Lattice Boltzmann meso-seepage research of reconstructed soil based on the quartet structure generation set
-
摘要:
多孔介质模型的重构问题是土体细观渗流机理研究的基础和关键。由四参数随机生长法(QSGS)构建土体模型,采用格子玻尔兹曼方法(LBM),通过MATLAB自编程序研究重构土在不同条件下的细观渗流机理。结果表明:随模型尺寸增大,孔隙连通程度显著提高,300×300格点大小的模型连通孔隙率增长幅度(34.38%)最大,继续扩大模型尺寸发现增加不明显;流体粒子在孔隙连通性好、孔径大的区域,会形成主渗流通道,且存在指进效应,孔道中间流速最大,可达0.0324,越靠近孔壁流速越小;大孔隙率土的流速比小孔隙率土大,而低孔隙率土中的流速相比大孔隙土更稳定;LBM模拟渗透率与经典K-C公式计算结果对比发现,孔隙率越高计算渗透率越准确(n=0.78,误差为10.22%);土颗粒越小,渗流孔道越细窄、分布越密集,对应的速度场分布更为均匀,同时流速也更小。该研究成果能较好地揭示重构土的细观渗流机理,也可为现有细观土体孔隙流研究提供一定借鉴。
Abstract:Reconstruction of the porous media model is the basis and key to the study of the meso-seepage mechanism of soil. The soil models are constructed by the quartet structure generation set (QSGS), and the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is used to examine the meso-seepage mechanism of the reconstructed soil under different conditions through MATLAB self-programming. The results show that the degree of pore connectivity increases significantly as the model size increases. The 300×300 grid size model has the largest increase in the connected porosity (34.38%). If the model size continues to be expanded, the increase is not obvious. Fluid particles can form the main seepage channel in the area with good pore connectivity and large pore size, and there is a fingering effect. The flow velocity in the middle of the pore channel is the largest, up to 0.0324. The flow velocity is getting smaller and smaller when it gets closer and closer to the pore wall. The velocity of the large porosity soil is larger than that of the small porosity soil, and the velocity of the low porosity soil is more stable than that of the large porosity soil. Comparing the calculation results of LBM simulation permeability with those of the typical K-C formula, it is found that the higher the porosity, the more accurate the calculation of permeability (n=0.78, the error is 10.22%). The smaller the soil particles, the narrower the seepage channels and the denser the distribution. The corresponding velocity field distribution is more uniform, and the flow velocity is also smaller. The research results can better reveal the meso-seepage mechanism of the reconstructed soil, and can also provide a certain reference for the existing meso-soil pore flow research methods.
-
Key words:
- Lattice Boltzmann /
- meso-seepage /
- quartet structure generation set /
- soil particle size /
- permeability
-

-
表 1 验证算例参数表 (格子单位)
Table 1. Validation calculation example parameter table (grid unit)
参数 L D δx δt Re pin pout 计算值 10 50 1 1 100 1.0006 1.0000 表 2 不同尺寸模型孔隙参数(格子单位)
Table 2. Pore parameters of different size models (grid unit)
模型尺寸 孔隙率n 孔隙数量/个 平均等效孔径 连通孔隙率 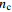
50 0.64 5 10 0.19 100 13 12.5 0.27 200 88 9.6 0.32 300 139 11.5 0.43 400 251 11.4 0.44 500 462 10.5 0.46 表 3 LBM模拟渗透率与K-C模型计算渗透率对比结果(格子单位)
Table 3. Comparison results of the LBM simulated permeability and K-C model calculated permeability (grid unit)
孔隙率n LBM渗透率 K-C渗透率 误差/% 0.50 0.7658 1.0028 23.63 0.64 2.6856 2.3626 13.67 0.78 5.4187 4.9160 10.22 -
[1] HANES J, CHIBA M, LANGER R. Degradation of porous poly(anhydride-co-imide) microspheres and implications for controlled macromolecule delivery[J]. Biomaterials,1998,19(1/2/3):163 − 172.
[2] 吴蒙, 秦勇, 王晓青, 等. 中国致密砂岩储层流体可动性及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(1):35 − 51. [WU Meng, QIN Yong, WANG Xiaoqing, et al. Fluid mobility and its influencing factors of tight sandstone reservoirs in China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(1):35 − 51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张晨阳, 张泰丽, 张明, 等. 东南沿海地区玄武岩残积土雨水运移特征及滑坡失稳数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):42 − 50. [ZHANG Chenyang, ZHANG Taili, ZHANG Ming, et al. Rainfall infiltration characteristics and numerical simulation of slope instability in the basalt residual soil in the coastal area of Southeast China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 蔡沛辰, 阙云, 李显. 非饱和花岗岩残积土水-气两相驱替过程数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):54 − 63. [CAI Peichen, QUE Yun, LI Xian. Numerical simulation of water-gas two-phase displacement process in unsaturated granite residual soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):54 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 蔡沛辰, 阙云, 李显. 围压条件下原状花岗岩残积土细观渗流数值模拟[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(3):400 − 406. [CAI Peichen, QUE Yun, LI Xian. Numerical simulation of meso-seepage flow in undisturbed granite residual soil under confining pressure[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(3):400 − 406. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 钱尼贵. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的路面路基细观渗流特性及试验研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.
QIAN Nigui. Analysis and experimental investigation of mesoscopic seepage characteristics of pavement and subgrade based on lattice boltzmann method[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] BROADWELL J E. Shock structure in a simple discrete velocity gas[J]. Physics of Fluids,1964,7(8):1243. doi: 10.1063/1.1711368
[8] MAIER R S, KROLL D M, BERNARD R S, et al. Pore-scale simulation of dispersion[J]. Physics of Fluids,2000,12(8):2065 − 2079. doi: 10.1063/1.870452
[9] PILOTTI M. Generation of realistic porous media by grains sedimentation[J]. Transport in Porous Media,1998,33(3):257 − 278. doi: 10.1023/A:1006598029153
[10] MADADI M, SAHIMI M. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of fluid flow in fracture networks with rough, self-affine surfaces[J]. Physical Review E,2003,67(2):1 − 12.
[11] ZHANG H F, GE X S, YE H. Randomly mixed model for predicting the effective thermal conductivity of moist porous media[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics,2006,39(1):220 − 226. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/39/1/032
[12] 周潇, 申林方, 阮永芬, 等. 基于四参数随机生长法重构土体的渗流细观数值模拟[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2015,33(4):316 − 321. [ZHOU Xiao, SHEN Linfang, RUAN Yongfen, et al. Reconstructed soil meso-numerical seepage simulation based on quartet structure generation set[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering,2015,33(4):316 − 321. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8530.14.0176
[13] 申林方, 王志良, 李邵军. 基于土体细观结构重构技术的渗流场数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(11):3307 − 3314. [SHEN Linfang, WANG Zhiliang, LI Shaojun. Numerical simulation for seepage field of soil based on mesoscopic structure reconfiguration technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(11):3307 − 3314. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] MCNAMARA G R, ZANETTI G. Use of the Boltzmann equation to simulate lattice-gas automata[J]. Physical Review Letters,1988,61(20):2332 − 2335. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.2332
[15] 冯杰, 解河海, 黄国如. 土壤大孔隙流机理及产汇流模型[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.
FENG Jie, XIE Hehai, HUANG Guoru, et al. The mechanism of soil macropore flow and the model of runoff generation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[16] WANG Q F, LI C W, ZHAO Y C, et al. Study of gas emission law at the heading face in a coal-mine tunnel based on the Lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Energy Science & Engineering,2020,8(5):1705 − 1715.
[17] SONG R, WANG Y, LIU J J, et al. Comparative analysis on pore-scale permeability prediction on micro-CT images of rock using numerical and empirical approaches[J]. Energy Science & Engineering,2019,7(6):2842 − 2854.
[18] 李仁民, 刘松玉, 方磊, 等. 采用随机生长四参数生成法构造黏土微观结构[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2010,44(10):1897 − 1901. [LI Renmin, LIU Songyu, FANG Lei, et al. Micro-structure of clay generated by quartet structure generation set[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2010,44(10):1897 − 1901. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2010.10.009
[19] 何雅玲, 王勇, 李庆. 格子Boltzmann方法的理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
HE Yaling, WANG Yong, LI Qing. Lattice Boltzmann method: theory and applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[20] KRUGER T, KUSUMAATMAJA H, KUZMIN A, et al. The Lattice Boltzmann method principles and practice[M]. New York: Springer, 2017.
[21] WOLF-GLADROW D A. Lattice gas cellular automata and lattice boltzmann models[M]. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2000.
[22] QIAN Y H, D'HUMIÈRES D, LALLEMAND P. Lattice BGK models for navier-stokes equation[J]. Europhysics Letters (EPL),1992,17(6):479 − 484. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/17/6/001
[23] CHAPMAN S, COWLING T G. The mathematical theory of non-uniform Gases[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1970.
[24] 郭照立, 郑楚光. 格子Boltzmann方法的原理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
GUO Zhaoli, ZHENG Chuguang. Theory and applications of lattice boltzmann method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[25] GUO Z L, ZHENG C G, SHI B C. Non-equilibrium extrapolation method for velocity and pressure boundary conditions in the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Physics,2002,11(4):366 − 374. doi: 10.1088/1009-1963/11/4/310
[26] 李晶晶, 金磊, 程涛. 土石混合体细观渗流场的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(29):235 − 241. [LI Jingjing, JIN Lei, CHENG Tao. Numerical simulation of mesoscopic seepage field of soil-rock mixture based on lattice boltzmann method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(29):235 − 241. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.29.038
[27] 蔡沛辰, 阙云, 杨鹏飞. 原状花岗岩残积土大孔隙细观渗流场的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(4):531 − 536. [CAI Peichen, QUE Yun, YANG Pengfei. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of macropore meso-seepage field in undisturbed granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(4):531 − 536. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 杨峰, 王昊, 黄波, 等. 基于CT扫描的致密砂岩渗流特征及应力敏感性研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(4):475 − 482. [YANG Feng, WANG Hao, HUANG Bo, et al. Study on the stress sensitivity and seepage characteristics of tight sandstone based on CT scanning[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(4):475 − 482. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.045
[29] LATIEF F D E, FAUZI U. Kozeny-Carman and empirical formula for the permeability of computer rock models[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2012,50:117 − 123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.12.005
[30] KAVIANY M. Principles of heat transfer in porous media[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2012.
[31] 刘丹, 汪新智, 何玉荣. 随机四参数法生成多孔介质及渗流模拟[J]. 工程热物理学报,2021,42(1):210 − 214. [LIU Dan, WANG Xinzhi, HE Yurong. Lattice boltzmann simulation of flow in random porous media constructed by quartet structure generation set[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2021,42(1):210 − 214. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载:










