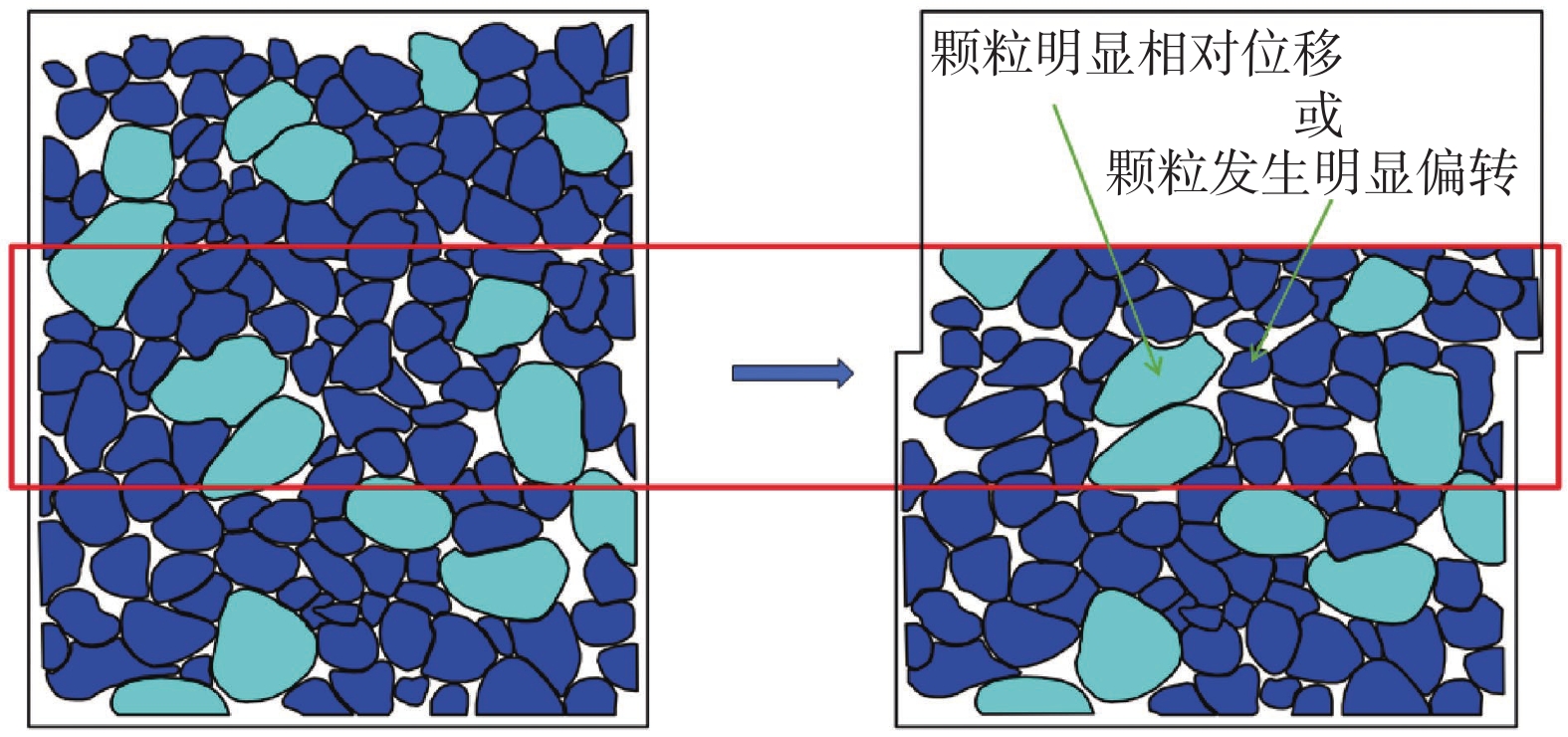
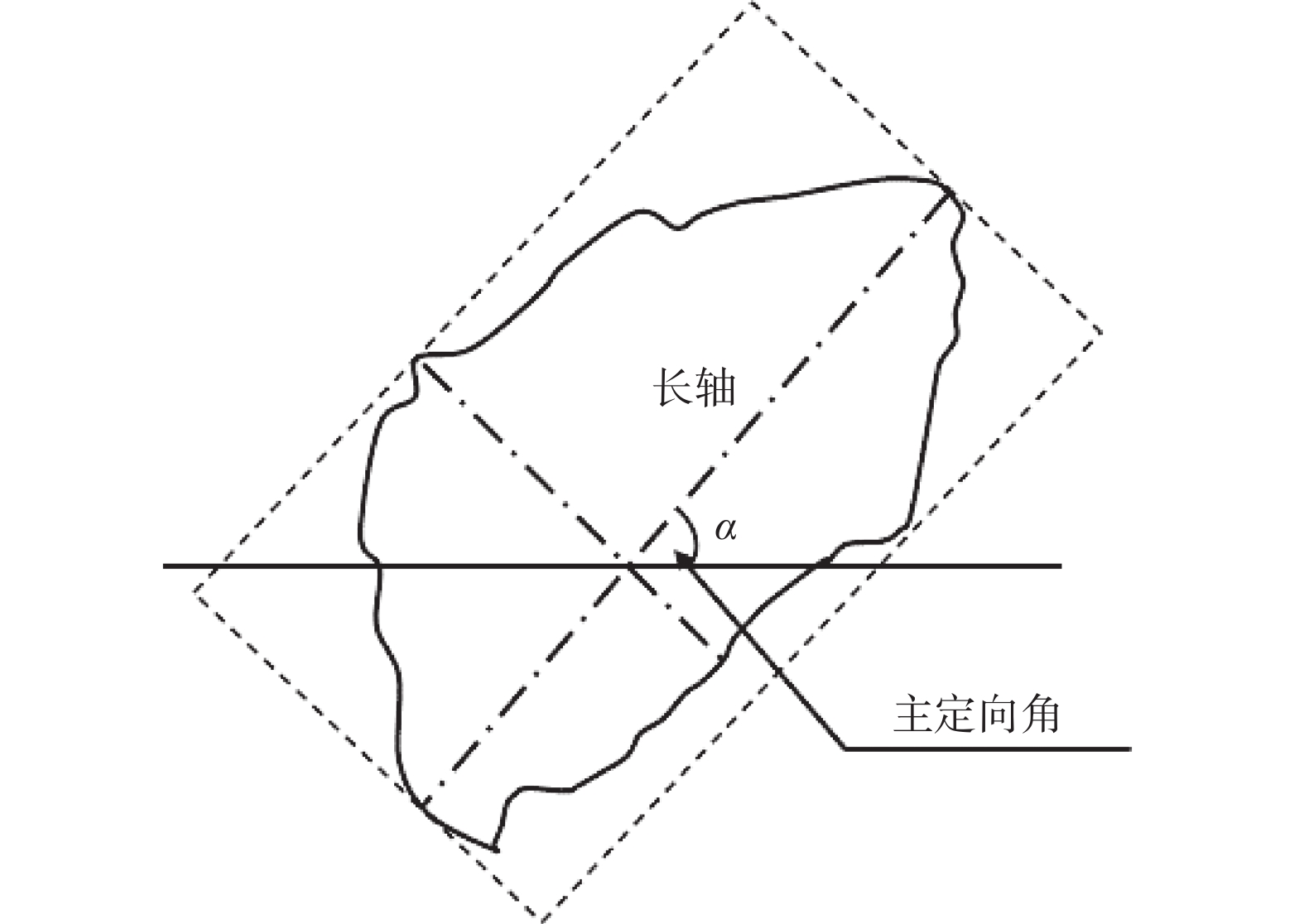
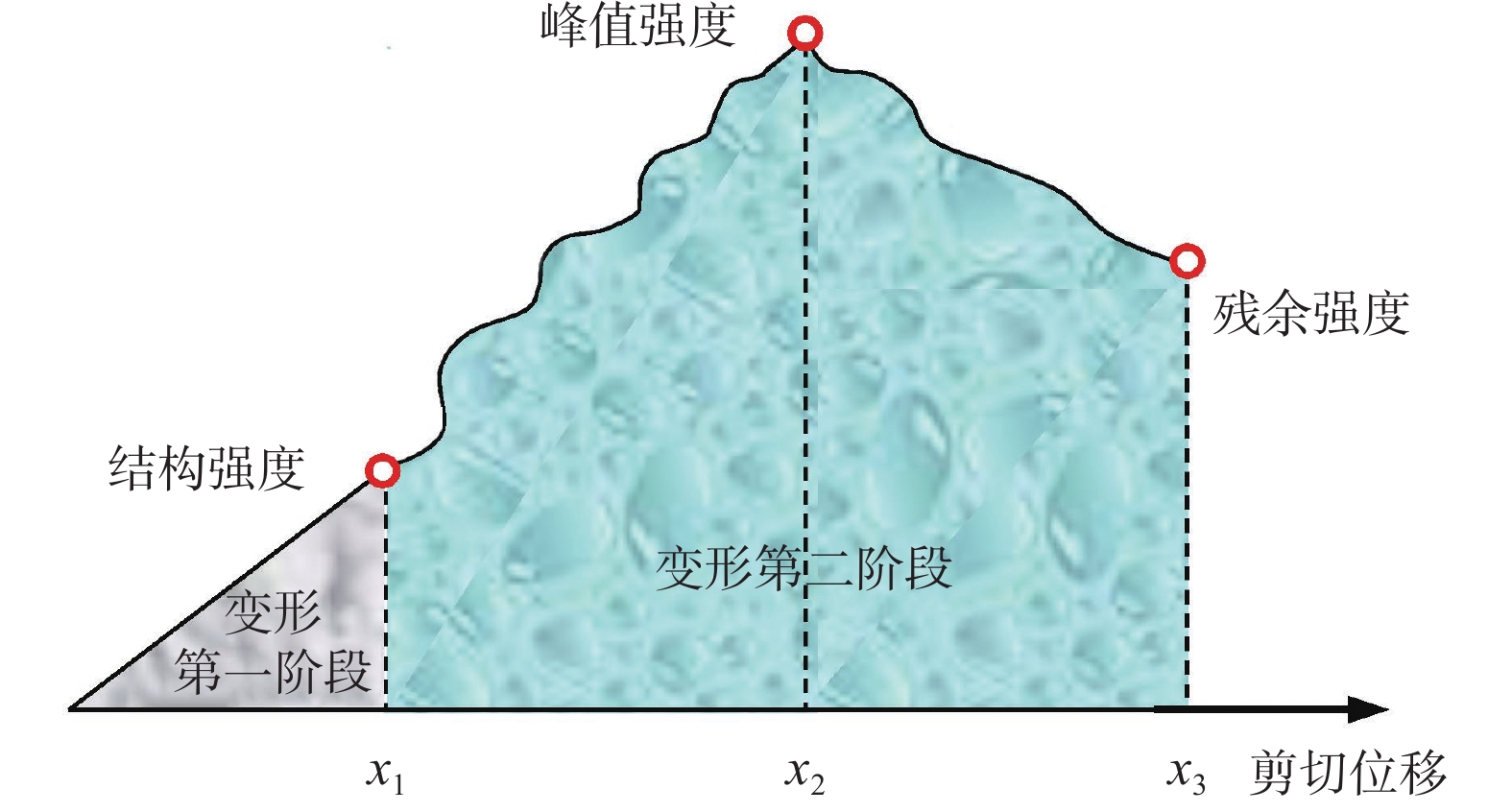
Research on the critical strength of the initial structure of the uncemented coarse-grained soil
-
摘要:
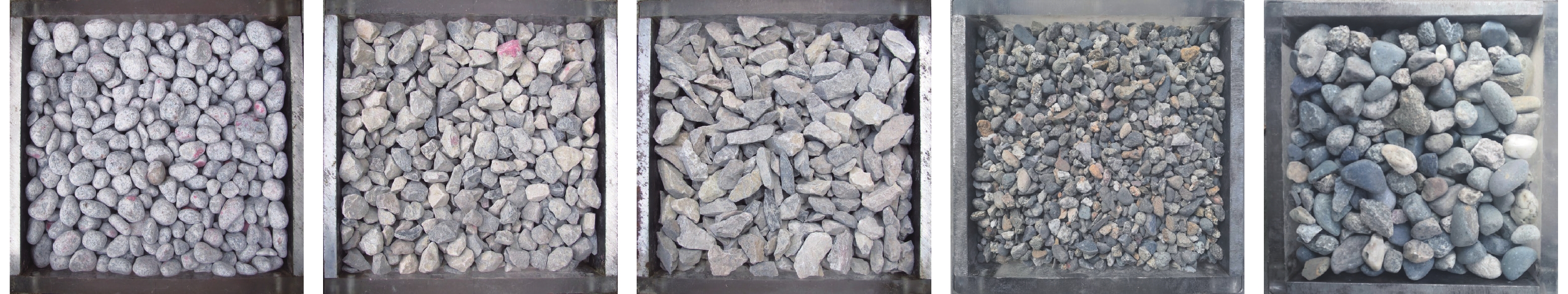
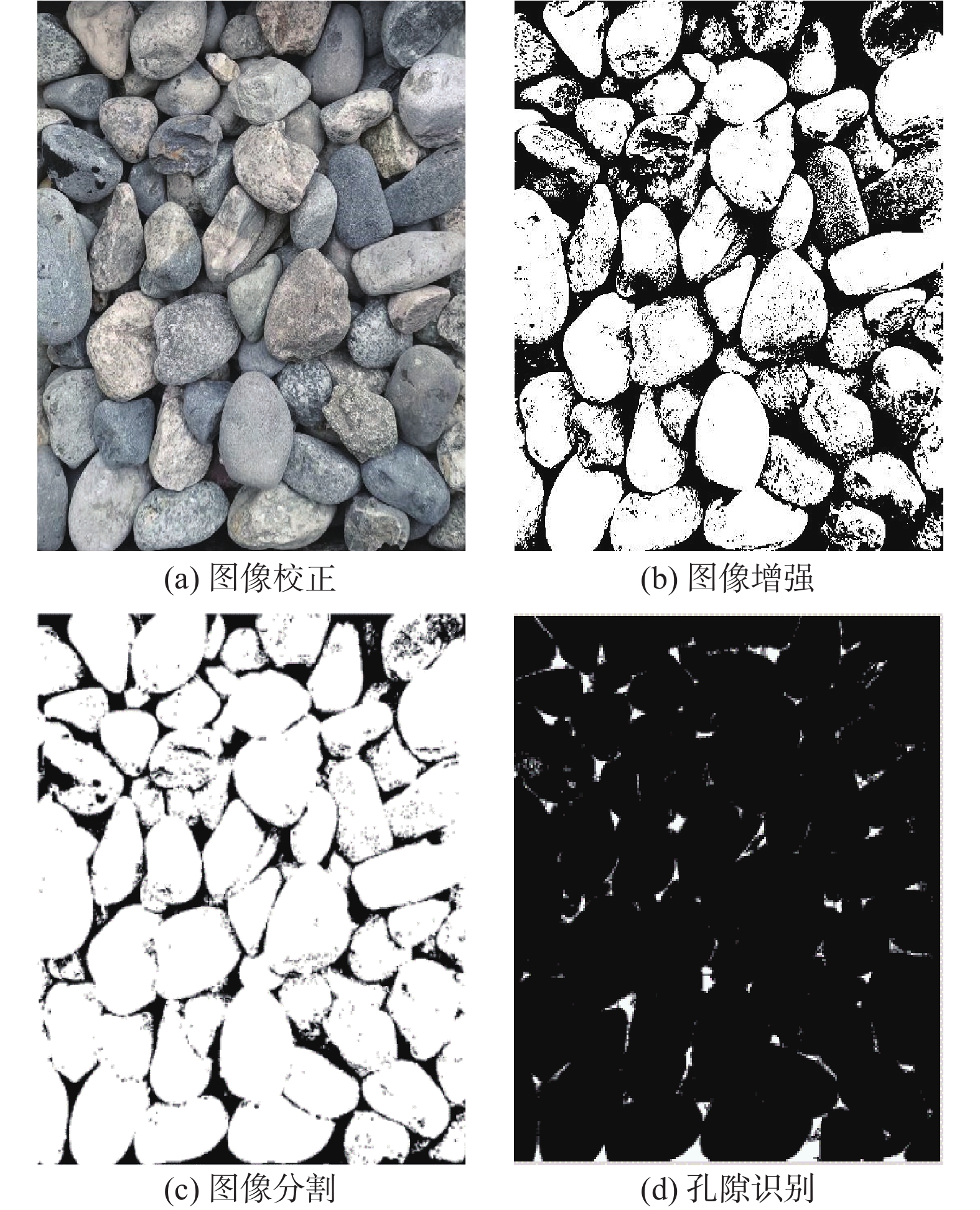
无论是原状土还是重塑土均存在初始结构性,土体初始结构所抵抗的剪应力为土体结构强度。为了研究无胶结粗粒土初始结构强度,定义了粗粒土剪切过程中初始结构变化点特征,并根据大于20 mm粗颗粒含量将粗粒土划分为4种结构类型,采用可视化直剪仪对不同结构特征的粗粒土进行直剪试验,通过剪切过程中粗粒土平面孔隙比、配位数、概率熵等3种初始结构指标的数值大小及变化趋势,来确定不同初始结构的粗粒土结构临界强度。结果表明:不同初始结构类型粗粒土在相同正应力、相同颗粒种类的情况下,其抗剪强度大小与结构强度占比大小的排序一致,表明了颗粒结构强度在抵抗剪应力的整个过程中起到了重要作用。4种初始结构类型粗粒土平均结构强度占比为36.27%,即结构强度占峰值抗剪强度的36.27%,其中排列接触结构的结构强度占比最高,为36.62%,其次为镶嵌结构36.61%,悬浮密实结构35.99%,叠置结构的结构强度占比最低,为35.87%。
Abstract:Both the undisturbed soil and remolded soil have initial structural properties, and the shear stress resisted by the initial structure of the soil is the structural strength of the soil. In order to study the initial structural strength of the uncemented coarse-grained soil, this paper defines the characteristics of the initial structural change points of the coarse-grained soil during the shearing process, and divides the coarse-grained soil into four structural types according to the content of the coarse-grained soils greater than 20 mm. Visual direct shear instrument direct shear tests are carried out on the coarse-grained soils with different structural characteristics, and the critical strength of the coarse-grained soils with different initial structures is determined through the numerical value and the change trend of the initial structure indexes of the coarse-grained soils during the shearing process. The results show that the shear strength of the coarse-grained soils with different initial structure types under the same normal stress and the same particle type are in the same order as the proportion of the structural strength, indicating that the particle structure strength plays a role in the whole process of the resisting shear stress. The average structural strength of the four initial structure types of the coarse-grained soils accountes for 36.27%, that is, the structural strength accountes for 36.27% of the peak shear strength. The arranged contact structure has the highest structural strength at 36.62%, followed by the mosaic structure 36.61%. The suspended dense structure is 35.99%, and the superimposed structure has the lowest proportion of the structural strength, which is 35.87%.
-
Key words:
- coarse-grained soil /
- shear strength /
- initial structure /
- structural strength /
- structure type
-

-
表 1 试样配比信息
Table 1. Sample ratio information
法向荷载
/kPaP20/% 叠置结构 镶嵌结构 排列接触结构 悬浮密实结构 50 80 60 40 15 100 80 60 40 15 150 80 60 40 15 200 80 60 40 15 表 2 初始结构信息提取结果
Table 2. Initial structure information extraction results
正应力/ kPa P20/% 平面孔隙率/% 概率熵 配位数 50 15 20.16 0.975 4.67 50 40 17.72 0.958 4.12 50 60 18.36 0.953 4.26 50 80 16.92 0.941 4.06 100 15 19.52 0.969 4.71 100 40 17.58 0.951 4.29 100 60 15.96 0.952 4.19 100 80 17.93 0.943 4.03 150 15 18.39 0.972 4.82 150 40 16.56 0.961 4.32 150 60 15.77 0.958 4.31 150 80 15.60 0.946 4.05 200 15 16.72 0.970 4.72 200 40 14.60 0.953 4.34 200 60 14.97 0.959 4.29 200 80 15.52 0.947 4.07 表 3 区间细化的各类型初始结构指标信息
Table 3. Initial structure index information for each type of interval refinement
剪切位移/mm 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 悬浮密实结构 配位数 4.731 4.731 4.735 4.736 4.736 4.736 4.737 4.737 4.737 4.738 孔隙比 18.673 18.674 18.686 18.689 18.689 18.690 18.690 18.691 18.691 18.692 概率熵 0.9713 0.9714 0.9715 0.9717 0.9717 0.9716 0.9718 0.9718 0.9719 0.9719 排列接触结构 配位数 4.268 4.268 4.268 4.268 4.269 4.269 4.271 4.270 4.271 4.272 孔隙比 16.611 16.612 16.612 16.613 16.613 16.614 16.618 16.622 16.623 16.624 概率熵 0.9557 0.9557 0.9557 0.9557 0.9558 0.9559 0.9560 0.9560 0.9560 0.9560 镶嵌结构 配位数 4.263 4.263 4.263 4.264 4.264 4.264 4.265 4.266 4.266 4.267 孔隙比 16.255 16.256 16.258 16.258 16.260 16.260 16.269 16.271 16.272 16.273 概率熵 0.9556 0.9556 0.9557 0.9557 0.9559 0.9560 0.9564 0.9567 0.9568 0.9570 叠置结构 配位数 4.052 4.053 4.053 4.053 4.054 4.055 4.055 4.056 4.056 4.056 孔隙比 16.482 16.483 16.484 16.485 16.489 16.490 16.492 16.493 16.495 16.498 概率熵 0.9443 0.9443 0.9444 0.9444 0.9446 0.9448 0.9448 0.9448 0.9449 0.9450 表 4 各类型初始结构强度及结构强度占比
Table 4. Initial structural strength of each type and the proportion of structural strength
初始结构
类型法向应力
/kPa结构强度
/kPa峰值抗剪
强度/kPa结构强度
占比/%结构强度占比
平均值/%悬浮密实结构 50 124.73 342.95 36.37 35.99 100 192.97 531.75 36.29 150 273.46 759.39 36.01 200 308.10 873.55 35.27 排列接触结构 50 135.96 367.86 36.96 36.62 100 231.33 623.20 37.12 150 326.55 899.83 36.29 200 383.91 1063.16 36.11 镶嵌
结构50 130.22 347.91 37.43 36.61 100 225.58 606.23 37.21 150 297.11 823.94 36.06 200 348.41 974.03 35.77 叠置
结构50 122.46 338.57 36.17 35.87 100 196.80 548.95 35.85 150 255.85 730.36 35.03 200 280.93 771.14 36.43 -
[1] 郭庆国. 粗粒土的工程特性及应用[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 1998.
GUO Qingguo. Engineering properties of coarse soil andits application[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River WaterConservancy Press, 1998. (in Chinese)
[2] ODA M, NEMAT-NASSER S, MEHRABADI M M. A statistical study of fabric in a random assembly of spherical granules[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,1982,6(1):77 − 94. doi: 10.1002/nag.1610060106
[3] CHRISTOFFERSEN J, MEHRABADI M M, NEMAT-NASSER S. A micromechanical description of granular material behavior[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1981,48(2):339 − 344. doi: 10.1115/1.3157619
[4] SATAKE M. A discrete-mechanical approach to granular materials[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science,1992,30(10):1525 − 1533. doi: 10.1016/0020-7225(92)90162-A
[5] ELIA G, AMOROSI A, CHAN A H C, et al. Fully coupled dynamic analysis of an earth dam[J]. Géotechnique,2011,61(7):549 − 563.
[6] 刘恩龙, 陈生水, 李国英, 等. 循环荷载作用下考虑颗粒破碎的堆石体本构模型[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(7):1972 − 1978. [LIU Enlong, CHEN Shengshui, LI Guoying, et al. A constitutive model for rockfill materials incorporating grain crushing under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(7):1972 − 1978. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.07.009
[7] MANOUCHEHRIAN A, SHARIFZADEH M, MARJI M F, et al. A bonded particle model for analysis of the flaw orientation effect on crack propagation mechanism in brittle materials under compression[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,2014,14(1):40 − 52. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2013.05.008
[8] 王占军, 陈生水, 傅中志. 堆石料的剪胀特性与广义塑性本构模型[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(7):1931 − 1938. [WANG Zhanjun, CHEN Shengshui, FU Zhongzhi. Dilatancy behaviors and generalized plasticity constitutive model of rockfill materials[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(7):1931 − 1938. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 高政国, HAYLEY H SHEN. 基于颗粒组构特性的散体材料本构模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(增刊1): 93-98
GAO Zhengguo, HAYLEY H SHEN. A study of constitutive model for granular material based on characters of discrete particles arranged[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(Sup 1): 93-98. (in Chinese with English abstract
[10] 蒋明镜, 刘静德, 孙渝刚. 基于微观破损规律的结构性土本构模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(6):1134 − 1139. [JIANG Mingjing, LIU Jingde, SUN Yugang. Constitutive model for structured soils based on microscopic damage law[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(6):1134 − 1139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李吴刚, 杨钢, 刘文化, 等. 基于结构性参数的土本构模型研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报,2021,61(1):84 − 91. [LI Wugang, YANG Gang, LIU Wenhua, et al. Study of constitutive model for soils based on structural parameter[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology,2021,61(1):84 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7511/dllgxb202101012
[12] 谢定义, 齐吉琳. 土结构性及其定量化参数研究的新途径[J]. 岩土工程学报,1999,21(6):651 − 656. [XIE Dingyi, QI Jilin. Soil structure characteristics and new approach in research on its quantitative parameter[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1999,21(6):651 − 656. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.06.003
[13] 张宁宁, 骆亚生. 非饱和黄土的结构性与强度特性的关系[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,46(5):1838 − 1844. [ZHANG Ningning, LUO Yasheng. Relationship between structure and strength property of unsaturated loess[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2015,46(5):1838 − 1844. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.05.036
[14] 王勇. 黄土结构性特征及其对土体抗剪强度的影响[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.
WANG Yong. Structural characteristics of loess and its effect on soil shear strength[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract
[15] 郭庆国. 粗粒土的抗剪强度特性及其参数[J]. 陕西水力发电,1990,6(3):29 − 36. [GUO Qingguo. Shear strength characteristics and parameters of coarse-grained soil[J]. Shaanxi Hydropower Journal,1990,6(3):29 − 36. (in Chinese)
[16] 马露. 无黏性土的压缩特性及模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):72 − 77. [MA Lu. Compression characteristics and models of cohesionless soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):72 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 魏婕, 魏玉峰, 黄鑫. 颗粒形状对粗粒土剪切变形影响的细观研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):114 − 122. [WEI Jie, WEI Yufeng, HUANG Xin. A meso-scale study of the influence of particle shape on shear deformation of coarse-grained soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):114 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 王晓帅, 王子寒, 景晓昆, 等. 粗粒土大型直剪试验宏细观研究与离散元模拟[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版),2020,37(3):279 − 286. [WANG Xiaoshuai, WANG Zihan, JING Xiaokun, et al. A macro-micro study and distinct element simulation on large-scale shear test of coarse-grained soil[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University (Science and Engineering),2020,37(3):279 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2020.03279
[19] 屈智炯. 粗粒土在高土石坝的应用研究[J]. 水电站设计,1998,14(1):83 − 88. [QU Zhijiong. Research on Application of Coarse Grained Soil in High Earth-rock Dam[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,1998,14(1):83 − 88. (in Chinese)
[20] 王家全, 周岳富, 唐咸远, 等. 可视大模型加筋土直剪数采仪的研发与应用[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(5):1533 − 1540. [WANG Jiaquan, ZHOU Yuefu, TANG Xianyuan, et al. Development and application of large size direct shear test apparatus with visual and digital collection functions for reinforced soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(5):1533 − 1540. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 何亮, 魏玉峰, 潘远阳, 等. 基于能量耗散机制的粗粒土圆度损伤特性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):120 − 126. [HE Liang, WEI Yufeng, PAN Yuanyang, et al. Analyses of roundness damage characteristics of coarse-grained soil based on energy dissipation mechanism[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):120 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王冠, 陈坚. 路基粗粒土抗剪强度影响因素分析[J]. 路基工程,2015(3):154 − 157. [WANG Guan, CHEN Jian. Analysis on factors affecting shear strength of coarse-grained soil of subgrade[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2015(3):154 − 157. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 刘汉龙, 孙逸飞, 杨贵, 等. 粗粒料颗粒破碎特性研究述评[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(4):361 − 369. [LIU Hanlong, SUN Yifei, YANG Gui, et al. A review of particle breakage characteristics of coarse aggregates[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences),2012,40(4):361 − 369. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 王光进, 杨春和, 张超, 等. 粗粒土三轴试验数值模拟与试样颗粒初始架构初探[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(2):585 − 592. [WANG Guangjin, YANG Chunhe, ZHANG Chao, et al. Numerical simulation triaxial tests for coarse-grained soil and preliminary study of initial fabric of sample grain[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(2):585 − 592. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.02.043
[25] 郭庆国. 关于粗粒土工程特性及其分类的探讨[J]. 水利水电技术,1979,10(6):53 − 57. [GUO Qingguo. Discussion on engineering characteristics and classification of coarse-grained soil[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,1979,10(6):53 − 57. (in Chinese)
[26] 陈坚. 颗粒堆积结构对高速铁路路基粗粒土填料工程性质影响机制研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014
CHEN Jian. Study on mechanism of effect of particle packing structure on engineering properties of coarse-ggrained soil filling high-speed railway embankment[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract
-



 下载:
下载: