隆起构造特征与油气勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(2):131-143.
LEI B H,ZHANG Y G,WANG M J, et al. Structural characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration prospect of the Laoshan Uplift in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2022,42(2):131-143.
[42] 吴飘,陈建文,赵青芳,等. 南黄海盆地二叠系高-过成熟烃源岩的生物标志化合物特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(4):150-166.
WU P,CHEN J W,ZHAO Q F, et al. Characteristics of biomarkers and the geological significance in highly to over-mature Permian source rocks in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(4):150-166.
[43] 梁杰,张鹏辉,陈建文,等. 南黄海盆地中—古生代海相地层油气保存条件[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(5):10-19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.05.002
LIANG J,ZHANG P H,CHEN J W, et al. Hydrocarbon preservation conditions in Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2017,37(5):10-19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.05.002
[44] 陈建文,许明,雷宝华,等. 华北—扬子板块碰撞结构的识别:来自南黄海海域的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(3):1-12.
CHEN J W,XU M,LEI B H, et al. Collision of North China and Yangtze Plates:evidence from the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2020,40(3):1-12.
[45] FU Y L,YAN B,LIANG J, et al. Influence of basement high and detachment on the kinematics of a fold-and-thrust belt in the central South Yellow Sea Basin,China:insights from analog modeling[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2024,160:106648. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106648
[46] 许明,陈建文,雷宝华,等. 南黄海海域中生代前陆盆地形成的构造背景[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):13-24.
XU M,CHEN J W,LEI B H, et al. Tectonic background of Mesozoic foreland basin development in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):13-24.
[47] 张玉玺,陈建文,张银国. 下扬子—南黄海地区下三叠统“错时相”沉积及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(4):68-76.
ZHANG Y X,CHEN J W,ZHANG Y G. Anachronistic facies and its origin of the Lower Triassic in the Lower Yangtze-South Yellow Sea area[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2021,37(4):68-76.
[48] 米立军,吴克强,刘志峰,等. 从扬子地区海相烃源岩分布规律看南黄海盆地中—古生界有利勘探领域[J]. 中国海上油气,2022,34(2):1-13. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.02.001
MI L J,WU K Q,LIU Z F, et al. Favorable exploration field analysis of Mesozoic-Paleozoic in South Yellow Sea Basin from the distribution characteristics of marine source rocks in the Yangtze region[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2022,34(2):1-13. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.02.001
[49] 徐旭辉,周小进,彭金宁. 从扬子地区海相盆地演化改造与成藏浅析南黄海勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质,2014,36(5):523-531. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201405523
XU X H,ZHOU X J,PENG J N. Exploration targets in south Yellow Sea through analysis of tectono-depositional evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of marine basin in Yangtze area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2014,36(5):523-531. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201405523
[50] 朱伟林,米立军. 中国海域含油气盆地图集[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2010.
ZHU W L,MI L J. Atlas of Oil and Gas Basins,China Sea[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2010.
[51] 庞玉茂,张训华,肖国林,等. 下扬子南黄海沉积盆地构造地质特征[J]. 地质论评,2016,62(3):604-616.
PANG Y M,ZHANG X H,XIAO G L, et al. Structural and geological characteristics of the South Yellow Sea Basin in Lower Yangtze Block[J]. Geological Review,2016,62(3):604-616.
[52] 陈建文,袁勇,施剑,等. 中国海域深部“高富强”地震探测技术与南黄海盆地海相地层的发现[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2019,42(3):46-57.
CHEN J W,YUAN Y,SHI J, et al. “High,rich,and strong” seismic technologies for deeper layers in offshore China and discoveries in marine strata of South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development,2019,42(3):46-57.
[53] 吴飘,陈建文,张银国,等. 南黄海地区二叠系孤峰组硅质烃源岩的地球化学特征及上升流成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(1):138-158.
WU P,CHEN J W,ZHANG Y G, et al. Geochemical characteristics and upwelling origin of siliceous source rocks in the Permian Gufeng Formation of the South Yellow Sea area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(1):138-158.
[54] YUAN Y,WANG J Q,CHEN J W, et al. Carbon dioxide storage potential of Cenozoic saline aquifers in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Energies,2023,16(4):1578. doi: 10.3390/en16041578
[55] ZHANG H R,YUAN Y,CHEN J W, et al. Pore structure characteristics and reservoir classification of tight sandstones within the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in the Laoshan Uplift,South Yellow Sea Basin:implications for hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,2024,12(5):732. doi: 10.3390/jmse12050732
[56] 曲希玉. 南黄海盆地北部中、新生界沉积特征及油气远景[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2004.
QU X Y. Sedimentary Characteristics and Oil and gas prospect for the Mesozoic and Cenozoic in northern South Yellow Sea Basin[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2004.
[57] 袁勇,陈建文,梁杰,等. 南黄海崂山隆起二叠系砂岩储层特征及其油气勘探前景[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(5):181-193.
YUAN Y,CHEN J W,LIANG J, et al. Characteristics and hydrocarbon prospects of the Permian sandstone reservoirs of the Laoshan Uplift,South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2021,41(5):181-193.
[58] 吴淑玉,刘俊,陈建文,等. 南黄海崂山隆起石炭系—下二叠统孔隙型碳酸盐岩储层预测[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(5):136-148.
WU S Y,LIU J,CHEN J W, et al. Prediction of pore-dominated Carboniferous-Lower Permian carbonate reservoir at the Laoshan Uplift,South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2020,40(5):136-148.
[59] 张银国,肖国林,吴志强,等. 南黄海盆地北部坳陷古近系沉积特征及其沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(10):26-33.
ZHANG Y G,XIAO G L,WU Z Q, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of the Paleogene in the Northern Depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2014,30(10):26-33.
[60] 蔡佳,赵志刚,张喜林,等. 南黄海盆地北部坳陷北凹阜宁组沉积相研究[J]. 地质学刊,2014,38(4):530-535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2014.04.530
CAI J,ZHAO Z G,ZHANG X L, et al. On sedimentary facies in Funing Formation of Northern Sag in North Depression in South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Geology,2014,38(4):530-535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2014.04.530
[61] 蔡佳,崔敏,刘志峰,等. 南黄海盆地南五凹古近系戴南组沉积相及储盖组合分析[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,37(4):395-402.
CAI J,CUI M,LIU Z F, et al. Sedimentary facies and analyze on reservoir-seal assemblage of the Dainan Formation of Paleogene in Nan 5 Sag,South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science),2014,37(4):395-402.
[62] 蔡佳,吴克强,王鹏,等. 南黄海盆地南部坳陷古近系阜宁组沉积相分析[J]. 地质学刊,2016,40(1):125-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.01.125
CAI J,WU K Q,WANG P, et al. Sedimentary facies of the Paleogene Funing Formation in the South Depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Geology,2016,40(1):125-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.01.125
[63] 王振鸿,胡明毅,汤济广,等. 南黄海盆地南部坳陷晚白垩世—第四纪构造演化对油气的控制[J]. 化工矿产地质,2014,36(3):129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2014.03.001
WANG Z H,HU M Y,YANG J G, et al. Control on petroleum by tectonic evolution of the Late Cretaceous-Quaternary in the South Depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,2014,36(3):129-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2014.03.001
[64] 庞玉茂,张训华,郭兴伟,等. 南黄海北部盆地中、新生代构造热演化史模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2017,60(8):3177-3190. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170824
PANG Y M,ZHANG X H,GUO X W, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectono-thermal evolution modeling in the northern South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2017,60(8):3177-3190. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170824
[65] 熊忠,江志强,孙鹏,等. 南黄海盆地北部坳陷北凹断裂特征与构造演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(3):75-84.
XIONG Z,JIANG Z Q,SUN P, et al. Characteristics and tectonic evolution of the fault system in the north sag of Northern Depression of South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2018,38(3):75-84.
[66] 李楠. 南黄海盆地北部坳陷构造演化及沉积相研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学,2010.
LI N. Research on structural evolution and sedimentary facies in north depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China,2010.
[67] BACHU S. Screening and ranking of sedimentary basins for sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change[J]. Environmental Geology,2003,44(3):277-289. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0762-9
[68] 皮仲. 6.0 ka以来黄海暖流和黄海冷水团的演化[D]. 青岛:中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所),2023.
PI Z. Evolution of the Yellow Sea warm current and the Yellow Sea cold water mass since 6.0 ka[D]. Qingdao:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology Chinese Academy of Sciences),2023.
[69] 孙旭东. 南黄海大地热流、地层生热率与热结构分析[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2020.
SUN X D. Analysis of heat flow,heat generation rate and thermal structure in the South Yellow Sea[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing) ,2020.
[70] 姜光政,高堋,饶松,等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2892-2910.
JIANG G Z,GAO P,RAO S, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China (4th edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2892-2910.
[71] 徐曦,胡瀚文,张加洪,等. 中国东部新生代沉积盆地热状态与油气成藏潜力:以苏北—南黄海盆地为例[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(6):928-937. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202006928
XU X,HU H W,ZHANG J H, et al. Deep thermal state and hydrocarbon accumulation potential of Cenozoic sedimentary basins in East China:a case study of Subei-South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2020,42(6):928-937. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202006928
[72] 武守诚. 中国油气盆地的系统研究[J]. 石油学报,1993,(4):20-34. doi: 10.7623/syxb199303003
WU S C. A systematic study of the Chinese petroliferous basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,1993,(4):20-34. doi: 10.7623/syxb199303003
[73] 高顺莉,徐曦,周祖翼. 南黄海北部盆地晚白垩世以来构造变形与盆地成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(6):924-933. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150607
GAO S L,XU X,ZHOU Z Y. Structural deformation and genesis of the northern sub-basin in South Yellow Sea since Late Cretaceous[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2015,36(6):924-933. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150607
[74] 李旭东,刘绍文,王丽. 江苏—南黄海地区地震活动时空分布特征及其孕震构造分析[J]. 高校地质学报,2018,24(4):551-562.
LI X D,LIU S W,WANG L. Spatiotemporal pattern of earthquake activities and seismotectonics in Jiangsu and adjacent Southern Yellow Sea Area[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2018,24(4):551-562.
[75] United States Geological Survey. Earthquake Hazards Program[EB/OL]. [2024-09-29]. https://www.usgs.gov/programs/earthquake-hazards.
[76] 施振飞,张振城,叶绍东,等. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜宁组储层次生孔隙成因机制探讨[J]. 沉积学报,2005,23(3):429-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.008
SHI Z F,ZHANG Z C,YE S D, et al. The mechanism of secondary pores in the reservoir of Funing Formation in Gaoyou Depression of Subei Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2005,23(3):429-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.008
[77] 王林. 苏北盆地金湖凹陷阜宁组阜一、阜二段储层孔隙结构特征研究[D]. 武汉:长江大学,2018.
WANG L. Study on the pore structure characteristics of the reservoirs of the Fu 1 Member and the Fu 2 Member of Funing Formation in the Jinhu Depression,Subei Basin[D]. Wuhan:Yangtze University,2018.
[78] EMAMI-MEYBODI H,HASSANZADEH H,GREEN C P, et al. Convective dissolution of CO2 in saline aquifers:progress in modeling and experiments[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,40:238-266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.04.003
-



 下载:
下载: