Classification and attribute analysis of water-storing structures in water deficient bedrock mountainous areas
-
摘要:
近十多年来,服务脱贫攻坚的基岩山区找水打井工作充分运用并丰富了蓄水构造理论,但缺乏对其类型的统一划分和属性的深入分析。以蓄水构造为理论指导,考虑地貌汇水、岩性赋水、构造控水等控制因素,以构造为主控因素,综合地形地貌、地层岩性和植被发育及开发利用实际价值等因素,系统总结划分出缺水基岩山区水平岩层、单斜、褶皱、断裂、接触、风化壳、复合、洞藏等8类20型35式蓄水构造,并借鉴、结合新构造控水理论和地下水系统理论分析总结不同尺度、不同类型蓄水构造的共性特征,从蓄水构造空间组合特征、边界水文地质性质、水动力条件、尺度效应、控水共生特征、开发利用实际价值等方面,提出了岩性与地质构造的相关性、透水与隔水的相对性、汇水与蓄水的平衡性、尺度与系统的统一性、形成与改造的继承性和规模与目的的匹配性等蓄水构造属性。研究成果细化完善了缺水基岩山区地下水蓄水构造类型划分,总结提炼了蓄水构造属性特征,深化了对蓄水构造概念内涵的理解与认识。既进一步推动了基岩山区水文地质学的研究,也可为缺水区找水定井提供参考,并指导缺水区水资源可持续利用。
Abstract:Since 2002, the China Geological Survey has successively organized and implemented hydrogeological survey and groundwater exploration in water deficient areas, such as severe water shortage areas in west China, Wumeng Mountain area, Yimeng mountain area and red bed area in southern Jiangxi, obtained a large number of exploration data conducive to promoting discipline development, and summarized the law of water abundance. In recent decades, water prospecting and well drilling in bedrock mountainous areas serving poverty alleviation have not been systematically summarized based on water storage structures and their attributes. This paper takes the water storage structure as the theoretical guidance, considers geomorphic catchment, lithological water accumulation, structural water control and other control factors, and takes structure as the main control factor. The factors such as topography, formation lithology, vegetation development and actual value of development and utilization are systematically summarized and water storage structures are divided into 8 types, further divided into 20 types, and more into 35 types, such as the horizontal rock stratum, monocline formation, fold, fault, contact zone, weathered crust, composite and cave reservoir. The common characteristics of different scales and types of water storage structures are analyzed and summarized with reference to and in combination with the neotectonic water control theory and groundwater system theory. From the aspects of spatial combination characteristics of water storage structure, boundary hydrogeological properties, hydrodynamic conditions, scale effect, symbiotic characteristics of water control and practical value of development and utilization, this paper puts forward the correlation between the lithology and geological structure, the relativity of permeability and water separation, the balance between catchment and water storage, the unity of scale and system, the inheritance of formation and transformation and the matching of scale and purpose. The research results refine and improve the classification of groundwater storage structure types in bedrock mountain areas with water shortage, summarize the attribute characteristics of water storage structure, deepen the understanding of the concept and connotation of water storage structure, not only further promote the research of hydrogeology in bedrock mountain areas, but also provide references for water prospecting and well locating in water shortage areas, and guide the sustainable utilization of water resources in water shortage areas.
-

-
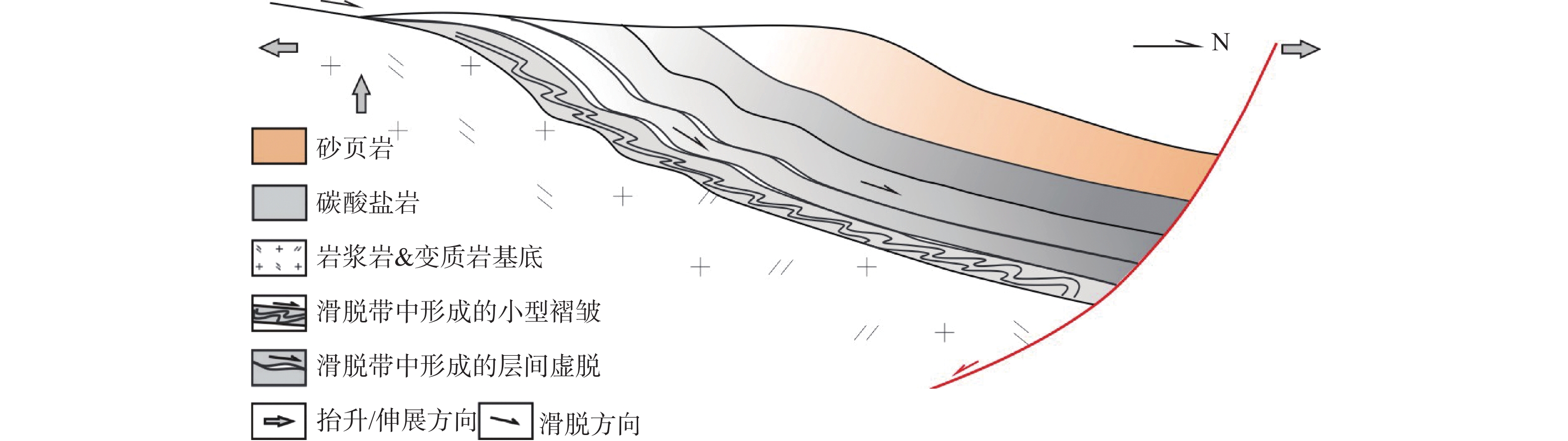
图 1 滑脱构造式蓄水构造示意图[24]
Figure 1.
图 2 喷发堆积式蓄水构造示意图(引自文献[25],有修改)
Figure 2.
图 3 碳酸盐岩与碎屑互层式蓄水构造示意图(引自文献[26],有修改)
Figure 3.
图 4 背斜式蓄水构造示意图(引自文献[20],有修改)
Figure 4.
图 5 单斜-断裂式蓄水构造示意图(引自文献[29],有修改)
Figure 5.
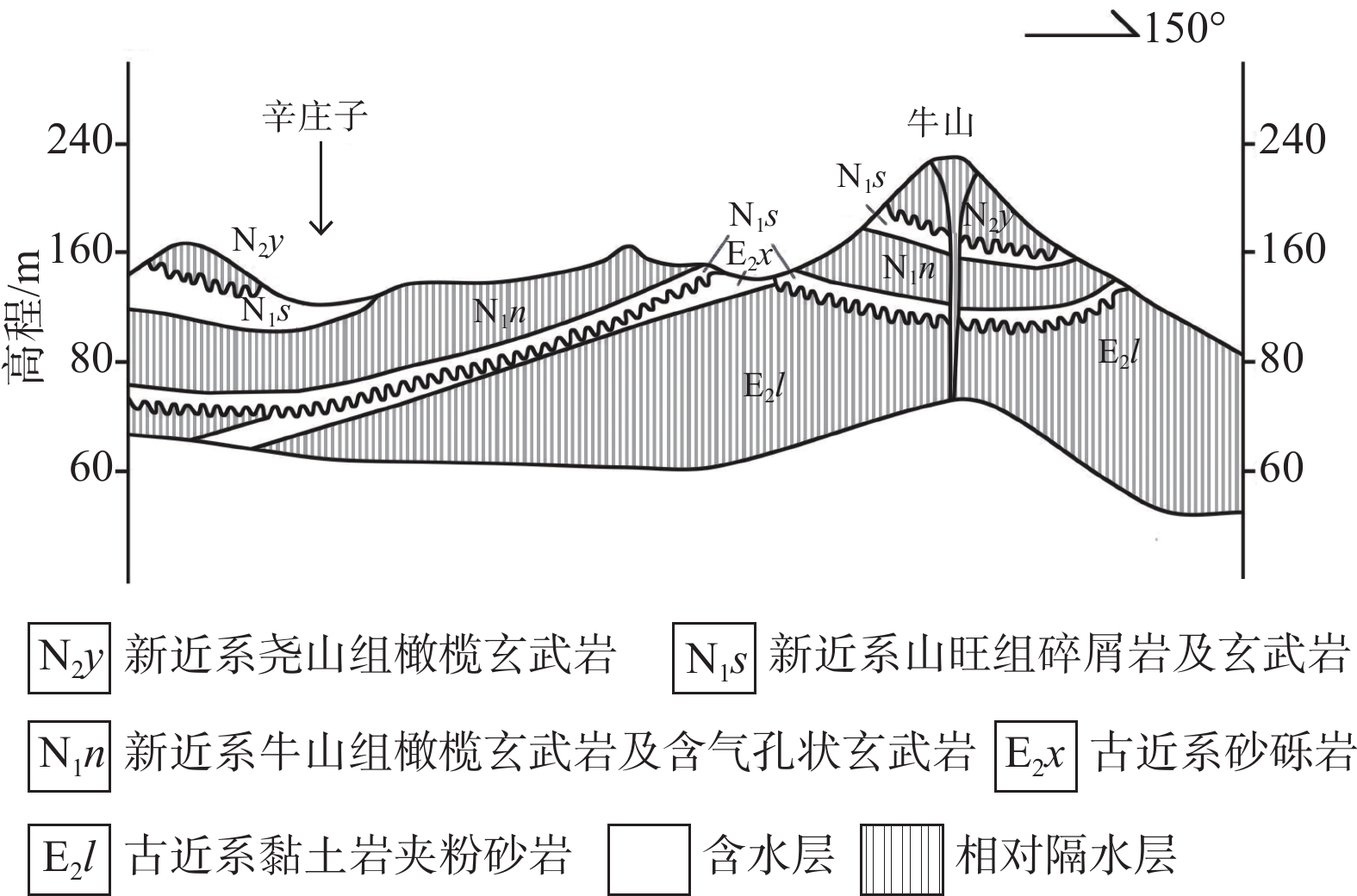
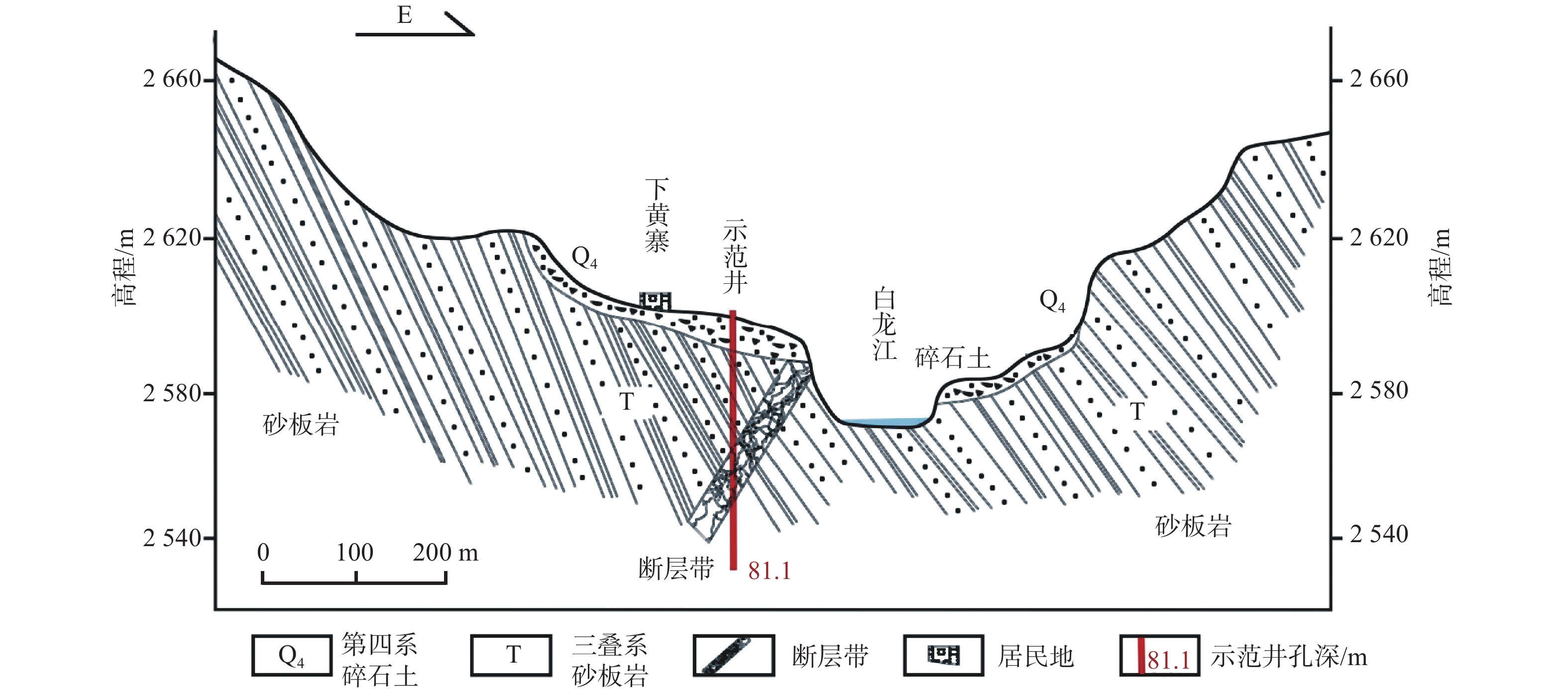
图 6 单斜-断裂式蓄水构造示意图[32]
Figure 6.
图 7 红层方山式蓄水构造示意图[33]
Figure 7.
表 1 缺水基岩山区蓄水构造类型划分
Table 1. Water storage structure types in water deficient bedrock mountainous areas
类 型 式 代表性地区 水平岩层
蓄水构造沉积动力型 红层方山式 赣南、西南红层区 喷发动力型 喷发堆积式 沂蒙山区临朐 单斜
蓄水构造碳酸盐岩型 单一碳酸盐岩式 沂蒙山区 碳酸盐岩与
碎屑岩互层式沂蒙山区鲁村盆地、
乌蒙山区碎屑岩型 砂岩式 陇东盆地庆阳地区 砂、泥岩互层式 乌蒙山区 砂砾岩式 赣南红层盆地 变质岩火成岩型 大理岩式 太行山区 玄武岩式 燕山山区 褶皱
蓄水构造向斜型 承压水式 沂蒙山区南麻盆地 潜水式 沂蒙山区莱芜盆地 背斜型 背斜式 沂蒙山区、乌蒙山区 断裂
蓄水构造断层型 断裂带式 沂蒙山区、乌蒙山区 断裂影响带式 沂蒙山区、乌蒙山区 断层交会式 沂蒙山区南鲁山自流区 断层岩块式 沂蒙山区 滑脱构造式 沂蒙山区莱芜盆地 断块型 地堑式 沂蒙山区沂源盆地 地垒式 青海东部碎屑岩区 垒堑式 陕西渭北岩溶区 叠瓦断块式 陕西渭北岩溶区 接触
蓄水构造侵入体接触型 阻水岩脉(墙)式 河北太行山、山西吕梁山、
乌蒙山、江西赣州地区导水岩脉(墙)式 不整合接触型 不整合接触式 宁夏中南部地区 风化壳
蓄水构造裸露型 片麻岩式 河北太行山地区 花岗岩式 海南琼中、江西赣州地区 碎屑岩式 川渝红层区、赣南地区 隐伏型 古风化壳式 辽宁西部山区 复合
蓄水构造向斜-岩体式 太行山区涞源盆地 断层-不整合接触式 沂蒙山区 单斜-断裂式 沂蒙山区 岩脉-侵入接触式 江西赣州兴国地区 风化壳-断层式 江西赣州宁都地区 洞藏
蓄水构造天然型 孔洞式 西南岩溶区、河北坝上高原 人为活动型 废弃矿洞(巷道)式 太行山区曲阳县、
陕西北部等地区 -
[1] 刘光亚. 基岩蓄水构造[J]. 河北地质学院学报,1978,1(1):19 − 39. [LIU Guangya. Bedrock theory of water storage structure[J]. Hebei Geological College,1978,1(1):19 − 39. (in Chinese)
[2] 刘光亚. 基岩地下水[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1979.
LIU Guangya. Bedrock groundwater[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1979. (in Chinese)
[3] 沈照理, 刘光亚, 杨成田, 等. 水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
SHEN Zhaoli, LIU Guangya, YANG Chengtian, et al. Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985. (in Chinese)
[4] 吉学亮, 尹学灵, 潘晓东, 等. 岩溶斜坡地带基于蓄水构造的地下水富集模式[J]. 科学技术与工程,2017,17(22):8 − 15. [JI Xueliang, YIN Xueling, PAN Xiaodong, et al. Groundwater enrichment model in Karst slope zone based on storage structure[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2017,17(22):8 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.22.002
[5] 贾德旺. 鲁南山区基岩蓄水构造类型及找水定井方法[J]. 地质学刊,2020,44(3):318 − 325. [JIA Dewang. Type of bedrock water storage structure and the method of water exploration and well determination in the southern mountainous area of Shandong[J]. Journal of Geology,2020,44(3):318 − 325. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2020.03.014
[6] 关琴, 徐聪聪, 叶倩, 等. 鲁中南新汶盆地地下水蓄水模式分析[J]. 山东国土资源,2021,37(5):41 − 48. [GUAN Qin, XU Congcong, YE Qian, et al. Analysis on groundwater storage model in Xinwen basin in central and southern Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources,2021,37(5):41 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 武选民, 文冬光, 郭建强, 等. 西部严重缺水地区人畜饮水地下水勘查示范工程[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2006.
WU Xuanmin, WEN Dongguang, GUO Jianqiang, et al. Groundwater exploration demonstration project of drinking water for human and livestock in western regions with serious water shortage[M]. Beijing: China Earth Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[8] 王新峰, 李伟, 曹红, 等. 基岩山区水文地质图编制新模式与实践[J]. 人民黄河,2016,38(5):10 − 14. [WANG Xinfeng, LI Wei, CAO Hong, et al. Initial analysis and practices of bedrock mountainous hydrogeology mapping theory[J]. Yellow River,2016,38(5):10 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2016.05.003
[9] 李伟, 王新峰, 邓启军, 等. 基于山区地下水非均一性特征的水文地质编图研究[R]. 北京: 国家自然科学基金成果, 2014: 1 − 43.
LI Wei, WANG Xinfeng, DENG Qijun, et al. Hydrogeological mapping based on heterogeneity of groundwater in mountainous areas[R]. Beijing: Achievements of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2014: 1 − 43. (in Chinese)
[10] 韩子夜, 武选民, 张福存, 等. 西宁盆地储水构造及其地下淡水赋存规律研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2006,33(5):66 − 70. [HAN Ziye, WU Xuanmin, ZHANG Fucun, et al. A study of groundwater-bearing structures and occurrence of fresh groundwater in the Xi'ning Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2006,33(5):66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.05.015
[11] 武选民, 文冬光, 张福存, 等. 我国西北人畜饮用缺水地区储水构造特征与工程范例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(1):22 − 26. [WU Xuanmin, WEN Dongguang, ZHANG Fucun, et al. Groundwater-bearing structures in Northwestern China and their application to water-taking works for water-shortage towns[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(1):22 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.005
[12] 武选民, 文冬光, 张福存, 等. 辽西山地缺水地区储水构造的特征和供水示范工程的建立[J]. 地质通报,2010,29(1):142 − 146. [WU Xuanmin, WEN Dongguang, ZHANG Fucun, et al. Groundwater-bearing structures in water deficient mountainous area, western Liaoning, China and set-up of civil water supply demonstration project[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2010,29(1):142 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.01.016
[13] 丁秉弼. 编制《朝阳地区蓄水构造类型图》的探索[J]. 河北地质学院学报,1989,12(2):231 − 236. [DING Bingbi. Exploration on compiling the type map of water storage structure in Chaoyang area[J]. Journal of Hebei Institute of Geosciences,1989,12(2):231 − 236. (in Chinese)
[14] 徐军祥, 康凤新, 张中祥, 等. 山东省重大水文地质问题——理论技术创新与应用[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2014.
XU Junxiang, KANG Fengxin, ZHANG Zhongxiang, et al. Major hydrogeological problems in Shandong Province - theoretical and technological innovation and application[M]. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[15] 张之淦, 陈伟海. 岩溶蓄水构造与找水—以广西来宾小平阳为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2000,27(6):1 − 5. [ZHANG Zhigan, CHEN Weihai. Water-bearing structures in Karst ternain: A case study in Xiaopingyang area, Laibin, Guangxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2000,27(6):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.06.001
[16] 武选民, 郭建强, 文冬光, 等. “逐步逼近式”找水方法及其在缺水地区水文地质勘查中的应用[J]. 西北地质,2009,42(4):102 − 108. [WU Xuanmin, GUO Jianqiang, WEN Dongguang, et al. The successive approximation method on groundwater exploration and its application in hydrogeological investigation in water-shortage areas[J]. Northwestern Geology,2009,42(4):102 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2009.04.012
[17] 刘新号. 基于蓄水构造类型的山区综合找水技术[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(6):8 − 12. [LIU Xinhao. Integrated techniques of locating groundwater in mountain areas based on groundwater-impounding types[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(6):8 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李伟, 朱庆俊, 王洪磊, 等. 西南岩溶地区找水技术方法探讨[J]. 地质与勘探,2011,47(5):918 − 923. [LI Wei, ZHU Qingjun, WANG Honglei, et al. On methods of finding water in the Karst zones of southwest China[J]. Geology and Exploration,2011,47(5):918 − 923. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 汪云, 杨海博, 郑梦琪, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水蓄水构造特征及勘查定井研究[J]. 水利水电技术,2019,50(3):52 − 65. [WANG Yun, YANG Haibo, ZHENG Mengqi, et al. Study on characteristics of groundwater storage structures and well explorating and locating within Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2019,50(3):52 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 潘晓东, 梁杏, 唐建生, 等. 黔东北高原斜坡地区4种岩溶地下水系统模式及特点—基于地貌和蓄水构造特征[J]. 地球学报,2015,36(1):85 − 93. [PAN Xiaodong, LIANG Xing, TANG Jiansheng, et al. The patterns and characteristics of four Karst groundwater systems in Northeast Guizhou slope zone based on the landscape and reservoir structure[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2015,36(1):85 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.01.10
[21] SOPHOCLEOUS M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2002,10(1):52 − 67. doi: 10.1007/s10040-001-0170-8
[22] 中国地质调查局. 水文地质手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
China Geological Survey. Hydrogeological manual[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012. (in Chinese)
[23] 中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心. 扶贫找水打井理论总结与技术方法创新成果[R]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2020.
Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology. Theoretical summary and technological innovation of water exploration and well drilling for poverty alleviation[R]. Beijing: China Geological Survey, 2020. (in Chinese)
[24] 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 等. 鲁中山区下寒武统朱砂洞组似层状含水层成因分析[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(3):653 − 663. [LIU Yuanqing, ZHOU Le, LI Wei, et al. Genetic analysis of Lower Cambrian Zhushadong Formation layered aquifer in the central mountain area of Shandong Province[J]. Geological Review,2019,65(3):653 − 663. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李巨芬, 李伟, 冯庆达, 等. 山东临朐盆地新构造运动特征及其对地下水的控制作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):28 − 36. [LI Jufen, LI Wei, FENG Qingda, et al. Characteristics of the new tectonic movement and its control of groundwater in the Linqu Basin in Shandong[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 潘晓东, 曾洁, 任坤, 等. 贵州毕节岩溶斜坡地带地下水赋存规律与钻探成井模式[J]. 地球学报,2018,39(5):606 − 612. [PAN Xiaodong, ZENG Jie, REN Kun, et al. Groundwater occurrence characteristics and drilling well models in Karst slope zone, Bijie, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2018,39(5):606 − 612. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.071501
[27] 钱学溥. 中国蓄水构造类型[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.
QIAN Xuepu. Types of water storage structures in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[28] 肖楠森. 新构造裂隙水[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1981(4):22 − 25. [XIAO Nansen. Neotectonic fissure water[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1981(4):22 − 25. (in Chinese)
[29] 李志勇, 黎义勇, 黄长生, 等. 赣江流域红层盆地典型构造样式与地下水动力学模式[J]. 地质通报,2020,39(12):1873 − 1882. [LI Zhiyong, LI Yiyong, HUANG Changsheng, et al. Typical structural geology and groundwater dynamics in red beds basins of Ganjiang River Basin, South China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2020,39(12):1873 − 1882. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 张福存, 鄢毅, 刘安云, 等. 西南红层浅层地下水特征及其开发利用模式[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(3):53 − 56. [ZHANG Fucun, YAN Yi, LIU Anyun, et al. Characteristics and development models of shallow groundwater in the red strata of southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(3):53 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.03.014
[31] 张丽君, 顾承启, 范炎虎, 等编译. 国外干旱区地下水资源勘查评价方法现状与进展[R]. 北京: 地质矿产部地质环境管理司, 1997.
ZHANG Lijun, GU Chengqi, FAN Yanhu, et al. Present situation and progress of groundwater resources exploration and evaluation methods in arid areas abroad[R]. Beijing: Department of Geological Environment Management, Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1997. (in Chinese)
[32] 安永会, 张二勇. 找水打井典型案例汇编[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
AN Yonghui, ZHANG Eryong. Collection of typical cases of water exploration and well drilling [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[33] 王新峰, 宋绵, 龚磊, 等. 赣南缺水区地下水赋存特征及典型蓄水构造模式解析—以兴国县为例[J]. 地球学报,2018,39(5):573 − 579. [WANG Xinfeng, SONG Mian, GONG Lei, et al. An analysis of characteristics of groundwater occurrence and typical model of water-storage structures in water-deficient areas of southern Jiangxi Province: A case study of Xingguo County[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2018,39(5):573 − 579. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.071402
-



 下载:
下载: