A study of the similar material characteristics of fragmenting rock mass physical model
-
摘要:
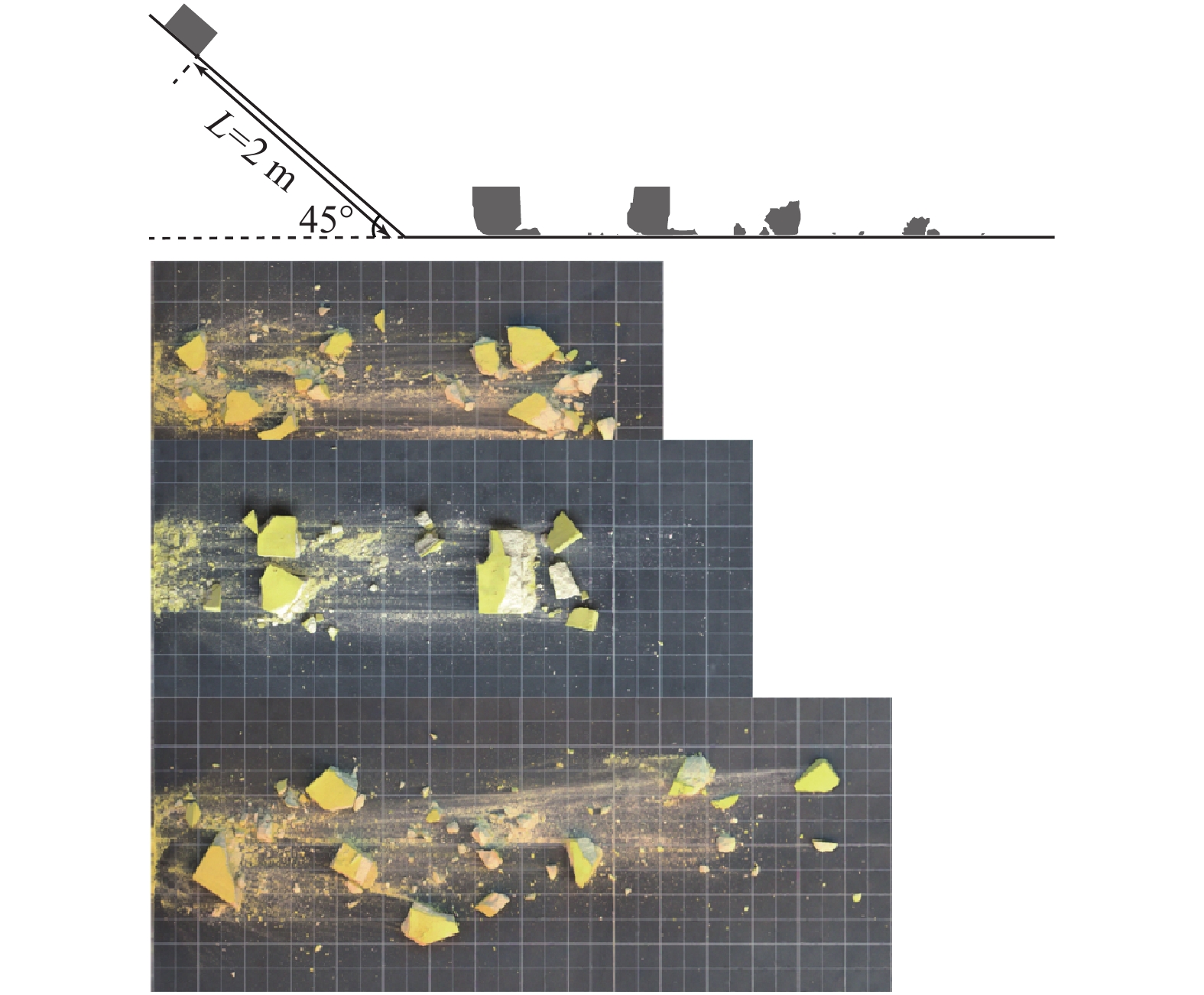
高速远程滑坡物理模型试验中,岩石相似材料的选择是模型试验成功的关键,然而目前滑坡相似材料强度高、难以在缩尺试验中模拟滑坡破碎过程。以重晶石、石英砂为骨料,石膏为胶结剂,羧甲基纤维素钠、甘油、水作为辅助材料,进行可破碎岩石相似材料的配比试验。采用控制变量法研究重晶石与石英砂比例(重石比)、骨料与胶结物比例(骨胶比)、羧甲基纤维素钠含量、拌合水量、甘油含量对相似材料物理力学性质的影响。试验结果表明:所有配比情况下各相似材料物理力学参数的范围分别为单轴抗压强度为0.12~1.47 MPa,弹性模量为25.51~148.12 MPa,黏聚力为1.63~87.39 kPa,内摩擦角为22.70°~35.89°,脆性指标主要分布在0.033~0.145之间;重石比主要控制岩石相似材料的内摩擦角;骨胶比减小,对应的黏聚力和内摩擦角先增大后减小;羧甲基纤维素钠对材料的单轴抗压强度、弹性模量、黏聚力等材料的力学特性以及材料的脆性指标影响均比较大,其中对单轴抗压强度的影响最大。因此,控制羧甲基纤维素钠和拌合水量的含量,并合理调节重石比与骨胶比,在相似比约为1∶600的试验尺度下,最终确定了适用于高速远程滑坡碎屑化过程模拟的低强度高脆性岩石相似材料的配比区间。
Abstract:Similar materials in the physical model test of avalanche are the key to the success of the model test. However, the strength of similar materials is high at present, it is difficult to be fractured within the scope of the experiment. The materials can reproduce the clastic process of landslide in the scale model experiment. Thus, we choose five raw materials to formulate similar materials. The five raw materials are barite, quartz sand, gypsum, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, glycerin and water content. Five influencing factors are analyzed, including the ratio of barite to quartz sand, the ratio of aggregate to gypsum, contents of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and glycerin, and water content. The aggregate consists of barite and quartz sand. The results show that (1) in all the experiments, the uniaxial compressive strength ranges from 0.12 to 1.47 MPa, the elastic modulus, from 25.51 to 148.12 MPa, the cohesion, from 1.63 kPa to 87.39 kPa, the angle of internal friction, from 22.70° to 35.89°, and the brittleness index, from 0.033 to 0.145. (2) The ratio of barite to quartz sand has the great effect on the angle of internal friction. (3) With the decrease in the ratio of aggregate and cement, the cohesion first increases and then decreases. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose has the greatest influence on the parameters of the similar materials, especially the uniaxial compressive strength. Therefore, it is important to control the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, glycerin and water content and adjust the mass ratio of barite to quartz sand and the mass ratio of aggregate and cement. The obtained similar materials can be used to simulate the clastic process of avalanche when the similarity ratio is approximately 1∶600.
-
Key words:
- rockslide /
- rock similar material /
- fragmentation /
- low strength and high brittleness /
- model test
-

-
表 1 相似材料配制中主要物理量之间相似比
Table 1. Ratios of the key parameters in the similar materials production
物理量 量纲 相似比 物理量 量纲 相似比 应力 ML−1T−2 1∶600 内摩擦角 M0L0T0 1∶1 弹性模量 ML−1T−2 1∶600 长度 L 1∶600 应变 M0L0T0 1∶1 密度 ML−3 1∶1 泊松比 M0L0T0 1∶1 重力加速度 LT−2 1∶1 黏聚力 ML−1T−2 1∶600 表 2 模型相似材料力学参数
Table 2. The mechanical parameters of the similar materials
强度参数 抗压强度/MPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 原岩 100~250 30~50 45~60 40~69 0.1~0.3 相似材料 0.17~0.42 0.050~0.083 45~60 0.067~0.120 0.1~0.3 表 3 模型相似材料配比方案
Table 3. Matching schemes of the model materials
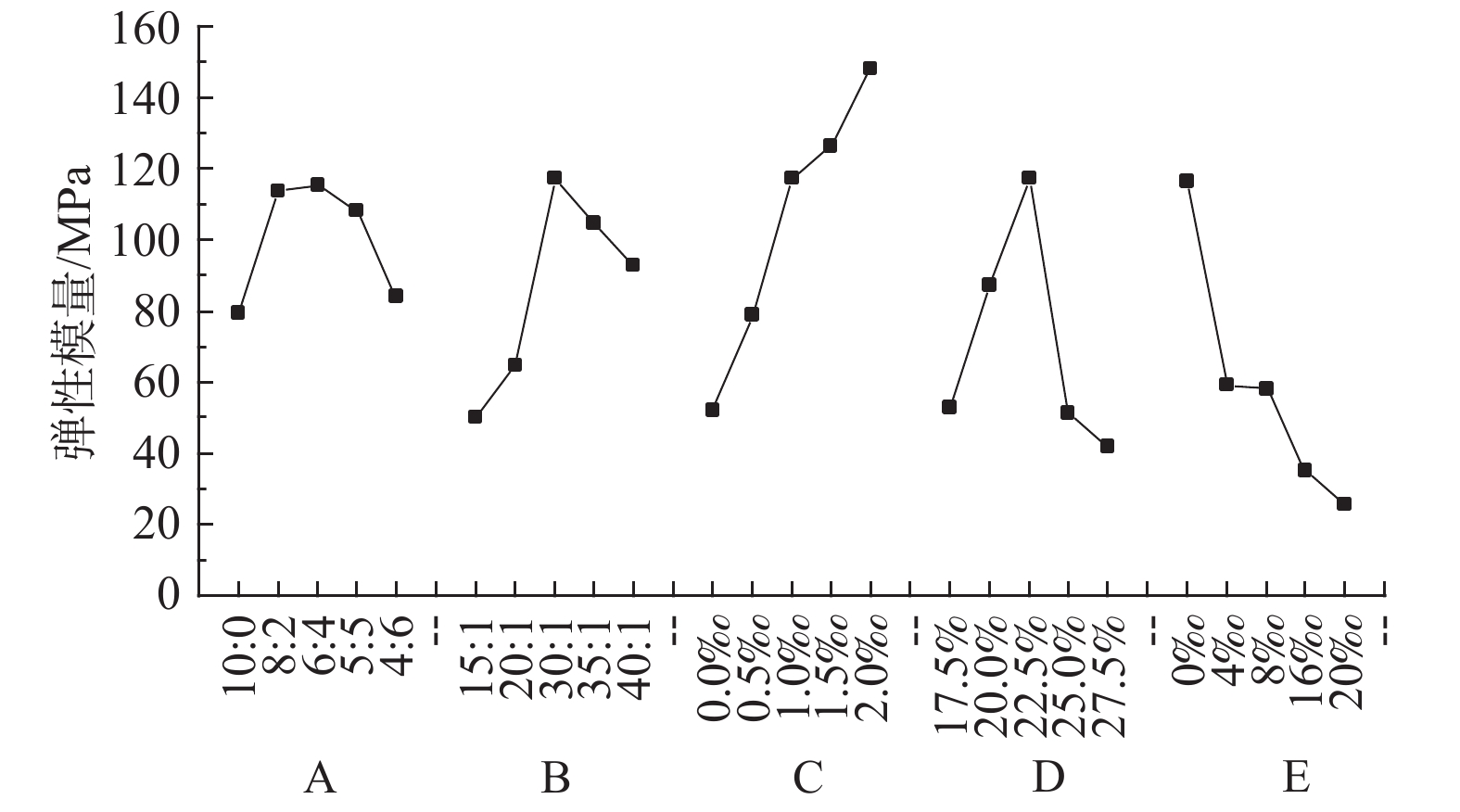
编号 重石比 骨胶比 羧甲基纤维素钠含量/‰ 拌合水量/% 甘油含量/‰ S1 10∶0 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S2 8∶2 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S3 6∶4 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S4 5∶5 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S5 4∶6 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S6 7∶3 15∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S7 7∶3 20∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S8 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S9 7∶3 35∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S10 7∶3 40∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S11 7∶3 30∶1 0.0 22.50 0.5 S12 7∶3 30∶1 0.5 22.50 0.5 S13 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S14 7∶3 30∶1 1.5 22.50 0.5 S15 7∶3 30∶1 2.0 22.50 0.5 S16 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 17.50 0.5 S17 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 20.00 0.5 S18 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.5 S19 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 25.00 0.5 S20 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 27.50 0.5 S21 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 0.0 S22 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 4.0 S23 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 8.0 S24 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 16.0 S25 7∶3 30∶1 1.0 22.50 20.0 表 4 试验结果
Table 4. Experimental results
物理力学参数 抗压强度/
MPa弹性模量/
MPa黏聚力/
kPa内摩擦角/
(°)密度/
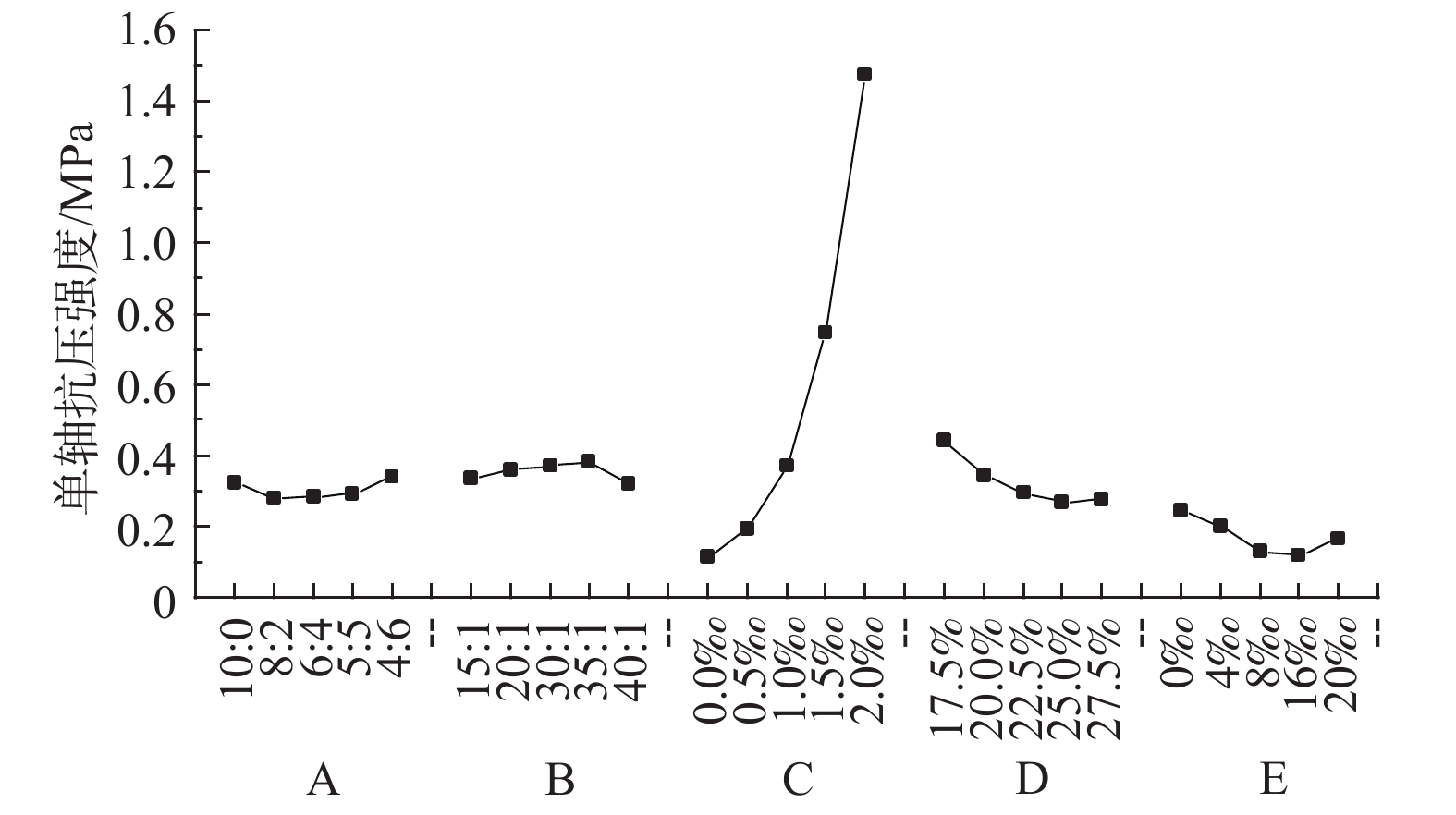
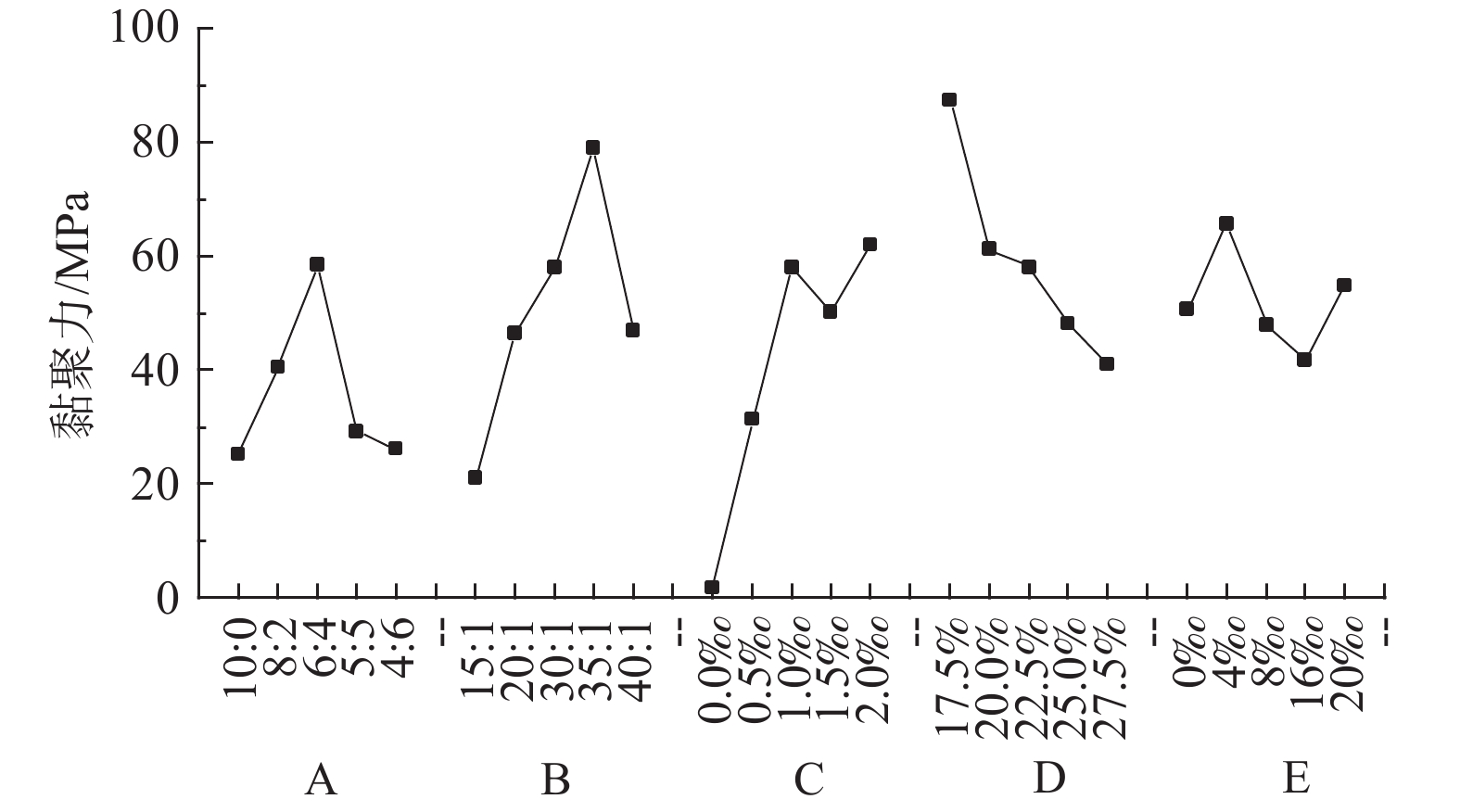
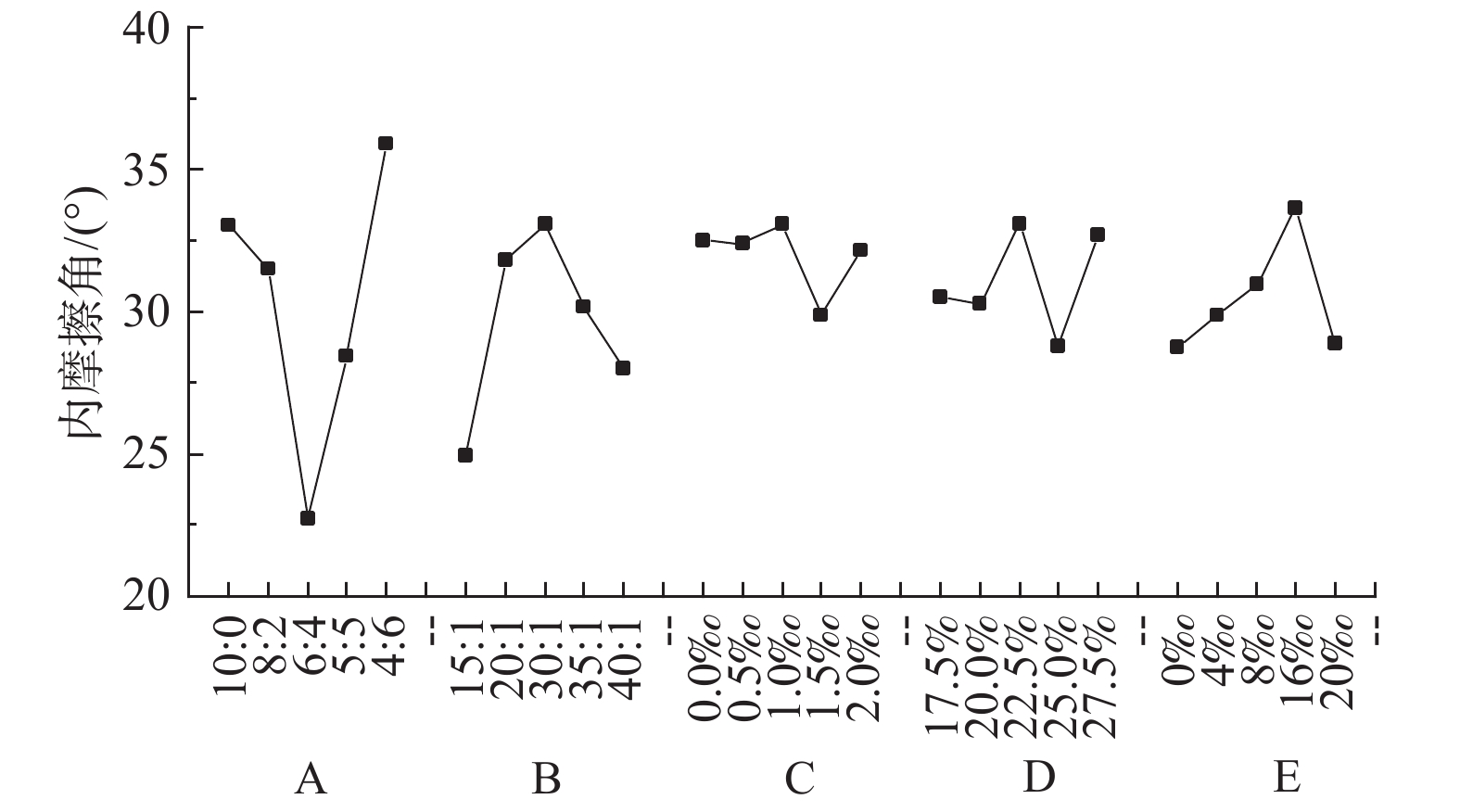
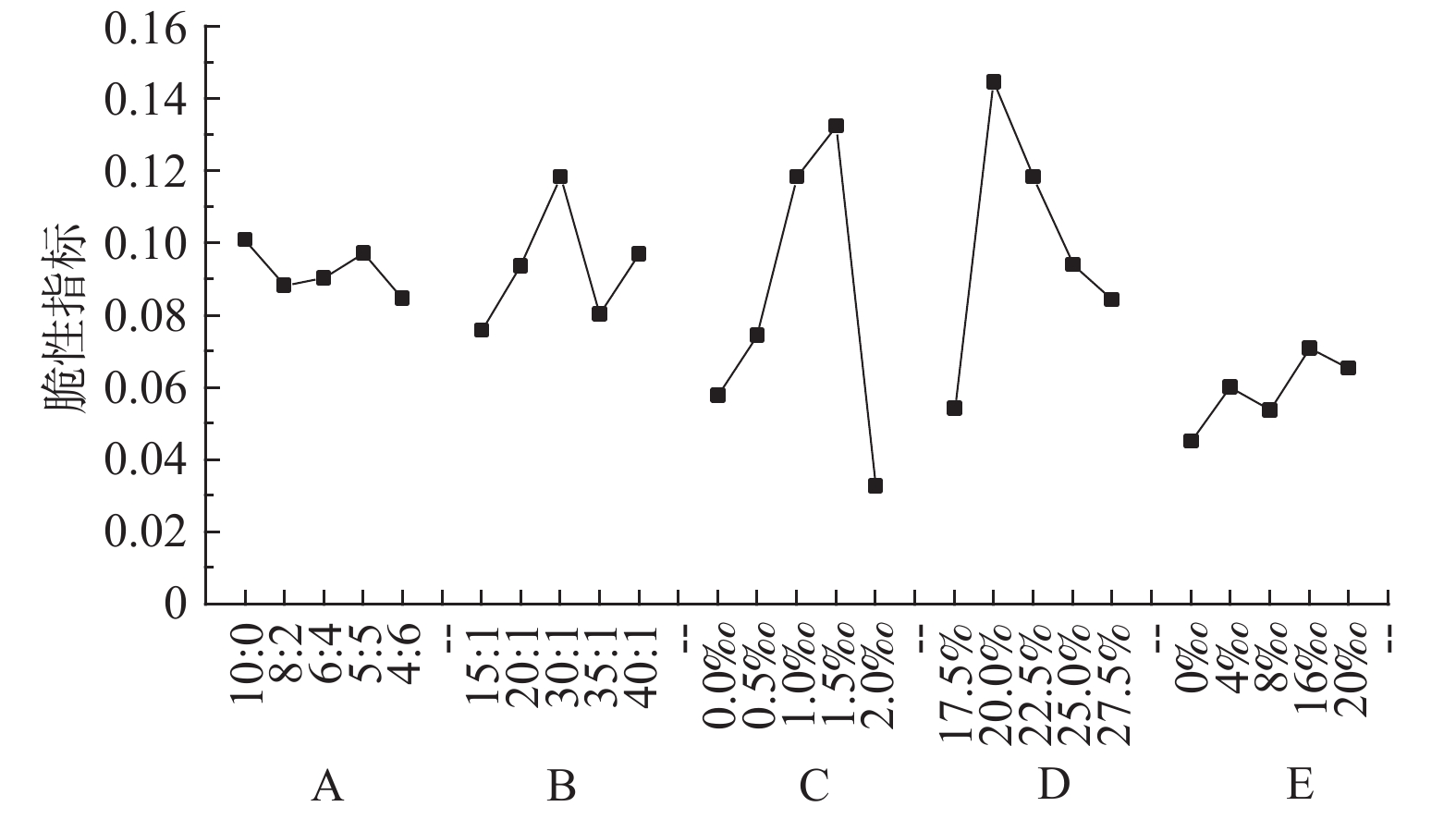
(g·cm−3)S1 0.3238 79.49 25.16 33.02 1.729 S2 0.2795 113.90 40.56 31.49 1.812 S3 0.2832 115.26 58.45 22.70 1.861 S4 0.2920 108.15 29.20 28.45 1.881 S5 0.3383 84.06 26.08 35.89 1.855 S6 0.3357 50.02 20.93 24.92 1.809 S7 0.3578 64.86 46.42 31.82 1.800 S8 0.3699 117.39 58.00 33.10 1.818 S9 0.3818 104.79 79.10 30.19 1.800 S10 0.3190 92.67 46.95 27.98 1.804 S11 0.1154 52.28 1.63 32.50 1.859 S12 0.1937 78.95 31.29 32.41 1.812 S13 0.3699 117.39 58.00 33.10 1.804 S14 0.7483 126.22 50.20 29.86 1.832 S15 1.4727 148.12 61.99 32.13 2.220 S16 0.4408 53.10 87.39 30.51 1.844 S17 0.3446 87.45 61.21 30.29 1.803 S18 0.2952 117.39 58.00 33.10 1.818 S19 0.2704 51.32 48.12 28.77 1.779 S20 0.2779 41.82 41.04 32.71 1.815 S21 0.2436 116.41 50.70 28.76 1.804 S22 0.2019 59.35 65.63 29.86 1.843 S23 0.1316 58.18 47.91 30.95 1.805 S24 0.1167 35.02 41.63 33.65 1.837 S25 0.1648 25.51 54.82 28.88 1.885 表 5 单轴抗压强度敏感性分析
Table 5. Sensitivity analysis of the compressive strength
水平 A B C D E 1 0.32376 0.3357 0.11542 0.44076 0.24355 2 0.27947 0.35778 0.19366 0.34457 0.20190 3 0.28315 0.36988 0.36988 0.29523 0.13162 4 0.29197 0.38184 0.74828 0.27044 0.11672 5 0.33831 0.31899 1.47266 0.27786 0.16476 极差 0.05884 0.06285 1.35724 0.17032 0.12683 标准差 0.02620 0.02547 0.55552 0.07047 0.05185 表 6 弹性模量敏感性分析
Table 6. Sensitivity analysis of the elastic modulus
水平设置 A B C D E 1 79.49 50.02 52.28 53.10 116.41 2 113.90 64.86 78.95 87.45 59.35 3 115.26 117.39 117.39 117.39 58.18 4 108.15 104.79 126.22 51.32 35.02 5 84.06 92.67 148.12 41.82 25.51 极差 35.77 67.37 95.84 75.57 90.90 标准差 17.08 27.95 38.47 31.54 35.33 表 7 黏聚力敏感性分析
Table 7. Sensitivity analysis of cohesion
水平设置 A B C D E 1 25.16 20.93 1.63 87.39 50.70 2 40.56 46.42 31.29 61.21 65.63 3 58.45 57.99 57.99 57.99 47.91 4 29.20 79.10 50.20 48.12 41.63 5 26.08 46.95 61.99 41.04 54.82 极差 33.28 58.17 60.37 46.35 24.00 标准差 14.03 21.08 24.79 17.70 8.94 表 8 内摩擦角敏感性分析
Table 8. Sensitivity analysis of the internal friction angle
水平 A B C D E 1 33.02 24.92 32.50 30.51 28.76 2 31.49 31.82 32.41 30.29 29.86 3 22.70 33.10 33.10 33.10 30.95 4 28.45 30.19 29.86 28.77 33.65 5 35.89 27.98 32.13 32.71 28.88 极差 13.19 8.18 3.23 4.33 4.89 标准差 5.03 3.24 1.24 1.80 2.01 表 9 脆性指标敏感性分析
Table 9. Sensitivity analysis of the brittleness degree
水平设置 A B C D E 1 0.101 0.076 0.058 0.054 0.045 2 0.088 0.093 0.074 0.145 0.060 3 0.090 0.118 0.118 0.118 0.053 4 0.097 0.080 0.132 0.094 0.071 5 0.085 0.097 0.033 0.084 0.065 标准差 0.007 0.017 0.042 0.034 0.010 表 10 归一化后的标准差
Table 10. Standard deviation after normalization
归一化后的标准差 A B C D E 单轴抗压强度 0.036 0.035 0.761 0.097 0.071 弹性模量 0.114 0.186 0.256 0.210 0.235 黏聚力 0.162 0.244 0.286 0.205 0.103 内摩擦角 0.377 0.243 0.093 0.135 0.151 脆性指标 0.061 0.153 0.381 0.314 0.092 表 11 相似材料理论值与试验值
Table 11. Theoretical and experimental values of similar materials
相似材料强度参数 抗压强度/
MPa黏聚力/
kPa内摩擦角/
(°)弹性模量/
MPa理论值 0.17~0.42 50.0~83.3 45.0~60.0 66.7~115.0 实测值 0.12~1.47 25.5~148.1 22.70~35.89 25.5~148.1 -
[1] 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报,2007,25(1):72 − 84. [CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Zhuoyuan, HUANG Ruiqiu. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches: state of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2007,25(1):72 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007
[2] 吴锦华, 袁智洪, 周泳峰. 古滑坡泥灰岩模拟相似材料实验研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(10):81 − 86. [WU Jinhua, YUAN Zhihong, ZHOU Yongfeng. Experimental study on simulated similar materials of ancient landslide marl[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2019,38(10):81 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 崔雪婷, 张子东, 范珊. 基于相似理论的力学模型实验材料研究[J]. 人民珠江,2019,40(5):82 − 86. [CUI Xueting, ZHANG Zidong, FAN Shan. Research on mechanical model test materials based on the similar theory[J]. Pearl River,2019,40(5):82 − 86. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2019.05.014
[4] 徐楚, 胡新丽, 何春灿, 等. 水库型滑坡模型试验相似材料的研制及应用[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(11):4287 − 4293. [XU Chu, HU Xinli, HE Chuncan, et al. Development and application of similar material for reservoir landslide model test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(11):4287 − 4293. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 肖先煊, 许模. 水库滑坡变形特征的模型试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(5):107 − 112. [XIAO Xianxuan, XU Mo. Deformation behavior of landslide in reservoir by model tests[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(5):107 − 112. (in Chinese)
[6] LOURENÇO S D N, SASSA K, FUKUOKA H. Failure process and hydrologic response of a two layer physical model: Implications for rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Geomorphology,2006,73(1/2):115 − 130.
[7] KHOSRAVI M H, PIPATPONGSA T, TAKAHASHI A, et al. Arch action over an excavated pit on a stable scarp investigated by physical model tests[J]. Soils and Foundations,2011,51(4):723 − 735. doi: 10.3208/sandf.51.723
[8] TAKE W A, BOLTON M D, WONG P C P, et al. Evaluation of landslide triggering mechanisms in model fill slopes[J]. Landslides,2004,1(3):173 − 184. doi: 10.1007/s10346-004-0025-1
[9] 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 张柯宏, 等. 高速远程滑坡裹气流态化模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(10):2775 − 2786. [WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Kehong, et al. Study of fluidized characteristics of rock avalanches under effect of entrapped air[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(10):2775 − 2786. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王玉峰, 许强, 程谦恭, 等. 复杂三维地形条件下滑坡–碎屑流运动与堆积特征物理模拟实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(9):1776 − 1791. [WANG Yufeng, XU Qiang, CHENG Qiangong, et al. Experimental study on the propagation and deposit features of rock avalanche along 3D complex topography[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(9):1776 − 1791. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 郝明辉, 许强, 杨兴国, 等. 高速滑坡-碎屑流颗粒反序实验及其成因机制探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(3):472 − 479. [HAO Minghui, XU Qiang, YANG Xingguo, et al. Physical modeling tests on inverse grading of particles in high speed landslide debris[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(3):472 − 479. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 郑光. 滑坡-碎屑流远程运动距离研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
ZHENG Guang. Study on the long-runout distance of rock avalanche[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 眭静, 姜元俊, 樊晓一, 等. 碎屑流冲击刚性挡墙的力学模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(1):121 − 132. [SUI Jing, JIANG Yuanjun, FAN Xiaoyi, et al. An impact model of granular flows on a rigid wall[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(1):121 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] GAËTAN P, EMMANUEL T, MOHAMED N. A physical model use as a rheometer to determine the friction parameter of granular flow[J]. Rock Mechanics,2000,22(2):117 − 122.
[15] DAVIES T R, MCSAVENEY M J, HODGSON K A. A fragmentation-spreading model for long-runout rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1999,36(6):1096 − 1110. doi: 10.1139/t99-067
[16] BLASIO F V D, CROSTA G B. Fragmentation and boosting of rock falls and rock avalanches[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2015,42(20):8463 − 8470. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064723
[17] PERINOTTO H, CHNEIDER J L, BACHÈLERY P, et al. The extreme mobility of debris avalanches: a new model of transport mechanism[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2015,120(12):8110 − 8119. doi: 10.1002/2015JB011994
[18] LOCAT P, COUTURE R, LEROUEIL S, et al. Fragmentation energy in rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2006,43(8):830 − 851. doi: 10.1139/t06-045
[19] BOWMAN E T, TAKE W A, RAIT K L, et al. Physical models of rock avalanche spreading behaviour with dynamic fragmentation[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2012,49(4):460 − 476. doi: 10.1139/t2012-007
[20] HAUG Ø T. ROSENAU M, LEEVER, K, et al. Modelling fragmentation in rock [C]// SASSA K, CANUTI C, YIN Y P. Landslide science for a safer geoenvironment, volume 2: Methods of landslide studies. Switzerland: Springer, 2014: 93-100.
[21] HAUG Ø T, ROSENAU M, LEEVER K, et al. On the energy budgets of fragmenting rockfalls and rockslides: Insights from experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface,2016,121(7):1310 − 1327. doi: 10.1002/2014JF003406
[22] 杜应吉. 地质力学模型实验的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西北水资源与水工程,1996,7(2):64 − 67. [DU Yingji. Research status and development trend of geomechanics model test[J]. Northwest Water Resources and Water Engineering,1996,7(2):64 − 67. (in Chinese)
[23] 袁文忠. 相似理论与静力学模型实验[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 1998: 18-42.
YUAN Wenzhong. Theory of similarily and statics model test[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 1998: 18-42. (in Chinese)
[24] 刘玲霞, 李向全, 周志超, 等. 强震条件下谢家店滑坡碎屑流发生机制试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(3):104 − 109. [LIU Lingxia, LI Xiangquan, ZHOU Zhichao, et al. An experimental study of the initiation mechanism of landslide debris flow under a strong earthquake[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(3):104 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.03.019
[25] 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡特征及减灾研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2000,27(4):8 − 11. [YIN Yueping. Rapid huge landslide and hazard reduction of Yigong River in the Bomi of Tibet[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2000,27(4):8 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.04.003
[26] 戴兴建, 殷跃平, 邢爱国. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃坝链生灾害全过程模拟与动态特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):1 − 8. [DAI Xingjian, YIN Yueping, XING Aiguo. Simulation and dynamic analysis of Yigong rockslide-debris avalanche-dam breaking disaster chain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 张涛, 杨志华, 张永双,等. 四川茂县新磨村高位滑坡铲刮作用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):142 − 149. [ZHAN Tao, YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. An analysis of the entrainment of the Xinmo high-position landslide in Maoxian county, Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):142 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 温铭生, 陈红旗, 张鸣之,等. 四川茂县"6·24"特大滑坡特征与成因机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(3):1 − 7. [WEN Mingsheng, CHEN Hongqi, ZHANG Mingzhi, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism analysis of the“6·24”catastrophic landslide of the June 24 of 2017, at Maoxian,Sichuan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 陈陆望, 白世伟. 脆性岩体岩爆倾向性相似材料概化配比实验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(增刊):1054 − 1058. [CHEN Luwang, BAI Shiwei. Proportioning test study on similar material generalization of rockburst tendency of brittle rock-mass[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2006,27(Sup):1054 − 1058. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 李天斌, 王湘锋, 孟陆波. 岩爆的相似材料物理模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(1):2610 − 2616. [LI Tianbin, WANG Xiangfeng, MENG Lubo. Physical simulation study of similar materials for rockburst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(1):2610 − 2616. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 周辉, 陈珺, 张传庆, 等. 低强高脆岩爆模型材料配比试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(6):2039 − 2049. [ZHOU Hui, CHEN Jun, ZHANG Chuanqing, et al. Experimental study of the rockburst model material with low-strength and high-brittleness[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(6):2039 − 2049. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李光, 马凤山, 徐佩华. 原料组分对动力学相似材料性质影响的试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(3):676 − 681. [LI Guang, MA Fengshan, XU Peihua. Experimental study on property of dynamic similar material made of different raw materials[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(3):676 − 681. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 周辉, 孟凡震, 张传庆, 等. 基于应力-应变曲线的岩石脆性特征定量评价方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(6):1114 − 1122. [ZHOU Hui, MENG Fanzhen, ZHANG Chuanqing, et al. Quantitative evaluation of rock brittleness based on stress-strain curve[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(6):1114 − 1122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] MENG F Z, ZHOU H, ZHANG C Q, et al. Evaluation methodology of brittleness of rock based on post-peak stress-strain curves[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2015,48(5):1787 − 1805. doi: 10.1007/s00603-014-0694-6
[35] 耿晓阳, 张子新. 砂岩相似材料制作方法研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2015,11(1):23 − 28. [GENG Xiaoyang, ZHANG Zixin. Study on preparation methods for similar materials of sandstone[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2015,11(1):23 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] WANG Y F, CHENG Q G, LIN Q W, et al. Insights into the kinematics and dynamics of the Luanshibao rock avalanche(Tibetan Plateau, China) based on its complex surface landforms[J]. Geomorphology,2018,317:170183.
-




 下载:
下载: