Pumping tests analyses of a heterogeneous pore aquifer based on the Generalized Radial Flow model
-
摘要:
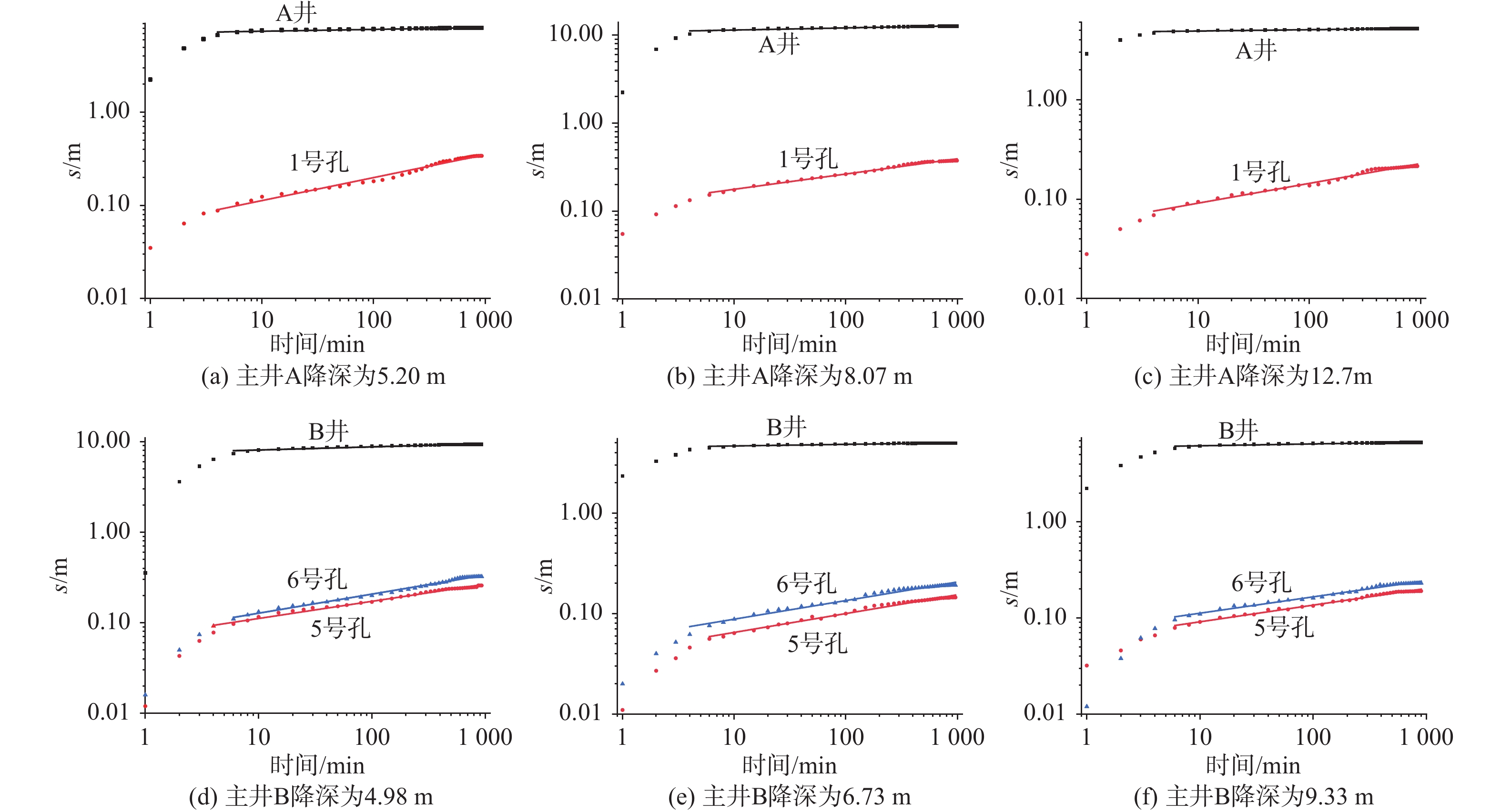
Theis模型、Dupuit模型等经典井流模型分析非均质含水层井流试验数据有一定的局限性,获取的参数不适合表征非均质含水层特性。而GRF模型可以获取含水层流动特性的数据。相比于Theis模型、Dupuit模型,GRF模型更能表征非均质含水层特性。以黄石东湖新村棋盘洲长江大桥的抽水试验数据为例,采用Theis模型和GRF模型计算含水层渗透系数,结合实际水文地质条件,对比分析不同方法计算的水文地质参数,并计算含水层水流维数和表观压力传导系数(Kf /Ssf)。结果表明:研究区含水层为细砂夹条带状黏土透镜体的非均质含水层,采用GRF模型计算结果更符合实际情况,渗透系数为 4.09×10−3cm/s;含水层水流维数为1.61,地下水为双线性流动状态,含水层对抽水试验的响应主要受黏土条带控制;观测井和抽水主井的Kf /Ssf呈非线性相关,进一步验证了含水层的非均质性。在非均质孔隙含水层中,应用多孔联合非稳定GRF井流试验方法不仅能确定水文地质参数,并且能丰富对含水层特性的认知。
Abstract:Classical models such as the Theis model and Dupuit model have certain limitations in analyzing pumping test data of heterogeneous aquifers, and the obtained parameters are not suitable for characterizing the heterogeneous aquifers. The GRF model, however, can obtain the data of flow characteristics of aquifers, which can better characterize the characteristics of heterogeneous aquifers than the Theis model and Dupuit model do. Based on the pumping test data of the Qianchenzhou Yangtze River Bridge in East Lake New Village of Huangshi, the Theis model and GRF model are used to calculate the aquiferous water flow dimension and the apparent hydraulic diffusion coefficient (Kf /Ssf ), and the hydrological geological parameters calculated by different methods are combined with the actual hydrological geological conditions. The results show that the aquifer in the study area is a heterogeneous aquifer with fine sand intercalated with banded clay lens, so it is more reasonable to use the GRF model to calculate the parameters. The coefficient of permeability is 4.09×10−3 cm/s, and the flow dimension is 1.61. The flow regime is equivalent to the bilinear one, and the aquifer response to pumping is governed by the clay strip. The non-linear correlation of Kf /Ssf between the observation wells and pumping wells further confirms the heterogeneity of the aquifers. In the heterogeneous pore aquifers, the application of the porous combined unstable GRF well flow test method can not only determine hydrogeological parameters, but also enrich the cognition of aquifer characteristics.
-
Key words:
- heterogeneous porous medium /
- pumping test /
- coefficient of permeability /
- GRF model /
- flow dimension
-

-
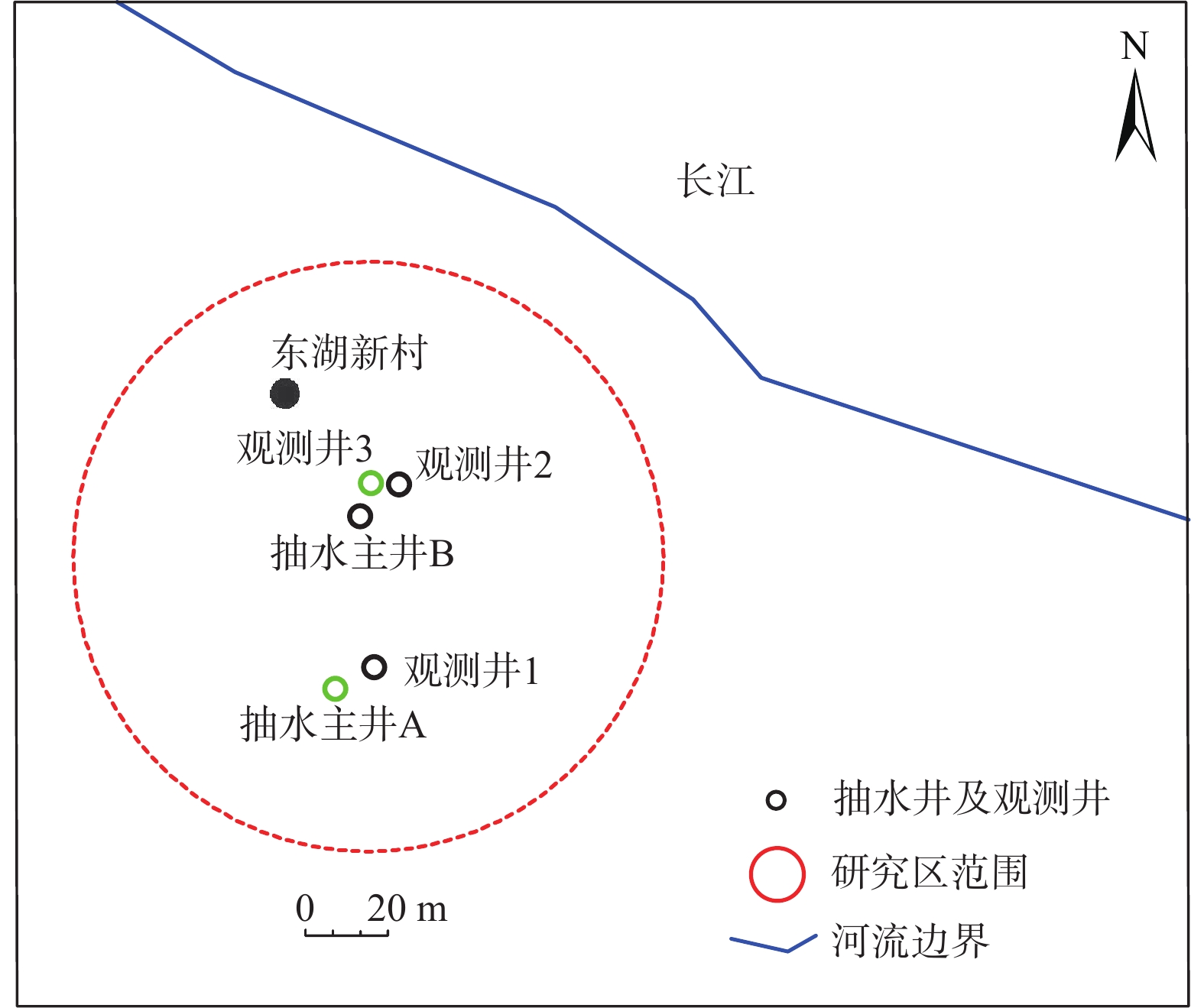
表 1 抽水试验设计降深
Table 1. Design drawdown of the pumping test
孔号 水位埋深/m 水位降深/m 抽水流量Q
/(m3·d−1)主井A 7.02 5.20 227.52 6.63 8.07 606.24 6.90 12.70 772.08 主井B 8.43 4.98 309.12 8.43 6.73 394.32 8.32 9.33 463.92 表 2 含水层水流维数
Table 2. Water flow dimension of the aquifer
抽水—观测系统 主井降深/m 含水层水流维数n 水流维数平均值 主井A 观测井1 5.20 1.51 1.61 8.07 1.65 12.70 1.60 主井B 观测井2
观测井34.98 1.58 1.62 6.73 1.63 1.63 9.33 1.66 1.65 表 3 不同方法计算的渗透系数
Table 3. Coefficient of permeability calculated by different methods
抽水—观测系统 主井降深/m 渗透系数/(10−4cm·s−1) 平均渗透系数/(10−4cm·s−1) Theis模型 GRF模型 Theis模型 GRF模型 主井A 观测井1 5.20 2.20 89.9 2.47 40.9 8.07 2.97 47.0 12.7 1.54 13.5 主井B 观测井2
观测井34.98 2.69 75.9 2.37 18.8 6.73 3.10 60.3 2.40 23.6 9.33 3.00 24.5 1.97 14.3 -
[1] 由明宇. 大理隐仙溪冲洪积扇含水层非均质性分布规律研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016.
YOU Mingyu. Study on the aquifer heterogeneity distribution of an alluvial-proluvial fan in Dali Yinxian stream, Yunnan [D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 赵瑞珏, 毛德强, 刘再斌, 等. 基于水力层析法的某煤矿承压含水层叠加放水试验分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):1 − 9. [ZHAO Ruijue, MAO Deqiang, LIU Zaibin, et al. An analysis of sequential water releasing tests of the confined aquifers in a coal mine based on hydraulic tomography[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 林加定. 非均质含水层水力层析扫描及其在巴音河冲洪积扇的应用[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2019: 1 − 108.
LIN Jiading. Hydraulic tomography on heterogenous aquifer and its application in the Bayin River Alluvial Fan[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2019: 1 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 沙俊强, 王为治, 欧阳平, 等. 长江底隧道抽水试验及水文地质参数计算[J]. 江苏建筑,2017(3):56 − 59. [SHA Junqiang, WANG Weizhi, OUYANG Ping, et al. Pumping tests and hydrogeological parameters calculation for the surrounding rocks of conveyance tunnel under the Yangtze River[J]. Jiangsu Construction,2017(3):56 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6270.2017.03.016
[5] 张东, 刘晓丽, 王恩志. 非均匀多孔介质等效渗透率的普适表达式[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):35 − 42. [ZHANG Dong, LIU Xiaoli, WANG Enzhi. A universal expression of the equivalent permeability of heterogeneous porous media[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):35 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] BARKER J A. A generalized radial flow model for hydraulic tests in fractured rock[J]. Water Resources Research,1988,24(10):1796 − 1804. doi: 10.1029/WR024i010p01796
[7] 李金轩, 余修日. 低渗透裂隙岩体压水试验资料分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(9):1476 − 1480. [LI Jinxuan, YU Xiuri. Analysis of constant-pressure well test data for low-permeability fractured rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(9):1476 − 1480. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.09.013
[8] BANGOY L M, BIDAUX P, DROGUE C, et al. A new method of characterizing fissured media by pumping tests with observation wells[J]. Journal of Hydrology,1992,138(1/2):77 − 88.
[9] RAFINI S, CHESNAUX R, FERROUD A. A numerical investigation of pumping-test responses from contiguous aquifers[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2017,25(3):877 − 894. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1560-x
[10] KUUSELA-LAHTINEN A, NIEMI A, LUUKKONEN A. Flow dimension as an indicator of hydraulic behavior in site characterization of fractured rock[J]. Groundwater,2003,41(3):333 − 341. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02602.x
[11] RAFINI S, LAROCQUE M. Insights from numerical modeling on the hydrodynamics of non-radial flow in faulted media[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2009,32(8):1170 − 1179. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.03.009
[12] DOUGHTY C, KARASAKI K. Flow and transport in hierarchically fractured rock[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2002,263(1/2/3/4):1 − 22.
[13] VERBOVŠEK T. Influences of aquifer properties on flow dimensions in Dolomites[J]. Groundwater,2009,47(5):660 − 668. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00577.x
[14] BOURDET D, WHITTLE T M, DOUGLAS A A, et al. A new set of type curves simplies well test analysis[J]. World Oil,1983,196(6):877 − 894.
[15] GIESE M, REIMANN T, LIEDL R, et al. Application of the flow dimension concept for numerical drawdown data analyses in mixed-flow Karst systems[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2017,25(3):799 − 811.
[16] SUI W B, MOU J Y, BI L F, et al. New flow regimes for well near constant pressure boundary[C]//All Days April 15-18, 2007. Buenos Aires: Argentina SPE, 2007: 1 − 12.
[17] BEAUHEIM R L , ROBERTS R M . Flow-dimension analysis of hydraulic tests to characterize water-conducting features[C]// Nea Workshop on Water-conducting Features in Radionuclide Migration. Barcelona: GEOTRAP Project Workshop Proceedings, 1998: 1 − 10.
[18] FERROUD A, RAFINI S, CHESNAUX R. Using flow dimension sequences to interpret non-uniform aquifers with constant-rate pumping-tests: a review[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019(2): 100003.
[19] DOUGHTY C. Generating one-column grids with fractal flow dimension[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2017,108:33 − 41.
[20] TIAB D. Analysis of pressure derivative data of hydraulically fractured wells by the Tiab's Direct Synthesis technique[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2005,49(1/2):1 − 21.
[21] DEWANDEL B, LACHASSAGNE P, ZAIDI F K, et al. A conceptual hydrodynamic model of a geological discontinuity in hard rock aquifers: Example of a quartz reef in granitic terrain in South India[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2011,405(3/4):474 − 487.
[22] AVCI C B, ŞAHIN A U, ÇIFTÇI E. A new method for aquifer system identification and parameter estimation[J]. Hydrological Processes,2013,27(17):2485 − 2497. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9352
[23] XIAO L, XU Y X. Diagnostic analysis of pumping tests using derivative of dlgs/dlgt with case study[J]. Ground water, 2014, 52 (Sup 1): 208 − 217.
[24] LE BORGNE T, BOUR O, DE DREUZY J R, et al. Equivalent mean flow models for fractured aquifers: Insights from a pumping tests scaling interpretation[J]. Water Resources Research,2004,40(3):W03512.
[25] 王俊智,李清波,王贵军,等. 近水平层状坝基岩体渗透结构及其工程意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(1):12 − 19. [WANG Junzhi, LI Qingbo, WANG Guijun, et al. Permeability structure of the horizontally-stratified dam foundation rock mass and its engineering significance[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(1):12 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] DUFFIELD G M. AQTESOLV for windows version 4.5 user’s guide[M]. Reston: HydroSOLVE Inc, 2007.
-




 下载:
下载: