A study of the predicted instability time of sudden loess landslides based on the SLO model
-
摘要:
突发型黄土滑坡灾前变形量小,加速阶段历时短,预警预报难度大。为探究该类滑坡失稳时间预测的新途径,降低滑坡造成的经济损失和人员伤亡,以2019年甘肃黑方台地区发生的4起滑坡为研究对象,基于改进的切线角模型确定滑坡变形阶段,提出以改进切线角为指标的简化累计计算方法;采用斜率模型(SLO模型)从滑坡各变形阶段起算进行失稳时间预测,从速度倒数变化趋势、滑坡成灾模式等方面分析预测结果差异。研究发现:(1)斜率模型在突发型黄土滑坡失稳时间预测方面具有一定的可行性,从80°切线角起算得到的预测精度最高;(2)以切线角为划分指标进行简化累计计算能降低数据波动对预测结果的影响,反映预测寿命变化趋势,提高预测精度;(3)速度倒数变化趋势呈“凹”型时提前预测概率大,速度倒数变化趋势呈“凸”型时滞后预测概率大,速度倒数变化趋势呈线性时模型预测精度较高;(4)该模型在黄土滑移崩塌型滑坡中的预测效果要优于静态液化型滑坡。
Abstract:The deformation and displacement of sudden loess landslides are small and the time of duration is short, which make early warning and forecast of landslides difficult. In order to explore a new way to predict the instability time of these landslides and reduce economic losses and casualties, four landslides in the Heifangtai area of Gansu Province in 2019 are taken as the research objects, and the deformation stage of landslide is determined with the improved tangent angle mode. A simplified cumulative calculation method based on the improved tangent angle is proposed. The SLO model is used to predict the instability time. The difference in the predicted results is analyzed from the speed change trend and disaster-causing mode. The results show that (1) the SLO model is of a certain feasibility in predicting the instability time of sudden loess landslides, and the predicted accuracy obtained from the tangent angle of 80° is the highest. (2) The simplified accumulative calculation performance using the tangent angle as the dividing index reduces the impact of data fluctuations on the predicted results and improves the predicted accuracy. (3) When the inverse velocity change trend is “concave”, the probability of early prediction is large.When the inverse velocity change trend is “convex”, the probability of early prediction is small. And when the inverse velocity change trend is linear, the prediction accuracy is relatively high. (4) The prediction effect of this model in loess fall landslides is better than that of loess flow landslides.
-
Key words:
- loess landslide /
- sudden landslide /
- time prediction /
- SLO model /
- tangent angle
-

-
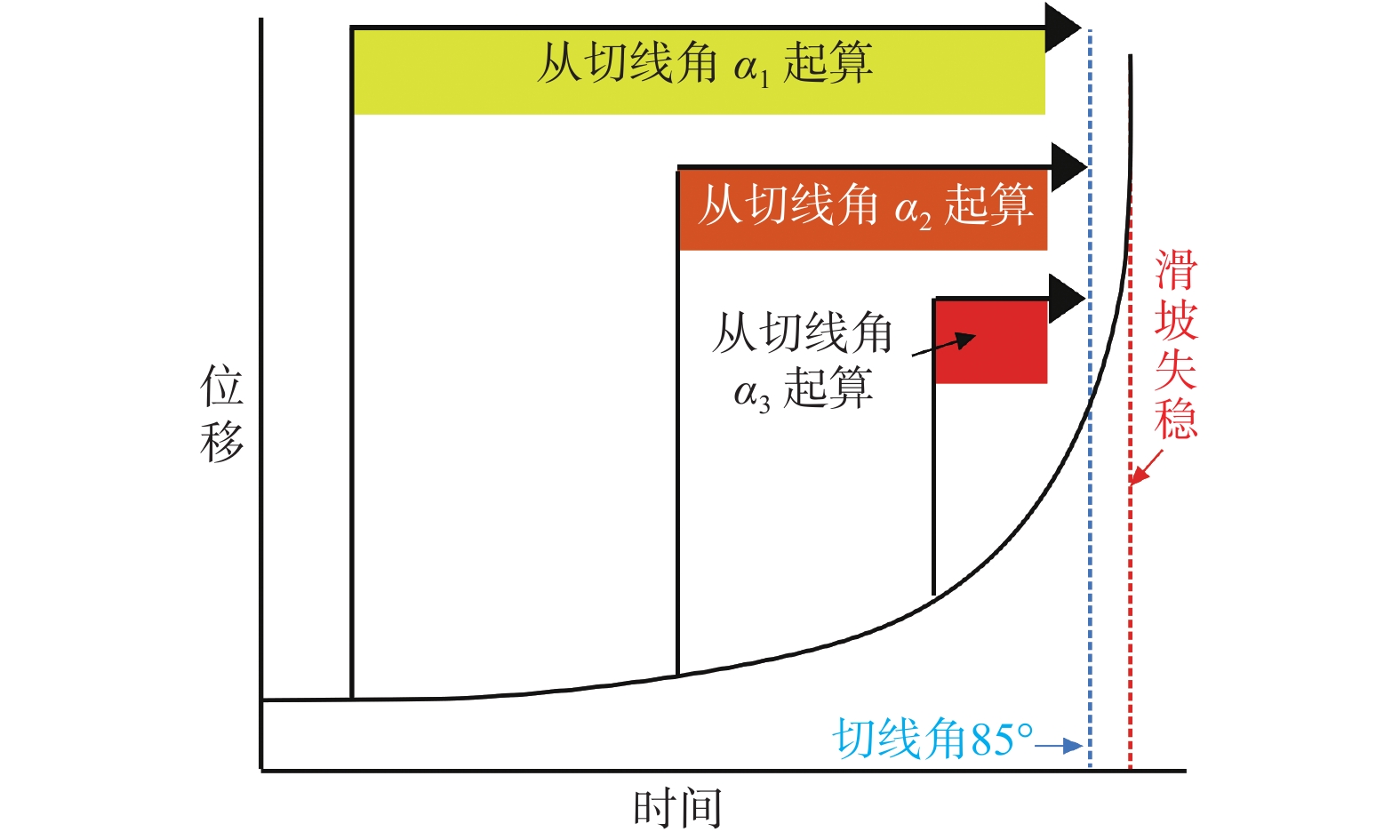
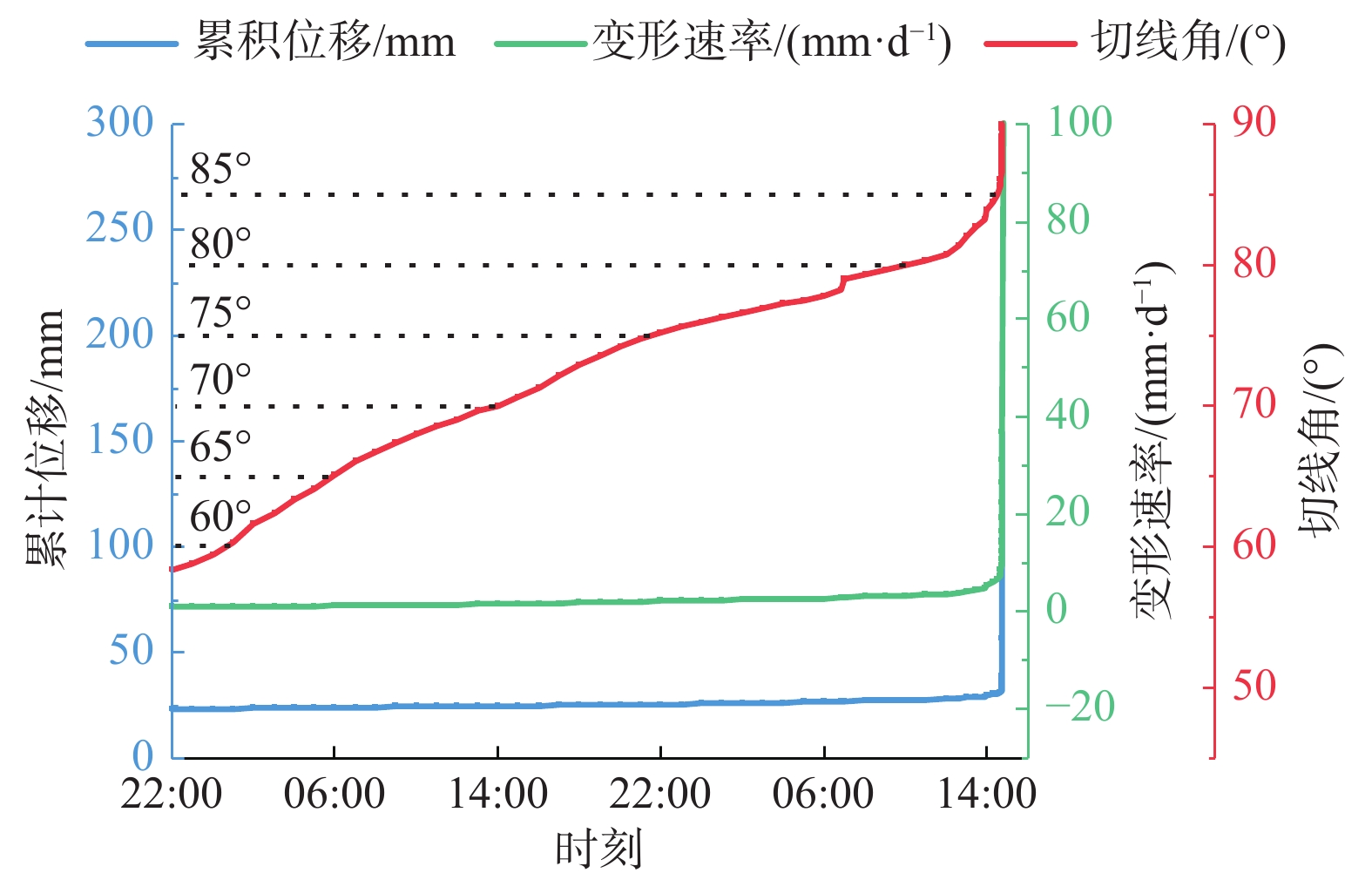
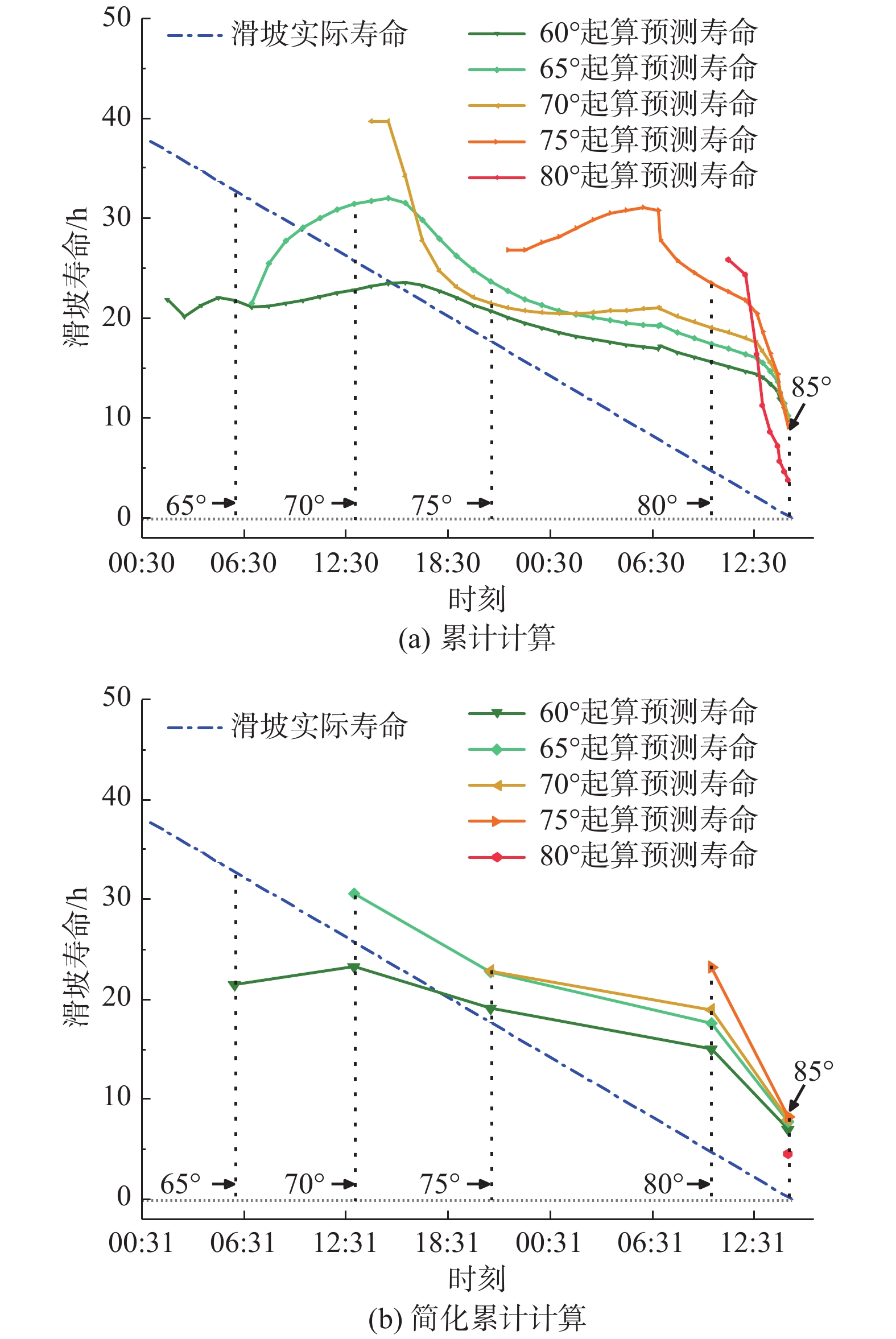
图 4 预测寿命图(据文献[22],有删改)
Figure 4.
图 11 静态液化型滑坡成灾模式图(据文献[27],有删改)
Figure 11.
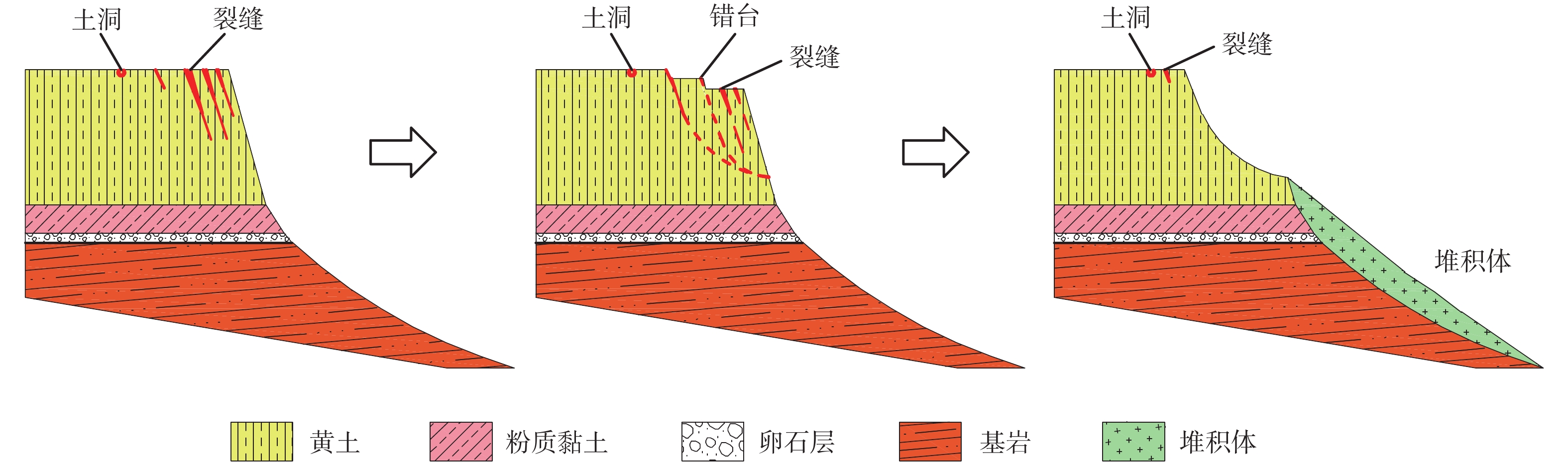
图 12 滑移崩塌型滑坡成灾模式图(据文献[27],有删改)
Figure 12.
表 1 2019年成功预警的滑坡
Table 1. Basic characteristics of landslides predicted in 2019
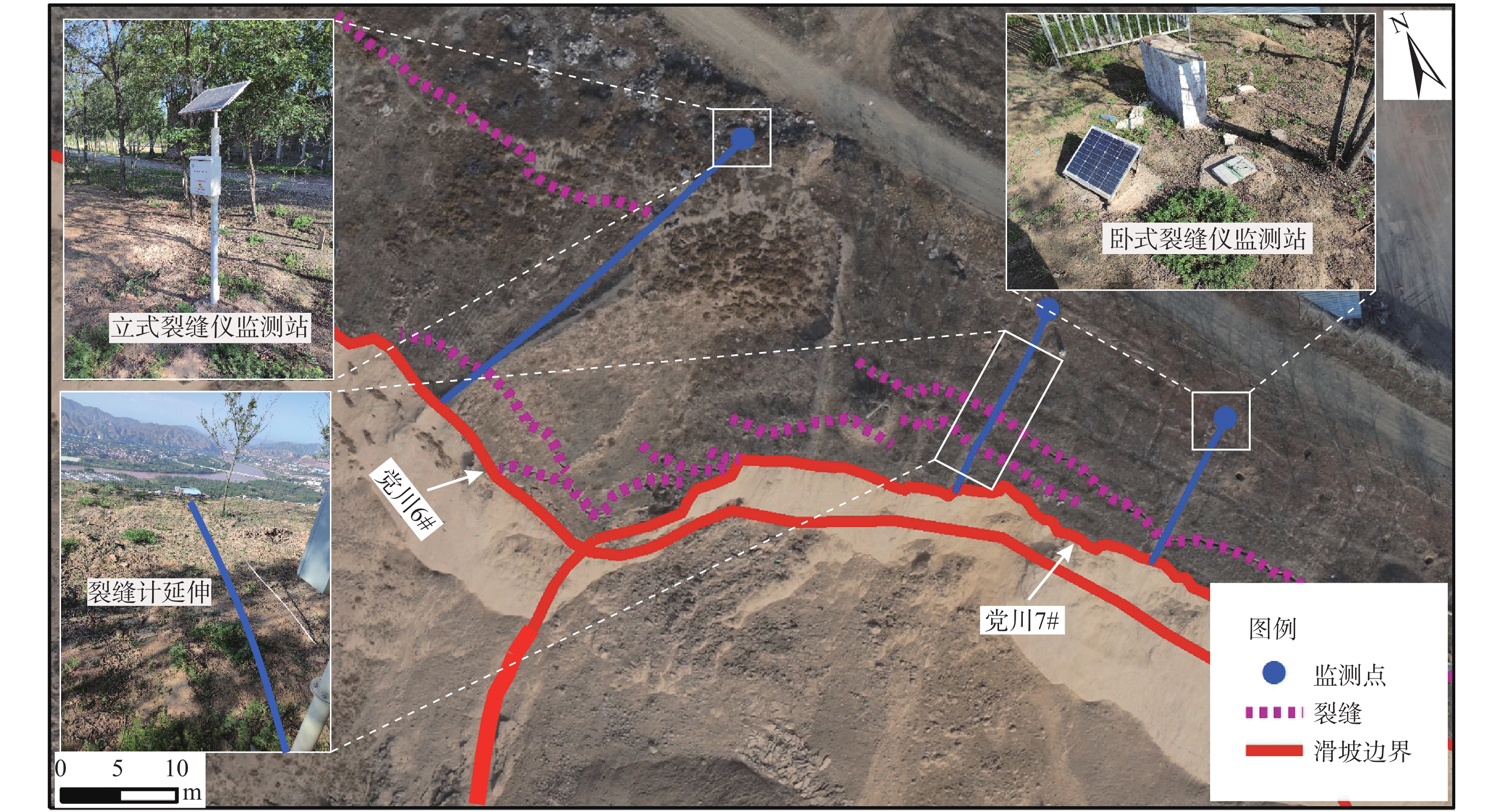
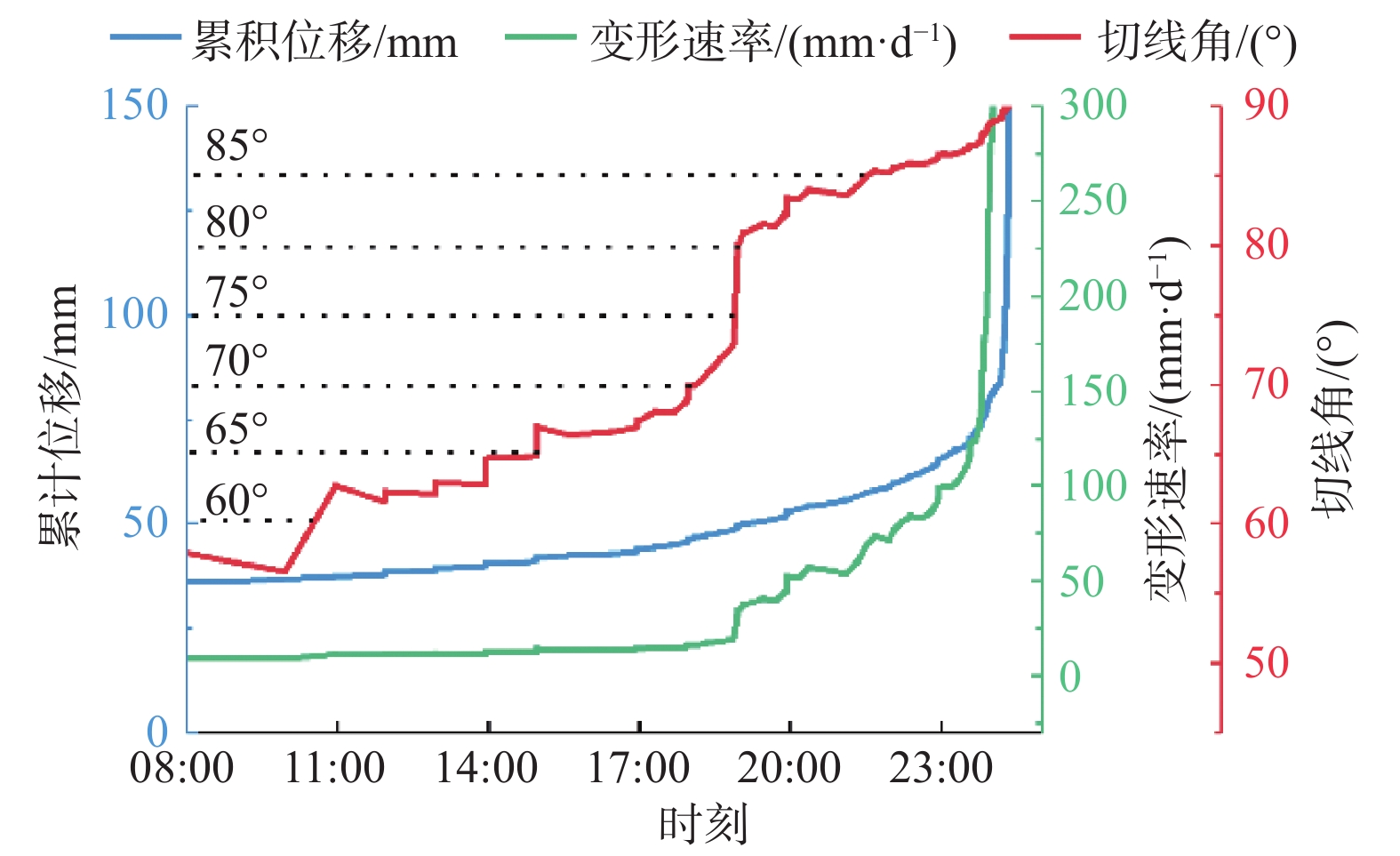
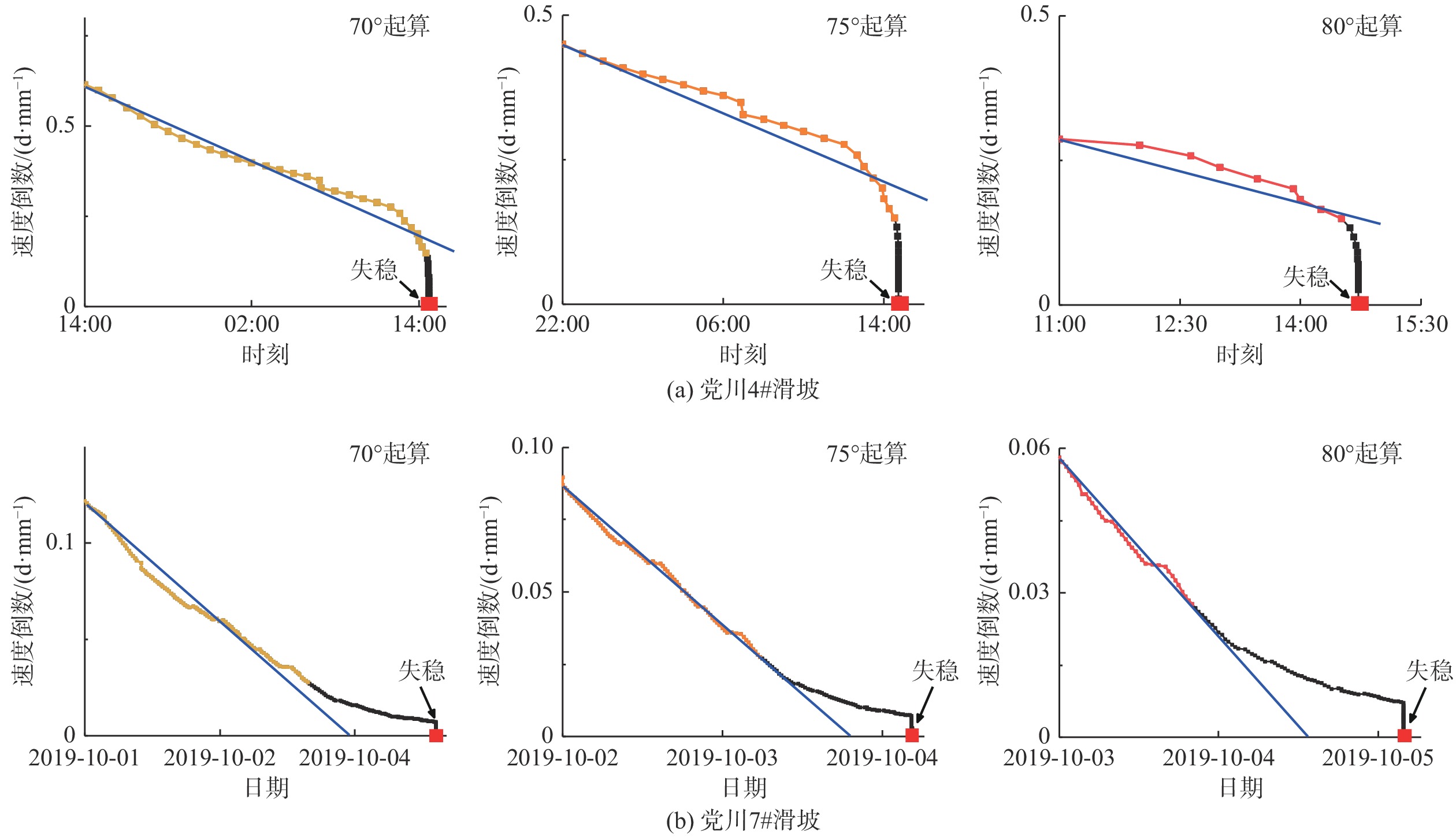
编号 滑坡 发生时间 滑坡类型 提前预警时间 1 陈家6# 2019-03-04 滑移崩塌型 2 h 2 党川6# 2019-03-26 滑移崩塌型 40 min 3 党川4# 2019-04-19 静态液化型 18 min 4 党川7# 2019-10-05 滑移崩塌型 32 h 表 2 党川6#滑坡预测结果均方根误差
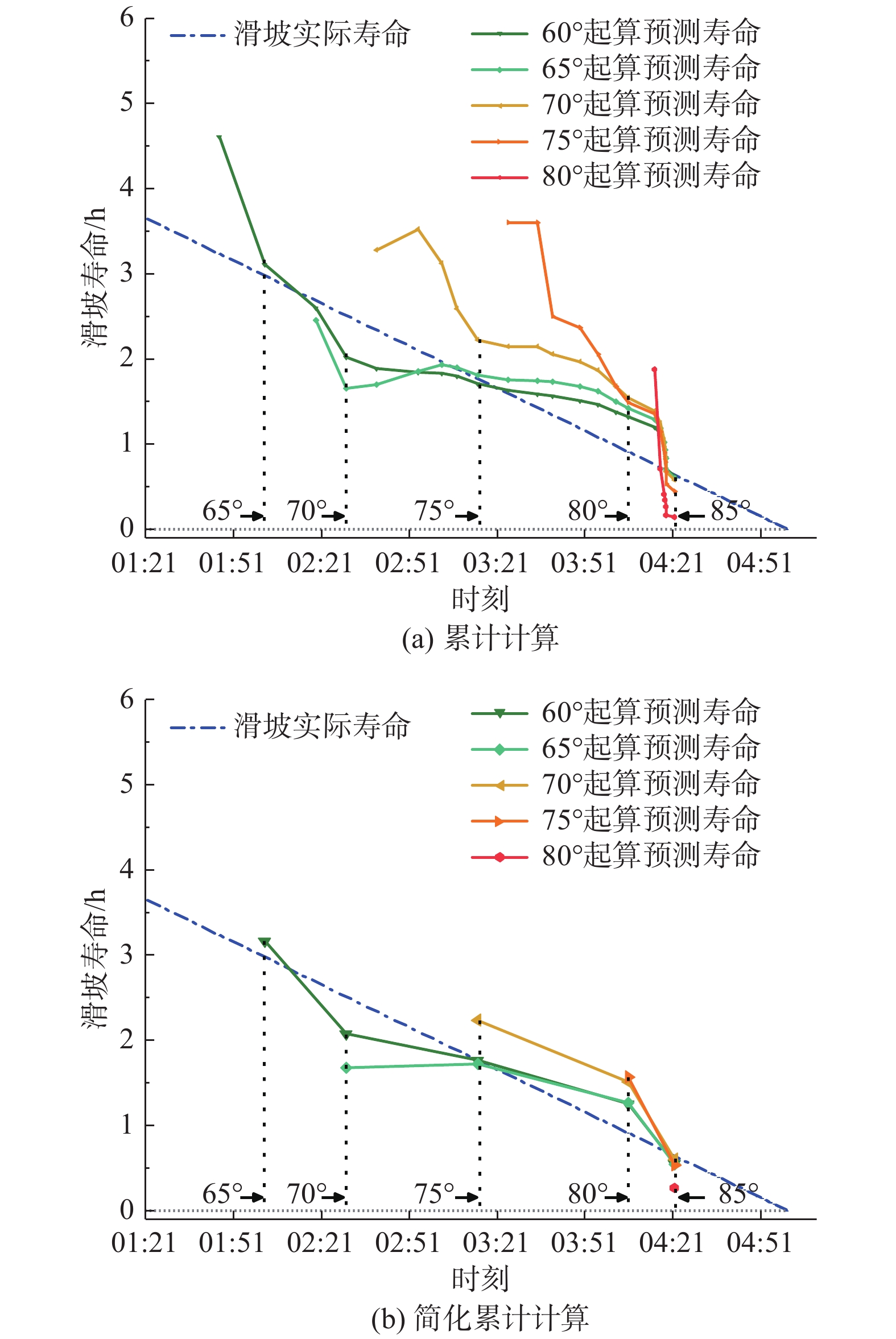
Table 2. RMSE of the predicted results of the Dangchuan 6# landslide
起算角度 累计计算/h 简化累计计算/h 60°起算 0.40 0.26 65°起算 0.40 0.45 70°起算 0.70 0.44 75°起算 1.00 0.47 80°起算 0.56 0.38 表 3 陈家6#和党川7#滑坡预测结果的均方根误差
Table 3. RMSE of the predicted results of the Chenjia 6# and Dangchuan 7# landslide
滑坡 起算角度 累计计算/h 简化累计计算/h 陈家6# 60°起算 10.54 5.22 65°起算 20.64 2.08 70°起算 3.15 1.49 75°起算 3.29 2.68 80°起算 2.36 0.07 党川7# 60°起算 41.49 39.74 65°起算 35.27 31.95 70°起算 28.71 24.72 75°起算 23.51 12.97 80°起算 18.23 9.74 表 4 党川4#滑坡预测结果均方根误差
Table 4. Predicted RMSE of the Dangchuan 4# landslide
起算角度 累计计算/h 简化累计计算/h 60°起算 8.77 7.57 65°起算 9.41 8.24 70°起算 11.24 9.80 75°起算 16.93 14.22 80°起算 12.48 4.28 -
[1] 张茂省. 引水灌区黄土地质灾害成因机制与防控技术—以黄河三峡库区甘肃黑方台移民灌区为例[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(6):833 − 839. [ZHANG Maosheng. Formation mechanism as well as prevention and controlling techniques of loess geo-hazards in irrigated areas: A case study of Heifangtai immigration area in the Three Gorges Reservoir of the Yellow River[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(6):833 − 839. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.06.002
[2] 彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等. 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(4):684 − 691. [PENG Jianbing, LIN Hungzhou, WANG Qiyao, et al. The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(4):684 − 691. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 亓星, 朱星, 修德皓, 等. 智能变频位移计在突发型黄土滑坡中的应用—以甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡为例[J]. 水利水电技术,2019,50(5):190 − 195. [QI Xing, ZHU Xing, XIU Dehao, et al. Application of intelligent variable frequency displacement meter to sudden loess landslide—a case of Heifangtai Loess Landslide[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2019,50(5):190 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 赵超英, 刘晓杰, 张勤, 等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡InSAR识别、监测与失稳模式研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):996 − 1007. [ZHAO Chaoying, LIU Xiaojie, ZHANG Qin, et al. Research on loess landslide identification, monitoring and failure mode with InSAR technique in Heifangtai, Gansu[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):996 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 史绪国, 张路, 许强, 等. 黄土台塬滑坡变形的时序InSAR监测分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. [SHI Xuguo, ZHANG Lu, XU Qiang, et al. Monitoring slope displacements of loess terrace using time series InSAR analysis technique[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1027 − 1034. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 亓星. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警研究——以甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017.
QI Xing. Sudden loess landslide monitoring and early warning research—a case study of Gansu landslide in Heifangtai Loess[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 亓星, 朱星, 许强, 等. 基于斋藤模型的滑坡临滑时间预报方法改进及应用[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4):832 − 839. [QI Xing, ZHU Xing, XU Qiang, et al. Improvement and application of landslide proximity time prediction method based on Saito model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(4):832 − 839. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 许强, 彭大雷, 何朝阳, 等. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警理论方法研究—以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(1):111 − 121. [XU Qiang, PENG Dalei, HE Chaoyang, et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warning for sudden loess landslide—a case study at Heifangtai terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(1):111 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] EMANUELE I, CARLA T, GIGLI G. Forecasting the time of failure of landslides at slope-scale: A literature review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2019,193:333 − 349. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.019
[10] 田尤, 杨为民, 李浩. 黄土滑坡发育特征参数的幂律相依性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):131 − 137. [TIAN You, YANG Weimin, LI Hao. Power law correlations between feature parameters of loess landslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):131 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张勇, 温智, 程英建. 四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):178 − 182. [ZHANG Yong, WEN Zhi, CHENG Yingjian. A discussion of the relationship between landslide disaster and rainfall types in Bazhong of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):178 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 盛逸凡, 李远耀, 徐勇, 等. 基于有效降雨强度和逻辑回归的降雨型滑坡预测模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):156 − 162. [SHENG Yifan, LI Yuanyao, XU Yong, et al. Prediction of rainfall-type landslides based on effective rainfall intensity and logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):156 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 晏同珍, 殷坤龙, 伍法权, 等. 滑坡定量预测研究的进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1988,15(6):8 − 14. [YAN Tongzhen, YIN Kunlong, WU Faquan, et al. Progress in research on quantitative prediction of landslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1988,15(6):8 − 14. (in Chinese)
[14] 李天斌, 陈明东. 滑坡时间预报的费尔哈斯反函数模型法[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,1996,7(3):13 − 17. [LI Tianbin, CHEN Mingdong. Time prediction of landslide using Verhulst inverse function model[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,1996,7(3):13 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 黄健敏, 赵国红, 廖芸婧, 等. 基于Logistic回归的降雨诱发区域地质灾害易发性区划及预报模型建立—以安徽歙县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(3):98 − 105. [HUANG Jianmin, ZHAO Guohong, LIAO Yunjing, et al. Research on rainfall induced regional geo-hazard forecast model based on the logistic regression[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(3):98 − 105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杨背背, 殷坤龙, 杜娟. 基于时间序列与长短时记忆网络的滑坡位移动态预测模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(10):2334 − 2343. [YANG Beibei, YIN Kunlong, DU Juan. A model for predicting landslide displacement based on time series and long and short term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(10):2334 − 2343. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 杨帆, 许强, 范宣梅, 等. 基于时间序列与人工蜂群支持向量机的滑坡位移预测研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(4):880 − 889. [YANG Fan, XU Qiang, FAN Xuanmei, et al. Prediction of landslide displacement time series based on support vector regression machine with artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(4):880 − 889. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 朱晓霞, 张力, 杨树文. 降雨引发的兰州黄土滑坡时空规律分析和临界降雨量预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(4):24 − 31. [ZHU Xiaoxia, ZHANG Li, YANG Shuwen. Characteristics of rainfall-induced loess landslides and their threshold rainfall in Lanzhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(4):24 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 许强, 黄润秋, 李秀珍. 滑坡时间预测预报研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2004,19(3):478 − 483. [XU Qiang, HUANG Runqiu, LI Xiuzhen. Research progress in time forecast and prediction of landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2004,19(3):478 − 483. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.021
[20] SAITO M. Forecasting time of slope failure by tertiary creep[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Mexico: [s. n.], 1969: 677-683.
[21] FUKUZONO T. A new method for predicting the failure time of a slope[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conference and Field Workshop on Landslides. Tokyo: Tokyo University Press, 1985: 145-150.
[22] MUFUNDIRWA A, FUJⅡ Y, KODAMA J. A new practical method for prediction of geomechanical failure-time[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2010,47(7):1079 − 1090. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.07.001
[23] VOIGHT B. A method for prediction of volcanic eruptions[J]. Nature,1988,332:125 − 130. doi: 10.1038/332125a0
[24] 黄建, 姚仰平. 高填方边坡失稳时间预测的实用模型[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(10):4057 − 4064. [HUANG Jian, YAO Yangping. A practical model for predicting the failure time of high fill slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(10):4057 − 4064. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 周飞, 许强, 巨袁臻, 等. 黑方台黄土斜坡变形破坏机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(1):157 − 163. [ZHOU Fei, XU Qiang, JU Yuanzhen, et al. A study of the deformation and failure mechanism of the Heifangtai loess slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(1):157 − 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 李骅锦, 许强, 何雨森, 等. 甘肃黑方台滑坡滑距参数的BP神经网络模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):141 − 146. [LI Huajin, XU Qiang, HE Yusen, et al. BP neural network model for analyzing the impact factors of the travel distance of the Heifangtai landslide in Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):141 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 彭大雷. 黄土滑坡潜在隐患早期识别研究——以甘肃黑方台为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
PENG Dalei. Study on early recognition for potentially loess landslide—a case study at Heifangtai terrace, Gansu Province, China[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):360 − 374. [XU Qiang. Understanding the landslide monitoring and early warning: consideration to practical issues[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):360 − 374. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 许强, 曾裕平, 钱江澎, 等. 一种改进的切线角及对应的滑坡预警判据[J]. 地质通报,2009,28(4):501 − 505. [XU Qiang, ZENG Yuping, QIAN Jiangpeng, et al. Study on a improved tangential angle and the corresponding landslide prewarning criteria[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2009,28(4):501 − 505. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.04.011
[30] FUKUI K, OKUBO S. Life expectancy and tertiary creep for rock[C]//Proceedings of the Fall Meeting Mining and Minerals Processing Institute of Japan. [S.l.]:Mining and Minerals Processing Institute of Japan, 1997: 91–94.
[31] 张一希. 黄土静态液化影响因素的试验研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019.
ZHANG Yixi. Experimental study on influencing factors of static liquefaction of the loess[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 许强, 魏勇, 彭大雷, 等. 泾阳南塬蒋刘4#滑坡特征及成因机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(1):123 − 130. [XU Qiang, WEI Yong, PENG Dalei, et al. Characteristics and failure mechanism of the Jiangliu 4# landslide in the southern tableland in Jingyang County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(1):123 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 许强, 彭大雷, 亓星, 等. 2015年4.29甘肃黑方台党川2#滑坡基本特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(2):167 − 180. [XU Qiang, PENG Dalei, QI Xing, et al. Dangchuan 2# landslide of April 29, 2015 in Heifangtai area of Gansu Province: Characteristices and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(2):167 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: