Research on efficiency of CO2 geological storage in saline aquifers in clastic rock reservoirs in Xihu Sag, East China Sea
-
摘要:
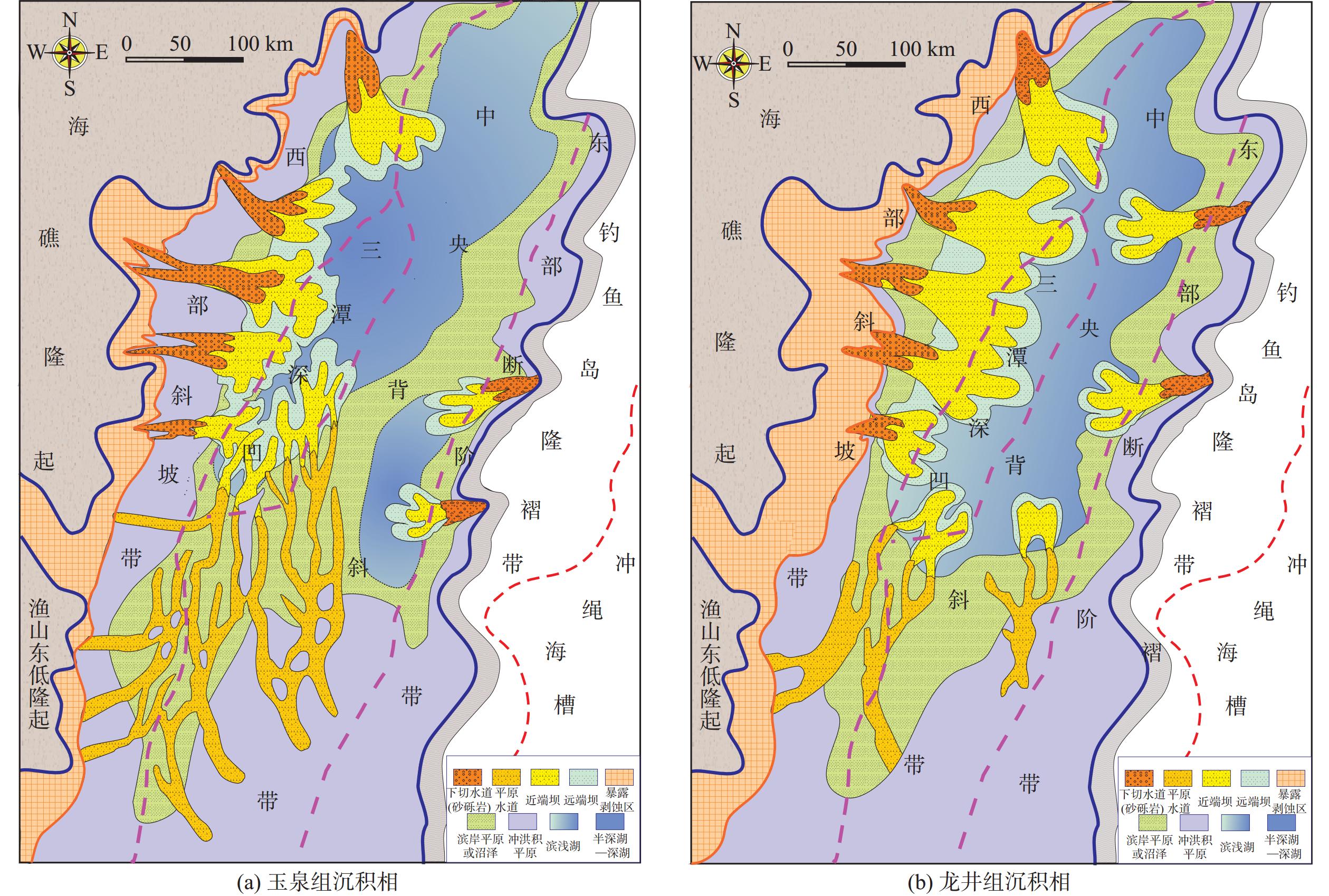
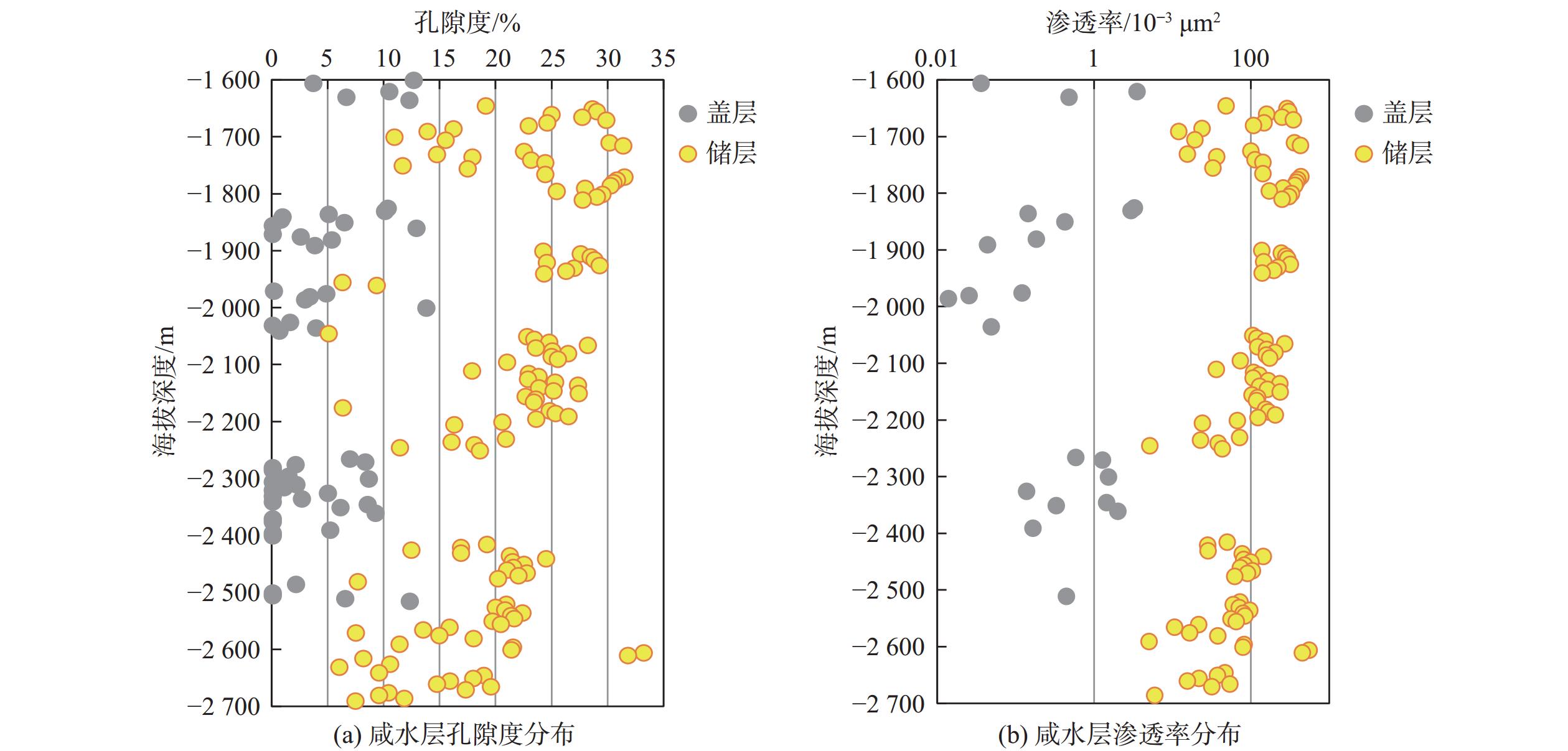
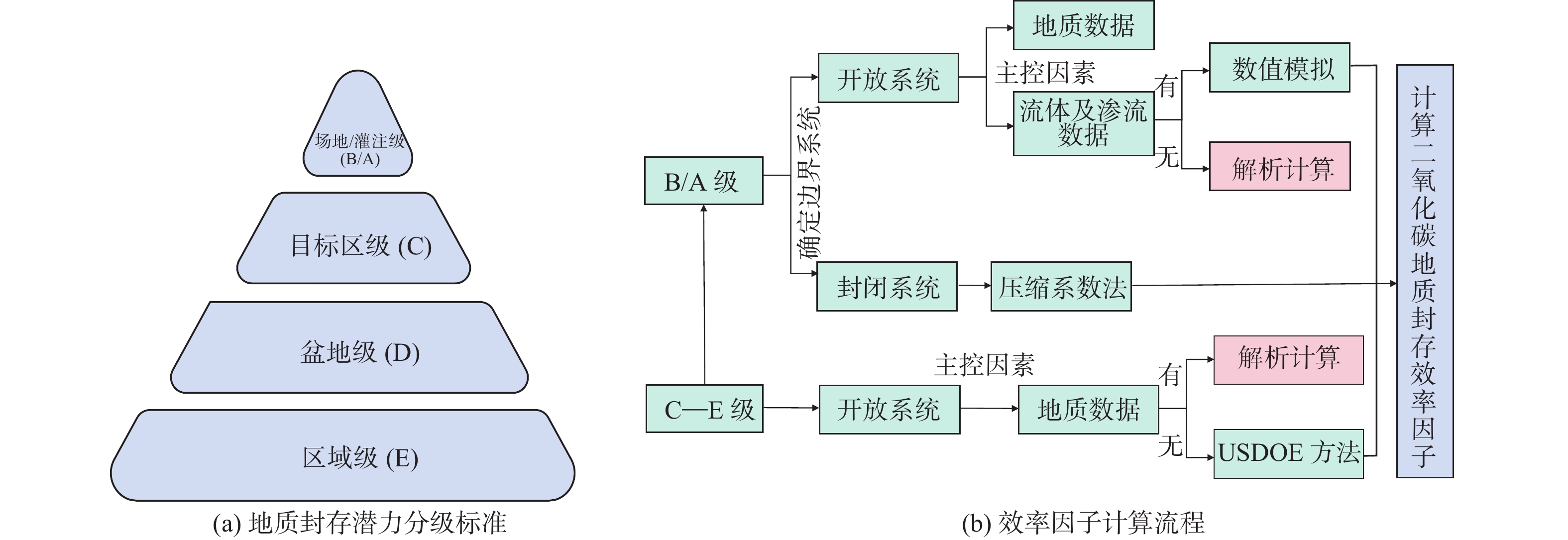
中国海域咸水层二氧化碳地质封存潜力巨大。但目前已有的效率因子取值差异大,使得有效封存量难以落实。为进一步提高有效封存量估算的准确性及区域适用性,本文通过系统梳理影响效率因子的关键因素,对比优选出普遍适用的效率因子计算方法。综合运用地震、钻井、测井及岩芯分析数据,采用统计学方法进行参数优化,以此提高计算的精度及准确性,并基于不同数据基础给出一套效率因子筛选计算流程。以东海西湖凹陷碎屑岩咸水层为例,分析结果表明,东海西湖凹陷中新统玉泉组及龙井组咸水层为碎屑岩沉积,砂体厚度大且发育多套储盖组合。其中,三角洲平原心滩优势沉积微相对二氧化碳地质封存最为有利,玉泉组效率因子为6.9%,相较于龙井组高2.9%。应用效率因子估算东海西湖凹陷玉泉组和龙井组咸水层有效封存量为8.2亿t,西部斜坡带玉泉组封存潜力最大,为东海西湖凹陷二氧化碳地质封存首选封存场址,可作为二氧化碳地质封存先行试验区。
Abstract:Potential for geological carbon dioxide storage in saline aquifers in Chinese maritime territories is substantial. However, considerable disparities in storage efficiency complicated the determination of the effective storage capacity. To enhance the accuracy and regional applicability of effective storage capacity estimation, we reviewed the key factors influencing efficiency coefficients and identified globally applicable methods for the calculation. By integrating seismic, drilling, logging, and core data, we employed statistical techniques for parameter optimization, with which both precision and accuracy of the calculations were improved. Additionally, we proposed a workflow from selecting and calculating efficiency coefficients based on various data sources. The saline water in clastic rocks in the Xihu sag, East China Sea was studied as the case. Results show that saline water in the Yuquan Formation and Longjing Formation are characterized by rich sand bodies with large thickness and multiple sets of reservoir-caprock. Among them, delta plain channel bar deposits are favorable microfacies for CO2 sequestration. Specifically, the storage efficiency of the Yuquan Formation is 6.9%, which is 2.9% higher than that of the Longjing Formation. Based on the storage efficiency, we estimated that the effective storage capacity of the saline aquifers in the Yuquan and Longjing formations in the Xihu Sag is approximately 820 million tons. The Yuquan Formation in the western slope zone exhibits the highest storage potential and could be the optimal place for CO2 sequestration in the Xihu Sag, and can be also considered a good candidate of a pilot area for CO2 sequestration.
-

-
表 1 不同封存效率因子研究方法对比
Table 1. Comparison of research methods for different storage efficiency
计算方法 封存机理 效率因子 主控因素 效率因子取值/% 评价方法 边界类型 适用规模 USDOE 2007 构造、束缚、
溶解、矿化封存
无 1~4 体积法 开放边界 目标区级 2010 岩性 1.2~4.1 CSLF 2007 束缚、溶解封存 
相渗特征 基于数值模拟 体积法 开放系统 目标区级 USGS 2010 构造、束缚封存  、
、
封存机理 构造机理10~60
束缚机理1~15体积法 开放系统 目标区级 2013 渗透率 1.4~22.0 IEA 2009 构造、束缚、
溶解、矿化封存
沉积环境、岩性 1.9~3.3 体积法 开放系统 场地级 ZHOU等 2008 岩石及流体压缩性 
压缩性、压力 0.08~0.75 压缩系数法 封闭系统 场地级 沈平平等 2009 束缚、溶解封存  、
、
封存机理 — 封存机理表征法 开放系统 盆地级 注:本表中适用规模分类采用国内分类标准;USDOE引用文献[8,20,26],CSLF引用文献[8,25],USGS引用文献[8,22,26],IEA引用文献[8,25,26],ZHOU等引用文献[8,12],沈平平等引用文献[24]。 表 2 USDOE和IEA地质参数取值
Table 2. Geological parameter value of USDOE and IEA
地质参数 USDOE IEA 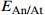
0.2~0.8 — 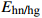
0.2~0.75 0.21~0.76 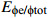
0.6~0.95 0.64~0.77 注:表格数据引用文献[8]。 表 3 不同岩相驱替效率取值表
Table 3. The values of displacement efficiency in different lithofacies
置信区间/% 碎屑岩 白云岩 灰岩 Ev×d=EV×Ed P10 7.4 16 10 P50 14 21 15 P90 24 26 21 E(USDOE) P10 0.51 0.64 0.4 P50 2 2.2 1.5 P90 5.4 5.5 4.1 注:表格数据引用文献[8]。 表 4 玉泉组和龙井组优势沉积微相二氧化碳封存效率因子
Table 4. Storage efficiency coefficients of dominant sedimentary microfacies in the Yuquan and Longjing formations
层系 沉积亚相 优势微相 EA Eh Eϕ E/% 玉泉组 三角洲平原 心滩 0.75 0.63 0.77 6.90 三角洲前缘 边滩 0.68 0.56 0.69 3.71 前三角洲 远砂坝 0.34 0.41 0.31 1.14 龙井组 三角洲平原 心滩 0.69 0.61 0.68 4.00 三角洲前缘 边滩 0.62 0.47 0.57 2.33 前三角洲 远砂坝 0.21 0.33 0.26 0.25 表 5 西湖凹陷咸水层二氧化碳有效封存量及丰度计算结果
Table 5. Estimation on the effective capacity and sequestration abundance in saline aquafers of the Xihu Sag
评价单元 层系 优势微相面积/
km2有效封存量/
106 t有效封存丰度/
(104 t/km2)西部斜坡带 玉泉组 8674 351.3 4.05 龙井组 9936 116.6 1.17 三潭深凹 玉泉组 2485 44.2 1.78 龙井组 1988 11.8 0.59 中央背斜带 玉泉组 6748 133.6 1.98 龙井组 7461 48.4 0.65 东部断阶带 玉泉组 6322 83.4 1.32 龙井组 5690 31.4 0.55 -
[1] 潘佳佳,李廉水. 中国工业二氧化碳排放的影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学与技术,2011,34(4):86-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.04.020
PAN J J,LI L S. Analysis of factors affecting industrial carbon dioxide emission in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2011,34(4):86-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.04.020
[2] 郭建强,文冬光,张森琦,等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存适宜性评价与示范工程[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2014.
GUO J. Q,WEN D G,ZHANG S Q,et al. Evaluation and demonstration project of carbon dioxide geological storage suitability in China[M]. Beijing:Geology Press,2014.
[3] 刘国伟. 中国等57国将在2030年实现碳达峰各国携手迈向碳中和[J]. 环境与生活,2021(1):8-23.
LIU G W. China and 57 other countries to reach peak carbon by 2030,countries join hands to move toward carbon neutrality[J]. Green Living,2021(1):8-23
[4] 陈建文,王嘹亮,王平康,等. 中国海域沉积盆地咸水层二氧化碳地质封存潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2024,44(3):98-114.
CHEN J W,WANG L L,WANG P K,et al. Carbon dioxide geological storage potential in saline aquifer of sedimentary basins in China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2024,44(3):98-114.
[5] 李光,刘建军,刘强,等. 二氧化碳地质封存研究进展综述[J]. 湖南生态科学学报,2016,3(4):41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6361.2016.04.008
LI G,LIU J J,LIU Q,et al. Review on geological storage of carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Hunan Ecological Science,2016,3(4):41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6361.2016.04.008
[6] 陈建文,孙晶,杨长清,等. 东海陆架盆地新生界咸水层二氧化碳封存地质条件及封存前景[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(10):14-21.
CHEN J W,SUN J,YANG C Q,et al. Geological conditions and prospects of carbon dioxide storage in the Cenozoic saline water layers of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2023,39(10):14-21.
[7] 李阳,王锐,赵清民,等. 含油气盆地咸水层二氧化碳封存潜力评价方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(2):424-430. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220851
LI Y,WANG R,ZHAO Q M,et al. A CO2 storage potential evaluation method for saline aquifers in a petroliferous basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2023,50(2):424-430. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220851
[8] STEFAN B. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2015,40:188-202.
[9] 张森琦,郭建强,刁玉杰,等. 规模化深部咸水含水层CO2地质储存选址方法研究[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(6):1640-1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.025
ZHANG S Q,GUO J Q,DIAO Y J,et al. Research on site selection methods for large-scale geological storage of CO2 in deep saline aquifers[J]. Geology in China,2011,38(6):1640-1651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.025
[10] SMITH D J,NOY D J,HOLLOWAY S,et al . The impact of boundary conditions on CO2 storage capacity estimation in aquifers[J]. Energy Procedia,2011,4:4828-4834. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.449
[11] CHANG K W,HESSE M A,NICOT J. Dissipation of over-pressure into ambient mudrocks during geological carbon dioxide storage[J]. Energy Procedia,2013,37:4457-4464. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.350
[12] ZHOU Q,BIRKHOIZER J T,TSANG C F,et al. A method for quick assessment of CO2 storage capacity in closed and semi-closed saline formations[J] International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2008,2(4):626-639.
[13] GORECK C D,SORENSEN J A,BREMER J M,et al. Development of storage coefficients for determining the effective CO2 storage resource in deep saline formations[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers,2009:SPE-126444-MS.
[14] FRAILEY S M,FINLEY R J. Classification of CO2 geologic storage:resource and capacity[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):2623-2630. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.02.029
[15] OKWEN R T,STEWART M T,CUNNINGHAM J A. Analytical solution for estimating storage efficiency of geologic sequestration of CO2[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2010,4(1):102-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2009.11.002
[16] OKWEN R T,YANG F,FRAILEY S. Effect of geologic depositional environment on CO2 storage efficiency[J]. Energy Procedia,2014,63:5247-5257. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.556
[17] SPAN P,WAGNER W. A new equation of state for carbon dioxide covering the fluid region from the triple point temperature to 1100 K at pressures up to 800 MPa[J]. Journal of Physical & Chemical Reference Data,1996,25(6):1509-1596.
[18] BRENNAN S T. The U. S. Geological Survey carbon dioxide storage efficiency value methodology:results and observa-tions[J]. Energy Procedia,2014,63:5123-5129. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.542
[19] KOPP A,CLASS H,HELMIG R. Investigations of CO2 storage capacity in deep saline aquifers. Part 1. Dimensional analysis of flow processes and reservoir characteristics[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2009,3(3):263-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.10.002
[20] SUNDQUIST E T,ACKERMAN K V,BLISS N B,et al. Carbon sequestration atlas of the United States and Canada[R]. United States Geological Survey,2012.
[21] GOODMAN A, BROMHAL G, STRAZISAR B, et al. Comparison of methods for geologic storage of carbon dioxide in saline formations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,18:329-342.
[22] United States Geological Survey Geologic Carbon Dioxide Storage Resources Assessment Team. National assessment of geologic carbon dioxide storage resources-results[R]. Reston:United States Geological Survey,2013.
[23] BLONDES M S, BRENNAN S T, MERRILL M D, et al. National assessment of geologic carbon dioxide storage resources:methodology implementation [R]. Reston:United States Geological Survey, 2013.
[24] 沈平平,廖新维,刘庆杰. 二氧化碳在油藏中埋存量计算方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2009,36(2):216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2009.02.012
SHEN P P,LIAO X W,LIU Q J. Methodology for estimation of CO2 storage capacity in reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2009,36(2):216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2009.02.012
[25] GOODMAN A,BROMHAL G,STRAZISAR B,et al. Comparison of methods for geologic storage of carbon dioxide in saline formations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,18,329-342.
[26] GOODMAN A,HAKALA A ,BROMHAL G,et al. U. S. DOE methodology for the development of geologic storage potential for carbon dioxide at the national and regional scale[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(4):952-965.
[27] 薛煜恒,李坤,尚娅敏,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷孔雀亭区断裂体系特征及控藏效应[J]. 岩性油气藏,2025,37(1):161-169.
XUE Y H,LI K,SHANG Y M,et al. Characteristics and reservoir control effects of the fault system in Kongqueting area of Xihu Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2025,37(1):161-169.
[28] 赵勇,李久娣,杨鹏程,等. 东海陆架盆地咸水层CO2封存地质条件适宜性评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(4):129-139.
ZHAO Y,LI J D,YANG P C,et al. Evaluation on of geological suitability for CO2 storage in salty aquifers in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(4):129-139.
[29] 胡必规,张韫. 东海盆地油田水文地球化学特征与油气聚集关系探讨[J]. 海洋地质动态,1988,5:16-19.
HU B G,ZHANG Y. Relationship between hydrologic geochemistry and hydrocarbon accumulation in the East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Letters,1988,5:16-19.
-



 下载:
下载: