A study of the kaolin electro-osmotic consolidation characteristics and their numerical simulation
-
摘要:
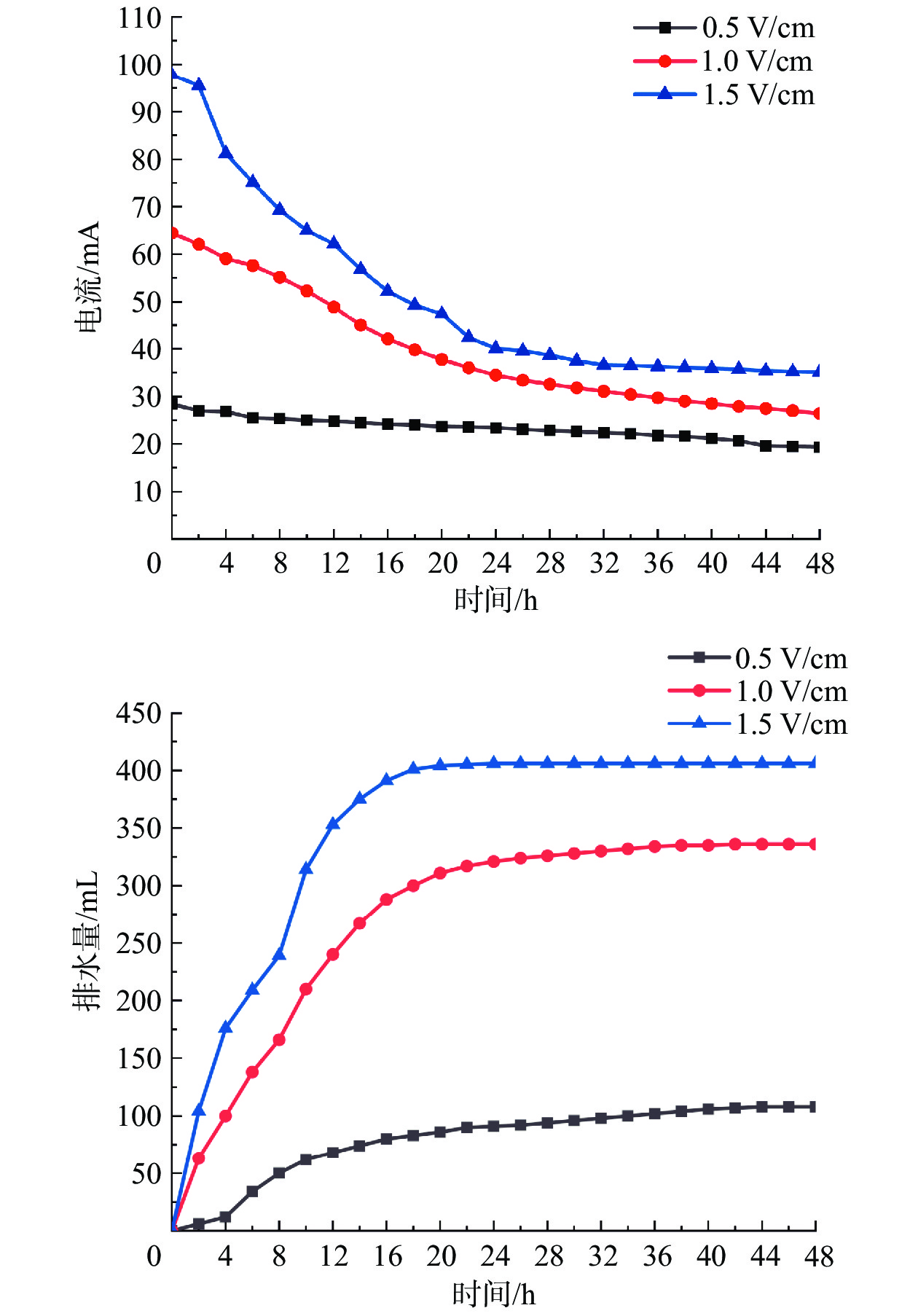
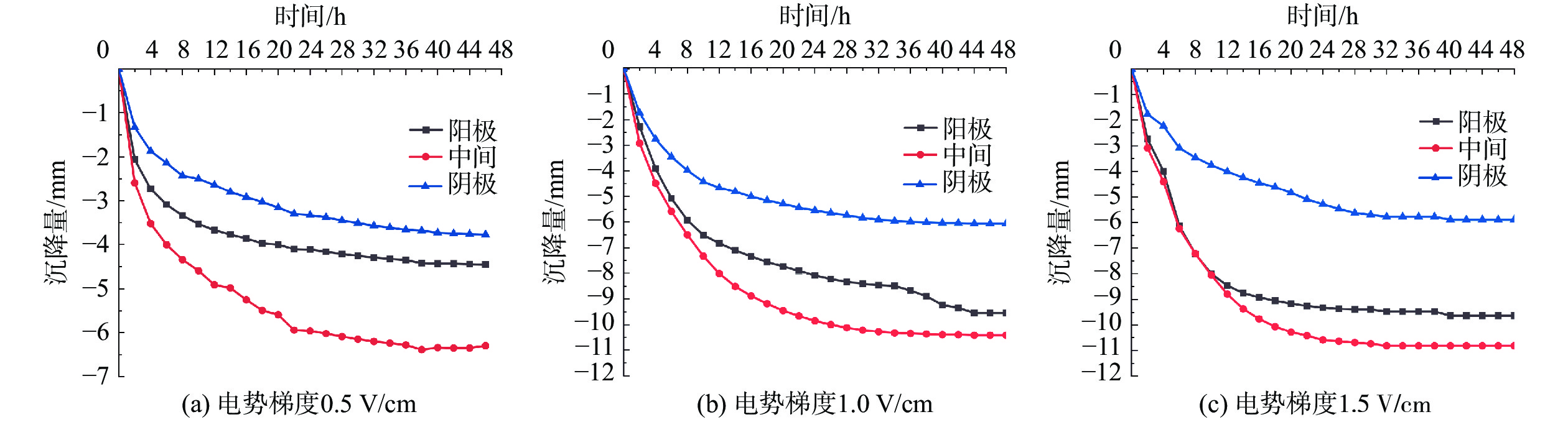
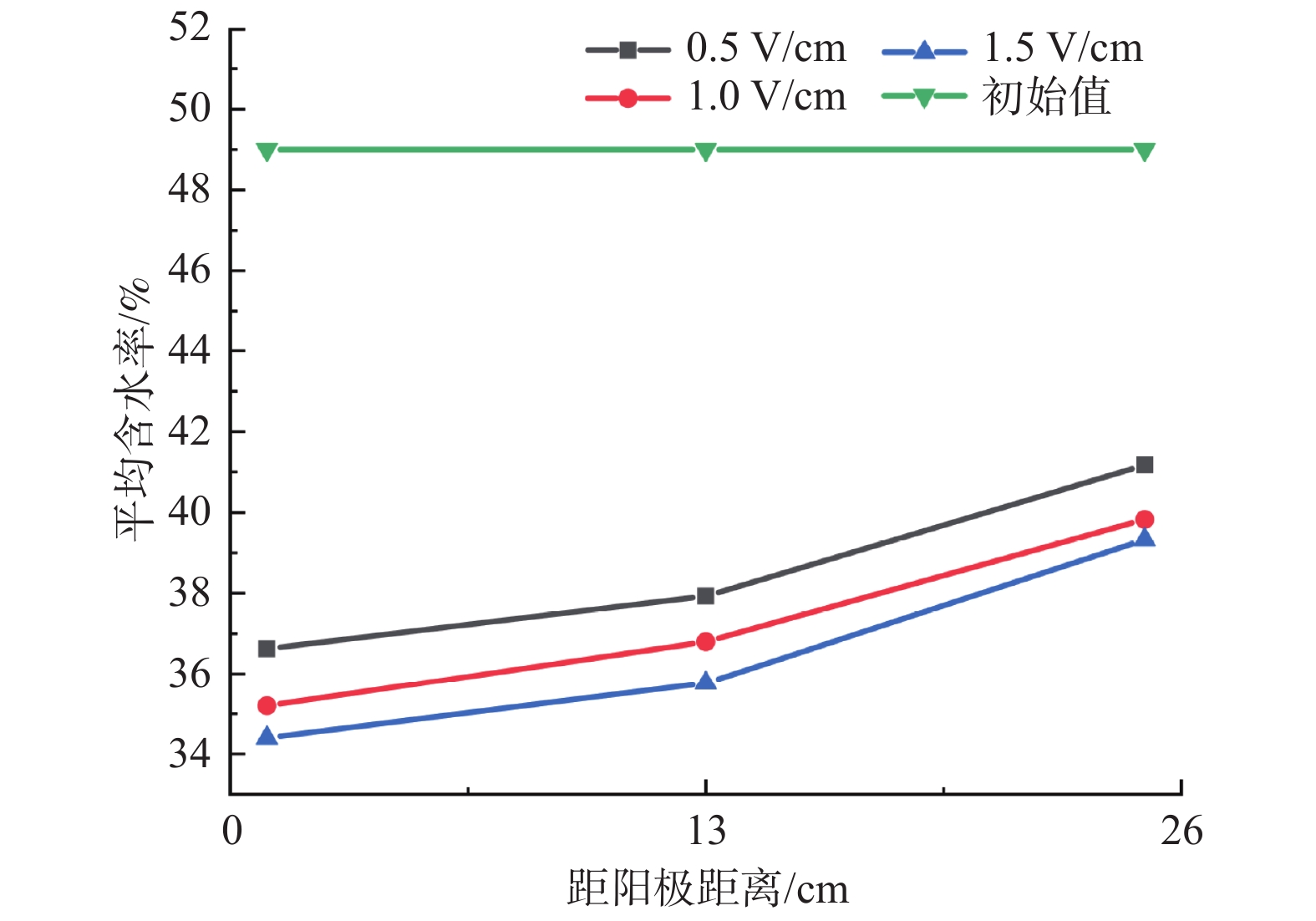
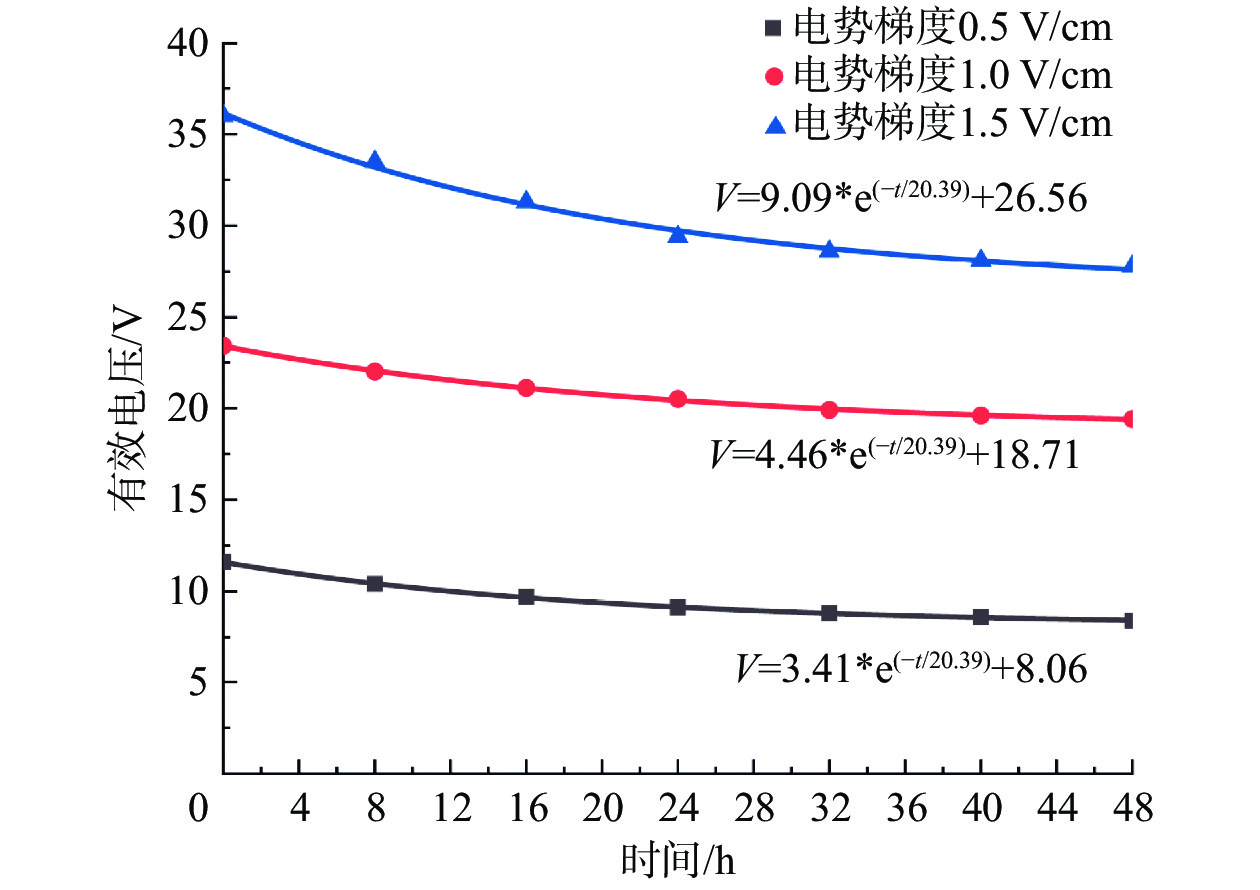
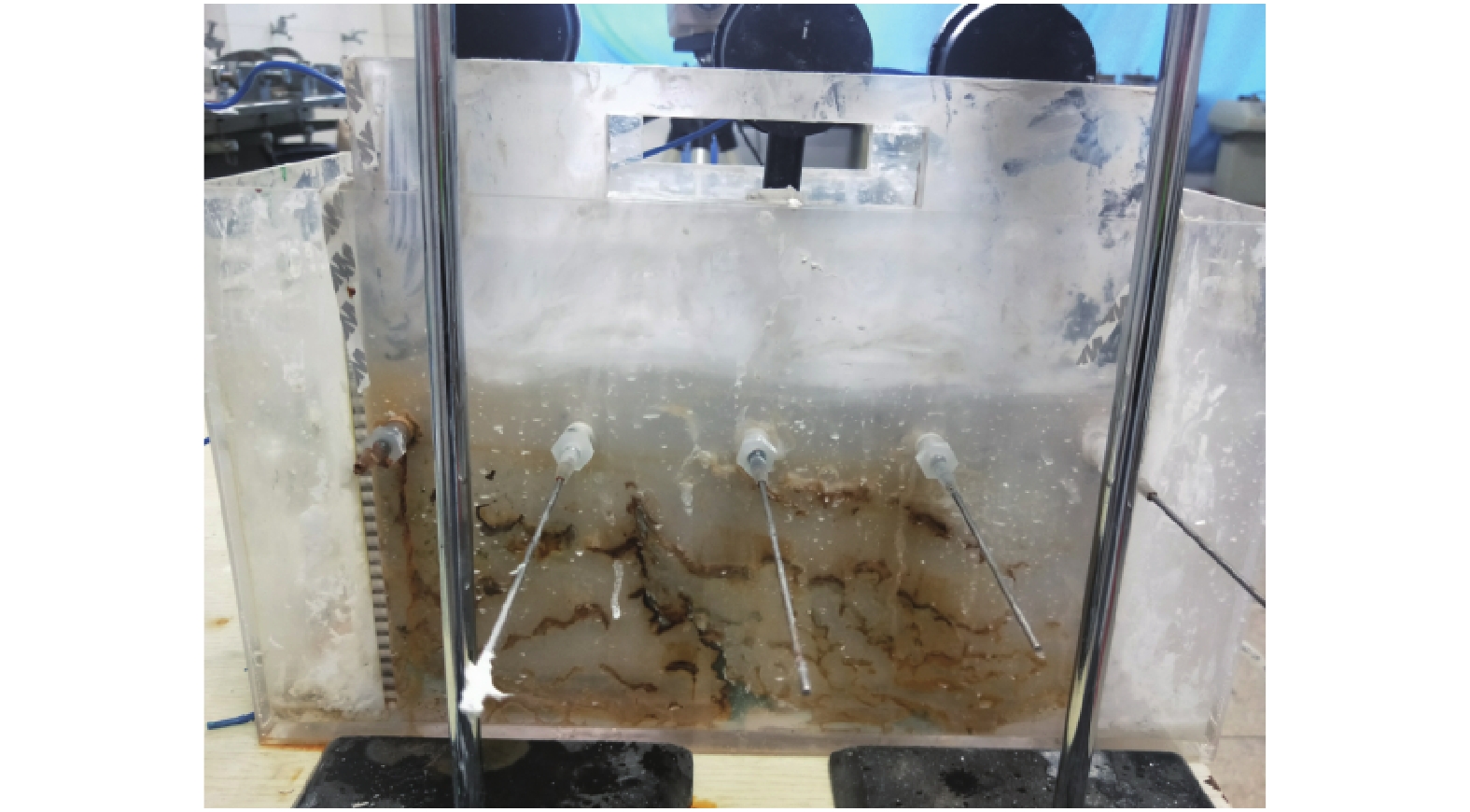
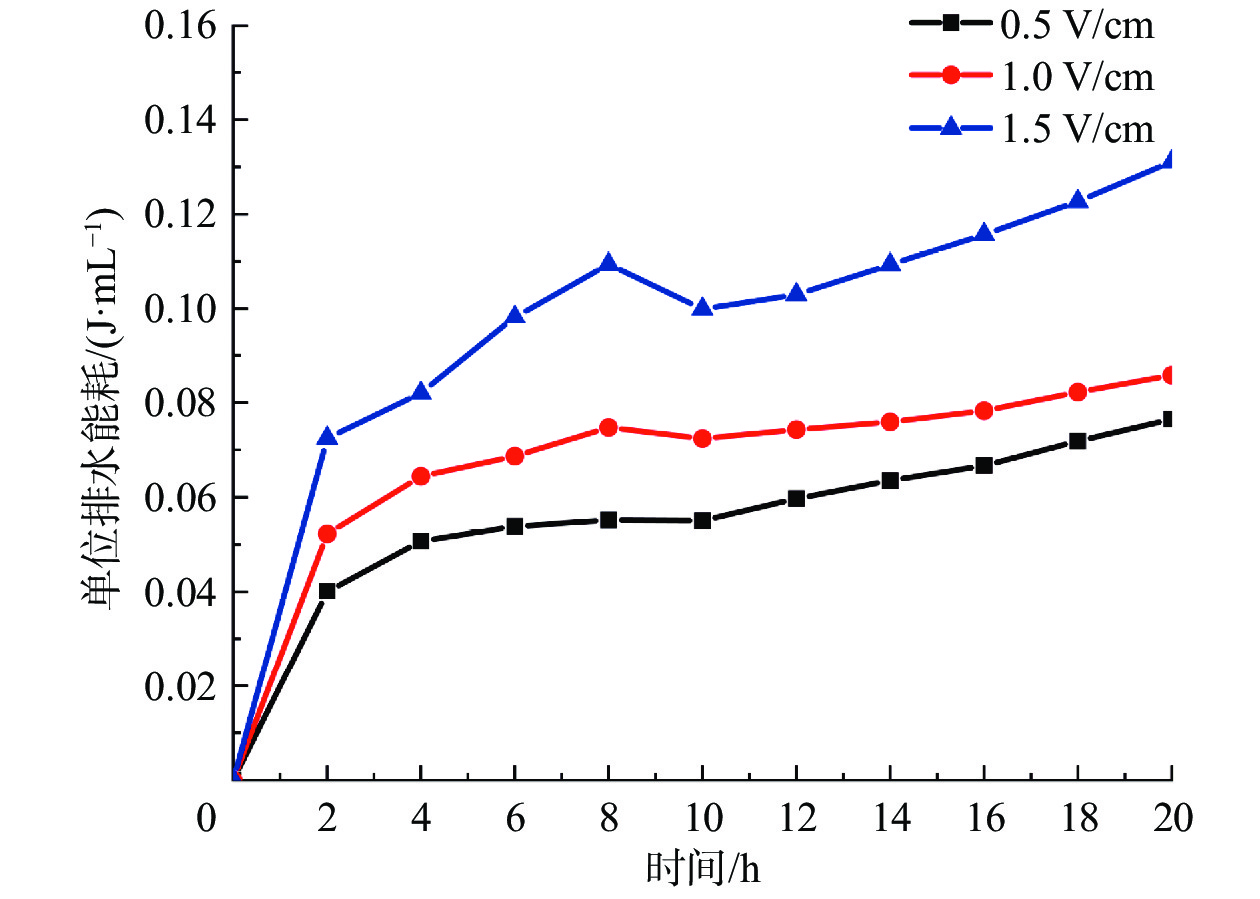
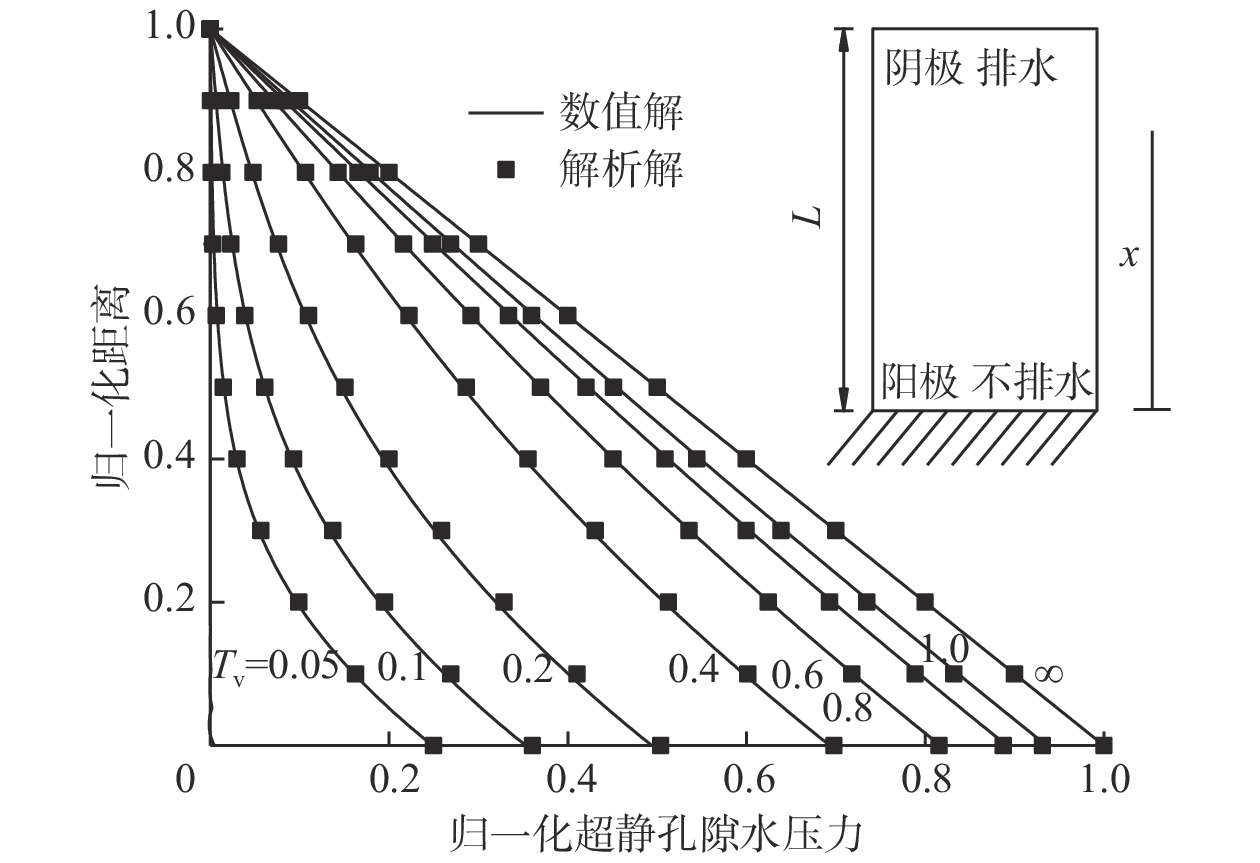
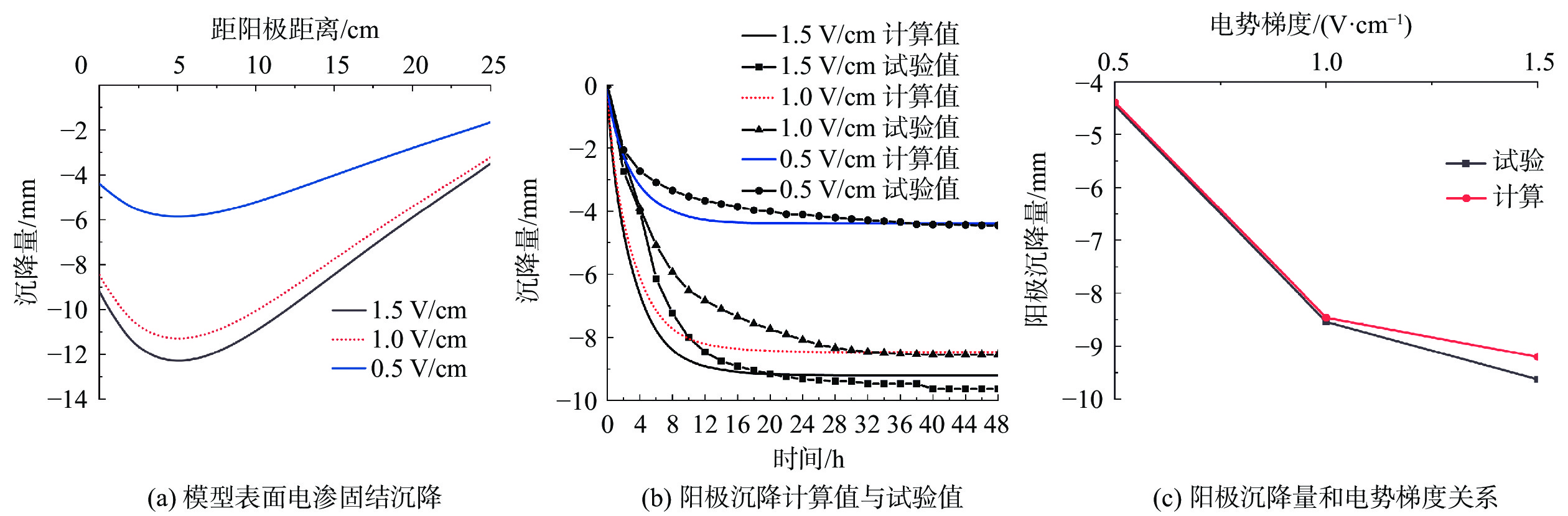
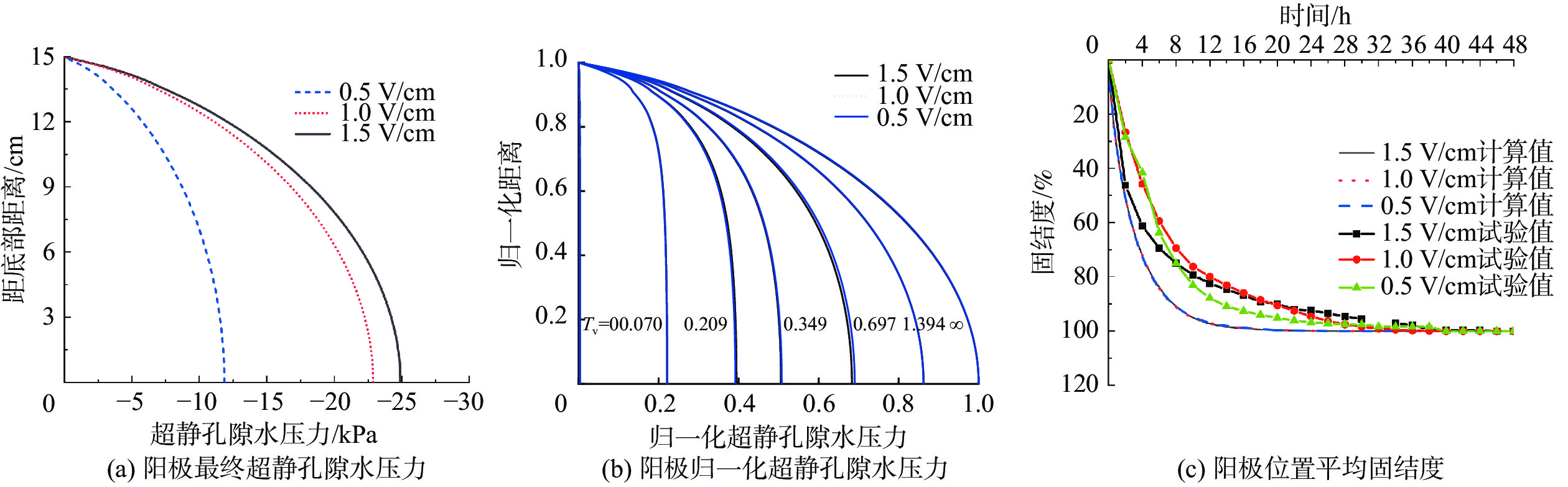
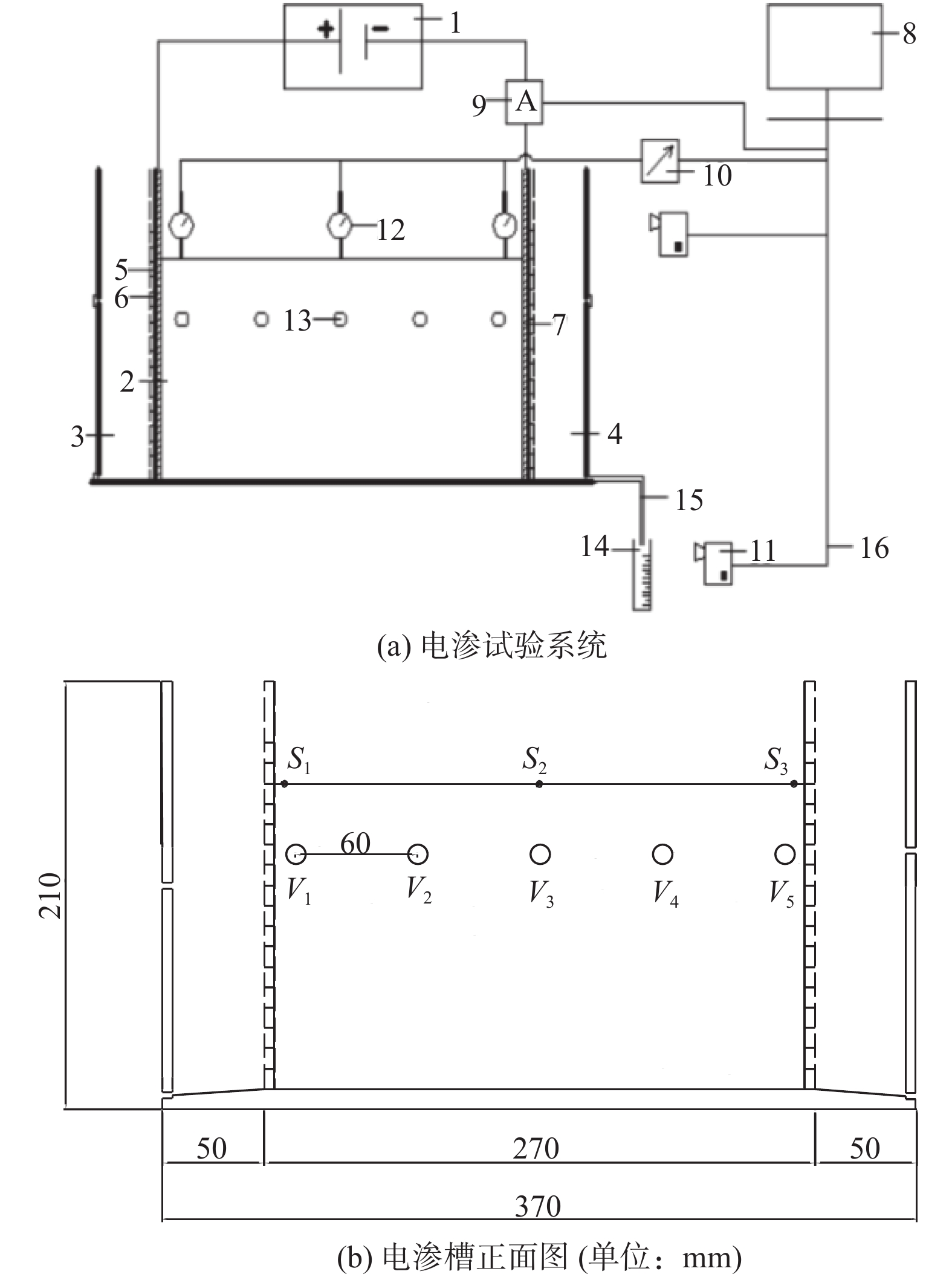
电渗固结是促进低渗透性软土排水固结的有效方法。为了揭示不同电势梯度影响高岭土电渗固结的基本规律,在自制电渗试验装置上对高岭土进行电渗试验。试验过程中测量电流、排水量、沉降量以及有效电压随时间的变化,并进行单位排水能耗分析。基于电渗固结多场耦合控制方程,实现土体电渗固结全耦合分析的有限元数值方法,计算结果与解析解吻合良好,验证了程序的有效性。为预测不同电势梯度下土体沉降量随时间的变化关系,分别对0.5,1.0,1.5 V/cm 3种电势梯度电渗固结试验进行数值模拟分析,获得模型表面沉降量分布、阳极超静孔隙水压力时空发展规律、阳极位置固结度等曲线,计算结果和试验结果吻合良好,可为实际电渗试验提供理论指导。
Abstract:Electro-osmotic consolidation is an effective way to promote consolidation of soft soil with low permeability. In order to investigate the basic law of electro-osmotic consolidation behavior of soft clay under different potential gradients, electro-osmotic tests are carried out for kaolin with a self-made device. Changes of current, displacement, settlement and potential with time are measured during the tests, and energy consumption per unit drainage is also analyzed. Based on the electro-osmosis consolidation coupling governing equations, the electro-osmosis of soil consolidation full coupling analysis of finite element programs is developed. The finite element program is developed to examine the fully coupled soil electro-osmotic consolidation behavior based on the multi-field coupling governing equations of electro-osmotic consolidation. The numerical analysis is in good agreement with the analytical results, which proves the efficiency of the program. To predict the settlement of soft clay with time under different potential gradients, numerical analysis is performed to study the electro-osmosis consolidation tests of kaolin clay under three potential gradients: 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 V/cm, respectively. Numerical simulation analysis for the surface subsidence distribution model, the space-time development of anode excess pore water pressure, and the degree of consolidation of the anode are performed. The numerical analysis results for the settlement are in good agreement with those obtained from the experiments. The results can provide theoretical guidance for practical electro-osmosis tests.
-
Key words:
- electro-osmosis tests /
- potential gradients /
- consolidation tests /
- numerical analysis
-

-
[1] CASAGRANDE I L. Electro-osmosis in soils[J]. Géotechnique,1949,1(3):159 − 177.
[2] LAMONT-BLACK J, JONES C J F P, ALDER D. Electrokinetic strengthening of slopes - Case history[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2016,44(3):319 − 331. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2016.01.001
[3] 胡黎明, 洪何清, 吴伟令. 高岭土的电渗试验[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2010,50(9):1353 − 1356. [HU Liming, HONG Heqing, WU Weiling. Electro-osmosis tests on Kaolin clay[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2010,50(9):1353 − 1356. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] HAMIR R B, JONES C J F P, CLARKE B G. Electrically conductive geosynthetics for consolidation and reinforced soil[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2001,19(8):455 − 482. doi: 10.1016/S0266-1144(01)00021-8
[5] 李瑛, 龚晓南, 张雪婵. 电压对一维电渗排水影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(3):709 − 714. [LI Ying, GONG Xiaonan, ZHANG Xuechan. Experimental research on effect of applied voltage on one-dimensional electroosmotic drainage[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(3):709 − 714. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.03.012
[6] 金志伟, 阎长虹, 李良伟, 等. 低含水率盾构泥浆的真空-电渗联合泥水分离技术试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):103 − 110. [JIN Zhiwei, YAN Changhong, LI Liangwei, et al. An experimental study of vacuum negative pressure incorporated with electro-osmosis in mud-water dehydration for shield slurry with low water content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):103 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] ESRIG, MELVIN I. Pore pressures, consolidation, and electrokinetics[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics & Foundations Division,1968,94(4):899 − 922.
[8] 徐伟, 刘斯宏, 王柳江, 等. 真空预压联合电渗法加固软基的固结方程[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2011,39(2):169 − 175. [XU Wei, LIU Sihong, WANG Liujiang, et al. Analytical theory of soft ground consolidation under vacuum preloading combined with electro-osmosis[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2011,39(2):169 − 175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 胡黎明, 吴伟令, 吴辉. 软土地基电渗固结理论分析与数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(12):3977 − 3983. [HU Liming, WU Weiling, WU Hui. Theoretical analysis and numerical simulation of electroosmosis consolidation for soft clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(12):3977 − 3983. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.12.045
[10] 龚明星, 王档良, 詹贵贵. 考虑有效电势变化的软土一维电渗固结理论[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(4):61 − 66. [GONG Mingxing, WANG Dangliang, ZHAN Guigui. 1-D electro-osmotic consolidation theory considering variation in effective potential in soft soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(4):61 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] WU H, HU L M. Analytical and numerical model of electro-osmotic consolidation for soft soil improvement[C]//Geo-Congress 2013. March 3-7, 2013, San Diego, California, USA. Reston, VA, USA: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2013: 2107-2116.
[12] TANG X W, XUE Z J, YANG Q, et al. Water content and shear strength evaluation of marine soil after electro-osmosis experiments[J]. Drying Technology,2017,35(14):1696 − 1710. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2016.1270299
[13] 苏金强, 王钊. 电渗的二维固结理论[J]. 岩土力学,2004,25(1):125 − 131. [SU Jinqiang, WANG Zhao. Theory of two-dimensional electro-osmotic consolidation of soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2004,25(1):125 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.01.027
[14] 谢新宇, 郑凌逶, 谢康和, 等. 电势梯度与电极间距变化的滨海软土电渗模型试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2019,52(1):108 − 114. [XIE Xinyu, ZHENG Lingwei, XIE Kanghe, et al. Experimental study on electro-osmosis of marine soft soil with varying potential gradient and electrode spacing[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2019,52(1):108 − 114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王宁伟, 孙守刚, 梁家豪, 等. 非金属电极在电渗排水中的应用[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2016,14(4):59 − 63. [WANG Ningwei, SUN Shougang, LIANG Jiahao, et al. The application of non-metallic electrodes in electroosmotic drainage[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2016,14(4):59 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2016.04.012
[16] YUAN J, HICKS M A. Large deformation elastic electro-osmosis consolidation of clays[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2013,54:60 − 68. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.05.012
[17] 王柳江, 刘斯宏, 汪俊波, 等. 电场-渗流场-应力场耦合的电渗固结数值分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(6):1904 − 1911. [WANG Liujiang, LIU Sihong, WANG Junbo, et al. Numerical analysis of electroosmostic consolidation based on coupled electrical field-seepage field-stress field[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(6):1904 − 1911. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.06.046
[18] 吴辉, 胡黎明. 考虑电导率变化的电渗固结模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(4):734 − 738. [WU Hui, HU Liming. Numerical simulation of electro-osmosis consolidation considering variation of electrical conductivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(4):734 − 738. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] TO P, MALEKZADEH M, SIVAKUGAN N, et al. 3D numerical model of electro-kinetic Sedimentation−Consolidation of dredged mud with variable parameters[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2020,38(4):4333 − 4348. doi: 10.1007/s10706-020-01298-2
[20] WU H, HU L M, WEN Q B. Numerical simulation of electro-osmotic consolidation coupling non-linear variation of soil parameters[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2017,103:92 − 98.
-



 下载:
下载: