Typical cases of global marine geological carbon storage and its implications for China
-
摘要:
海洋地质碳封存作为二氧化碳捕集、利用与封存(CCUS)的应用场景之一,是沿海地区实现碳减排的有效途径。本文通过全球海洋地质碳封存典型案例的解剖认为,中国海洋地质碳封存潜力大,下一步示范工程选址应重视目标级和场地级封存潜力评价,针对不同条件开展分类选址,并将地质风险监测贯穿示范工程始终。结合中国海域不同盆地CO2地质封存源汇匹配性和施工条件提出:海上油气田CO2伴生气咸水层封存项目是优先示范项目,CO2驱油气与封存协同项目具有现实应用价值,枯竭油气藏封存项目是示范工程的重要选择,全链条规模化海上咸水层封存项目是未来发展方向。
Abstract:As one of the application scenarios of CCUS, marine carbon dioxide (CO2) geological storage is an effective way to achieve carbon emission reduction in coastal areas. Based on the analysis of typical cases of global marine CO2 geological storage, this paper believes that China has great potential for CO2 storage. In the next step, the site selection of pilot projects should pay attention to the evaluation of target-level and site-level sequestration potential, carry out classified site selection according to different conditions, and monitor geological risks throughout the pilot projects. According to the source-sink match of CO2 geological storage in different basins in China's sea area and the construction conditions, the following is proposed: The CO2 associated gas storage project in offshore oil and gas fields is a type of priority pilot project, and the cooperation between CO2 enhanced oil/gas recovery and storage has practical application value. The storage project of depleted oil and gas reservoirs is an important choice for pilot projects, and the whole-chain large-scale offshore saline aquifer CO2 reservoir storage project is the future development direction.
-
Key words:
- marine geology /
- CO2 storage /
- saline aquifer /
- depleted oil and gas reservoirs /
- CCUS
-

-
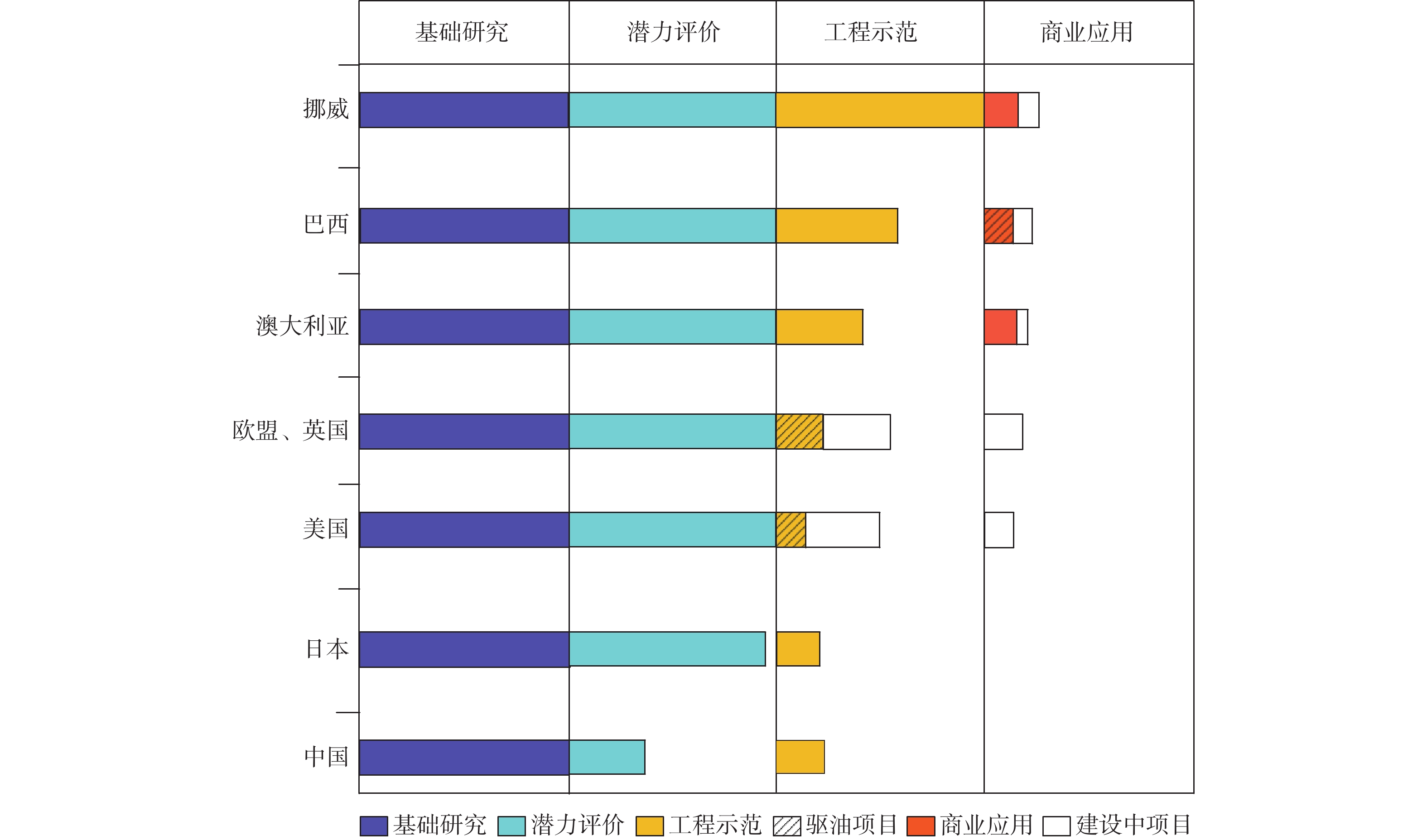
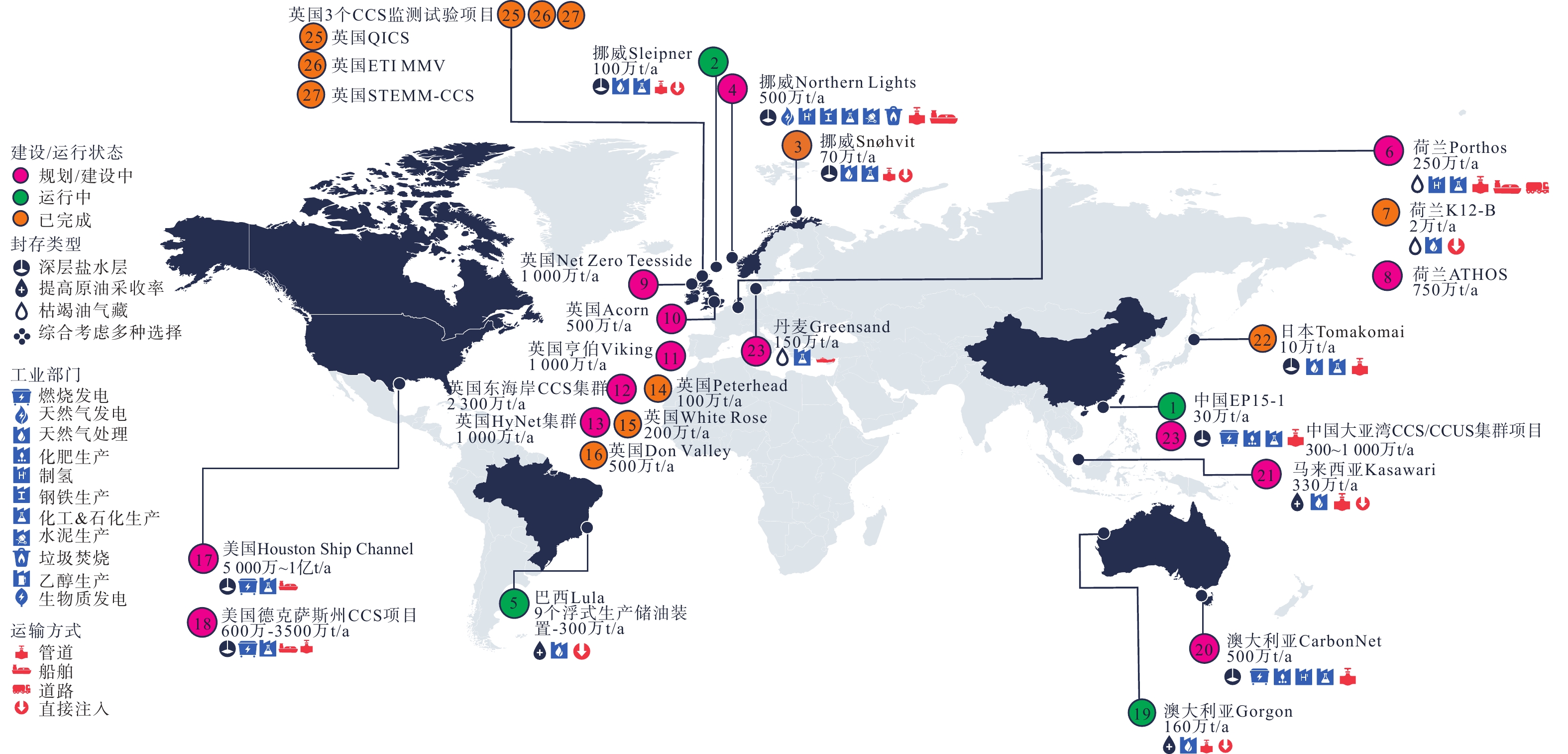
表 1 全球主要海洋地质碳封存示范工程一览表
Table 1. Major global pilot projects marine CO2 geological storage
序号 项目名称 示范内容 规划/投运年份 规模/(万t/a) 2024年状态 CO2源 封存/利用方式 1 中国EP15-1 海上伴生气 咸水层 2021年启动,2023年灌注 约30 运行中 2 挪威Sleipner 海上伴生气 咸水层 1996年投运 100 运行中 3 挪威Snøhvit 海上伴生气 咸水层 2008年投运 70 已结束 4 挪威Northern Lights 陆上工业气 咸水层 150~500 规划中 5 巴西Lula 海上伴生气 CO2-EOR驱油 2011年投运 300 运行中 6 荷兰Porthos 陆上工业气 枯竭气藏 250 规划中 7 荷兰K12-B 海上伴生气 枯竭油气层 2004—2017年 2 已结束 8 荷兰ATHOS 陆上工业气 枯竭气藏 2030年建成 750 规划中 9 英国Net Zero Teesside 陆上工业气 咸水层/枯竭油气藏 2026年投运 1 000 规划中 10 英国Acorn 陆上工业气 枯竭油气藏 500 规划中 11 英国亨伯Viking 陆上工业气 枯竭气田 2027年投运 1 000 规划中 12 英国东海岸CCS集群 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2027年投运 2 300 规划中 13 英国HyNet集群 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 1 000 规划中 14 英国Peterhead 陆上工业气 枯竭气藏 100 已暂停 15 英国White Rose 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2013—2015年 200 已终止 16 英国Don Valley 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2015年 500 已终止 17 美国休斯顿 Ship Channel 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 5 000~10 000 规划中 18 美国得克萨斯州CCS项目 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 600~3 500 规划中 19 澳大利亚Gorgon 海上伴生气 近枯竭气藏 2004、2005年两次试验 160 运行中 20 澳大利亚CarbonNet 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2030年投运 500 规划中 21 马来西亚Kasawari 陆上工业气 海底油田 330 规划中 22 日本Tomakomai 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2016—2019年 10 已结束 23 中国大亚湾CCS/CCUS集群项目 陆上工业气 海底咸水层 2022年6月启动 300~1 000 规划中 24 丹麦Greensand 枯竭油气田 150 规划中 25 英国QICS 海底咸水层 2010—2013年 已终止 26 英国ETI MMV 海底咸水层 2014—2018年 已终止 27 英国STEMM-CCS 海底咸水层 2016—2020年 已终止 注:CCS代表CO2捕集与封存;CCUS代表CO2捕集、利用与封存。 -
[1] 彭雪婷,吕昊东,张贤. IPCC AR6报告解读:全球碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)技术发展评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展,2022,18(5):580-590.
PENG X T,LYU H D,ZHANG X. Interpretation of IPCC AR6 report on carbon capture,utilization and storage(CCUS) technology development[J]. Climate Change Research,2022,18(5):580-590.
[2] The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change 2022:mitigation of climate change[R]. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,2022.
[3] 张贤,杨晓亮,鲁玺,等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存 (CCUS) 年度报告 (2023)[R]. 北京:中国21世纪议程管理中心,全球碳捕集与封存研究院,清华大学,2023.
ZHANG X,YANG X L,LU X,et al. Carbon capture,utilization,and storage (CCUS) progress in China (2023)[R]. Beijing:The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21,Global CCS Institute,Tsinghua University,2023.
[4] 蔡博峰,李琦,张贤,等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存 (CCUS) 年度报告 (2024):中国区域二氧化碳地质封存经济可行性研究[R]. 北京:生态环境部环境规划院,2024.
CAI B F,LI Q,ZHANG X,et al. Carbon capture,utilization,and storage (CCUS) progress in China (2024):economic feasibility study on geological carbon dioxide sequestration in China[R]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning,2024.
[5] 陈建文,王嘹亮,王平康,等. 中国海域沉积盆地咸水层二氧化碳地质封存潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2024,44(3):98-114.
CHEN J W,WANG L L,WANG P K,et al. Carbon dioxide geological storage potential in saline aquifer of sedimentary basins in China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2024,44(3):98-114.
[6] 米立军. 全球海上CO2封存现状及中国近海机遇与挑战[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(1):123-135.
MI L J. Current status of global CO₂ ocean sequestration and opportunities and challenges in China offshore areas[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2023,35(1):123-135.
[7] Global CCS Institute. Global status of CCS report 2019[R]. Global CCS Institute,2019.
[8] Global CCS Institute. Global status of CCS report 2020[R]. Global CCS Institute,2020.
[9] 陈建文,王嘹亮,王平康,等. 中国海域二氧化碳地质封存潜力评价[R]. 北京:中国地质调查局,2022.
CHEN J W,WANG L L,WANG P K,et al. Evaluation of geological carbon dioxide storage potential in China sea [R]. Beijing:China Geological Survey,2022.
[10] METZ B,DAVIDSON O,CONINCK H D,et al. IPCC special report on carbon dioxide capture and storage[R]. New York:Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,2005.
[11] Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum. Phase II final report-task force for review and identification of standards for CO2 storage capacity measurement[R]. Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum,2007.
[12] United States Department of Energy. Appendix B:methodology for development of geologic storage estimates for carbon dioxide[R]. Washington:United States Department of Energy,2008.
[13] International Energy Agency Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme. Development of storage coefficients for CO2 storage in deep saline formations[R]. International Energy Agency Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme,2009.
[14] GOODMAN A,BROMHAL G,STRAZISAR B,et al. Comparison of methods for geologic storage of carbon dioxide in saline formations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2013,18:329-342. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.07.016
[15] GOODMAN A,HAKALA A,BROMHAL G,et al. U. S. DOE methodology for the development of geologic storage potential for carbon dioxide at the national and regional scale[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(4):952-965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.03.010
[16] BACHU S,BONIJOLY D,BRADSHAW J,et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation:methodology and gaps[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2007,1(4):430-443. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00086-2
[17] BACHU B. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,40:188-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.01.007
[18] BACHU S. Screening and ranking of sedimentary basins for sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change[J]. Environmental Geology,2003,44(3):277-289. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0762-9
[19] WEIR G J,WHITE S P,KISSLING W M. Reservoir storage and containment of greenhouse gases[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1995,36(6/9):531-534. doi: 10.1016/0196-8904(95)00060-Q
[20] LINDEBERG E. Escape of CO2 from aquifers[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1997,38:S235-S240. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00275-0
[21] YAMAMOTO H,ZHANG K,KARASAKI K,et al. Large-scale numerical simulation of CO2 geologic storage and its impact on regional groundwater flow:a hypothetical case study at Tokyo Bay[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):1871-1878. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.01.244
[22] United States Department of Energy. Carbon sequestration atlas(Fifth edition)[R]. Washington:United States Department of Energy,National Energy Technology Laboratory,2015.
[23] HALLAND E K. Offshore storage of CO2 in Norway,in geophysics and geosequestration[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,2019:195-208.
[24] BENTHAM M,MALLOWS T,LOWNDES J,et al. CO2 storage evaluation database (CO2 stored). The UK's online storage atlas[J]. Energy Procedia,2014,63:5103-5113. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.540
[25] International Energy Agency. 20 years of carbon capture and storage[R]. Paris:International Energy Agency,2016.
[26] CHADWICK A,ARTS R,BERNSTONE C,et al. Best Practice for the Storage of CO2 in Saline Aquifers: Observations and Guidelines from the SACS and CO2 Store Projects[M]. London:British Geological Survey,2008.
[27] Global CCS Institute. Global status of CCS 2021[R]. Melbourne:Global CCS Institute,2021.
[28] PIZARRO J O D E S,PETROBRAS P,BRANCO C C M. Planning and implementing an EOR project for the pre-salt Lula field[J]. World Oil,2012,233(8).
[29] TRUPP M,FRONTCZAK J,TORKINGTON J. The Gorgon CO2 injection project-2012 update[J]. Energy Procedia,2013,37:6237-6247. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.552
[30] THOMPSON N,ANDREWS J S,BJØRNARÅ T I. Assessing potential thermo-mechanical impacts on caprock due to CO2 injection:a case study from Northern Lights CCS[J]. Energies,2021,14(16):5054.
[31] UDEN J V. Dutch council of state green-lights Porthos project[J]. Environmental Law Management,2023,32(6):210-211.
[32] HARIS K,SHAJAHAN N,BERGèS B,et al. Evaluation of passive acoustic methods for ambient noise baseline and gas flow rate quantification at a proposed nearshore carbon capture and storage site in Australia[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2023,129:103961. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2023.103961
[33] TIP M. Commercialization of offshore CCS in the gulf of Mexico [R]. Austin:The Gulf Coast Carbon Center. 2021.
[34] Carbon Capture Journal Group. PETRONAS proceeds with Kasawari CCS project offshore Sarawak[J]. Carbon capture journal,2023.
[35] International Energy Agency. Net zero by 2050:a roadmap for the global energy sector [R]. Paris:International Energy Agency,2021.
[36] 中国碳核算数据库. 省级碳排放清单[R]. 北京:中国碳核算数据库(CEADs),2020.
China Emission Accounts and Datasets. Provincial CO2 emission inventories[R]. Beijing:China Emission Accounts and Datasets(CEADs), 2020.
[37] 于志超,杨思玉,刘立,等. 饱和CO2地层水驱过程中的水-岩相互作用实验[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(6):1032-1042.
YU Z C,YANG S Y,LIU L,et al. An experimental study on water-rock interaction during water flooding in formations saturated with CO2[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2012,33(6):1032-1042.
[38] 曹冲,张京伦,朱鸿昊,等. CO2-岩石-地层水相互作用实验[J]. 成都工业学院学报,2016,19(4):3-8.
CAO C,ZHANG J L,ZHU H H,et al. Experimental research on the interaction process between CO2-saturated rocks and formation water[J]. Journal of Chengdu Technological University,2016,19(4):3-8.
[39] 赵仁宝. 溶解气驱油藏中斜井和水平井流入动态[J]. 石油石化节能,1994,10(1):15-19.
ZHAO B R. Inflow behavior of inclined and horizontal wells in dissolved gas drive reservoirs[J]. Energy Conservation in Petroleum & Petrochemical Industry,1994,10(1):15-19.
[40] 李义曼,庞忠和. 二氧化碳地质封存中的水-岩反应动力学模拟:进展及问题[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版,2012(S2):352-360.
LI M Y,PANG Z H. Development and issue on kinetic model of water-rock interaction in CO2 geological sequestion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2012(S2):352-360.
[41] 马鑫,李旭峰,文冬光,等. 新疆准东地区场地尺度二氧化碳地质封存联合深部咸水开采潜力评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):196-205.
MA X,LI X F,WEN D G,et al. A study of the potential of field-scale of CO2 geological storage and enhanced water recovery in the eastern Junggar area of Xinjiang[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):196-205.
[42] 舒娇娇. 深部咸水层封存二氧化碳迁移规律研究[D]. 大连:大连海事大学, 2020.
SHU J J. Study on the migration of carbon dioxide in deep salt water layer[D]. Dalian:Dalian Maritime University. 2020.
[43] 沈平平,廖新维. 二氧化碳地质埋存与提高石油采收率技术[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2009.
SHEN P P,LIAO X W. Carbon Dioxide Geological Storage and Enhanced Oil Recovery Technology[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2009.
[44] 郭建强. 中国二氧化碳地质储存适宜性评价与示范工程[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2014.
GUO J Q. Suitability Evaluation and Demonstration Project of CO2 Geological Storage in China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2014.
[45] 李冠颖,郭俊志,谢其泰,等. 二氧化碳储存环境对油井水泥性质影响之研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(S2):346-350.
LI G Y,GUO J Z,XIE Q T,et al. Study of mechanical and microscopic properties of API G cement with additives exposed to CO2-rich environment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(S2):346-350.
[46] 杜槟. 二氧化碳封存场地三维地质建模及现场注入试验研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2016.
DU B. Carbon dioxide sequestration sites 3D geolog ical modeling and the injection test research[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2016.
[47] 刘雪雁,李鹏春,周蒂,等. 南海北部珠江口盆地惠州21-1油田CO2-EOR与碳封存潜力快速评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2017,33(3):56-65.
LIU X Y,LI P C,ZHOU D,et al. Quick assessment of CO2-EOR and CO2 sequestration potential in Huizhou 21-1 Oilfield,Pearl River Mouth Basin,northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2017,33(3):56-65.
[48] 张志超,柏明星,陈巧珍. 二氧化碳埋存井筒的腐蚀行为影响因素[J]. 腐蚀与防护,2021,42(4):54-61. doi: 10.11973/fsyfh-202104010
ZHANG Z C,BAI M X,CHEN Q Z. Influencing factors of corrosion behavior of carbon dioxide storage wellbore[J]. Corrosion & Protection,2021,42(4):54-61. doi: 10.11973/fsyfh-202104010
[49] 李琦,刘桂臻,蔡博峰,等. 二氧化碳地质封存环境风险评估的空间范围确定方法研究[J]. 环境工程,2018,36(2):27-32.
Li Q,LIU G Z,CAI B F,et al. Principle and methodology of determining the spatial range of environmental risk assessment of carbon dioxide geological storage[J]. Environmental Engineering,2018,36(2):27-32.
[50] 李琦,蔡博峰,陈帆,等. 二氧化碳地质封存的环境风险评价方法研究综述[J]. 环境工程,2019,37(2):13-21.
Li Q,CAI B F,CHEN F,et al. Review of environmental risk assessment methods for carbon dioxide geological storage[J]. Environmental Engineering,2019,37(2):13-21.
[51] 郝艳军,杨顶辉. 二氧化碳地质封存问题和地震监测研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展,2012,27(6):2369-2383. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.012
HAO Y J,YANG D H. Research progress of carbon dioxide capture and geological sequestration problem and seismic monitoring research[J]. Progress in Geophysics,2012,27(6):2369-2383. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.012
[52] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 二氧化碳捕集、利用与封存环境风险评估技术指南(试行)[S]. 北京:中华人民共和国环境保护部,2016.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Technical guideline on environmental risk assessment for carbon dioxide capture,utilization and storage (on trial)[S]. Beijing:Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China,2016.
[53] 彭轩明,曹珂. 浅海沉积盆地二氧化碳地质储存潜力与适宜性评价成果报告[R]. 青岛:青岛海洋地质研究所, 2013.
PENG X M,CAO K. Report on evaluation of CO2 geological storage potential and suitability in shallow sea sedimentary basins[R]. Qingdao:Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, 2013.
[54] 马馨蕊,梁杰,李清,等. 咸水层CO2地质封存研究进展及前景展望[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2024,40(10):1-18.
MA X R,LIANG J,LI Q,et al. Progress and prospects of CO2 geological storage in saline aquifer[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2024,40(10):1-18.
[55] 陈建文,孙晶,杨长清,等. 东海陆架盆地新生界咸水层二氧化碳封存地质条件及封存前景[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(10):14-21.
CHEN J W,SUN J,YANG C Q,et al. Geological conditions and prospects of carbon dioxide storage in the Cenozoic saline water layers of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2023,39(10):14-21.
[56] YUAN Y,WANG J,CHEN J,et al. Carbon dioxide storage potential of Cenozoic saline aquifers in the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Energies,2023,16(4):1578. doi: 10.3390/en16041578
[57] CHADWICK R A,WILLIAMS G A,FALCON-SUAREZ I. Forensic mapping of seismic velocity heterogeneity in a CO2 layer at the Sleipner CO2 storage operation,North Sea,using time-lapse seismics[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2019,90:102793. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102793
[58] FURRE A K,EIKEN O,ALNES H,et al. 20 years of monitoring CO2-injection at Sleipner[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,114:3916-3926. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1523
[59] GRUDE S,LANDRø M,DVORKIN J. Pressure effects caused by CO2 injection in the Tubåen Fm. ,the Snøhvit field[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2014,27:178-187.
[60] SHCHIPANOV A A,KOLLBOTN L,BERENBLYUM R. Characterization and monitoring of reservoir flow barriers from pressure transient analysis for CO2 injection in saline aquifers[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2019,91:102842. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102842
[61] WHITE J C,WILLIAMS G,CHADWICK A. Seismic amplitude analysis provides new insights into CO2 plume morphology at the Snohvit CO2 injection operation[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2018,79:313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2018.05.024
[62] KREFT E,GEEL C R,D'HOORE D,et al. CO2 storage and testing enhanced gas recovery in the K12-B reservoir[C] //23rd World Gas Conference,Amsterdam,2006.
[63] VAN DER MEER L G H,ARTS R J,GEEL C R,et al. K12-B:Carbon dioxide injection in a nearly depleted gas field offshore the Netherlands[M]//GROBE M,PASHIN J C,DODGE R L,Carbon Dioxide Sequestration in Geological Media State of the Science. AAPG Studies in Geology,2009:379-390.
[64] VANDEWEIJER V,HOFSTEE C,GRAVEN H. 13 years of safe CO2 injection at K12-B[C] //Fifth CO2 Geological Storage Workshop. Utrecht:European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers,2018:1-5.
[65] PETERSEN H I,SPRINGER N,WEIBEL R,et al. Sealing capability of the Eocene-Miocene Horda and Lark formations of the Nini West depleted oil field-implications for safe CO2 storage in the North Sea[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2022,118:103675. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2022.103675
[66] PETERSEN H I,AL-MASRI W F,RUDRA A,et al. Movable and non-movable hydrocarbon fractions in an oil-depleted sandstone reservoir considered for CO2 storage,Nini West Field,Danish North Sea[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2023,280:104399. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2023.104399
[67] TANAKA Y,SAWADA Y,TANASE D,et al. Tomakomai CCS demonstration project of Japan,CO2 injection in process[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,114:5836-5846. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1721
[68] IKEDA T, TSUJI T. Advanced surface-wave analysis for 3D ocean bottom cable data to detect localized heterogeneity in shallow geological formation of a CO2 storage site[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,39:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.04.020
[69] MECKEL T A,FENG Y E,TREVIñO R H,et al. High-resolution 3D marine seismic acquisition in the overburden at the Tomakomai CO2 storage project,offshore Hokkaido,Japan[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2019,88:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.05.034
[70] SAWADA Y,TANAKA J,SUZUKI C,et al. Tomakomai CCS demonstration project of Japan,CO2 injection in progress[J]. Energy Procedia,2018,154:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.002
[71] Northern Lights Joint Ventures. Northern Lights annual report 2023[R]. Stavanger:Northern Lights Joint Ventures,2024.
[72] MENEGUOLO R,SUNDAL A,MARTINIUS A W,et al. Impact of the lower Jurassic Dunlin Group depositional elements on the aurora CO2 storage site,EL001,northern North Sea,Norway[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2022,119:103723. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2022.103723
[73] GENTILE V,CAUCHOIS G,ÅLUND I,et al. Carbon footprint of the Northern Lights JV CO2 transport and storage value chain[R]. Stavanger:Northern Lights Joint Ventures,2023.
[74] 戴金星. 中国东部和大陆架二氧化碳气田(藏)及其气的类型[J]. 大自然探索,1996,15(4):18-20.
DAI J X. Types of carbon dioxide gas fields (reservoirs) and their gas in eastern China and continental shelf[J]. Discovery of Nature,1996,15(4):18-20.
[75] 何家雄,祝有海,黄霞,等. 南海北部边缘盆地不同类型非生物成因CO2成因成藏机制及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学,2011,22(6):935-941. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2011.06.935
HE J X,ZHU Y H,HUANG X,et al. Accumulation mechanisms for different geologic types of non-biological CO₂ and controlling factors in north marginal basin,South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2011,22(6):935-941. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2011.06.935
[76] 何家雄,刘全稳. 南海北部大陆架边缘盆地CO2成因和运聚规律的分析与预测[J]. 天然气地球科学,2004,15(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.01.003
HE J X,LIU Q W. The analysis and discussion to the characters on generative cause,migration and distribution of CO2 in the marginal basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2004,15(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.01.003
[77] 李军,邹华耀,周心怀,等. 渤海海域CO2成因与分布主控因素[J]. 中国海上油气,2012,24(2):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.02.004
LI J,ZOU H Y,ZHOU X H,et al. Carbon dioxide origin and the main controls over its distribution in Bohai Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2012,24(2):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.02.004
[78] 刘宝明,夏斌,李绪宣,等. 中国东部及南海西部陆缘CO2气藏形成机理[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2004,23(3):207-211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2004.03.005
LIU B M,XIA B,LI X X,et al. The genetic mechanism of CO2 in the East China and the western South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2004,23(3):207-211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2004.03.005
[79] 何家雄,李明兴,陈伟煌,等. 莺琼盆地天然气中CO2的成因及气源综合判识[J]. 天然气工业,2001,21(3):15-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2001.03.005
HE J X,LI M X,CHEN W H,et al. Origin of carbon dioxide in natural gas in Yingqiong Basin and its comprehensive gas source discrimination[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2001,21(3):15-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2001.03.005
[80] 王振峰,何家雄,裴秋波. 莺-琼盆地和珠江口盆地西部CO2成因及运聚分布特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),2003,17(5):293-297.
WANG Z F,HE J X,PEI Q B. The origin and migration-accumulation features of CO2 in Ying-Qiong Basin and the western Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China offshore Oil and Gas (Geology),2003,17(5):293-297.
[81] LUO D,YUAN Y,CHEN J,et al. Structural and reservoir characteristics of potential carbon dioxide storage sites in the northern South Yellow Sea Basin,offshore Eastern China[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,2024,12(10):1733. doi: 10.3390/jmse12101733
[82] 可行,陈建文,龚建明,等. 东海陆架盆地CO2地质封存适宜性评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(7):1-12.
KE X,CHEN J W,GONG J M,et al. Suitability evaluation of CO2 sequestration in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2023,39(7):1-12.
[83] 可行,陈建文,龚建明,等. 珠江口盆地二氧化碳地质封存条件及源汇匹配性分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(2):55-65.
KE X,CHEN J W,GONG J M,et al. Assessment on geological condition for carbon dioxide sequestration and source-sink matching in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2023,43(2):55-65.
[84] WANG J,YUAN Y,CHEN J W,et al. Geological conditions and suitability evaluation for CO2 geological storage in deep saline aquifers of the Beibu Gulf Basin (South China)[J]. Energies,2023,16(5):2360. doi: 10.3390/en16052360
-



 下载:
下载: