Influence of carbon dioxide invasion in the unsaturated zone on vegetation and soil
-
摘要:
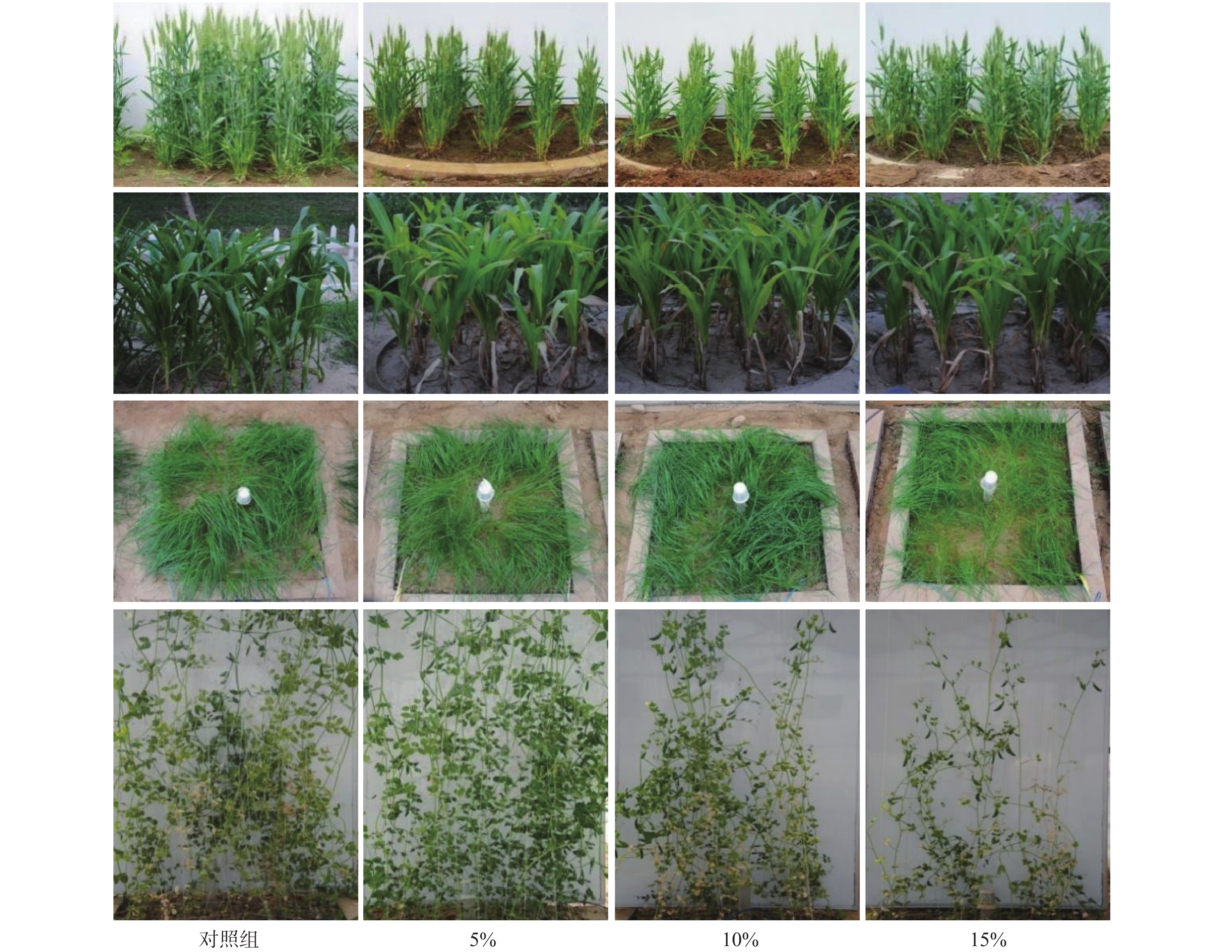
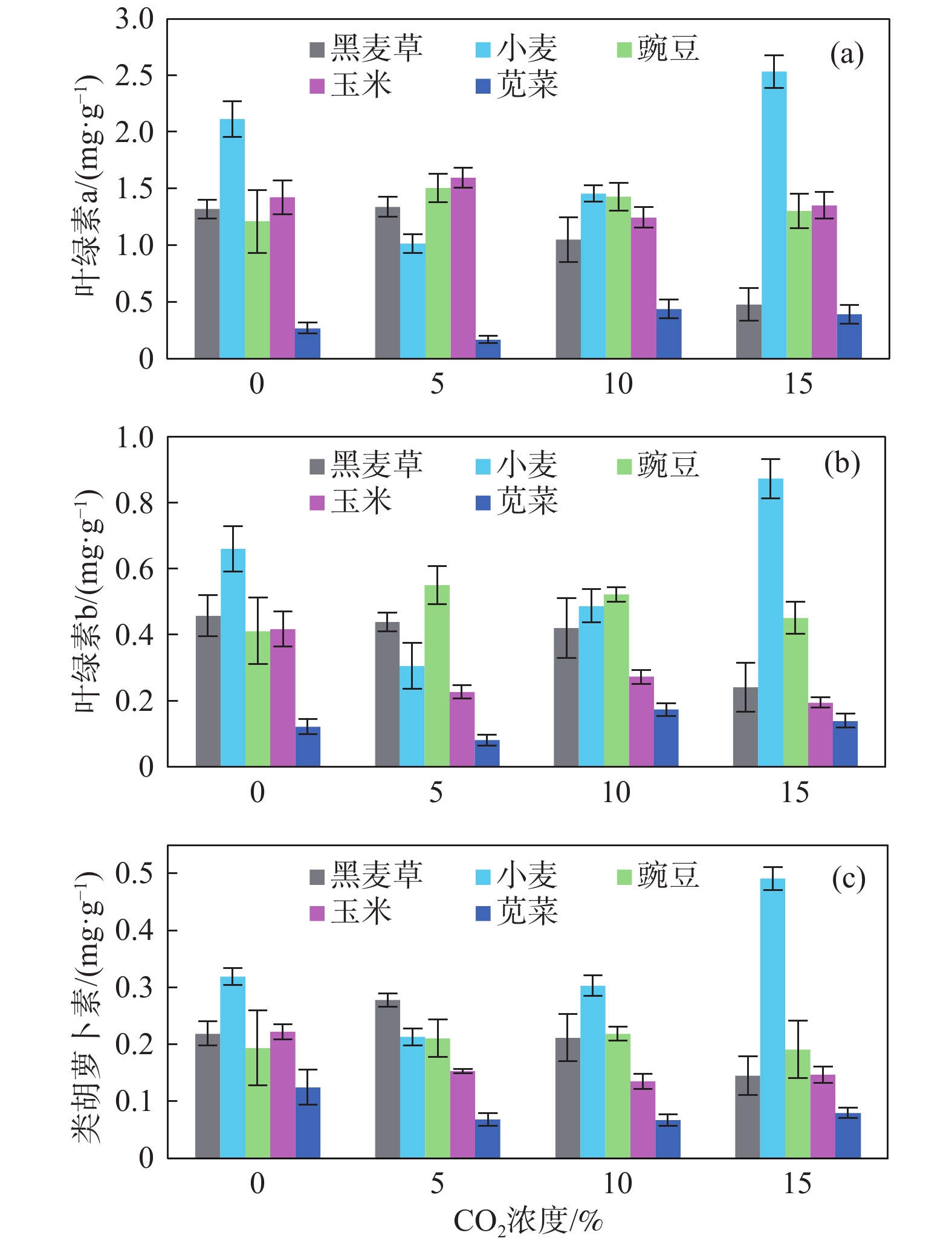
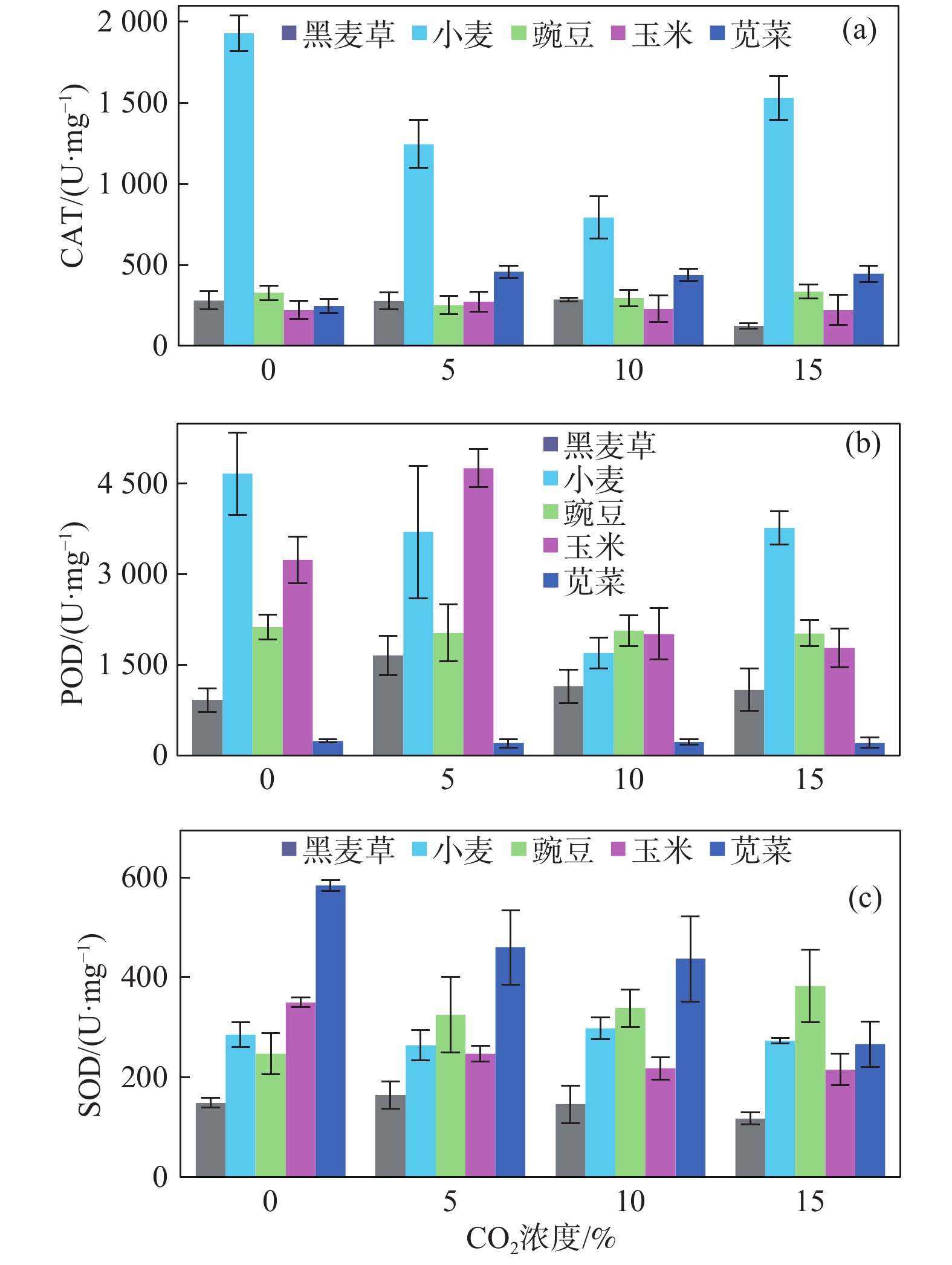
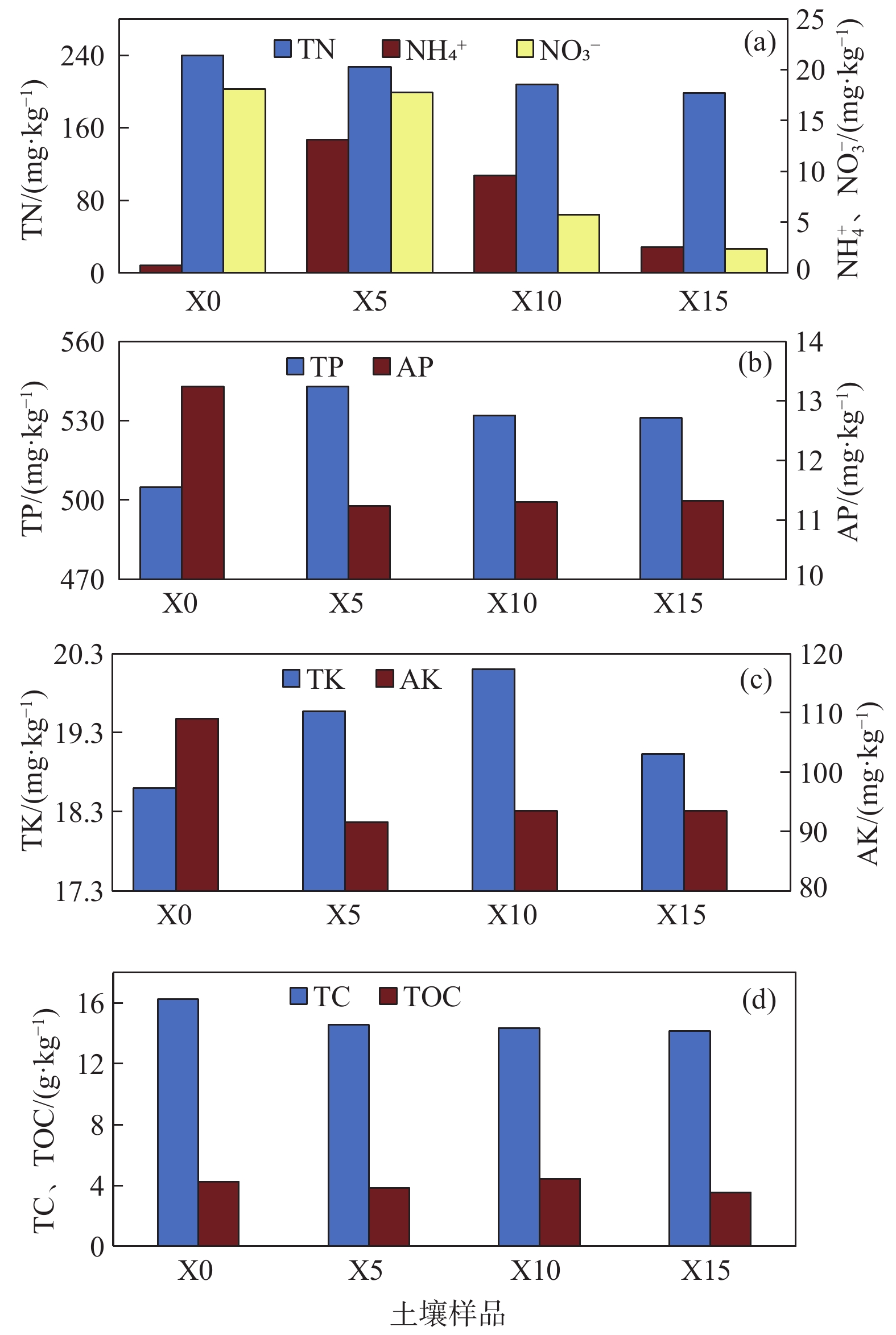
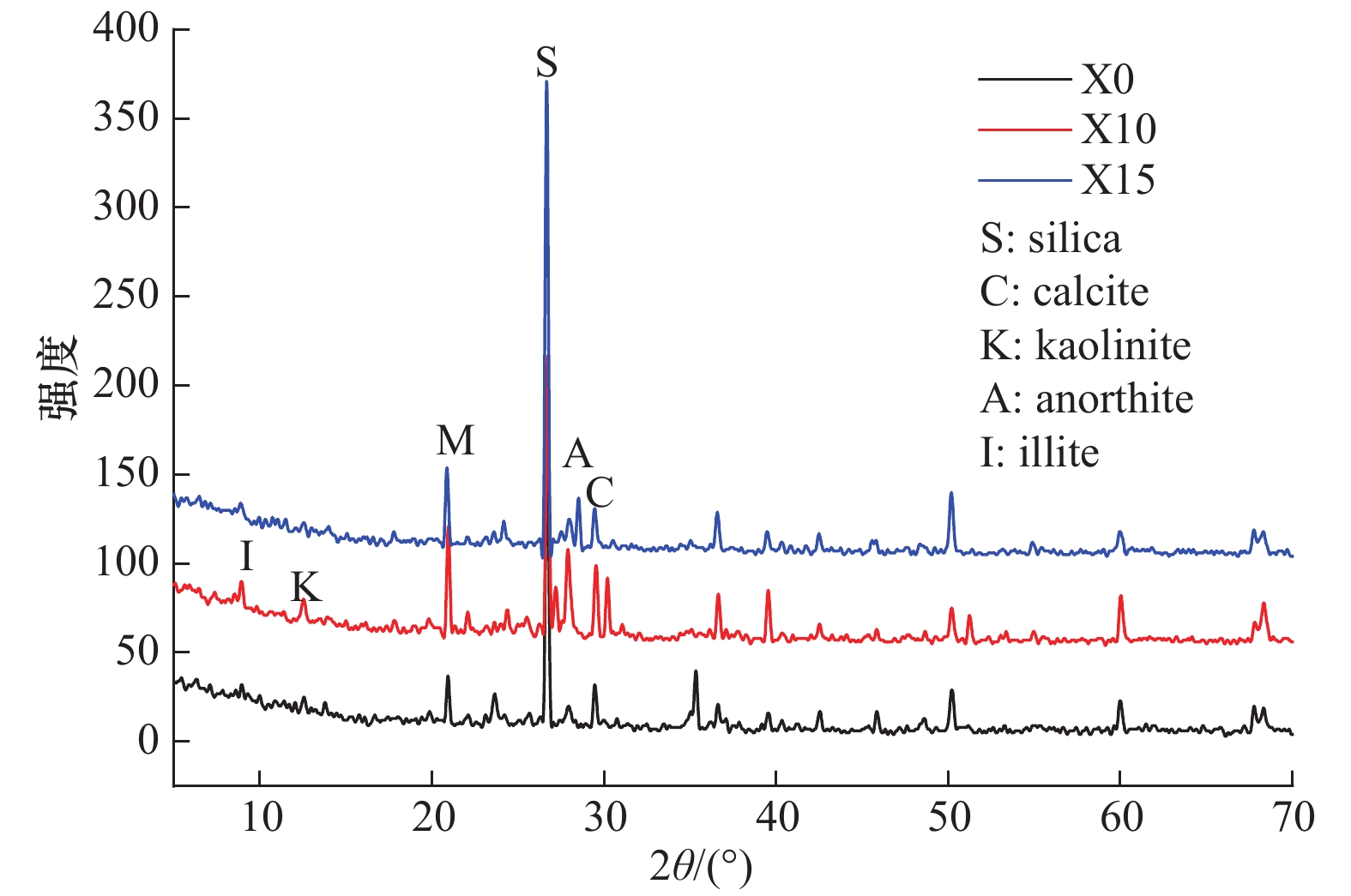
非饱和带属于地球关键带,与人类生存环境及安全健康关系密切,而CO2对生态环境及全球气候变化的影响至关重要。为了探索高浓度CO2入侵非饱和带对生态环境可能带来的风险,基于长安大学水与环境原位试验场CO2试验平台,向种植有5种典型植物(黑麦草、小麦、玉米、豌豆和苋菜)的土壤中长期注入浓度为5%、10%和15%的CO2气体,评估CO2入侵对植物和土壤的潜在影响。对表生植物及土壤样品(深度为20~30 cm)的理化性质分析表明:高浓度CO2明显抑制了植物的生长,会导致植株高度、叶片数和果实重量下降;土壤矿相和理化性质也有微小变化,表现为土壤pH值的变化以及氮、有效钾、有效磷等的减少。通过分析植物的光合作用、渗透调节作用以及抗氧化系统的变化,不同的植物对CO2胁迫表现出不同且复杂的响应,总体上C3单子叶植物黑麦草和C4单子叶植物玉米显示出比其他植物更高的敏感性,表明它们有潜力作为评估CO2生态影响的指示植物。
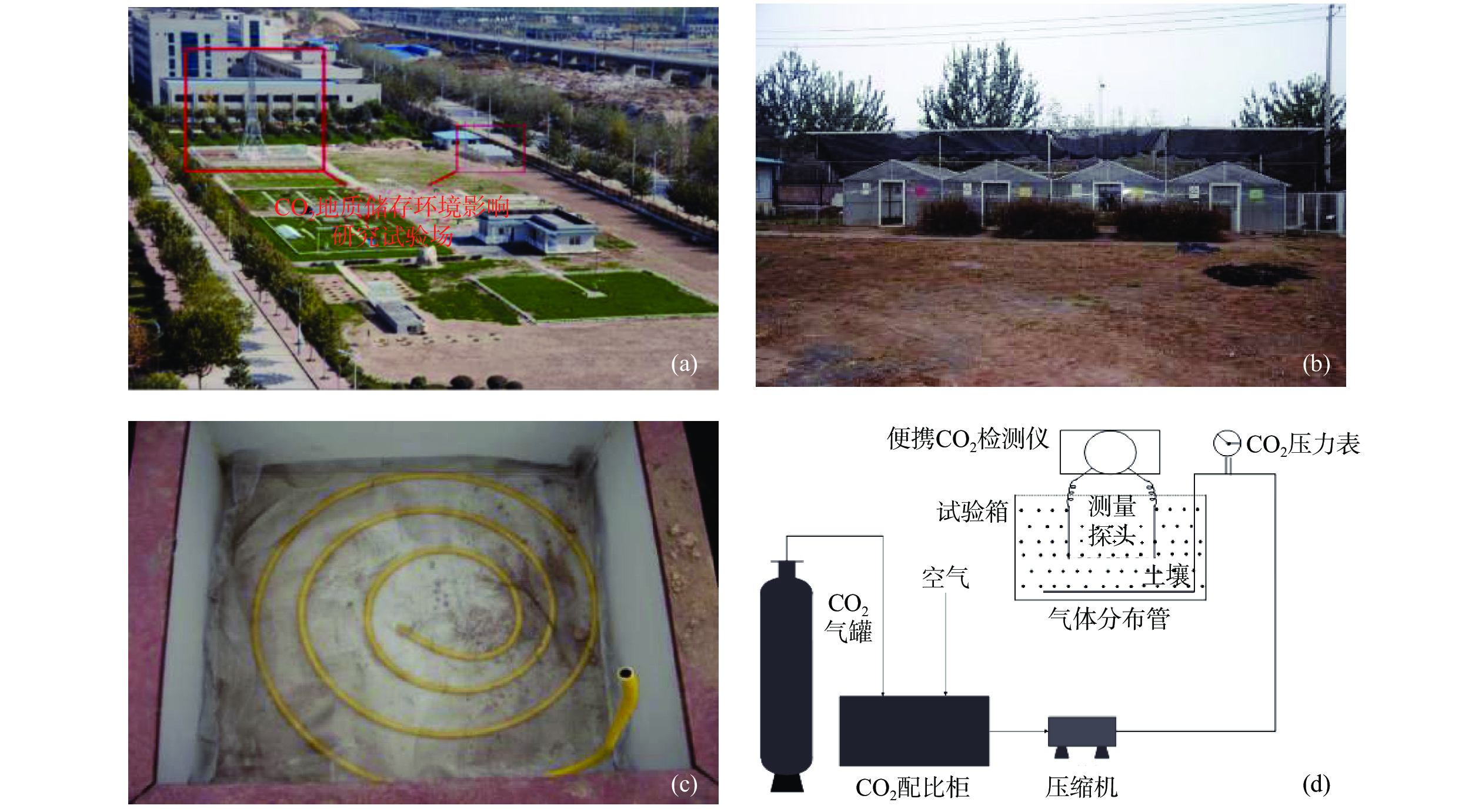
Abstract:The unsaturated zone is the critical zone of the earth, which is closely related to the human living environment and health safety. Carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in the ecological environment and global climate change. In order to explore the potential risk of high concentration CO2 invasion into the unsaturated zone to the ecological environment, and based on CO2 simulation platform of in situ research filed of water and environment of the Chang’an University, we present a controlled experiment, in which 5%, 10% and 15% pure CO2 was respectively injected into the local soil planted with five typical plants (ryegrass, wheat, corn, pea and amaranth) to assess the potential impact of CO2 invasion on the environment, specifically on soil and plants. Botanical investigation and chemical analyses of soil samples (at depth from 20 to 30 cm) shows a significant adverse impact of CO2 injection on plant growth, including declining plant height, number of leaves and fruit weight. Small changes were observed in mineralogy and bulk chemistry, showing the change of soil pH and reduction of nitrogen, available potassium, available phosphorus, etc. Different plants show different and complicated responses to CO2 stress, depending on plant life history, including photosynthetic pathways, osmoregulation and antioxidant systems. On the whole, C3 monocotyledon ryegrass and C4 monocotyledon corn show greater sensitivity than other plants, suggesting their potential as indicator plants for evaluation of CO2 impact on ecological environment.
-
Key words:
- unsaturated zone /
- CO2 invasion /
- environmental impact /
- vegetation /
- soil
-

-
表 1 不同CO2浓度下植物的可溶性蛋白浓度
Table 1. Soluble protein concentrations of the plants under CO2 exposure
/(mg·g−1) CO2浓度/% 黑麦草 小麦 豌豆 玉米 苋菜 0 23.73±4.70 19.87±3.97 16.14±1.94 15.62±2.34 0.86±0.08 5 18.84±2.82 12.49±1.47 13.69±1.70 8.04±0.95 0.79±0.09 10 12.98±1.53 13.16±1.99 15.52±1.44 12.62±1.07 4.03±0.70 15 12.00±1.83 13.34±2.67 15.24±1.86 21.50±4.88 3.54±0.12 表 2 不同CO2浓度下植物的可溶性糖浓度
Table 2. Soluble saccharide concentrations of the plants under CO2 exposure
/(μmol·g−1) CO2浓度/% 黑麦草 小麦 豌豆 玉米 苋菜 0 0.28±0.03 0.26±0.03 0.07±0.01 0.14±0.01 0.12±0.02 5 0.32±0.04 0.32±0.04 0.07±0.01 0.14±0.01 0.10±0.01 10 0.34±0.04 0.39±0.01 0.10±0.02 0.16±0.02 0.12±0.02 15 0.40±0.02 0.41±0.02 0.12±0.02 0.15±0.01 0.15±0.04 表 3 不同CO2浓度下植物的丙二醛浓度
Table 3. MDA concentrations of the plants under CO2 exposure
/(μmol·g−1) CO2浓度/% 黑麦草 小麦 豌豆 玉米 苋菜 0 0.0040±0.0026 0.0110±0.0010 0.0112±0.0024 0.0320±0.0030 0.0072±0.0002 5 0.0065±0.0039 0.0130±0.0030 0.0149±0.0032 0.0401±0.0030 0.0086±0.0002 10 0.0071±0.0027 0.0169±0.0020 0.0158±0.0027 0.0405±0.0040 0.0069±0.0008 15 0.0153±0.0015 0.0220±0.0030 0.0188±0.0030 0.0410±0.0050 0.0074±0.0023 表 4 不同CO2浓度下植物的脯氨酸浓度
Table 4. Proline concentrations of the plants under CO2 exposure
/(mg·g−1) CO2浓度/% 黑麦草 小麦 豌豆 玉米 苋菜 0 2622.80±493.87 253.91±48.29 115.82±15.12 26.45±5.07 40.94±11.35 5 2570.12±431.96 118.77±21.76 148.93±35.28 34.76±7.62 26.39±6.56 10 1690.37±234.54 224.89±15.94 161.87±25.23 17.47±4.37 14.74±0.91 15 1128.91±106.11 181.67±19.17 166.28±10.39 8.53±1.66 17.70±1.40 -
[1] 王齐鑫, 马传明, 花勐健, 等. 安徽省沉积盆地CO2地质储存适宜性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(5):121 − 130. [WANG Qixin, MA Chuanming, HUA Mengjian, et al. Suitability evaluation of geological storage of CO2 in sedimentary basin of Anhui Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):121 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] STENHOUSE M, ARTHUR R, ZHOU W. Assessing environmental impacts from geological CO2 storage[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):1895 − 1902. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.01.247
[3] 彭李晖, 王建军, 尤伟静, 等. 二氧化碳地质储存的主要环境问题及研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(5):104 − 110. [PENG Lihui, WANG Jianjun, YOU Weijing, et al. Environmental issues and advances of carbon dioxide geological storage[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(5):104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] MALE E J, PICKLES W L, SILVER E A, et al. Using hyperspectral plant signatures for CO2 leak detection during the 2008 ZERT CO2 sequestration field experiment in Bozeman, Montana[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2010,60(2):251 − 261. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0372-2
[5] 文冬光, 郭建强, 张森琦, 等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存研究进展[J]. 中国地质,2014,41(5):1716 − 1723. [WEN Dongguang, GUO Jianqiang, ZHANG Senqi, et al. The progress in the research on carbon dioxide geological storage in China[J]. Geology in China,2014,41(5):1716 − 1723. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.025
[6] VONG C Q, JACQUEMET N, PICOT-COLBEAUX G, et al. Reactive transport modeling for impact assessment of a CO2 intrusion on trace elements mobility within fresh groundwater and its natural attenuation for potential remediation[J]. Energy Procedia,2011,4:3171 − 3178. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.232
[7] 张森琦, 郭建强, 刁玉杰, 等. 规模化深部咸水含水层CO2地质储存选址方法研究[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(6):1640 − 1651. [ZHANG Senqi, GUO Jianqiang, DIAO Yujie, et al. Technical method for selection of CO2 geological storage project sites in deep saline aquifers[J]. Geology in China,2011,38(6):1640 − 1651. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.025
[8] 范基姣, 张森琦, 郭建强, 等. 水环境同位素技术在二氧化碳地质储存中的应用探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(1):106 − 109. [FAN Jijiao, ZHANG Senqi, GUO Jianqiang, et al. Application of environmental isotope technique to geological storage of carbon dioxide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(1):106 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] KHARAKA Y K, THORDSEN J J, KAKOUROS E, et al. Changes in the chemistry of shallow groundwater related to the 2008 injection of CO2 at the ZERT field site, Bozeman, Montana[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2010,60(2):273 − 284. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0401-1
[10] ARDELAN M V, STEINNES E. Changes in mobility and solubility of the redox sensitive metals Fe, Mn and Co at the seawater-sediment interface following CO2 seepage[J]. Biogeosciences,2010,7(2):569 − 583. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-569-2010
[11] HUESEMANN M H, SKILLMAN A D, CRECELIUS E A. The inhibition of marine nitrification by ocean disposal of carbon dioxide[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2002,44(2):142 − 148. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00194-1
[12] HARVEY O R, QAFOKU N P, CANTRELL K J, et al. Geochemical implications of gas leakage associated with geologic CO2 storage-A qualitative review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,4:23 − 36.
[13] YANG W, MAROTO-VALER M, Steven M D. Environmental consequences of potential leaks of CO2 in soil[J]. Energy Procedia,2011,4:3224 − 3230. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.239
[14] BEAUBIEN S E, CIOTOLI G, COOMBS P, et al. The impact of a naturally occurring CO2 gas vent on the shallow ecosystem and soil chemistry of a Mediterranean pasture (Latera, Italy)[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2008,2:373 − 387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.03.005
[15] LIU Y, HAN S J. Soil and root respiration under elevated CO2 concentrations during seedling growth of pinus sylvestris var. sylvestriformis[J]. Pedosphere,2007,17(5):600 − 665.
[16] ALLARD V, ROBIN C, NEWTON P C D, et al. Short and long-term effects of elevated CO2 on Lolium Perenne rhizodeposition and its consequences on soil organic matter turnover and plant N yield[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2006,38:1178 − 1187. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.10.002
[17] KANDELER E, MOSIER A R, MORGAN J A, et al. Response of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities to the transient elevation of carbon dioxide in a semi-arid grassland[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2006,38:2448 − 2460. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.02.021
[18] LI C R, WANG W K, DENG H Z, et al. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide on soil bacterial community structure[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2014,1010/1011/1012:422 − 428. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1010-1012.422
[19] KRVGER M, JONES D, FRERICHS J, et al. Effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on the vegetation and microbial populations at a terrestrial CO2 vent at Laacher See, Germany[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(4):1093 − 1098. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.05.002
[20] PFANZ H, VODNIK D, WITTMANN C, et al. Photosynthetic performance (CO2-compensation point, carboxylation efficiency, and net photosynthesis) of timothy grass (Phleum pratense L.) is affected by elevated carbon dioxide in post-volcanic mofette areas[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,2007,61(1):41 − 48. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.02.008
[21] STOCK W D, LUDWIG F, MORROW C, et al. Long-term effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on species composition and productivity of a southern African C4 dominated grassland in the vicinity of a CO2 exhalation[J]. Plant Ecology,2005,178(2):211 − 224. doi: 10.1007/s11258-004-3654-5
[22] MACEK I, PFANZ H, FRANCETIC V, et al. Root respiration response to high CO2 concentrations in plants from natural CO2 springs[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,2005,54(1):90 − 99. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.06.003
[23] AL-TRABOULSI M, SJOGERSTEN S, COLLS J, et al. Potential impact of CO2 leakage from carbon capture and storage systems on field bean (Vicia faba)[J]. Physiologia plantarum,2012,146(3):261 − 71. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01620.x
[24] WEST J M, PEARCE J M, COOMBS P. The impact of controlled injection of CO2 on the soilecosystem and chemistry of an English lowland pasture[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):1863 − 1870. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.01.243
[25] 伍洋. 地质封存CO2泄露对玉米和苜蓿影响模拟实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2012.
WU Yang. Simulation experimental research of the impact of CO2 leakage from geological storage on maize and alfalfa[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 伍洋, 马欣, 李玉娥, 等. 地质封存CO2泄露对农田生态系统的影响评估及耐受阈值[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(2):196 − 205. [WU Yang, MA Xin, LI Yue, et al. Impact assessment and the tolerance threshold value of CO2 leakage from geological storage on agro-ecosystem[J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2012,28(2):196 − 205. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.02.035
[27] 乔胜英. 土壤理化性质实验指导书[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2012.
QIAO Shengying. Soil physical and chemical properties test instruction[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[28] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000.
LI Hesheng. Principle and technology of plant physiological and biochemical experiments[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[29] 周婵, 邹志远, 杨允菲. 盐碱胁迫对羊草可溶性蛋白质含量的影响[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版),2009,41(3):94 − 96. [ZHOU Chan, ZOU Zhiyuan, YANG Yunfei. Effect of salt-alkali stress on soluble protein of leymus chinensis[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2009,41(3):94 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 周广. 高温胁迫对7种杜鹃生理生化特性的影响[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2010.
ZHOU Guang. Effect of the physiological and biochemical character of seven rhododendron L. plants under high temperature stress[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 余叔文, 汤章城. 植物生理和分子生物学[M]. 北京: 科技出版社, 1999: 39-745.
YU Shuwen, TANG Zhangcheng. Plant physiology and molecular biology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 39-745. (in Chinese)
[32] 赵江涛, 李晓峰, 李航, 等. 可溶性糖在高等植物代谢调节中的生理作用[J]. 安徽农业科学,2006(24):6423 − 6425. [ZHAO Jiangtao, LI Xiaofeng, LI Hang, et al. Research on the role of the soluble sugar in the regulation of physiological metabolism in higher plant[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2006(24):6423 − 6425. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2006.24.008
[33] 吉增宝, 王进鑫, 李继文, 等. 不同季节干旱及复水对刺槐幼苗可溶性糖含量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报,2009,29(7):1358 − 1363. [JI Zengbao, WANG Jinxin, LI Jiwen, et al. Dynamic changes of soluble sugar in the seedlings of robinia pseudoacacia under drought stress and rewatering in different seasons[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2009,29(7):1358 − 1363. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.07.011
[34] 张坤生, 田荟琳. 过氧化氢酶的功能及研究[J]. 食品科技,2007,32(1):8 − 10. [ZHANG Kunsheng, TIAN Huilin. Research and function of catalase in organism[J]. Food Science and Technology,2007,32(1):8 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2007.03.003
[35] 赵秀娟, 韩雅楠, 蔡禄. 盐胁迫对植物生理生化特性的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学,2011,50(19):3897 − 3899. [ZHAO Xiujuan, HAN Yanan, CAI Lu. Advances in research on physiological and biochemical effects of NaCl stress on plant[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science,2011,50(19):3897 − 3899. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2011.19.003
[36] 王秀香. 土壤水分胁迫对不同品种蓖麻叶片丙二醛含量的影响[J]. 科技资讯,2012(16):137 − 138. [WANG Xiuxiang. Influence of soil water stress on malondialdehyde content in the different varieties of castor leaves[J]. Science & Technology Information,2012(16):137 − 138. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2012.16.115
[37] 周青, 黄晓华. 逆境胁迫下作物积累脯氨酸的生理生态学意义[J]. 农业环境科学学报,1991,10(6):272 − 273. [ZHOU Qing, HUANG Xiaohua. Physiological ecology meaning of crop accumulated proline under adversity stress[J]. Agro-environmental Protection,1991,10(6):272 − 273. (in Chinese)
[38] 董建兴, 李义连, 杨国栋, 等. CO2-水-岩相互作用对盖层渗透率影响的数值模拟[J]. 地质科技情报,2012,31(1):115 − 121. [DONG Jianxing, LI Yilian, YANG Guodong, et al. Numerical simulation of CO2-Water-Rock interaction impact on caprock permeability[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2012,31(1):115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2012.01.019
[39] ZHAO X H, DENG H Z, WANG W K, et al. Impact of naturally leaking carbon dioxide on soil properties and ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):3001. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02500-x
[40] 昊恒, 张信贵, 韩立华. 水化学场变异对土体性质的影响[J]. 广西大学学报,1999(2):1 − 4. [WU Heng, ZHANG Xingui, HAN Lihua. The change of ground water chemical field affect properties of soilmass[J]. Journal of Guangxi University,1999(2):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 仵彦卿. 地下水与地质灾害[J]. 地下空间,1999,19(4):303 − 310. [WU Yanqing. Groundwater and geological disasters[J]. Underground Space,1999,19(4):303 − 310. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.1999.04.007
[42] 沈天宇. 高浓度CO2入侵对地下水隔水粘土层理化性质的影响[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018.
SHEN Tianyu. Effects of high concentration CO2 invasion on physicochemical properties of clay layer of groundwater[D]. Xiʼan: Changʼan University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] 朱春梧, 曾青, 朱建国, 等. 大气CO2浓度上升对植物地下竞争的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2007,15(4):185 − 189. [ZHU Chunwu, ZENG Qing, ZHU Jianguo, et al. Effect of elevated CO2 on below-ground plant competition[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2007,15(4):185 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: