A comparative numerical simulation study of single-phase flow and water-gas two-phase flow infiltration process in the vadose zone with the layered heterogeneous structure
-
摘要:
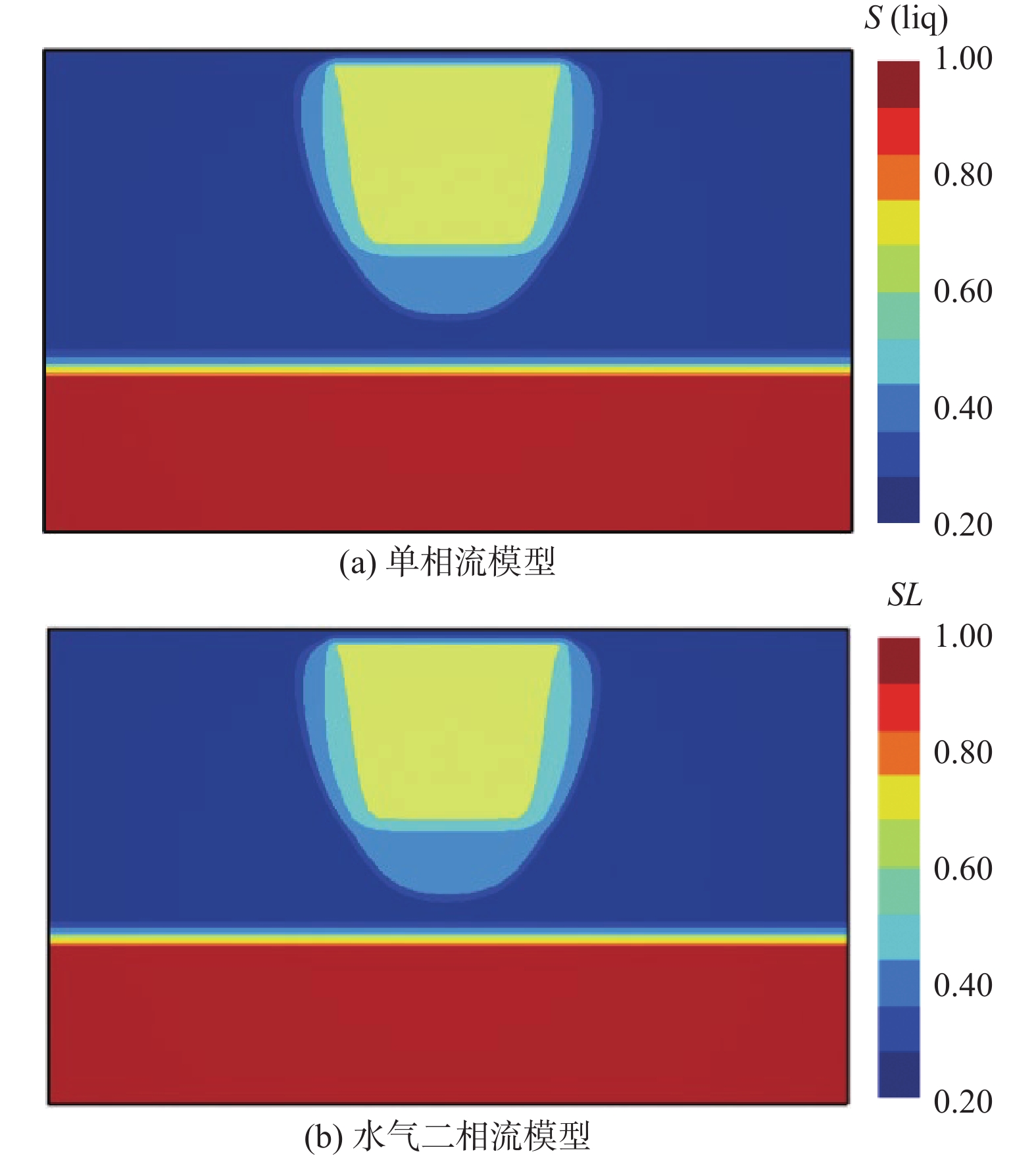
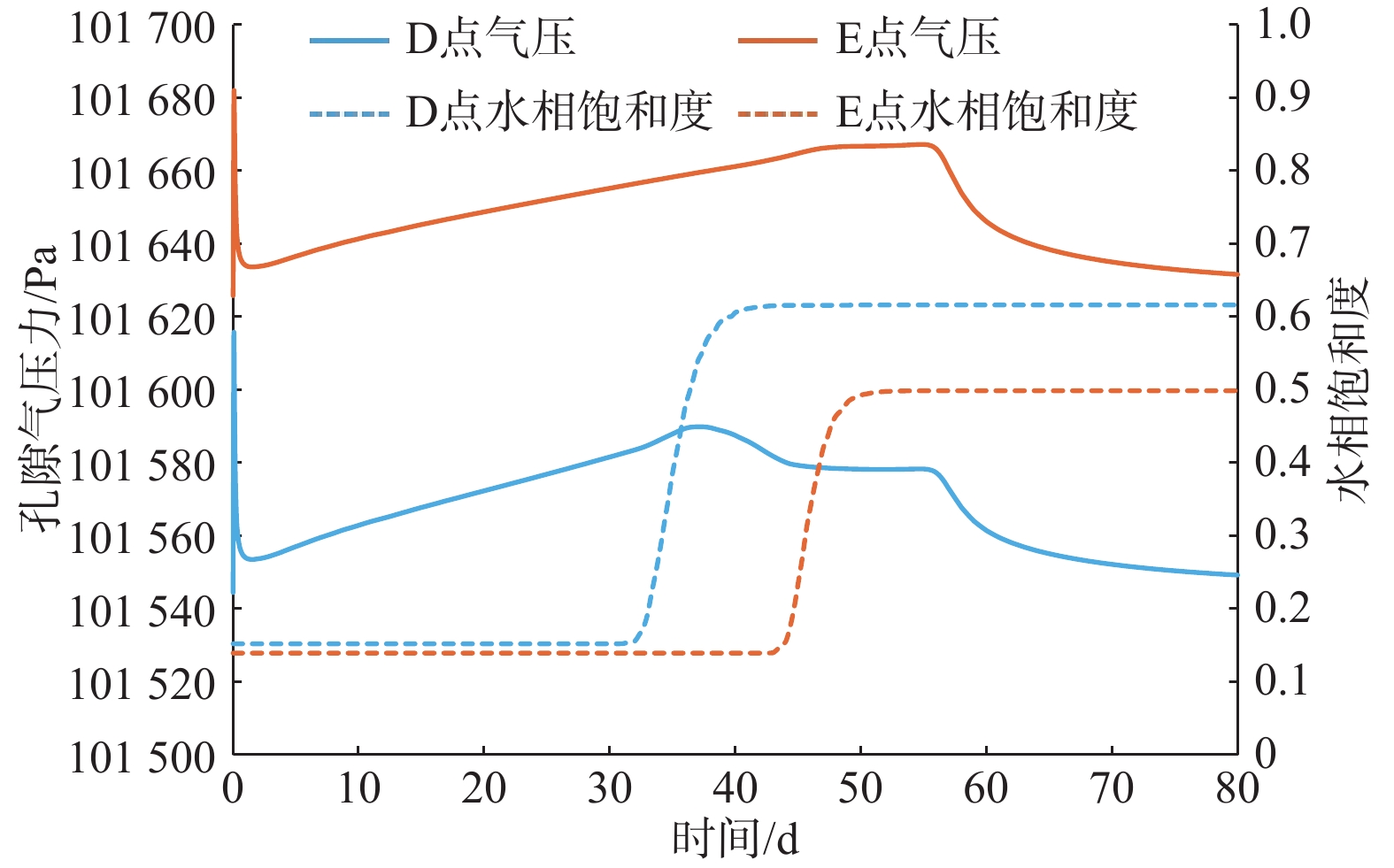
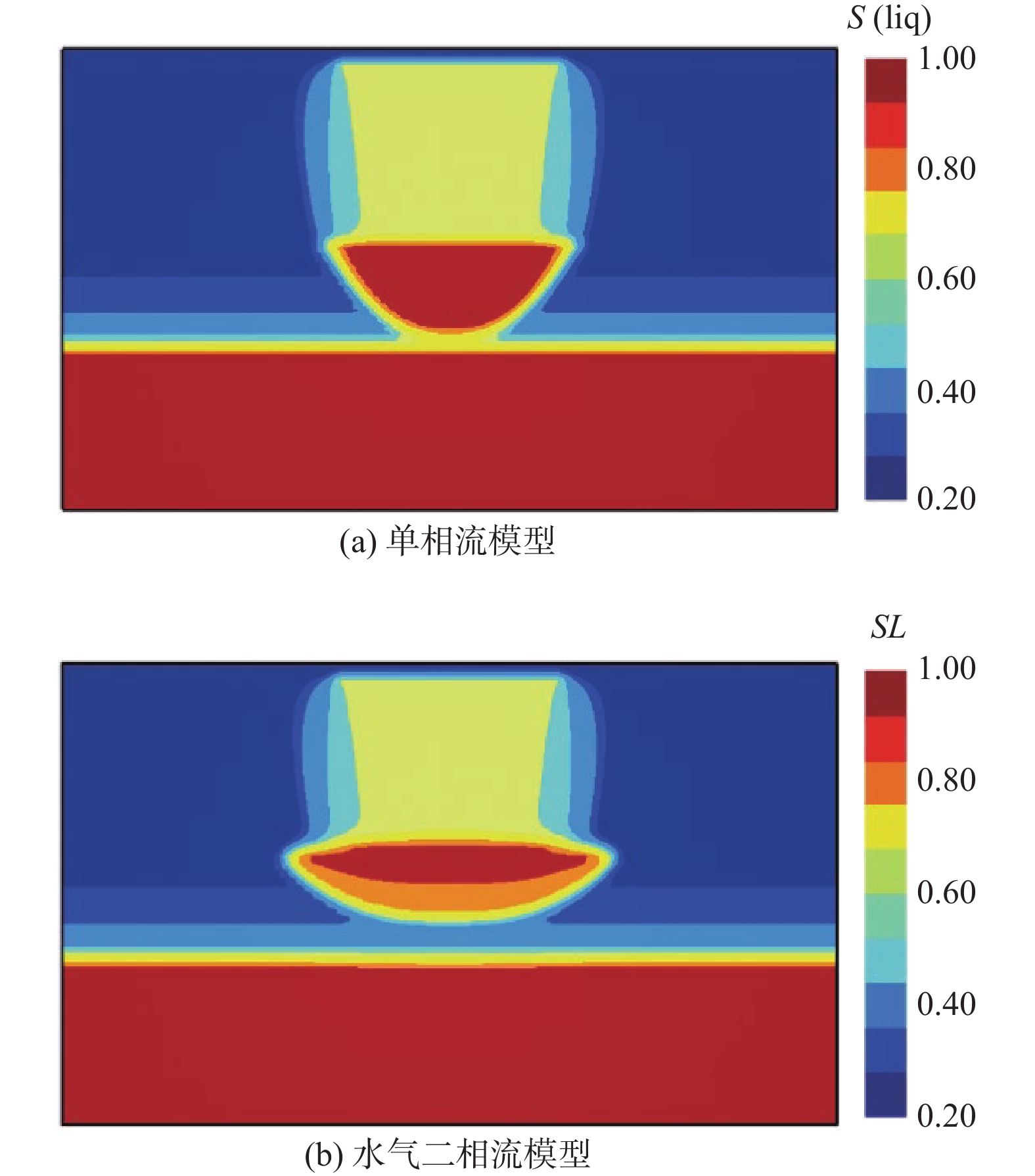
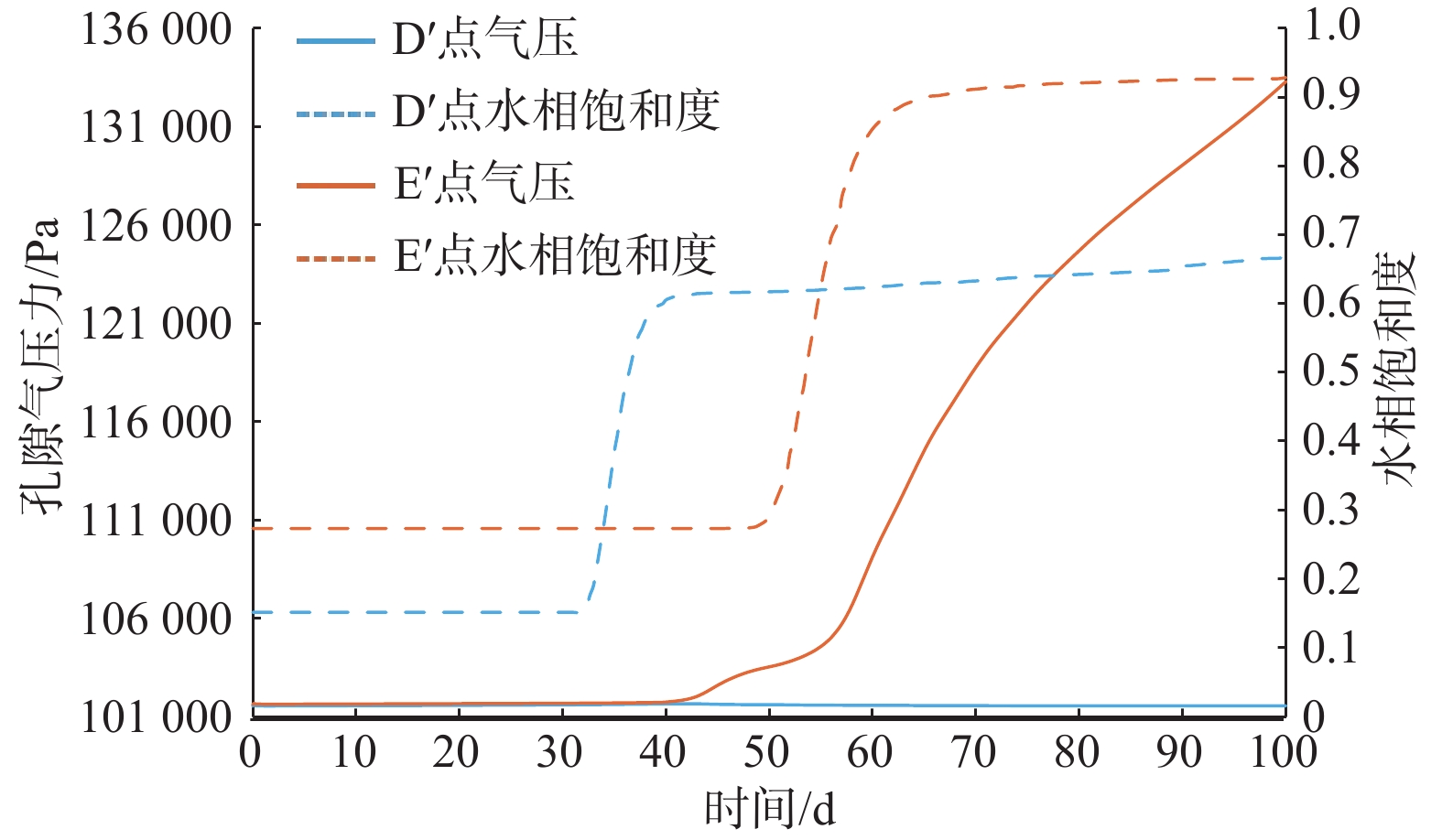
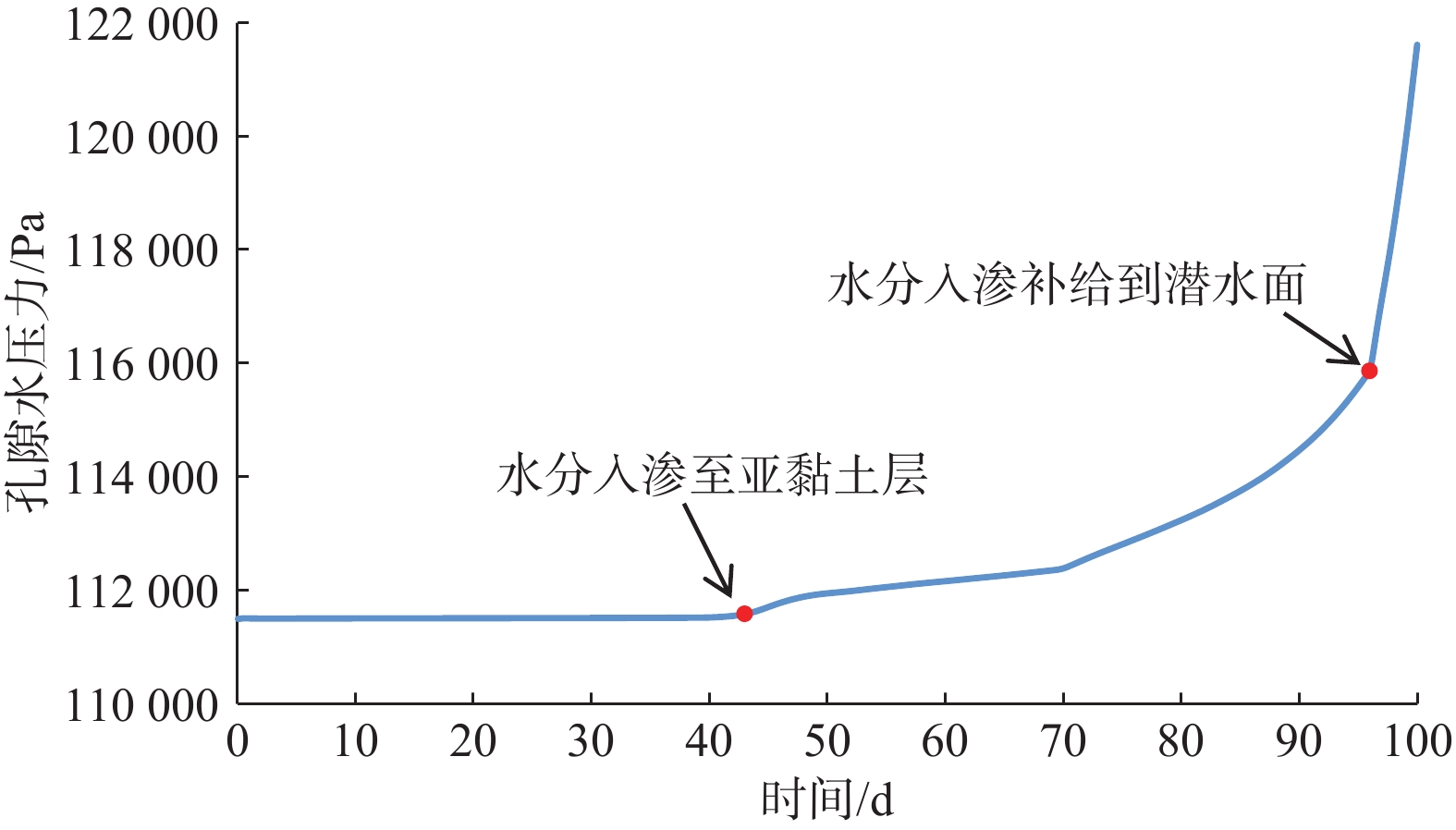
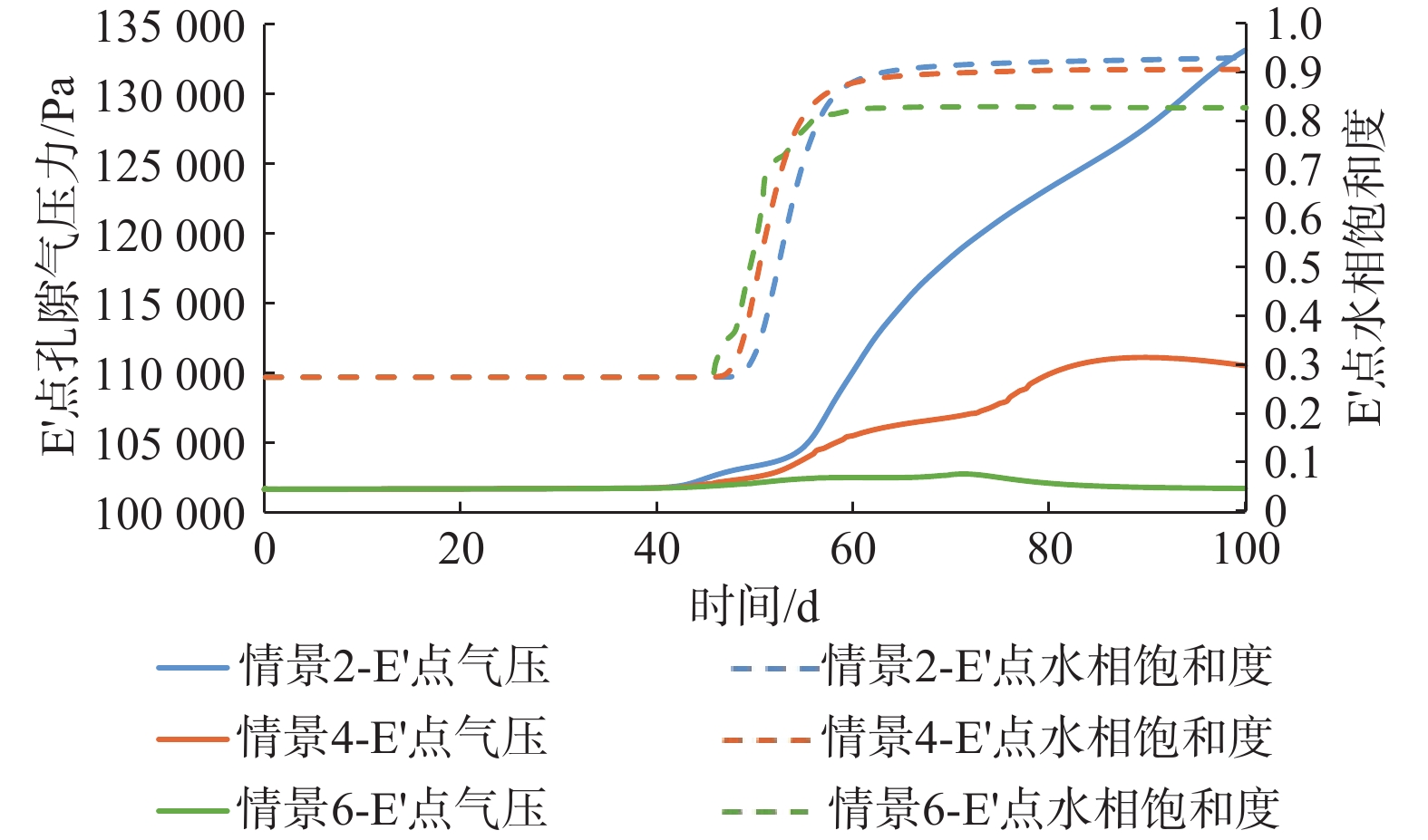
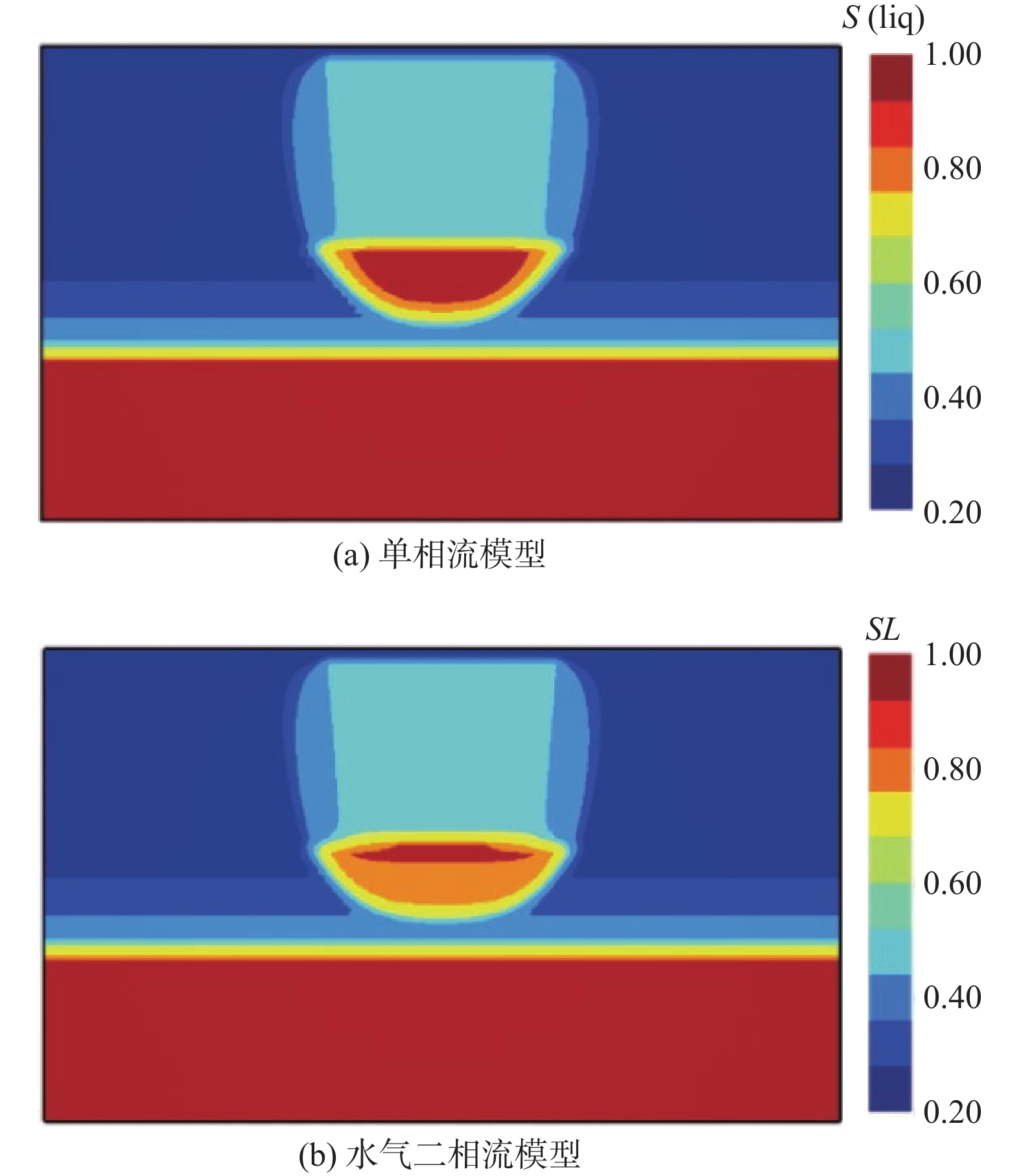
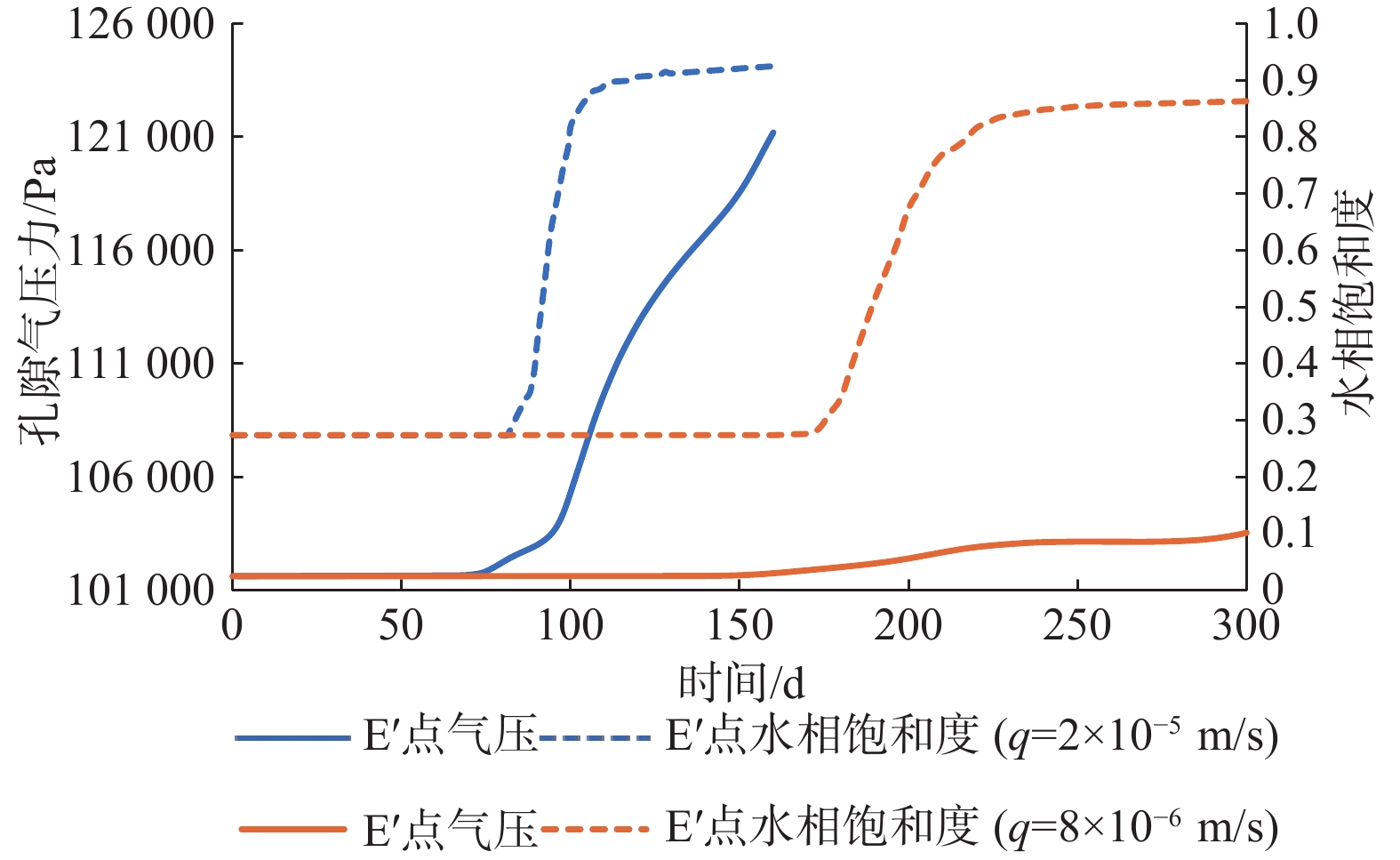
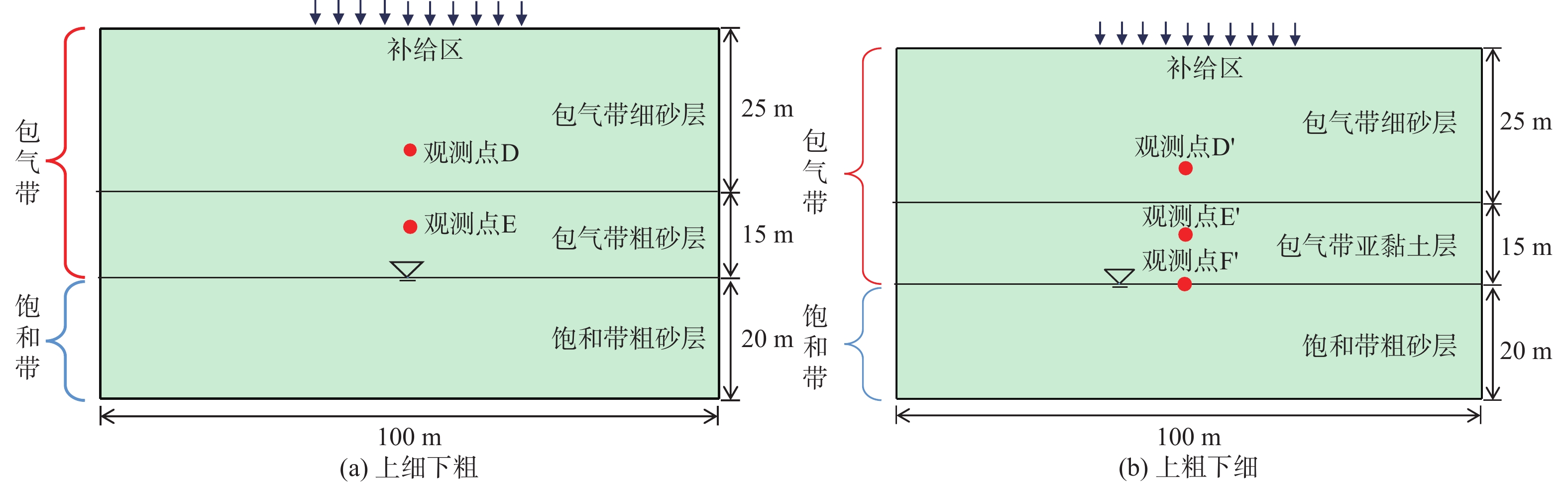
包气带水分入渗过程受多种因素的影响。定量研究层状非均质岩性结构和入渗速率对其影响,有助于解决根据不同条件选择单相流模型或水气二相流模型模拟包气带水分入渗过程的问题。结合填埋场等场地地层条件及污废水入渗特征,分别建立了“上细下粗”和“上粗下细”包气带层状非均质岩性结构水分入渗单相流和水气二相流模型,探讨不同层状非均质岩性结构条件下模型的适用性。在“上粗下细”岩性结构模型基础上,进一步探究入渗速率对水气两相运移结果的影响。基于论文模型研究表明:(1)在包气带岩性结构为“上细下粗”的条件下,气相的影响基本可以忽略,可直接采用单相流模型对包气带水分运移进行模拟;在“上粗下细”岩性结构和本次模型设定的底部压力保持不变及污废水泄漏前场地未接受降水入渗补给等条件下,当包气带上下层介质渗透率比值大于16倍时,气相会对水相运移产生明显影响,且下层介质渗透率越小、上下层介质渗透率比值越大,单相流与两相流的运移结果差别越大,需要采用水气二相流模型模拟包气带水分运移。(2)在包气带“上粗下细”岩性结构条件下,入渗速率越大,气相对水流入渗的阻滞作用越明显,此时包气带水分运移模拟应采用水气二相流模型。
Abstract:The infiltration process in the vadose zone is affected by many factors. A quantitative study of the influence of the layered heterogeneous lithological structure and infiltration rate on the process of water infiltration in the vadose zone is helpful in selecting a single-phase flow model or water-gas two-phase flow model for simulating the infiltration process in the vadose zone under different conditions. In this study, combined with stratum conditions of landfills and other sites and the infiltration characteristics of polluted or waste water, water infiltration single-phase flow and water-gas two-phase flow models are established under the “upper fine and lower coarse” and “upper coarse and lower fine” layered heterogeneous lithological structures of the vadose zone, in order to discuss the applicability of the models under different layered heterogeneous lithological structures. Based on the “upper coarse and lower fine” lithological structural model, the influence of infiltration rate on the results of water-gas two-phase migration is further explored. The results based on paper models show that (1) under the “upper fine and lower coarse” lithological structure condition of the vadose zone, the influence of the gas phase can be ignored and the single-phase flow model can be used to simulate water migration in the vadose zone. Under the settings of the “upper coarseness and lower fineness” lithological structure, the fixed bottom pressure and no precipitation infiltration before the leakage of sewage and wastewater in this model, gas phase has a significant impact on the water migration when the permeability ratio of the upper and lower media in the vadose zone is greater than about 16 times, and the lower the permeability of the underlying medium and the greater the permeability ratio of the upper and lower media, the greater the difference between the results of the single-phase flow and water-gas two-phase flow. It is necessary to use the water-gas two-phase flow model to simulate the water migration in the vadose zone. (2) Under the “upper coarseness and lower fineness” lithological structure condition of the adose zone, the greater the infiltration rate, the stronger the blocking effect of air on the water infiltration, and the water-gas two-phase flow model should be used to simulate the process of water migration in the vadose zone.
-

-
介质 密度/(kg·m−3) 渗透率/(10−12m2) 孔隙度 相对渗透率-饱和度关系曲线
(VG-M模型)毛细压力-饱和度关系曲线
(VG模型)λ Slr Sls Sgr λ Slr Sls Pmax 1/P0 粗砂 2 650 30 0.31 0.416 0.06 1 0.05 0.416 0.06 1 5×106 3.0×10−4 细砂 2 650 8.0 0.35 0.430 0.10 1 0.05 0.430 0.10 1 5×106 2.5×10−4 亚黏土 2 650 0.16 0.40 0.447 0.15 1 0.05 0.447 0.15 1 5×106 1.0×10−4 注:λ为经验参数,  为残余水饱和度,
为残余水饱和度,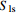 为饱和水饱和度,
为饱和水饱和度,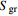 为残余气饱和度,Pmax为最大吸力,1/
为残余气饱和度,Pmax为最大吸力,1/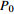 为土壤进气值的倒数。
为土壤进气值的倒数。表 2 不同模拟情景参数设置
Table 2. Parameter settings of different simulation cases
模拟情景设置 渗透率/(10−12m2) 上下层介质
渗透率比值上层介质(细砂) 8.0 / 情景1 下层介质1
(亚黏土)0.16 50 情景2 下层介质2 0.20 40 情景3 下层介质3 0.40 20 情景4 下层介质4 0.50 16 情景5 下层介质5 0.80 10 情景6 下层介质6 1.6 5 -
[1] COLMAN E A, BODMAN G B. Moisture and energy conditions during downward entry of water into moist and layered soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1945,9(C):3 − 11. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1945.036159950009000C0001x
[2] 王文焰, 张建丰, 汪志荣, 等. 砂层在黄土中的阻水性及减渗性的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1995,11(1):104 − 110. [WANG Wenyan, ZHANG Jianfeng, WANG Zhirong, et al. Experiment and study on water-tightness and infiltration reduction of sand layer in loess soils[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,1995,11(1):104 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 解文艳, 樊贵盛. 土壤质地对土壤入渗能力的影响[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2004,35(5):537 − 540. [XIE Wenyan, FAN Guisheng. Influence of soil structure on infiltration characteristics in field soils[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology,2004,35(5):537 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2004.05.010
[4] 张建丰. 黄土区层状土入渗特性及其指流的实验研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2004
ZHANG Jianfeng. Experimental study on infiltration characteristics and finger flow in layer soils of the loess area[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 郭会荣, 靳孟贵, 齐登红, 等. 基于地中渗透仪的入渗补给方式分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(4):107 − 111. [GUO Huirong, JIN Menggui, QI Denghong, et al. Characterization of groundwater recharge processes based on large lysimeters[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(4):107 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 王仕琴, 宋献方, 肖国强, 等. 基于氢氧同位素的华北平原降水入渗过程[J]. 水科学进展,2009,20(4):495 − 501. [WANG Shiqin, SONG Xianfang, XIAO Guoqiang, et al. Appliance of oxygen and hydrogen isotope in the process of precipitation infiltration in the shallow groundwater areas of North China Plain[J]. Advances in Water Science,2009,20(4):495 − 501. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 霍思远, 靳孟贵, 梁杏. 包气带弱渗透性黏土透镜体对降雨入渗补给影响的数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2013,43(5):1579 − 1587. [HUO Siyuan, JIN Menggui, LIANG Xing. Impacts of low-permeability clay lens in vadose zone onto rainfall infiltration and groundwater recharge using numerical simulation of variably saturated flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2013,43(5):1579 − 1587. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高业新, 张冰, 崔浩浩. 包气带水入渗过程中水化学组分运移规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(2):1 − 6. [GAO Yexin, ZHANG Bing, CUI Haohao. A study of the migration of chemical compositions in vadose water infiltration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(2):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 徐远志, 赵贵章, 母霓莎, 等. 包气带水分运移过程的影响因素综述[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2019,40(2):37 − 41. [XU Yuanzhi, ZHAO Guizhang, MU Nisha, et al. Review on factors affecting the process of water movement in vadose zone[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition),2019,40(2):37 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] WEI Y B, CHEN K P, WU J C. Estimation of the critical infiltration rate for air compression during infiltration[J]. Water Resources Research,2020,56(3):1 − 13.
[11] SUN D M, ZANG Y G, SEMPRICH S. Effects of airflow induced by rainfall infiltration on unsaturated soil slope stability[J]. Transport in Porous Media,2015,107(3):821 − 841. doi: 10.1007/s11242-015-0469-x
[12] WEI Y B, CHEN K P, WU J C, et al. Experimental study of the moisture distribution on the wetting front during drainage and imbibition in a 2D sand chamber[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2018,561:112 − 122. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.069
[13] 张杰, 韩同春, 豆红强, 等. 探讨变雨强条件下的入渗过程及影响因素[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(增刊1): 451-456
ZHANG Jie, HAN Tongchun, DOU Hongqiang, et al. Study of infiltration process and its influential factors under variable rainfall intensity[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(Sup1): 451-456. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 朱伟, 陈学东, 钟小春. 降雨入渗规律的实测与分析[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(11):1873 − 1879. [ZHU Wei, CHEN Xuedong, ZHONG Xiaochun. Observation and analysis of rainfall infiltration[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2006,27(11):1873 − 1879. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘刚, 童富果, 习念念, 等. 通气和封气条件下降雨对粘性土入渗速率、含水率及孔隙压力的影响试验[J]. 水电能源科学,2015,33(12):19 − 21. [LIU Gang, TONG Fuguo, XI Niannian, et al. Impact test of rainfall on clay soil infiltration rate, moisture content and pore pressure under aeration and gas sealing conditions[J]. Water Resources and Power,2015,33(12):19 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘秀花, 王蕊. 灌水量对包气带水分运移与滞留影响过程研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2016,34(5):262 − 268. [LIU Xiuhua, WANG Rui. Research on impact process of irrigation amount on moisture migration and retention in vadose zone[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2016,34(5):262 − 268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] SUN D M, ZANG Y G, FENG P, et al. Quasi-saturated zones induced by rainfall infiltration[J]. Transport in Porous Media,2016,112(1):77 − 104. doi: 10.1007/s11242-016-0633-y
[18] 施小清, 张可霓, 吴吉春. TOUGH2软件的发展及应用[J]. 工程勘察,2009,37(10):29 − 34. [SHI Xiaoqing, ZHANG Keni, WU Jichun. The history and application of TOUGH2 code[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2009,37(10):29 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] PRUESS K, OLDENBURG C M, MORIDIS G J. TOUGH2 user's guide version 2[R]. Office of Scientific and Technical Information, 1999.
[20] GUO H P, JIAO J J, WEEKS E P. Rain-induced subsurface airflow and lisse effect[J]. Water Resources Research,2008,44(7):767 − 768.
[21] 施小清, 吴吉春, 姜蓓蕾, 等. 包气带中降雨入渗单相流和二相流数值模拟对比[J]. 工程勘察,2011,39(1):38 − 45. [SHI Xiaoqing, WU Jichun, JIANG Beilei, et al. Comparison of numerical simulation based on water-gas two phase flow and single phase flow for the seepage in vadose zone[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2011,39(1):38 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李云良. 降雨条件下非饱和带水—气二相流模拟研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010
LI Yunliang. Simulation study of two-phases(water and air) flow in unsaturated zone under infiltration condition[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: